0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesInput and Output Devices Cheatsheets
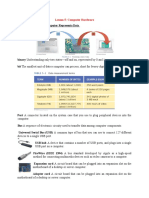
The document provides an overview of various input and output devices used in computing, including Optical Mark Recognition (OMR), Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR), Optical Character Recognition (OCR), and various types of pointing devices and scanners. It also details output devices such as monitors, printers, and audio output devices like speakers and headphones. Each device is described with its function and application in data processing and user interaction.
Uploaded by
naveenramdialCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesInput and Output Devices Cheatsheets
The document provides an overview of various input and output devices used in computing, including Optical Mark Recognition (OMR), Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR), Optical Character Recognition (OCR), and various types of pointing devices and scanners. It also details output devices such as monitors, printers, and audio output devices like speakers and headphones. Each device is described with its function and application in data processing and user interaction.
Uploaded by
naveenramdialCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6