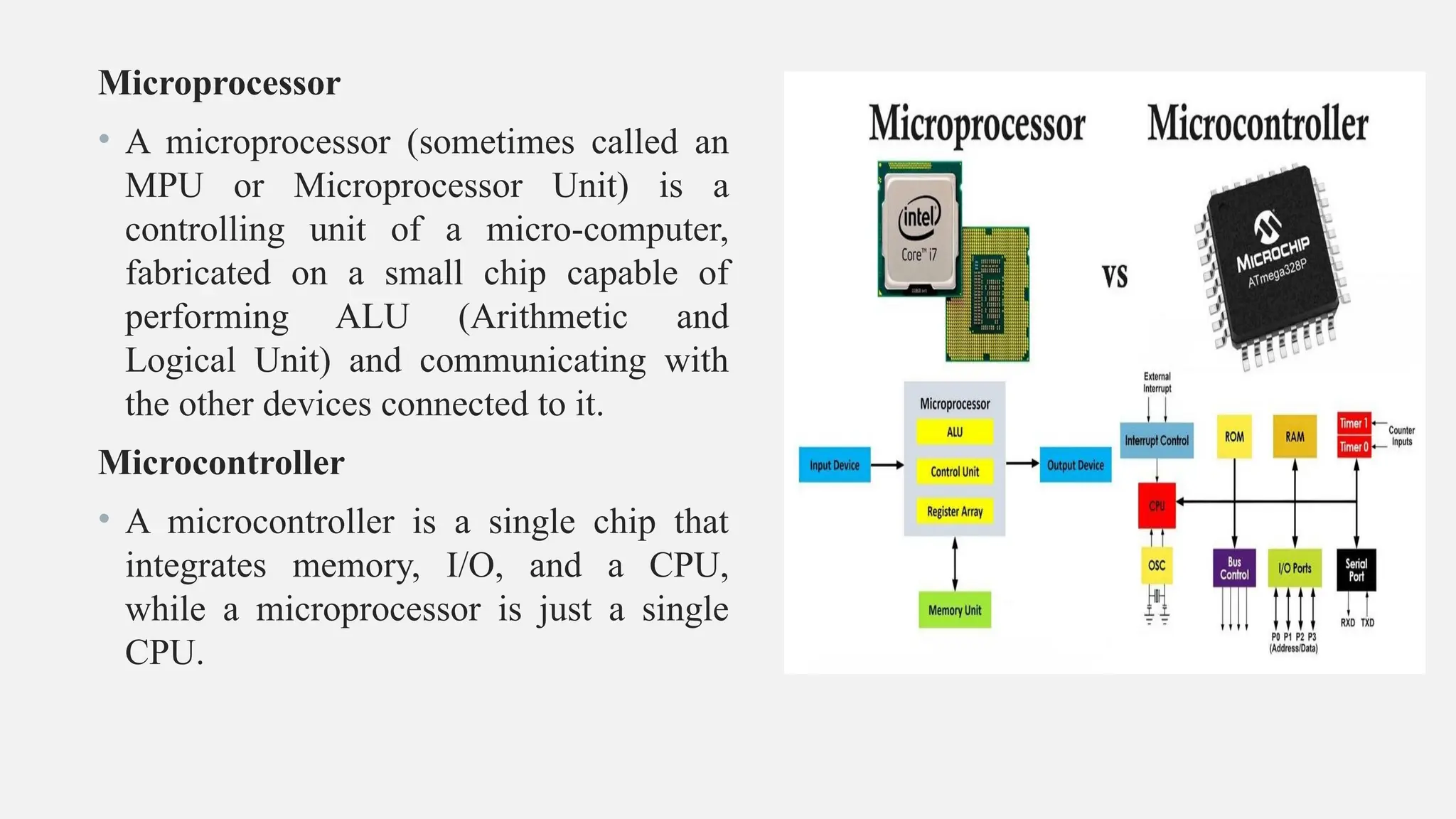
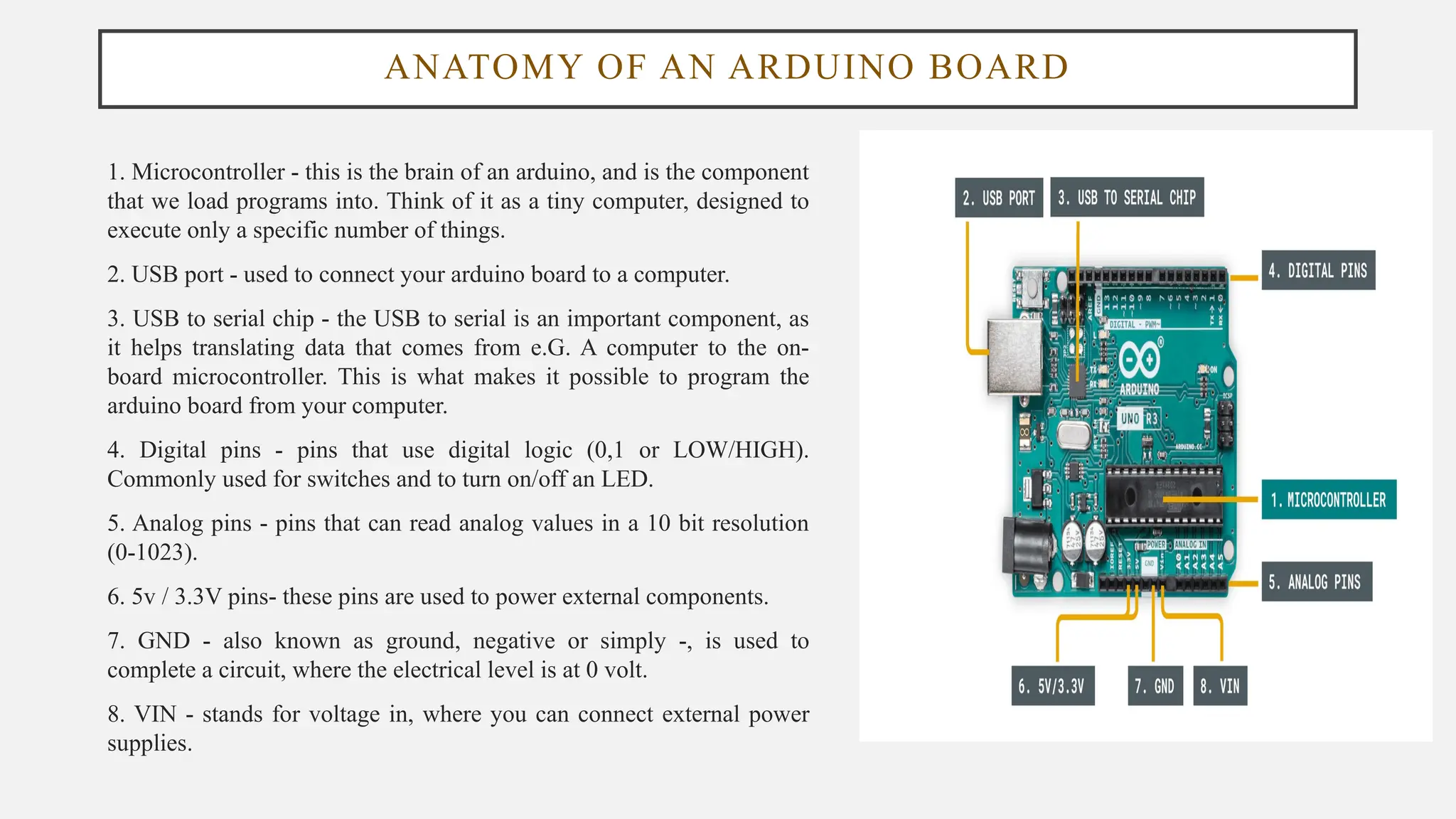
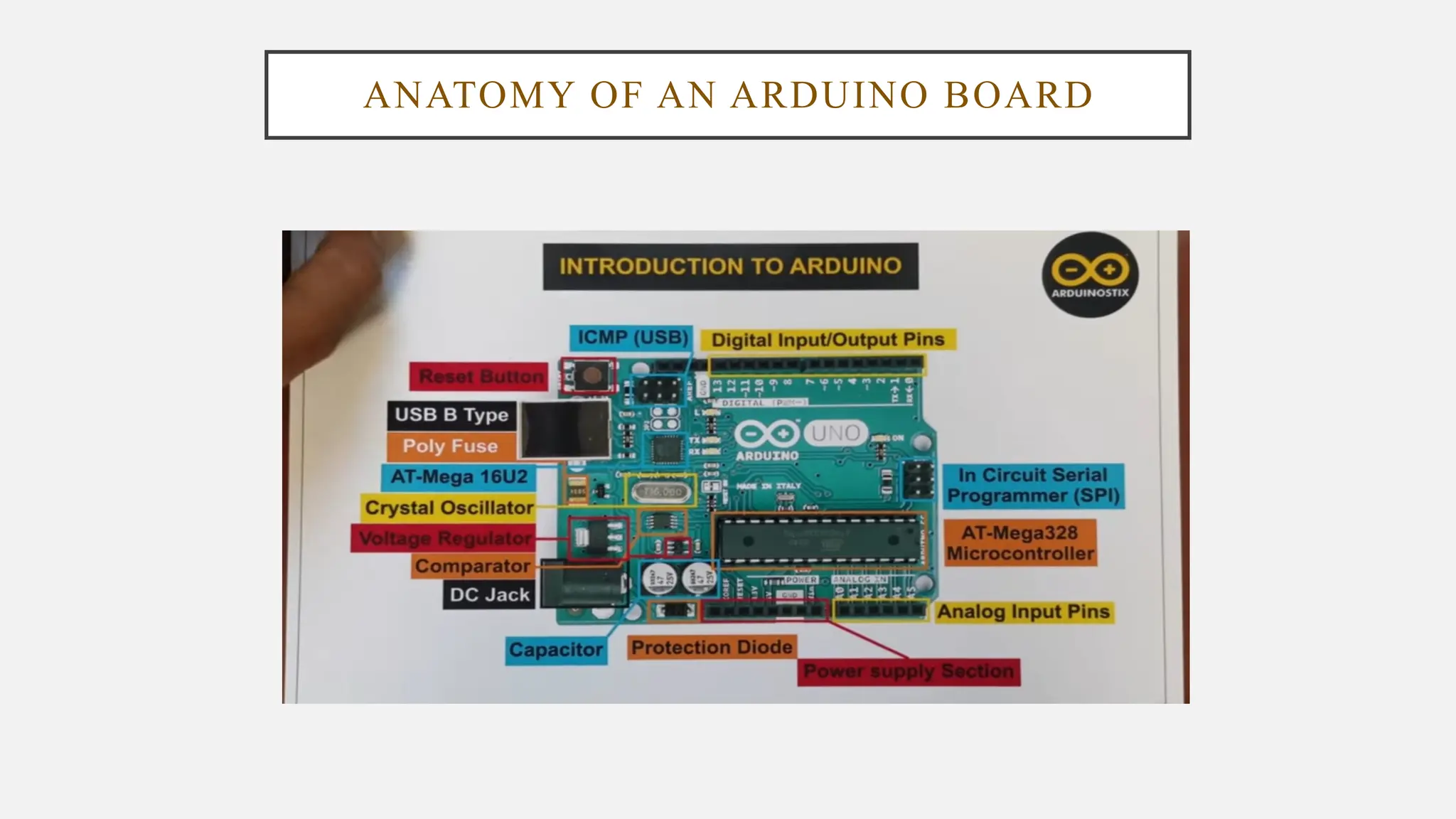
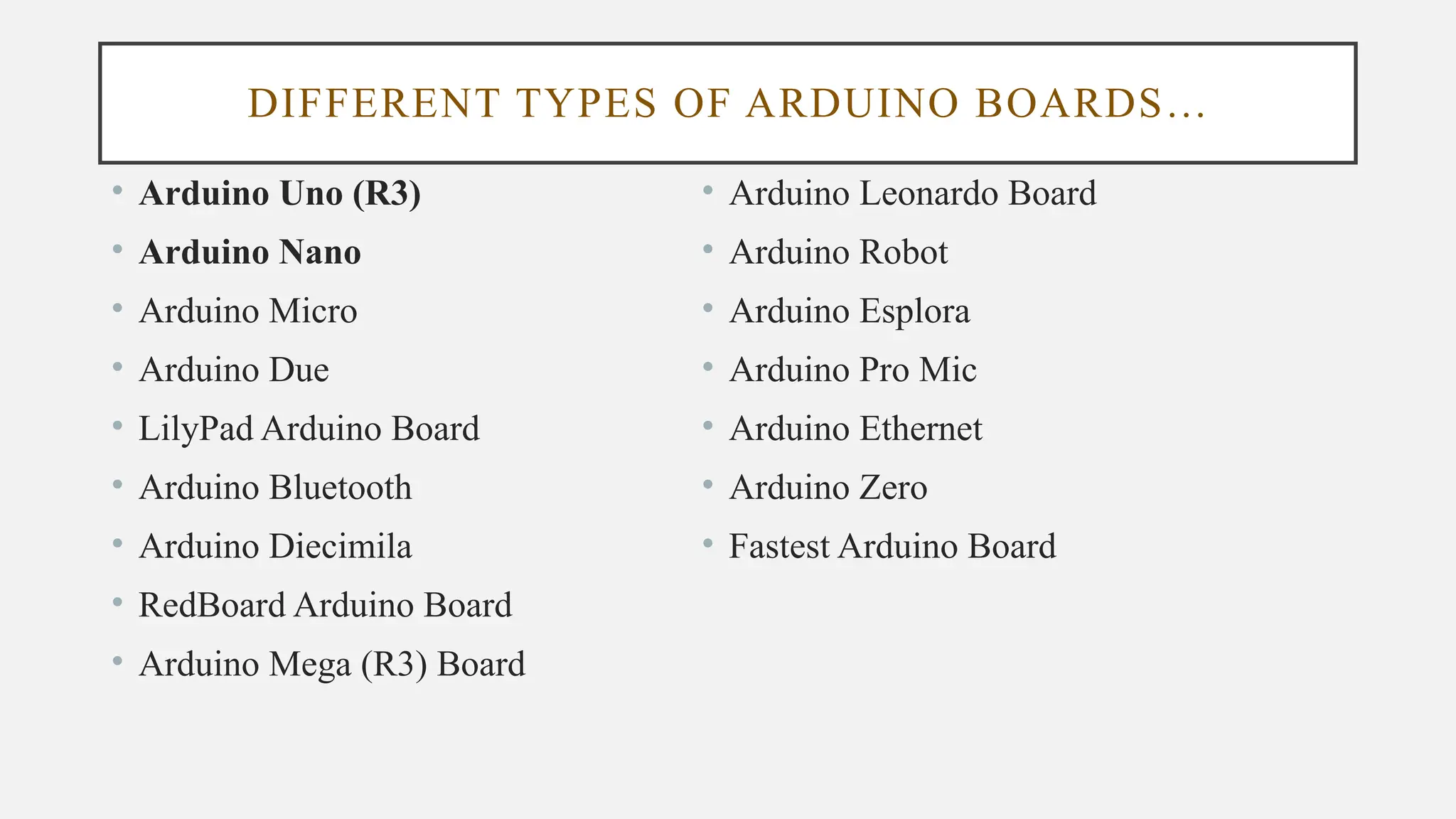
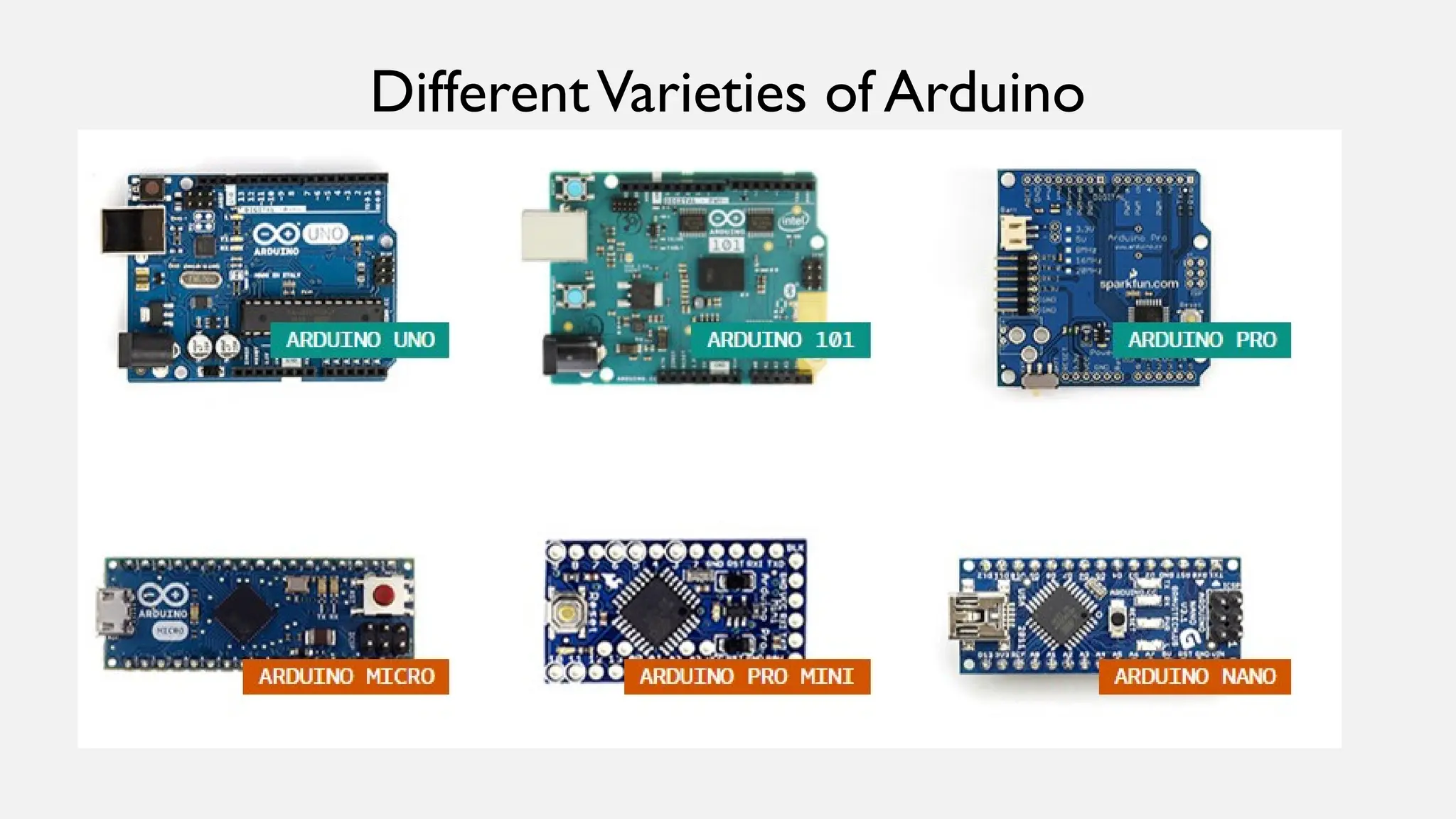
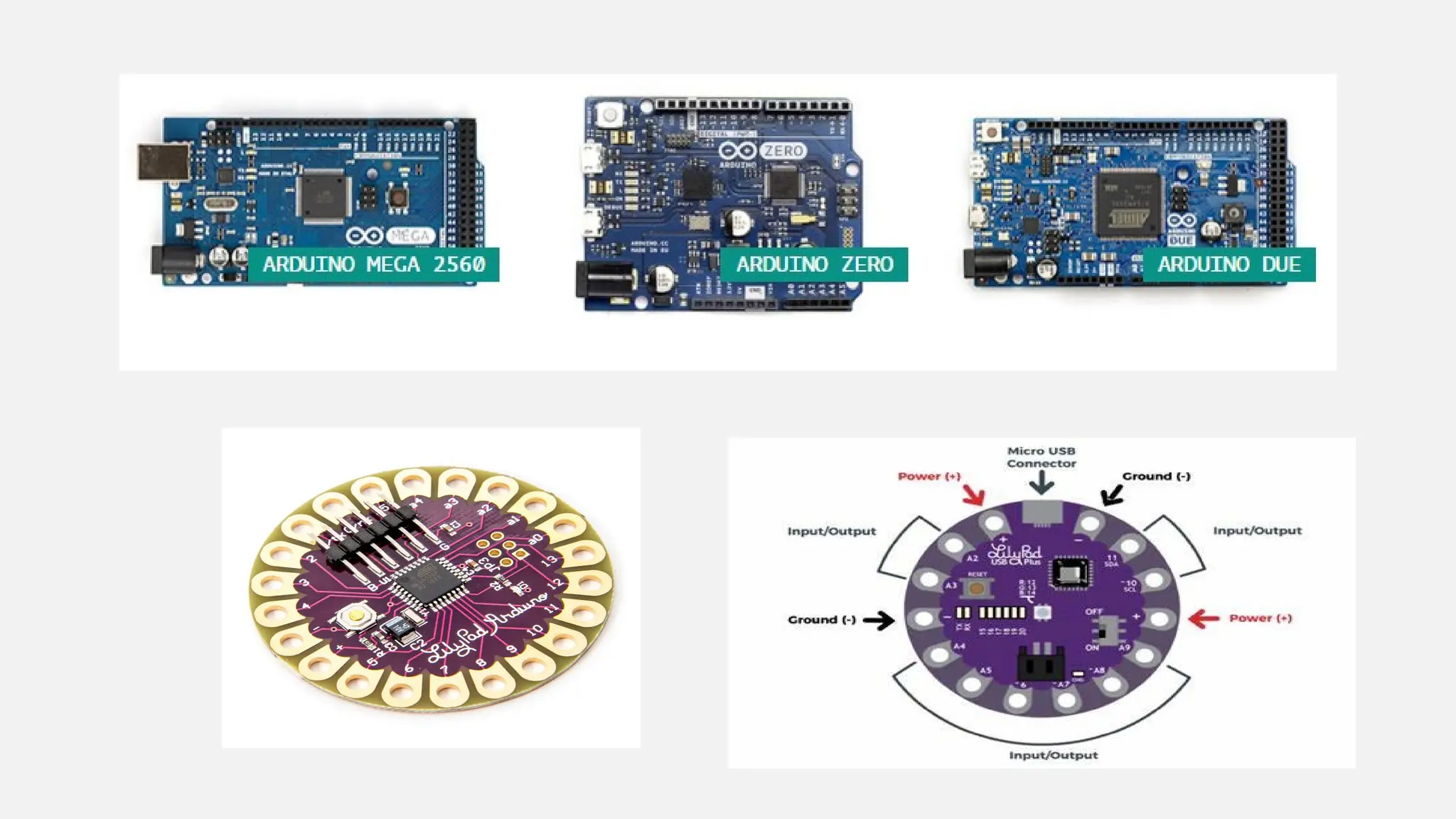
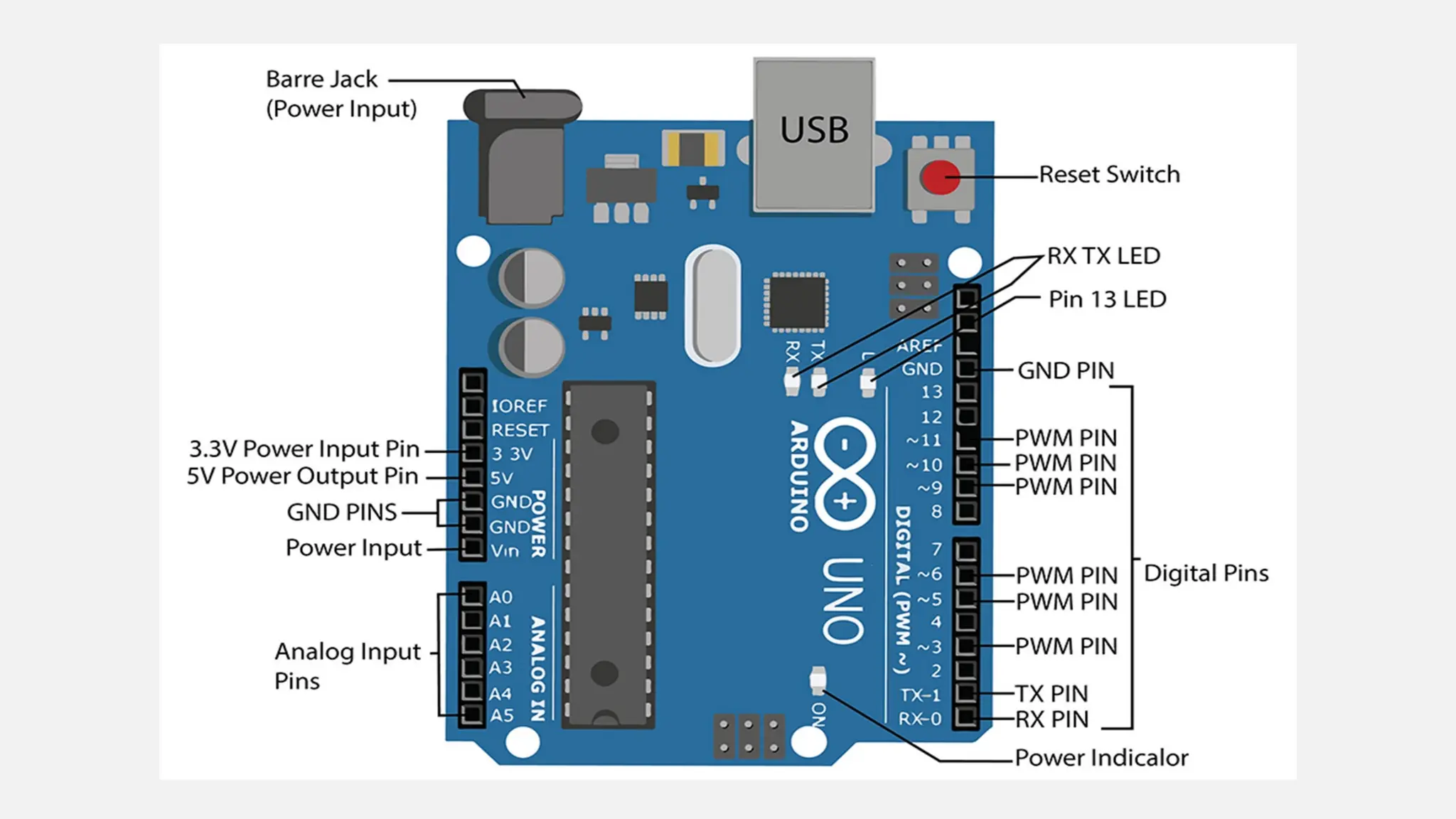
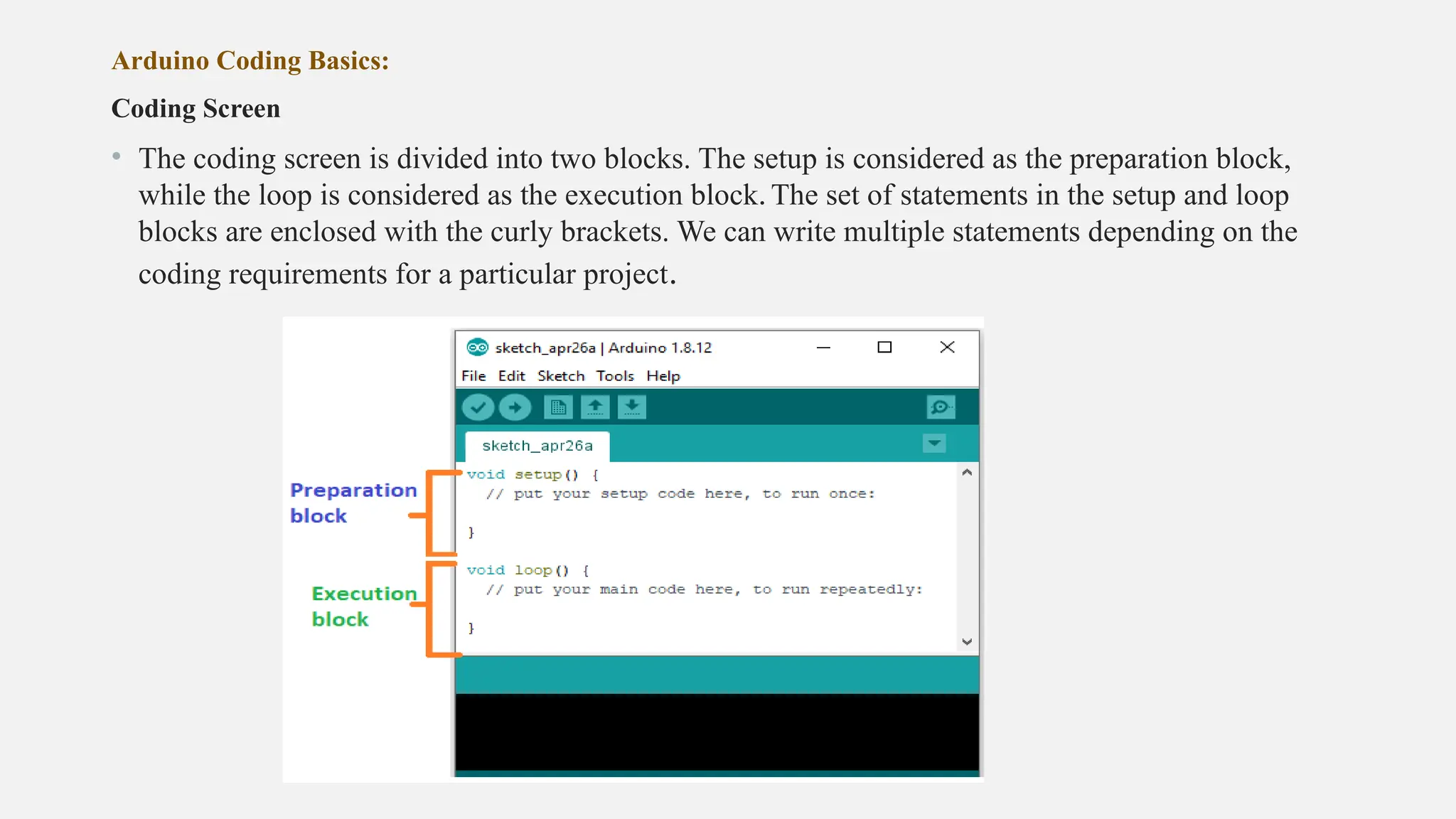
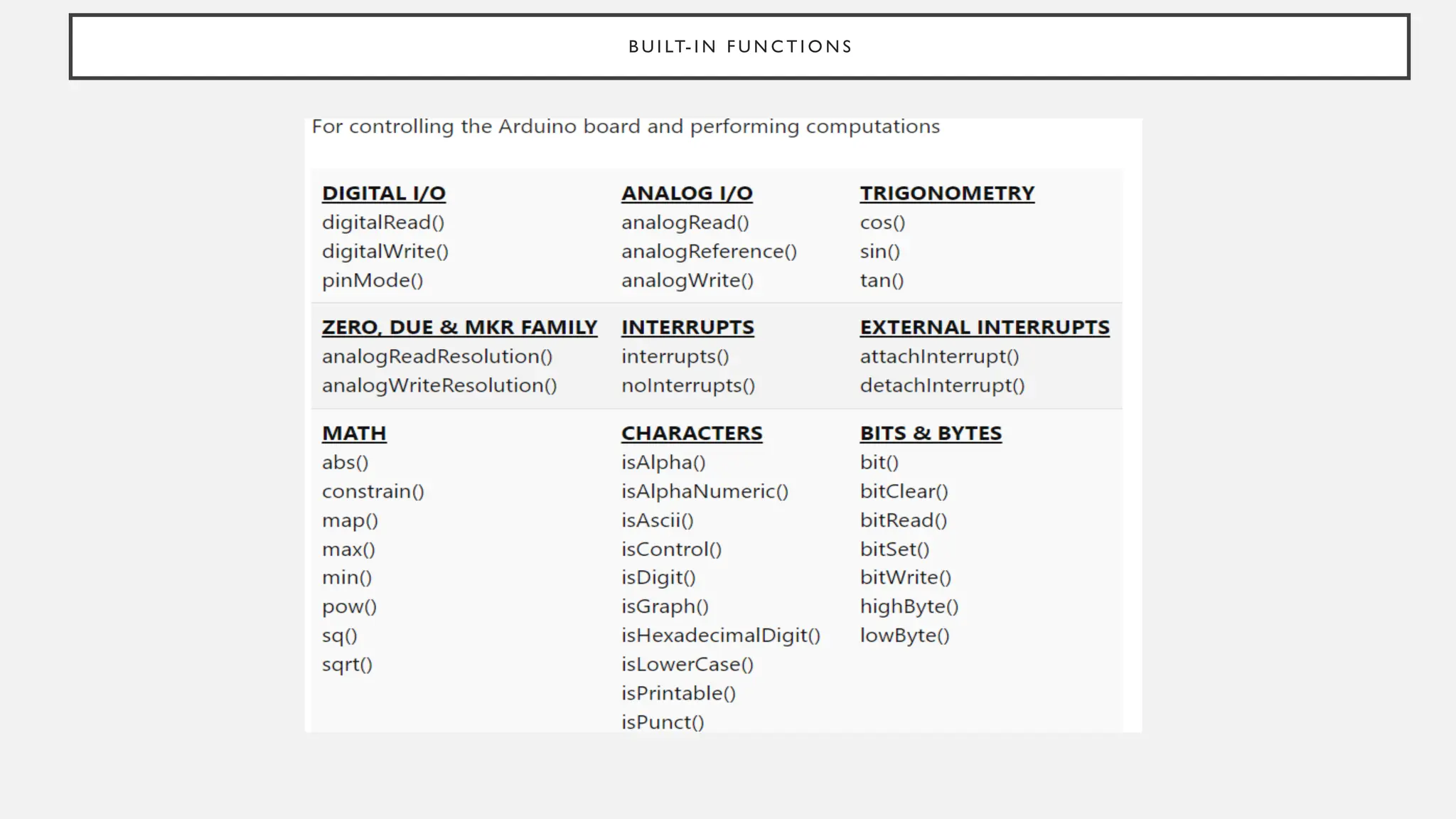
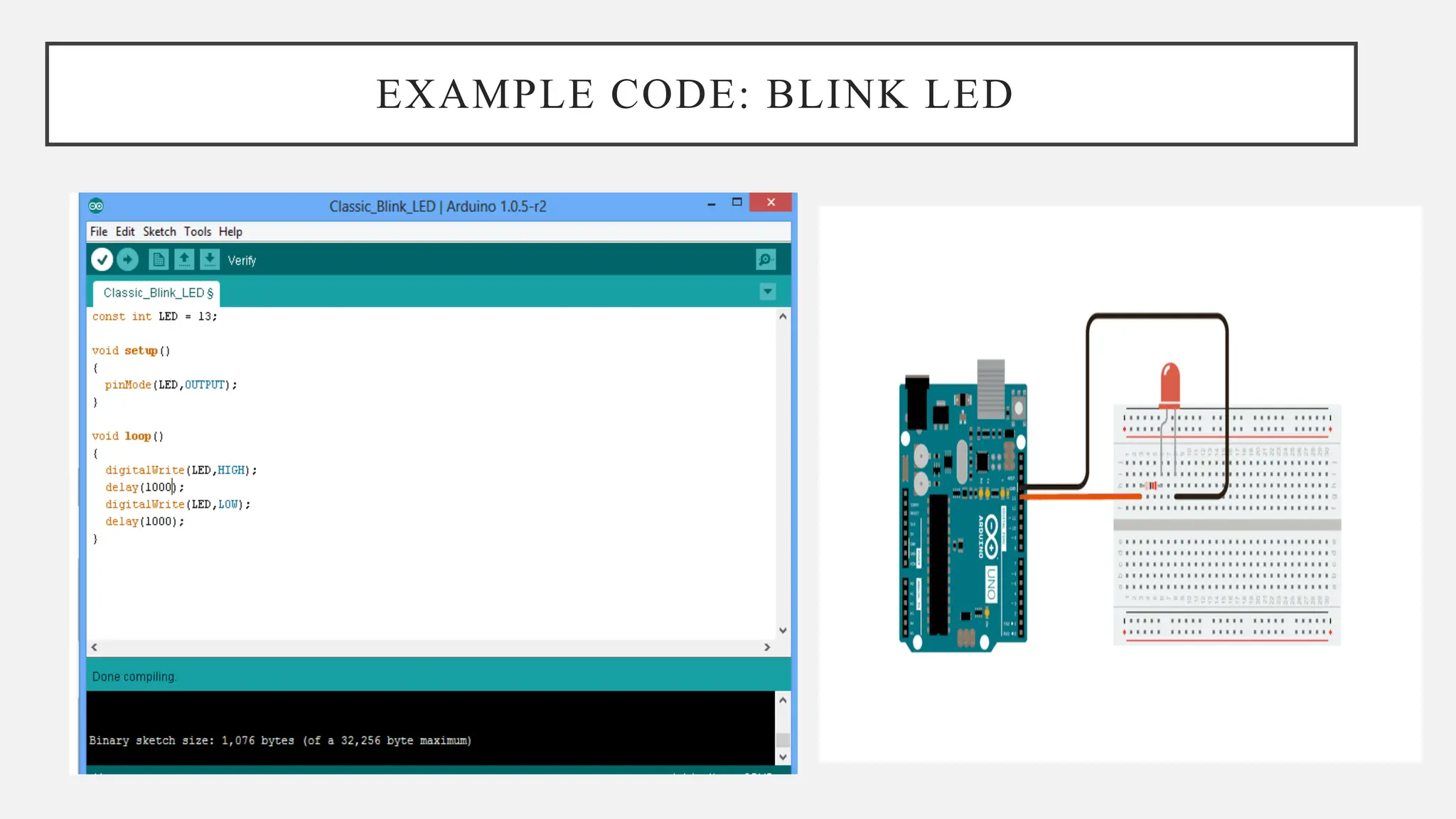
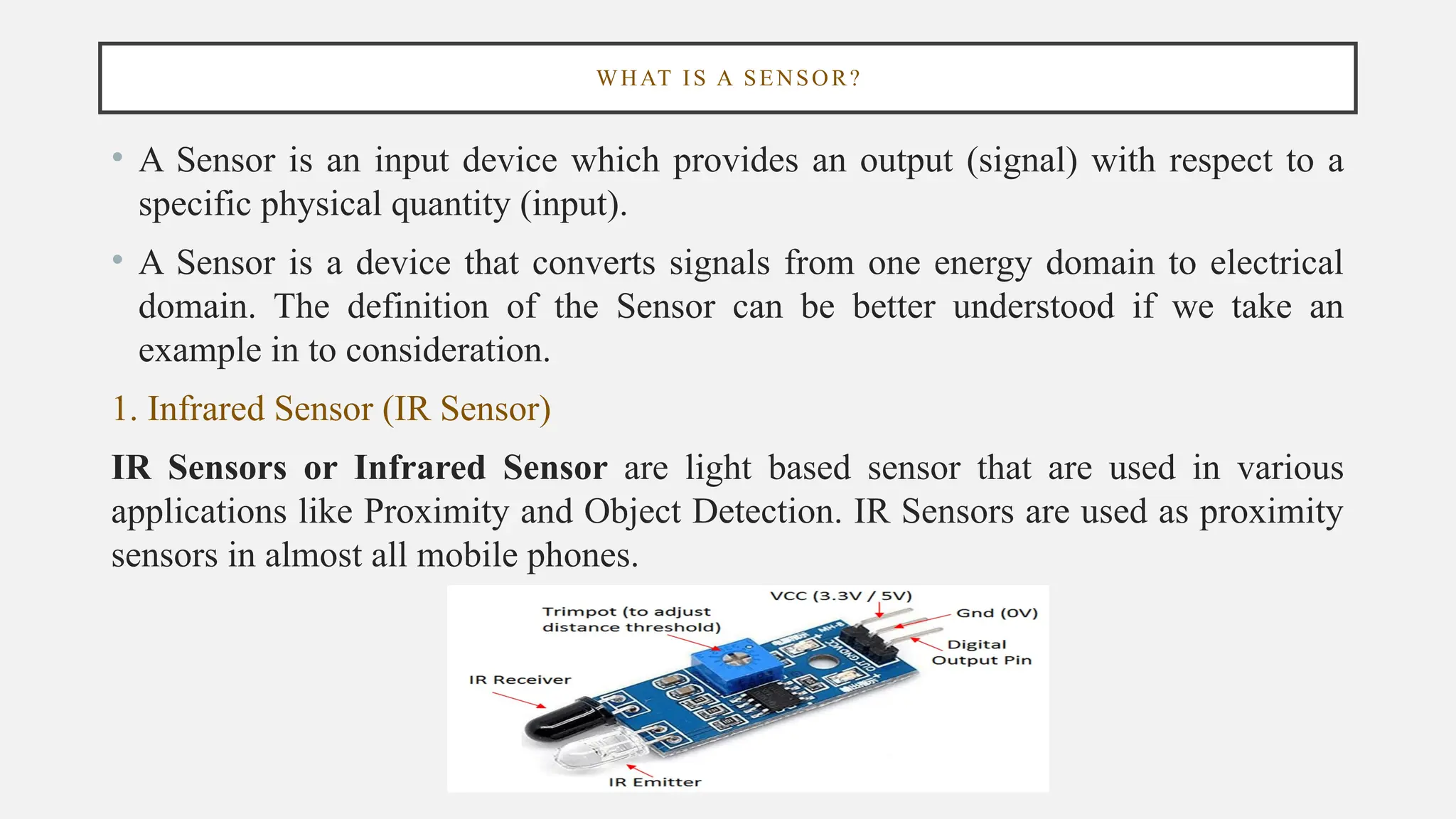
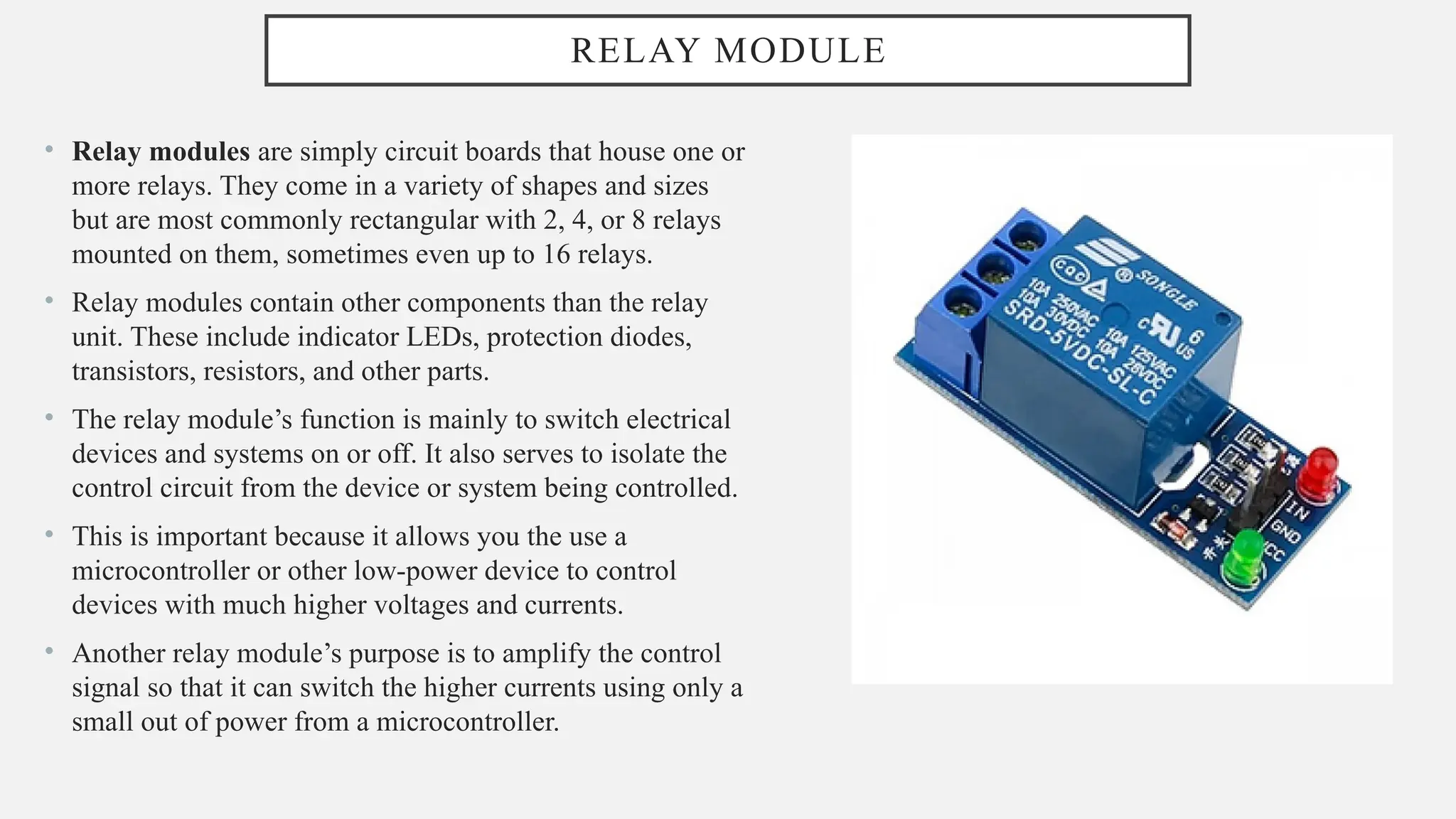
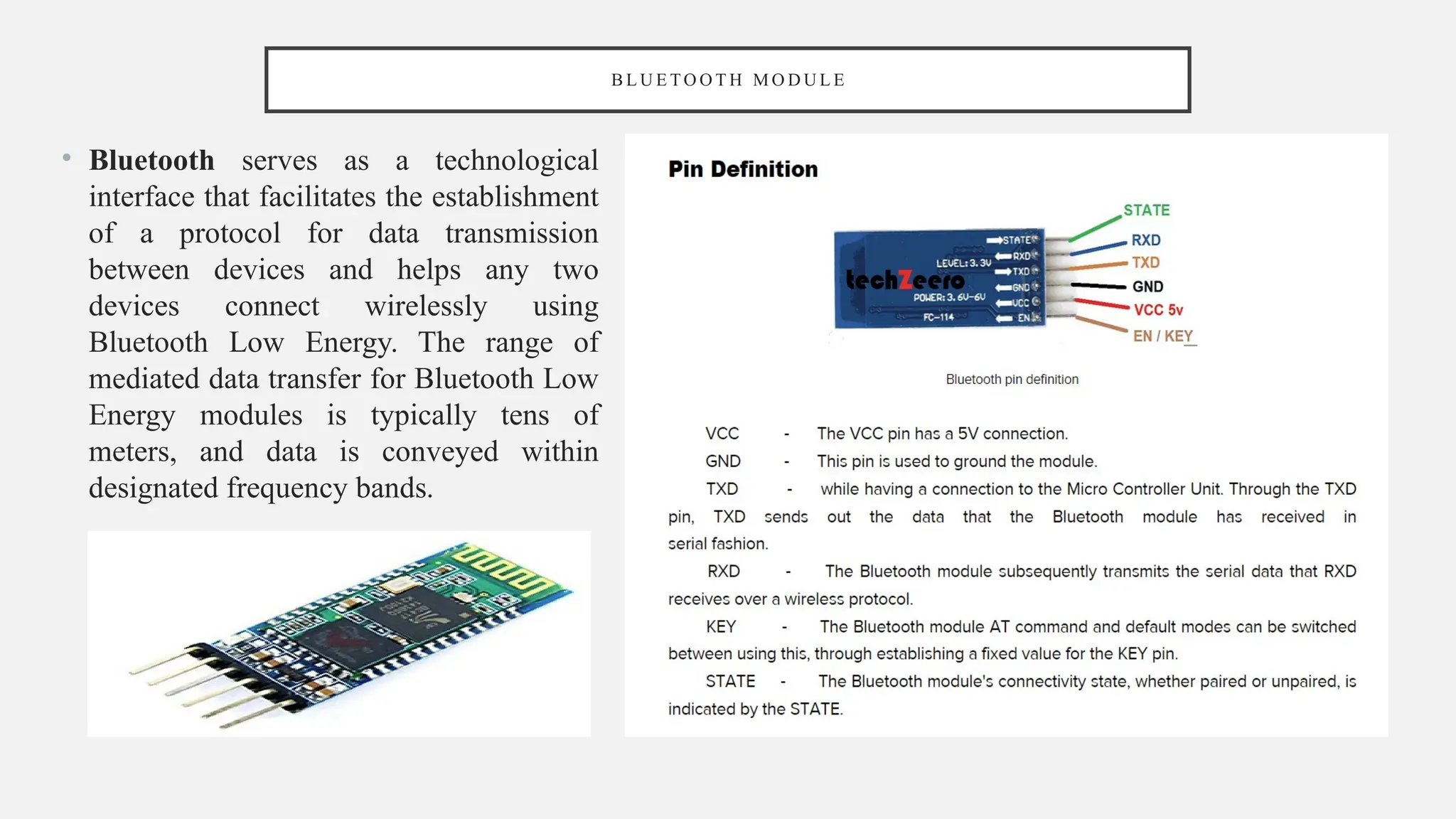
The document outlines a workshop on Arduino basics at JNN College of Engineering, covering topics such as the anatomy of Arduino boards, programming environments, and various applications of Arduino. It describes essential components, including microcontrollers, USB ports, and pins, as well as different Arduino board types and their coding basics. Additionally, the document explains how to use sensors, libraries, and relay modules, with practical applications in home automation, robotics, wearable technology, and education.