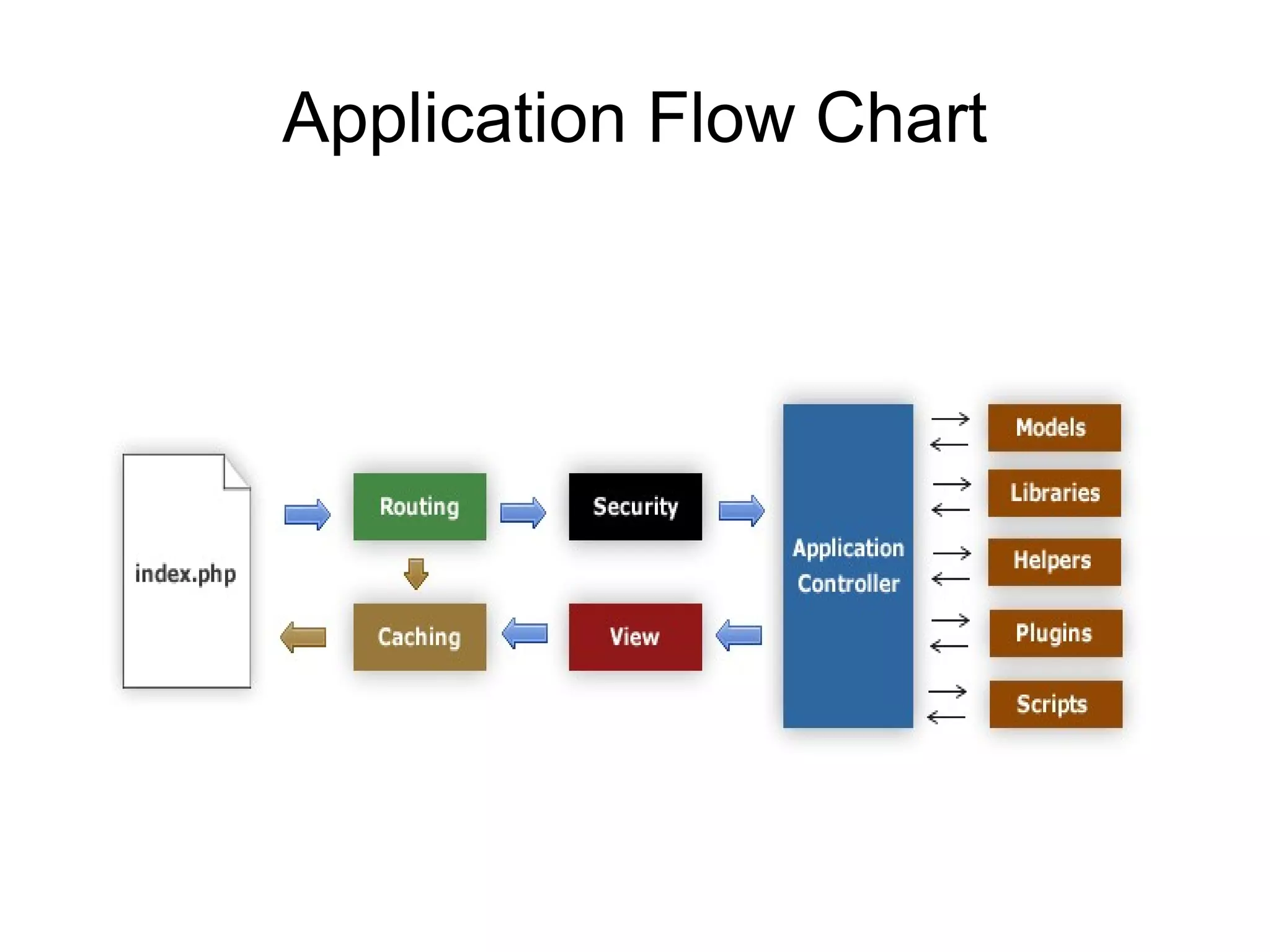
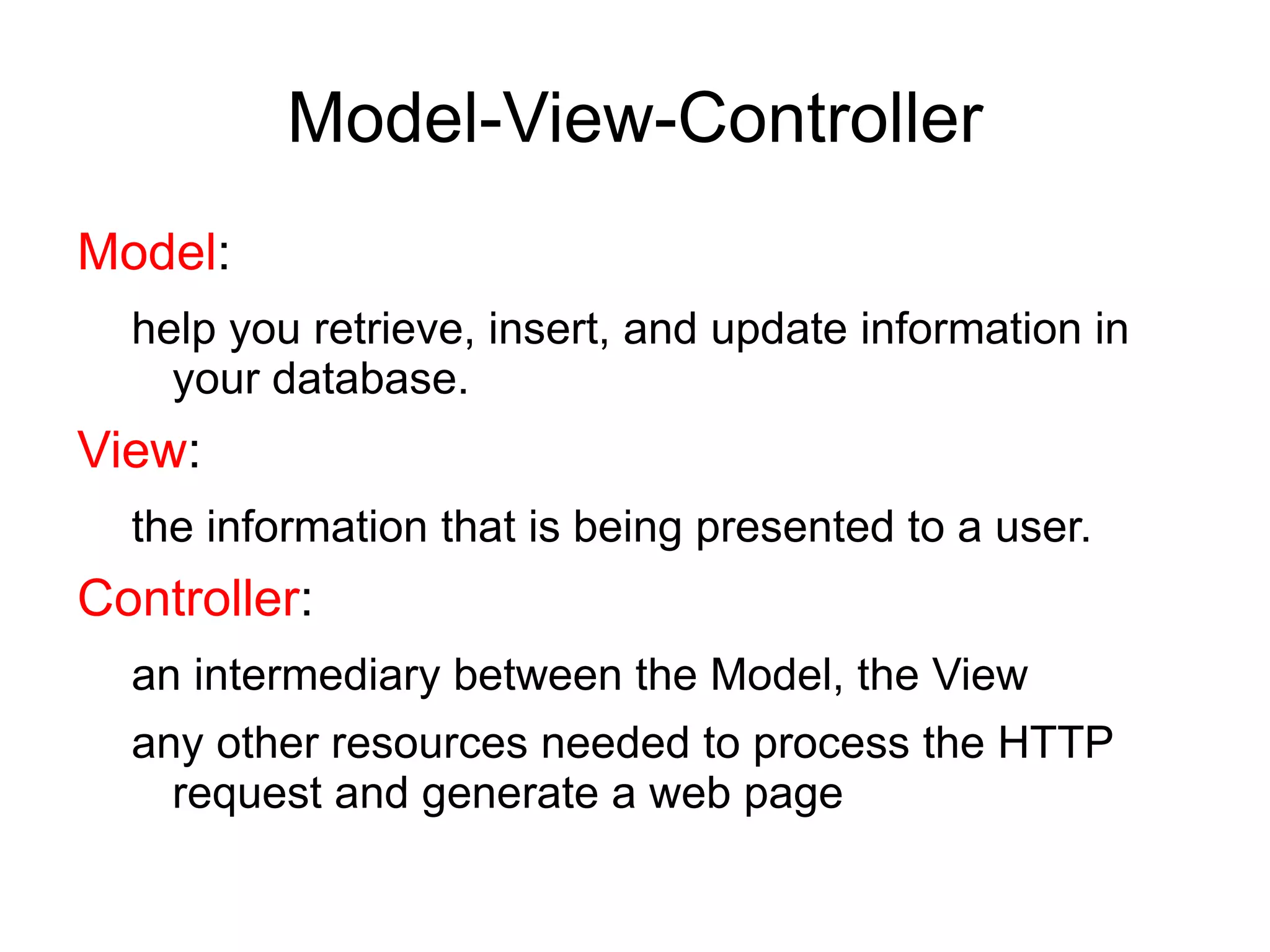
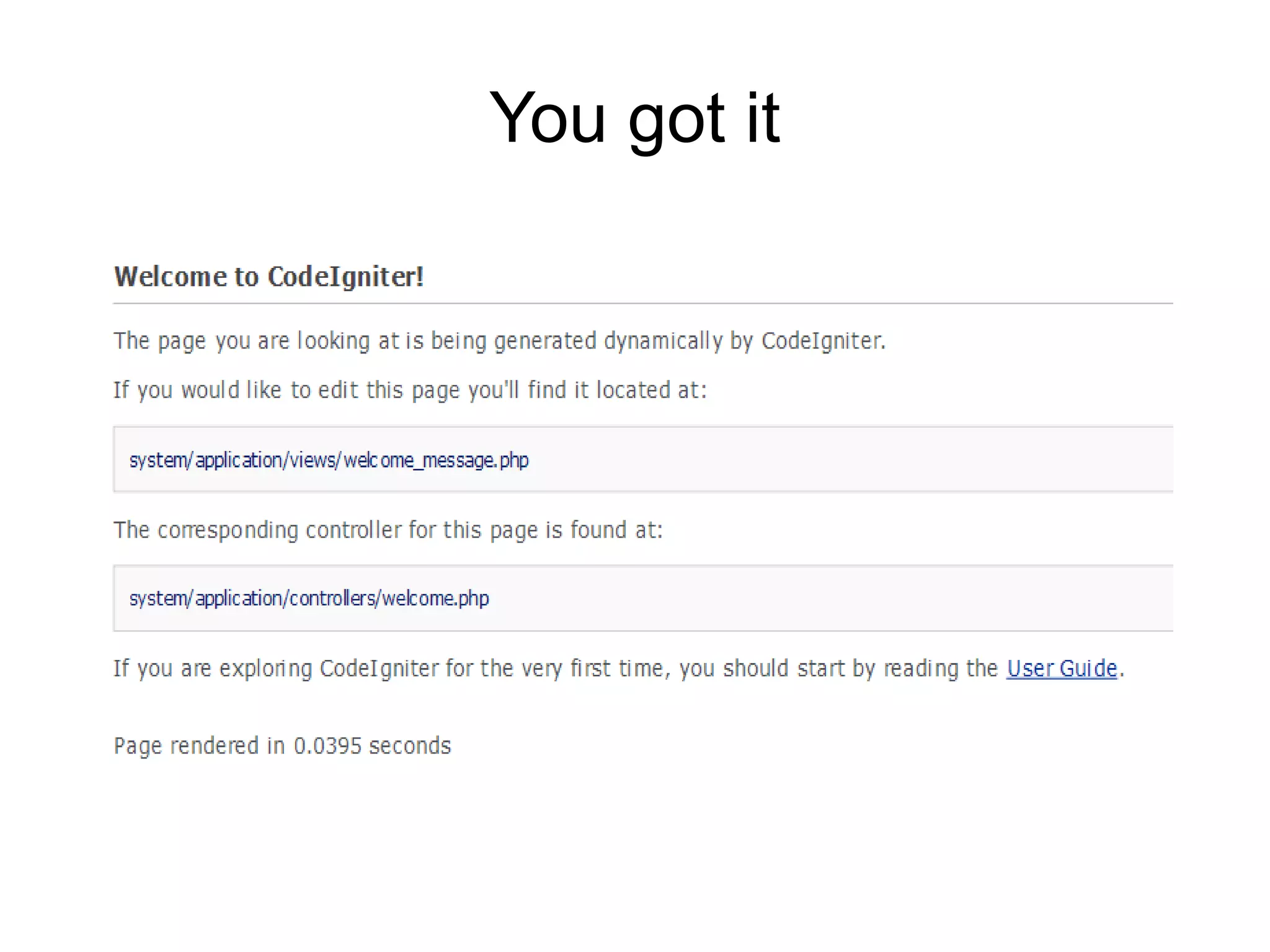
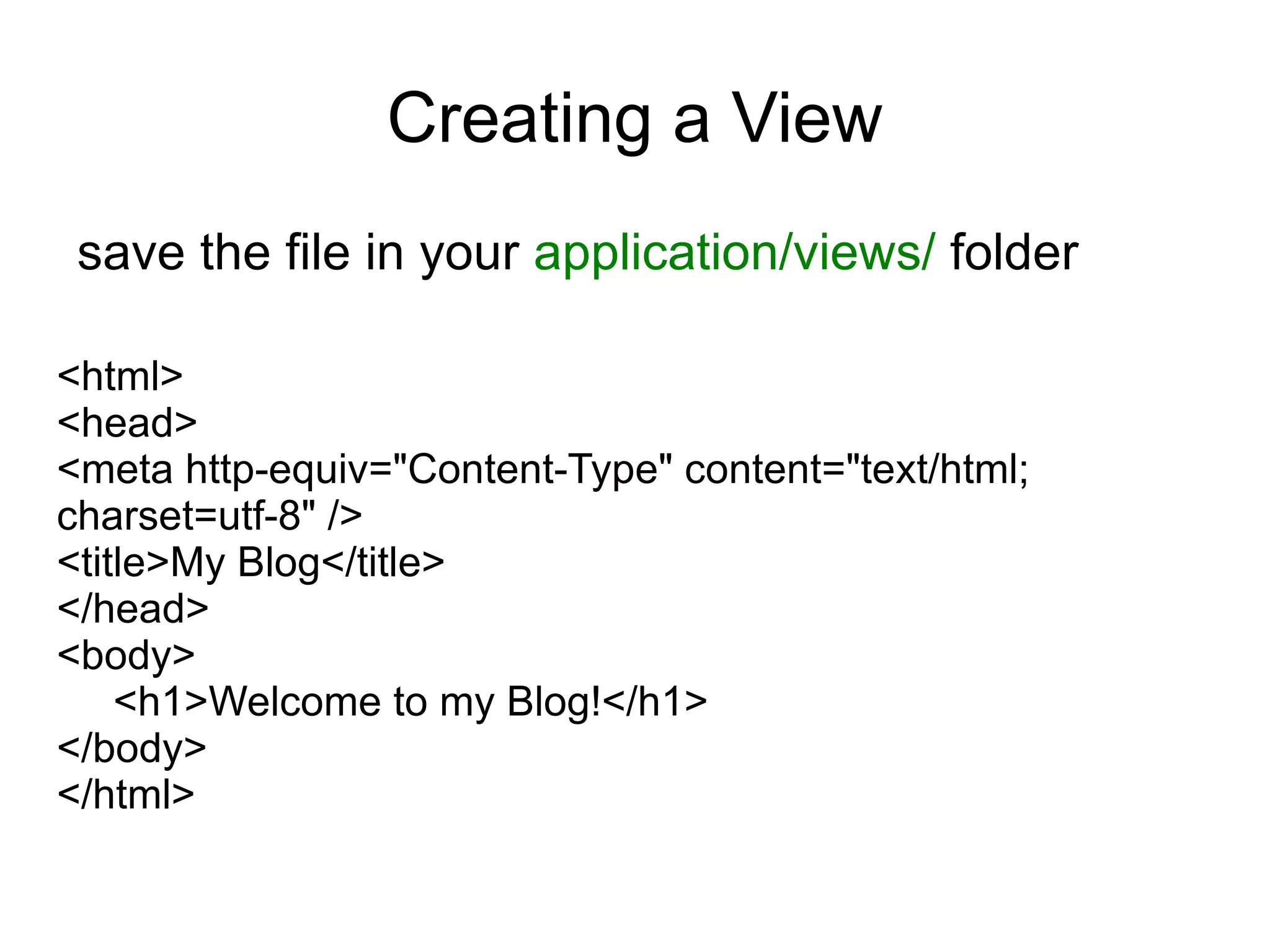
The document discusses CodeIgniter, an open source PHP MVC framework, and provides information about CodeIgniter features such as controllers, models, views, helpers, libraries, and working with databases using CodeIgniter's active record functions. It also covers topics like installing CodeIgniter, creating controllers and models, and loading views, helpers, and libraries.










![Initial Configuration: config.php
system/application/config/
$config['base_url'] = 'http://localhost/';
$config['index_page'] = '';
To make this work, you need to include an .htaccess file to
the CodeIgniter root directory.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeignitermvcframework-090719215302-phpapp01/75/CodeIgniter-PHP-MVC-Framework-18-2048.jpg)
![default settings
$config['charset'] = “UTF-8”;
$config['cache_path'] = '';
$config['permitted_uri_chars'] = 'a-z 0-9~%.:_-';
$config['log_date_format'] = 'Y-m-d H:i:s';
$config['global_xss_filtering'] = TRUE;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeignitermvcframework-090719215302-phpapp01/75/CodeIgniter-PHP-MVC-Framework-19-2048.jpg)
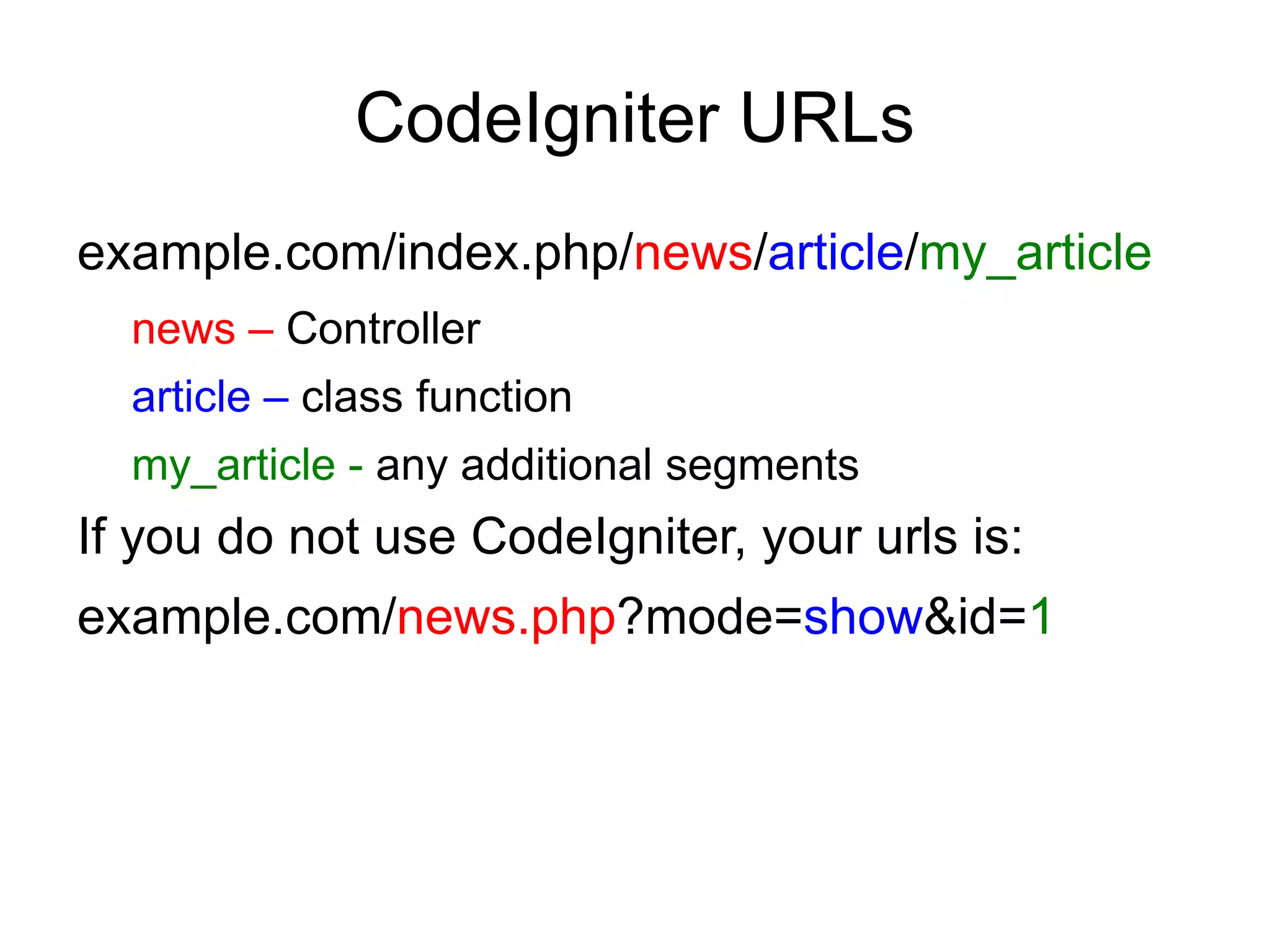
![Removing the index.php file
(Apache)
By default, the index.php file will be included in
your URLs:
example.com/index.php/news/article/my_article
using a .htaccess file with some simple rules
Edit httpd.conf
Unmark LoadModule rewrite_module
modules/mod_rewrite.so
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond $1 !^(index.php|images|robots.txt)
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ /index.php/$1 [L]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeignitermvcframework-090719215302-phpapp01/75/CodeIgniter-PHP-MVC-Framework-21-2048.jpg)


![Enabling Query Strings
In some cases you might prefer to use query
strings URLs:
index.php?c=products&m=view&id=345
index.php?c=controller&m=method
$config['enable_query_strings'] = FALSE;
$config['controller_trigger'] = 'c';
$config['function_trigger'] = 'm';
Reduce the google search keywords](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeignitermvcframework-090719215302-phpapp01/75/CodeIgniter-PHP-MVC-Framework-24-2048.jpg)
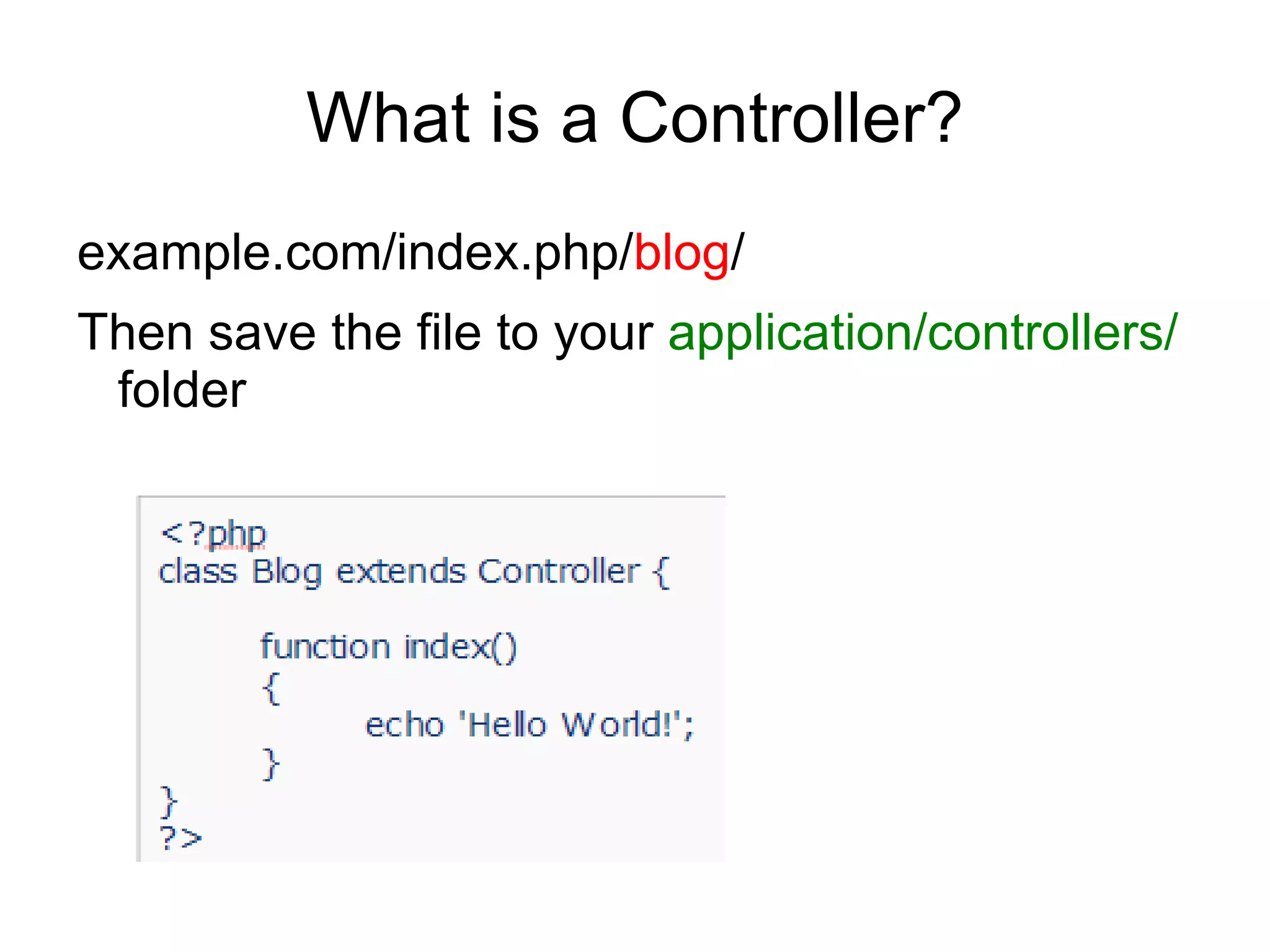

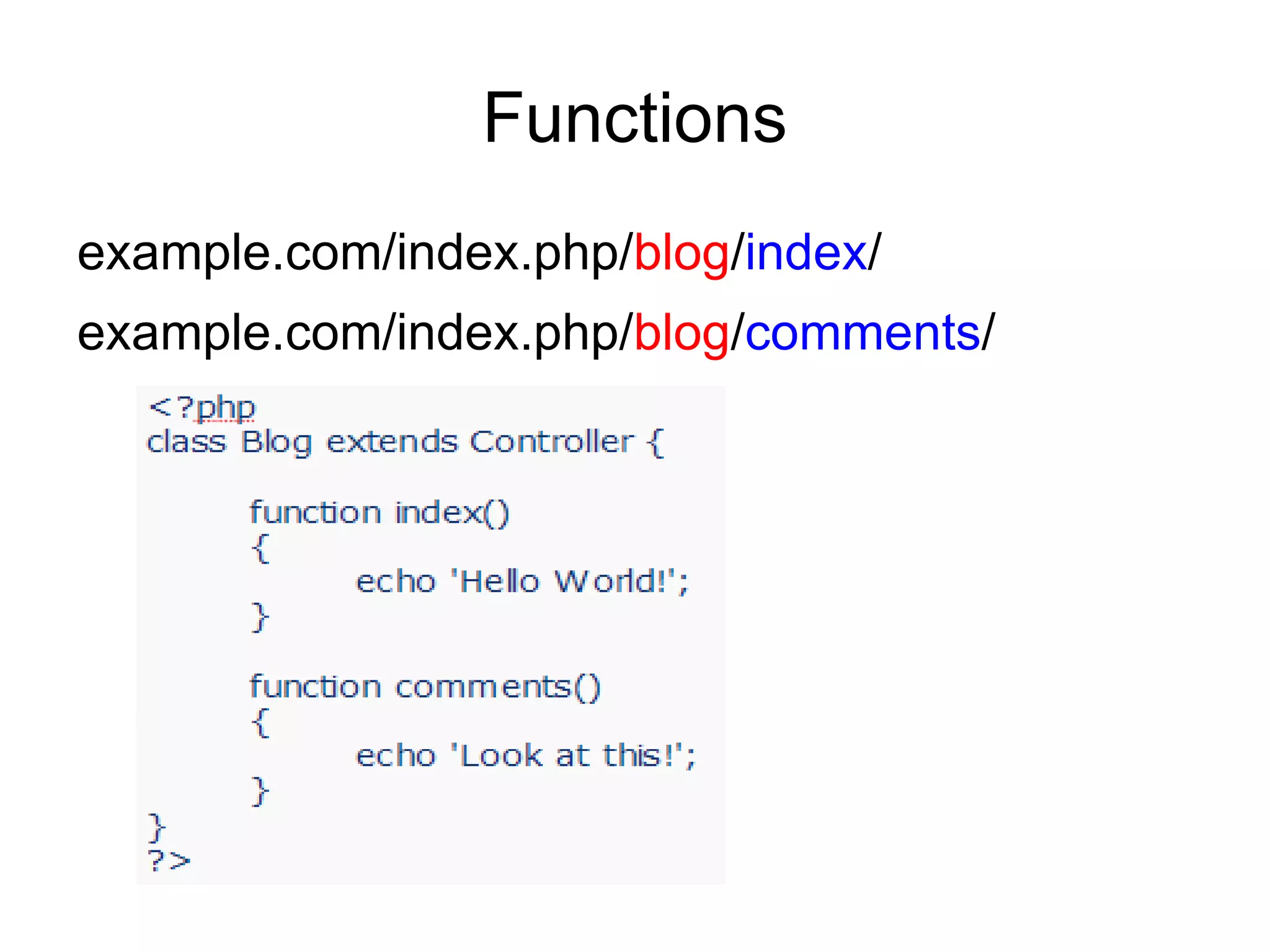


![Defining a Default Controller
open your application/config/routes.php file and
set this variable:
$route['default_controller'] = 'Blog';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeignitermvcframework-090719215302-phpapp01/75/CodeIgniter-PHP-MVC-Framework-30-2048.jpg)
![URI Routing: routes.php
Routing rules are defined in your
application/config/routes.php file
example.com/class/function/id/
http://www.example.com/site/pages/4
http://www.example.com/about_us/
$route['about_us'] = “site/pages/4”;
$route['blog/joe'] = "blogs/users/34";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeignitermvcframework-090719215302-phpapp01/75/CodeIgniter-PHP-MVC-Framework-31-2048.jpg)
![Regular Expressions
$route['products/([a-z]+)/(d+)'] = "$1/id_$2";
$route['default_controller'] = 'welcome';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeignitermvcframework-090719215302-phpapp01/75/CodeIgniter-PHP-MVC-Framework-32-2048.jpg)
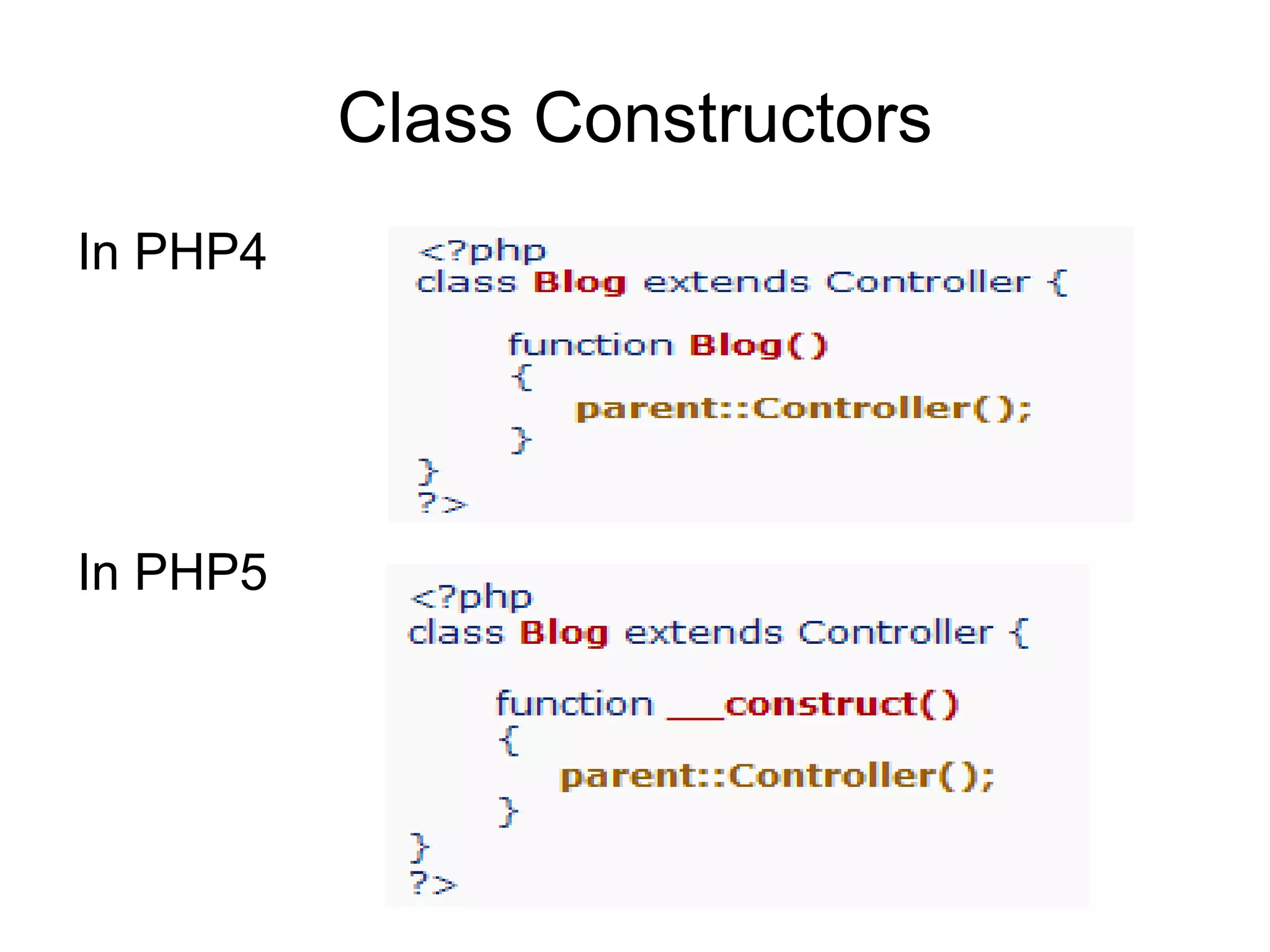

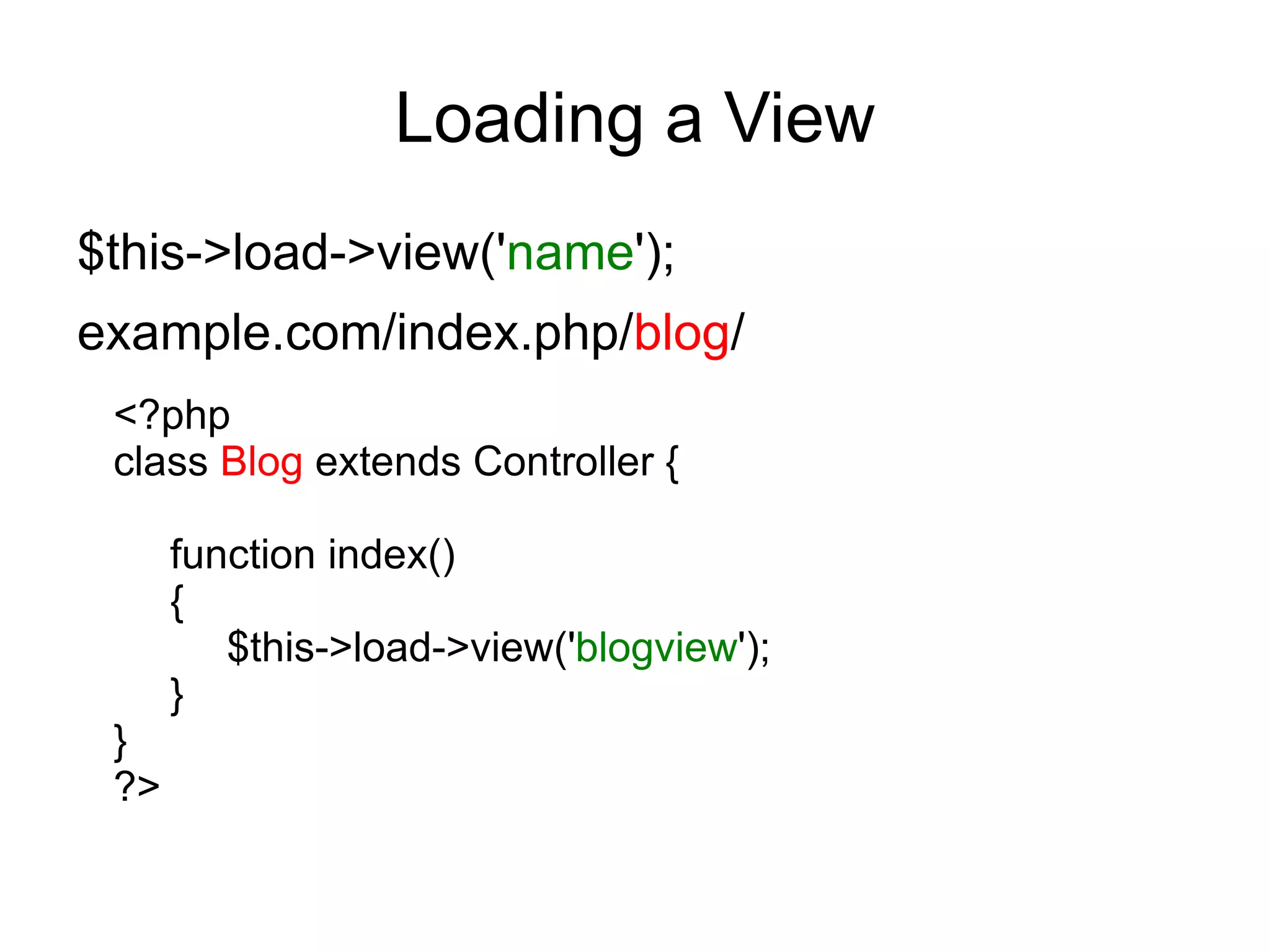
![Loading multiple views
<?php
class Blog extends Controller {
function index()
{
$data['page_title'] = 'Your title';
$this->load->view('header');
$this->load->view('menu');
$this->load->view('content', $data);
$this->load->view('footer');
}
}
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeignitermvcframework-090719215302-phpapp01/75/CodeIgniter-PHP-MVC-Framework-37-2048.jpg)

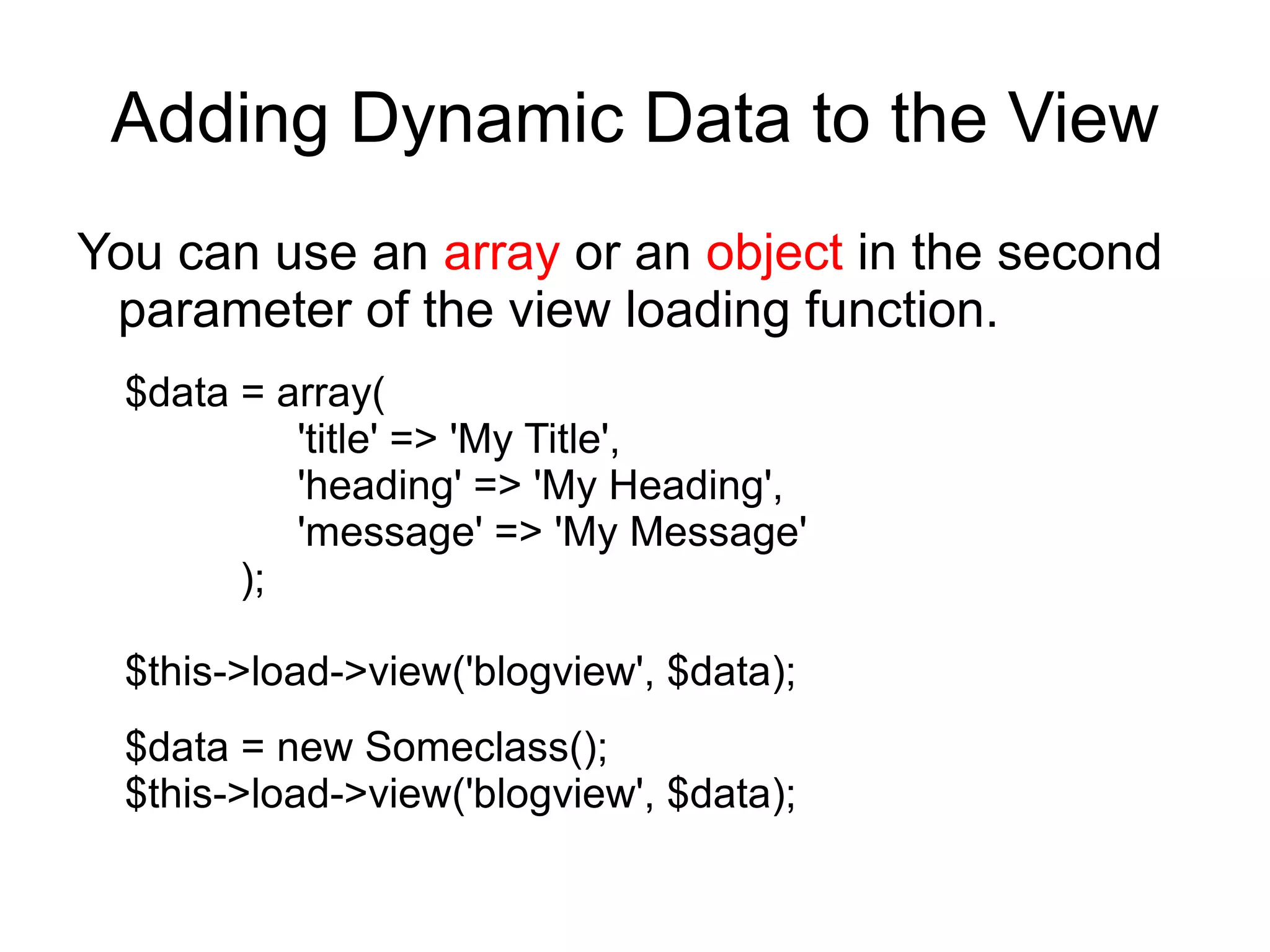
![example
<?php
class Blog extends Controller {
function index()
{
$data['title'] = "My Real Title";
$data['heading'] = "My Real Heading";
$this->load->view('blogview', $data);
}
}
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeignitermvcframework-090719215302-phpapp01/75/CodeIgniter-PHP-MVC-Framework-40-2048.jpg)
![Creating Loops: Controller
<?php
class Blog extends Controller {
function index()
{
$data['todo_list'] = array('Clean House', 'Call Mom',
'Run Errands');
$data['title'] = "My Real Title";
$data['heading'] = "My Real Heading";
$this->load->view('blogview', $data);
}
}
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeignitermvcframework-090719215302-phpapp01/75/CodeIgniter-PHP-MVC-Framework-41-2048.jpg)





![How to Auto-loading Helpers?
To autoload resources, open the
application/config/autoload.php file and add the
item you want loaded to the autoload array
$autoload['libraries'] =
array('database','session','email','validation');
$autoload['helper'] =
array('url','form','text','date','security');
$autoload['plugin'] = array('captcha');
$autoload['model'] = array();
$autoload['config'] = array();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeignitermvcframework-090719215302-phpapp01/75/CodeIgniter-PHP-MVC-Framework-47-2048.jpg)



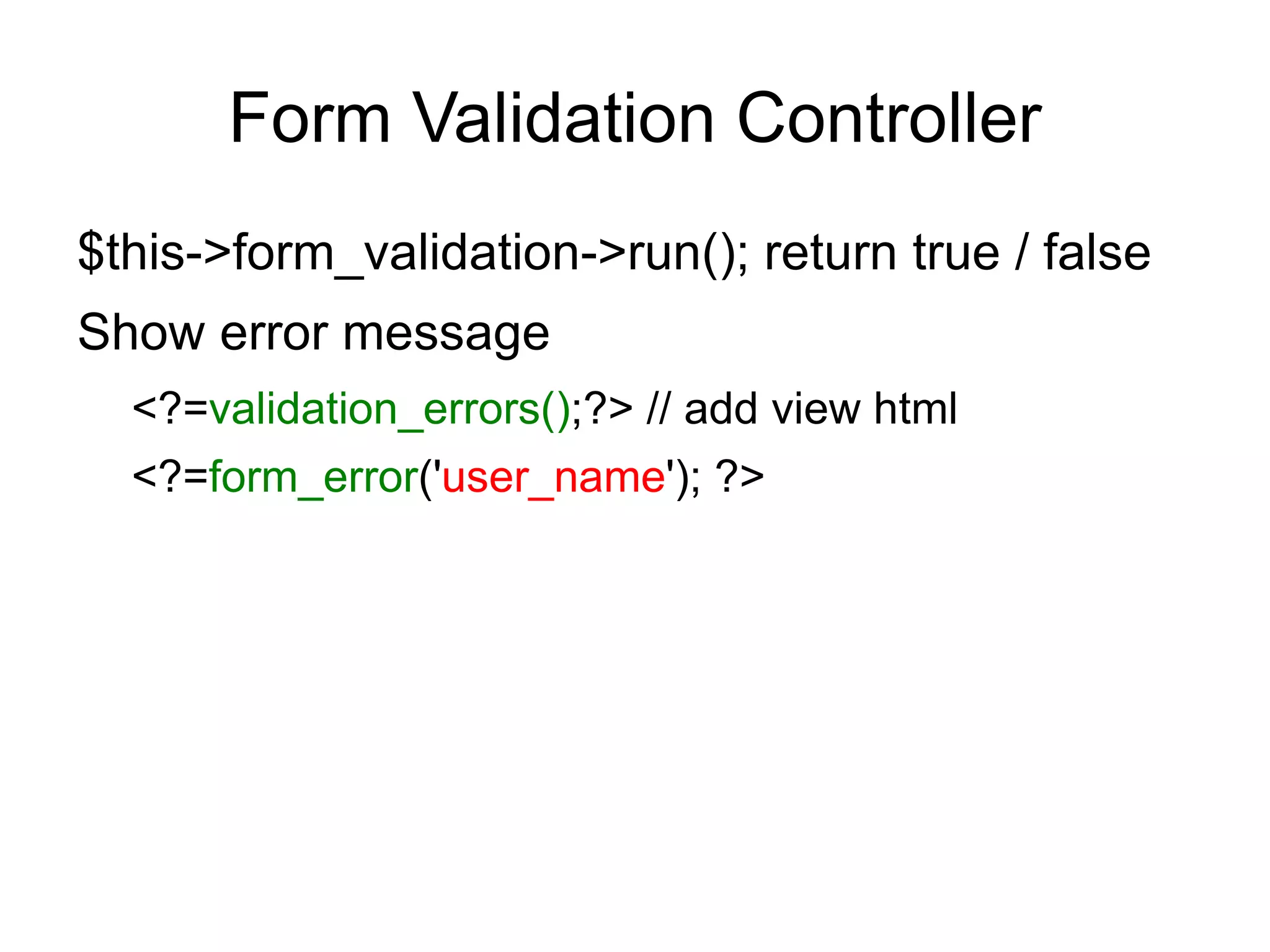
![Form Validation
Setting Validation Rules
$this->form_validation->set_rules('username', 'Username',
'required|min_length[5]|max_length[12]');
$this->form_validation->set_rules('password', 'Password',
'required|matches[passconf]');
$this->form_validation->set_rules('passconf', 'Password
Confirmation', 'required');
$this->form_validation->set_rules('email', 'Email', 'required|
valid_email');](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeignitermvcframework-090719215302-phpapp01/75/CodeIgniter-PHP-MVC-Framework-52-2048.jpg)







![Example: controller loads a model
class Blog extends Controller
{
function index()
{
$this->load->model('Blog');
$data['query'] = $this->Blog->get_last_ten_entries();
$this->load->view('blog', $data);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeignitermvcframework-090719215302-phpapp01/75/CodeIgniter-PHP-MVC-Framework-63-2048.jpg)
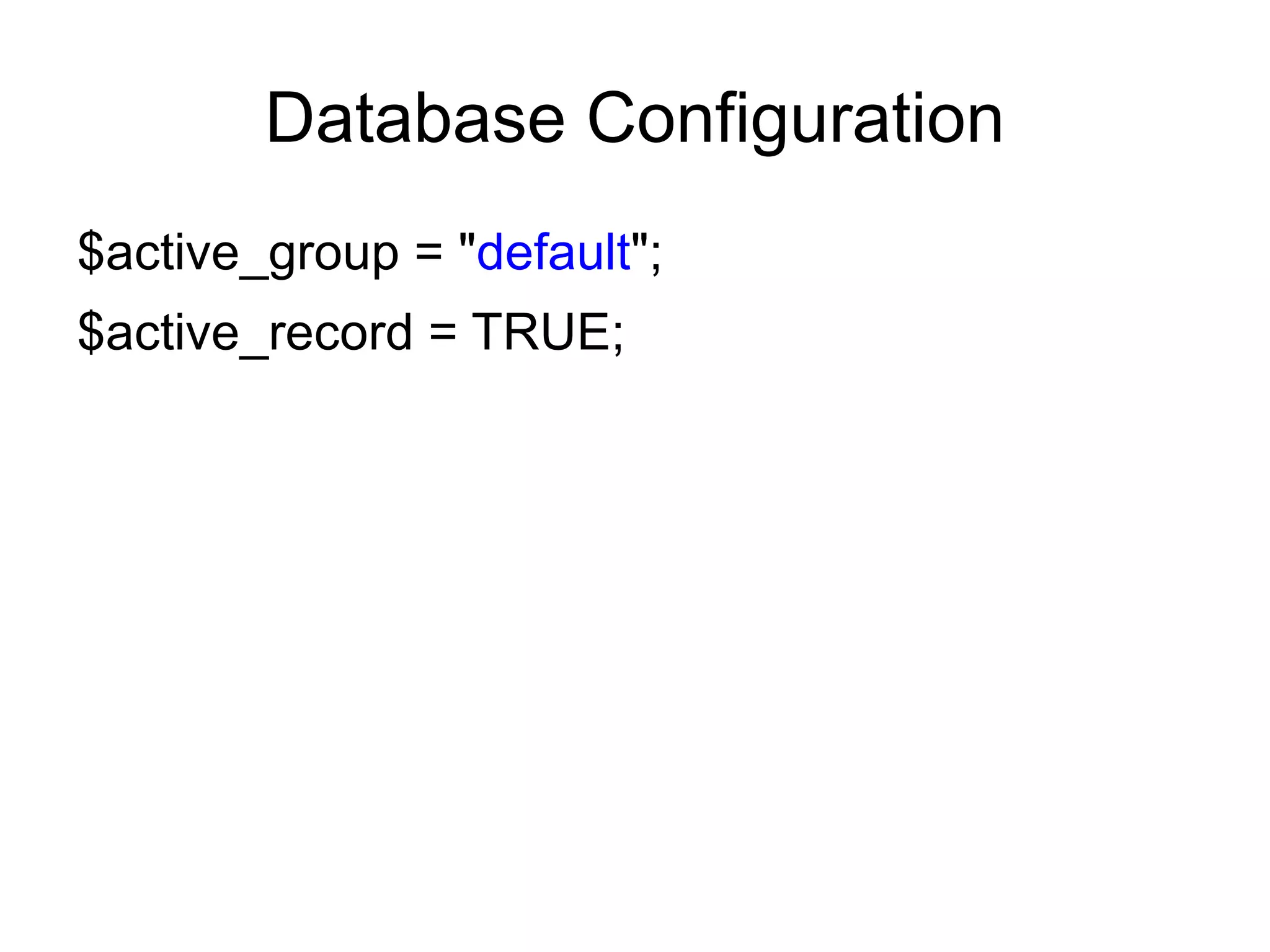
![Database Configuration
Edit: application/config/database.php
$db['default']['hostname'] = "localhost";
$db['default']['username'] = "root";
$db['default']['password'] = "";
$db['default']['database'] = "database_name";
$db['default']['dbdriver'] = "mysql";
$db['default']['dbprefix'] = "";
$db['default']['pconnect'] = FALSE;
$db['default']['cache_on'] = FALSE;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeignitermvcframework-090719215302-phpapp01/75/CodeIgniter-PHP-MVC-Framework-64-2048.jpg)


![Generating Query Results
result_array():
single result row: $query->row_array();
$query = $this->db->query("YOUR QUERY");
foreach ($query->result_array() as $row)
{
echo $row['title'];
echo $row['name'];
echo $row['body'];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeignitermvcframework-090719215302-phpapp01/75/CodeIgniter-PHP-MVC-Framework-68-2048.jpg)












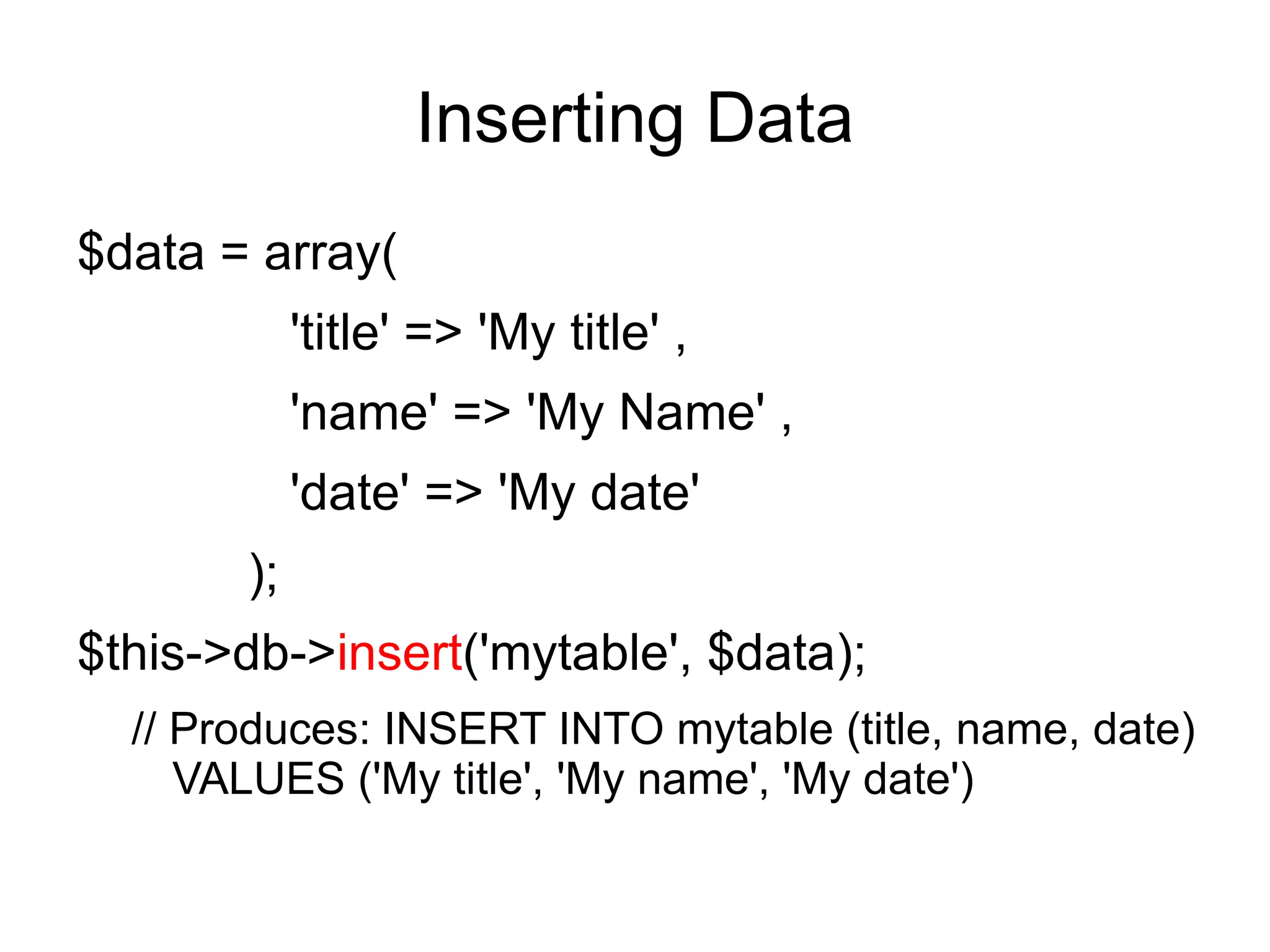
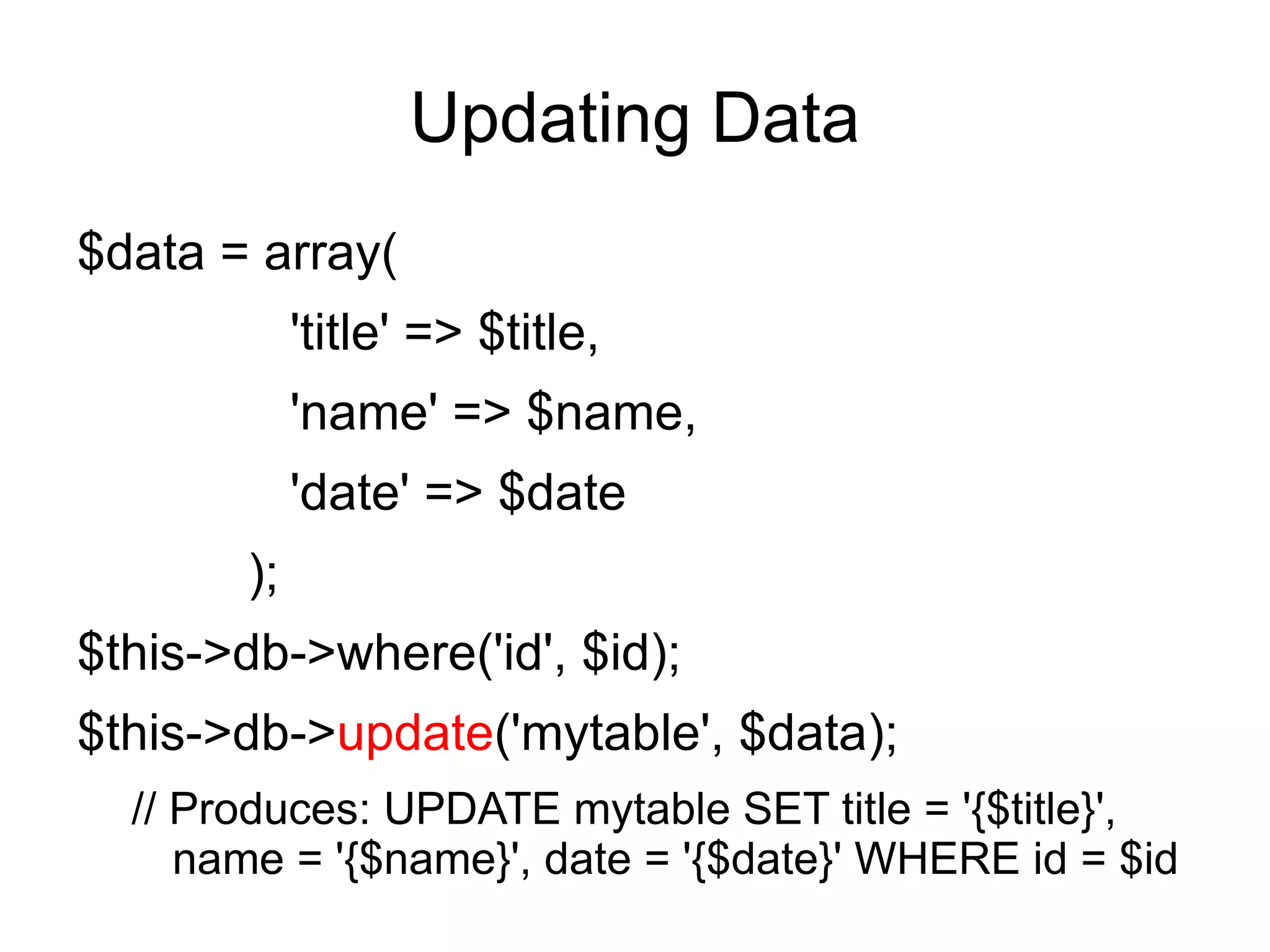


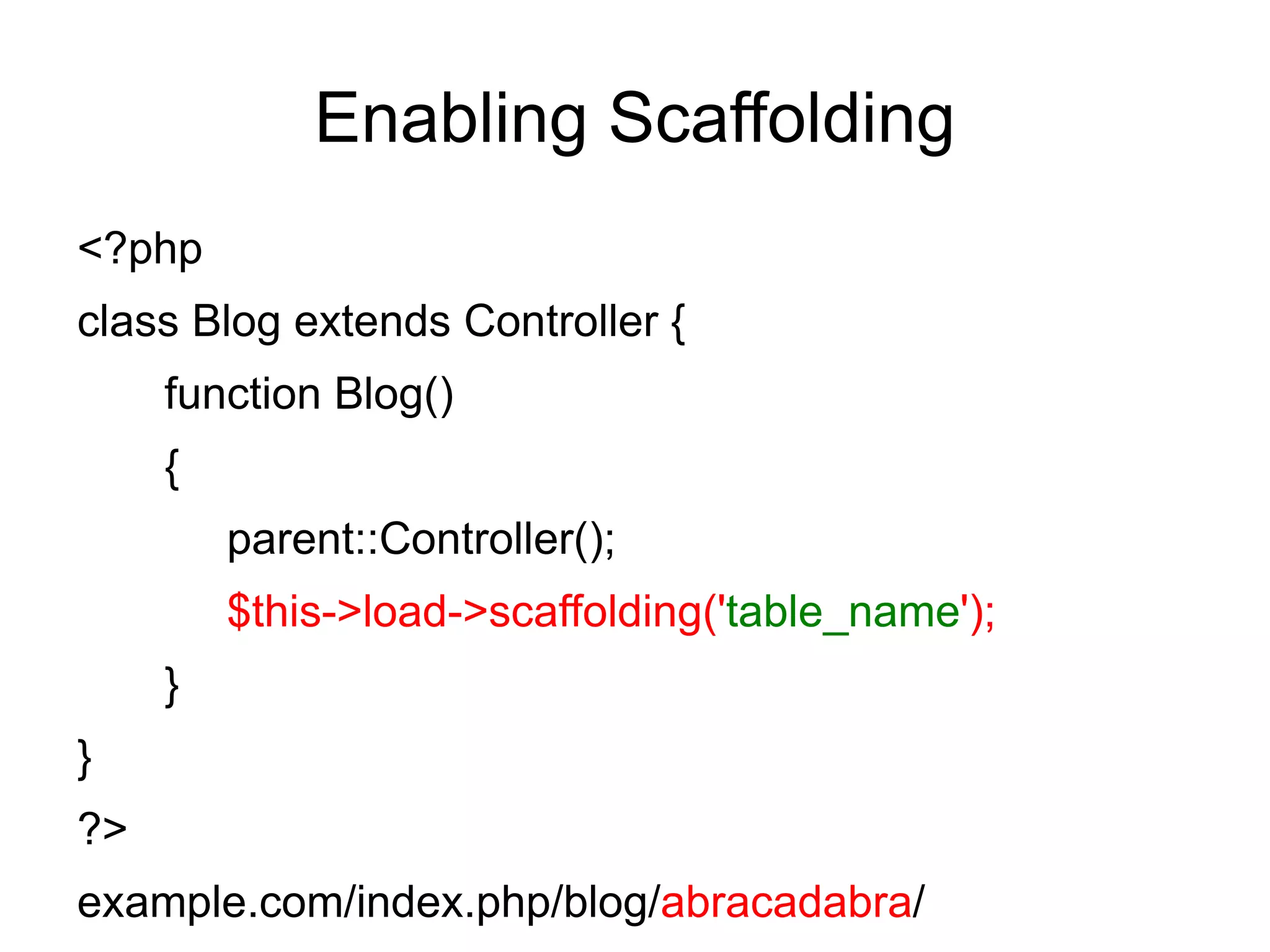
![Scaffolding
It feature provides a fast and very convenient
way to add, edit, or delete information in your
database during development.
To set a secret word, open your
application/config/routes.php file and look for
this item:
$route['scaffolding_trigger'] = '';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeignitermvcframework-090719215302-phpapp01/75/CodeIgniter-PHP-MVC-Framework-85-2048.jpg)