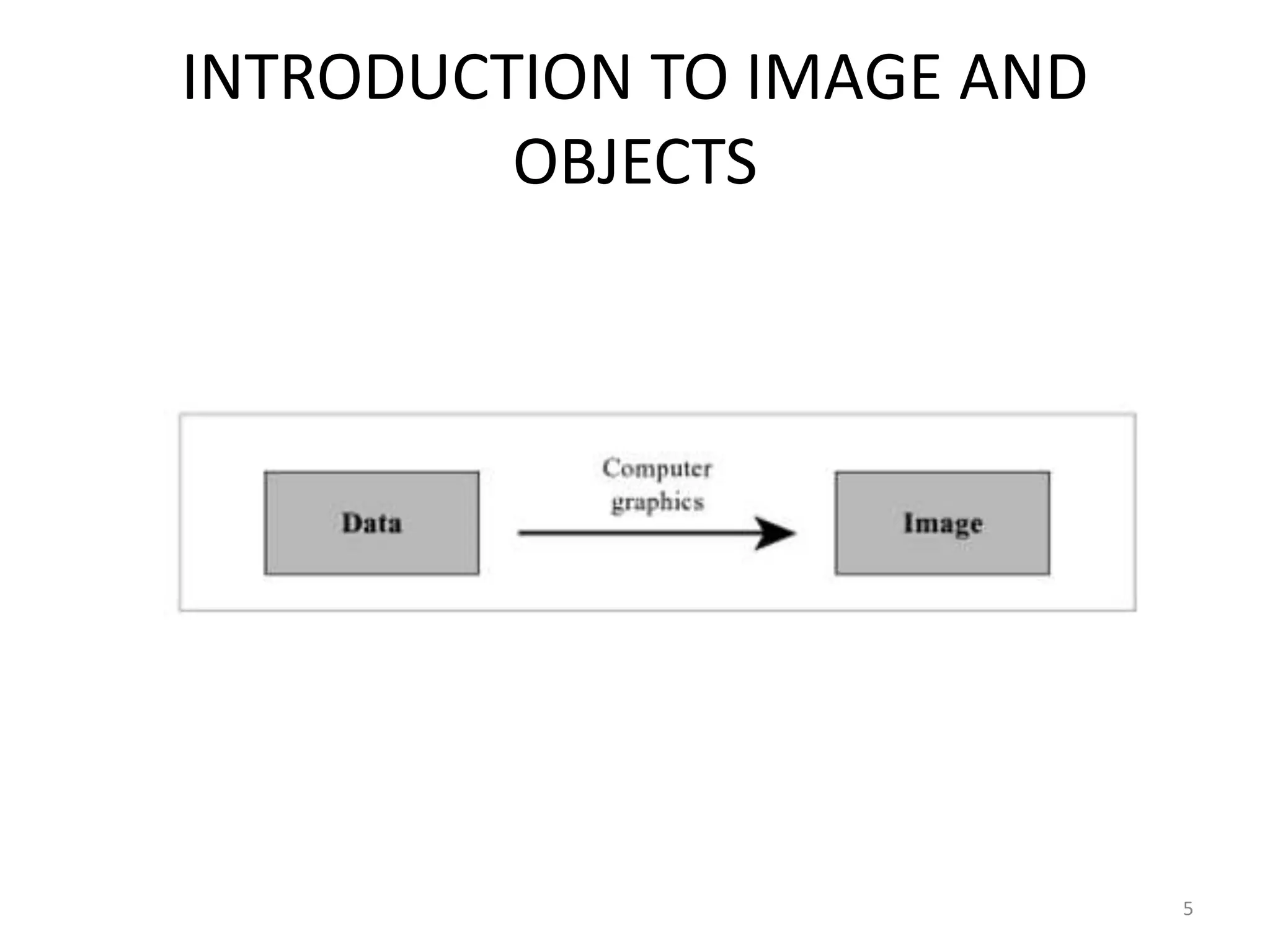
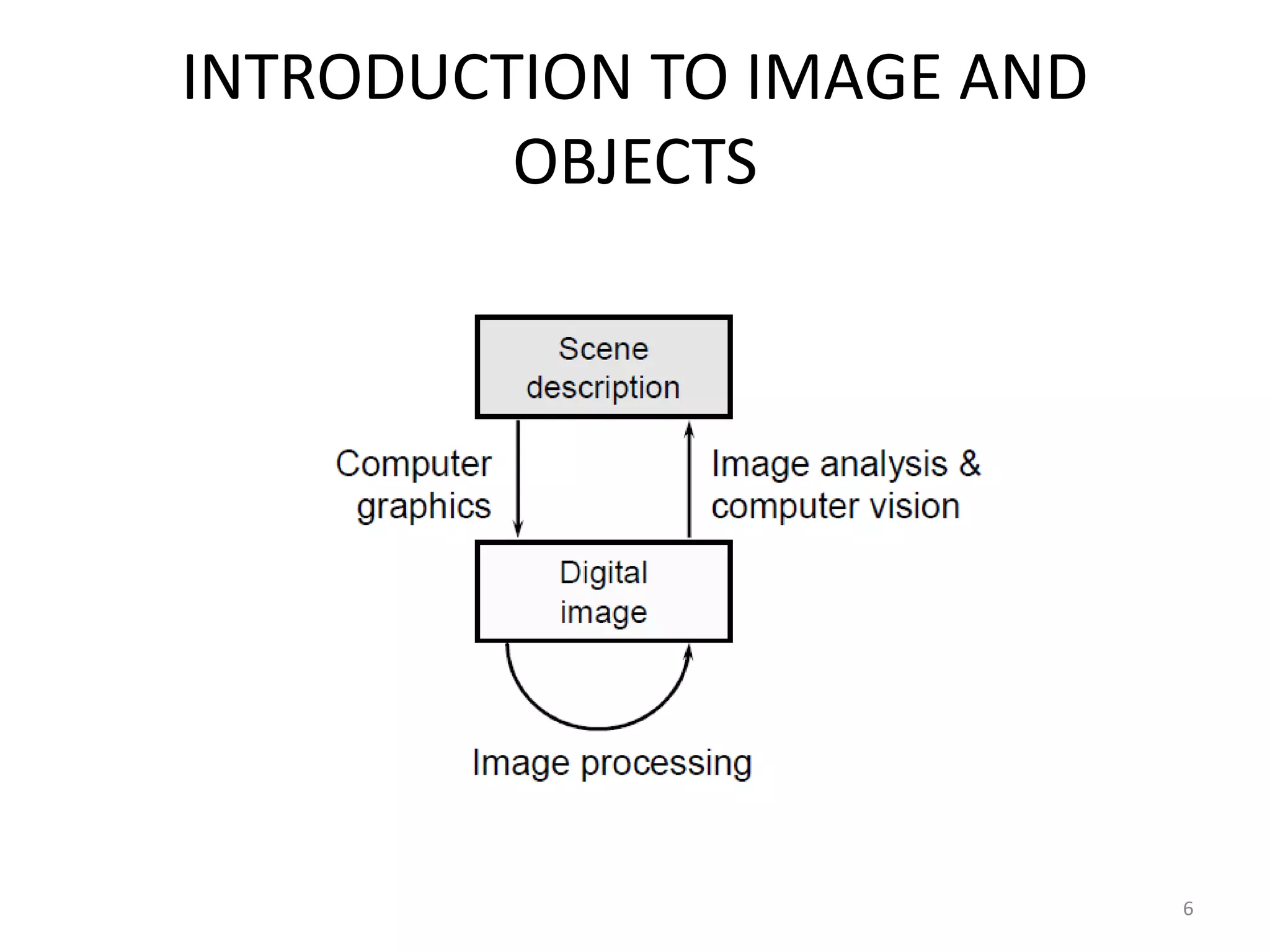
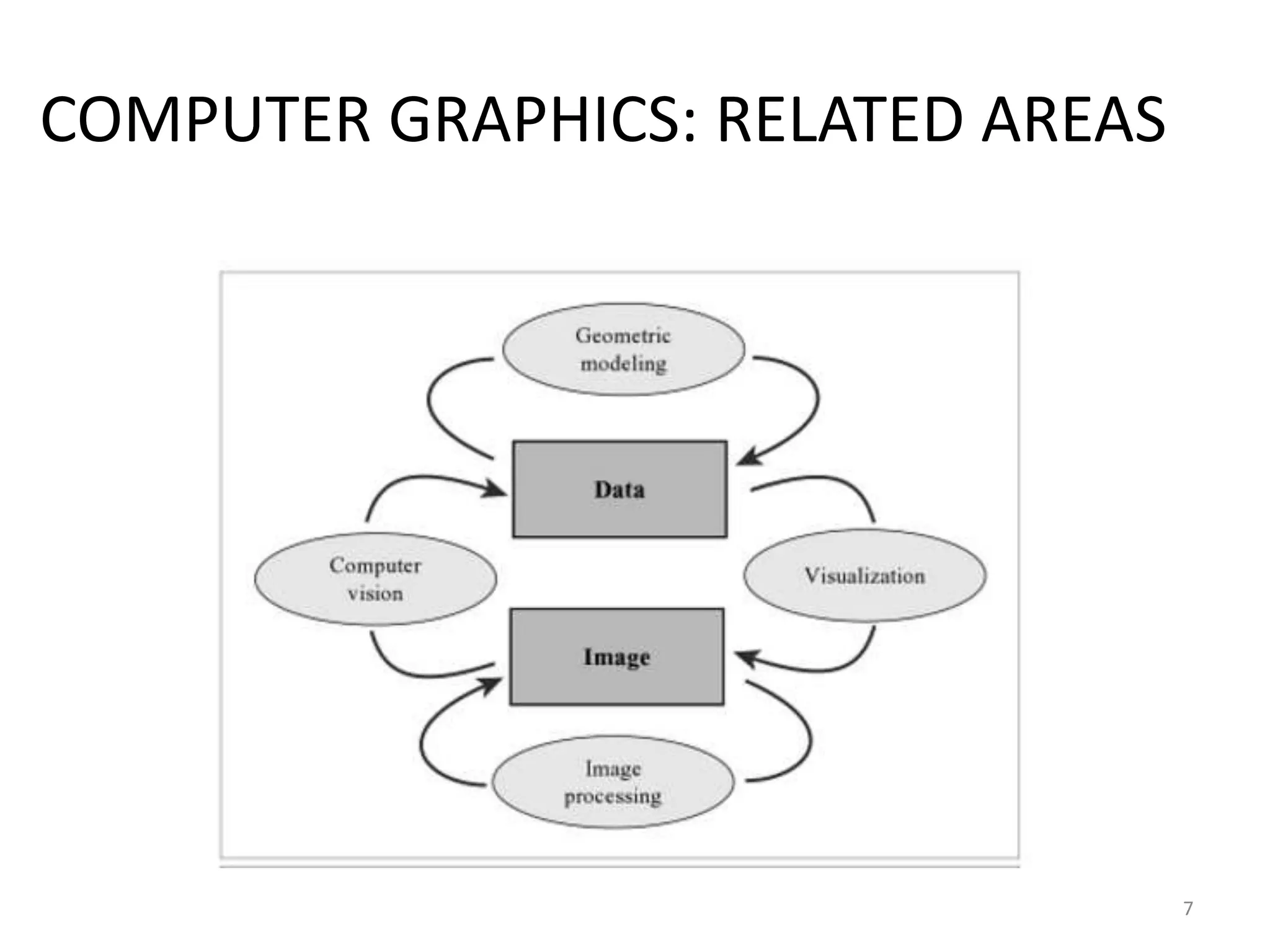
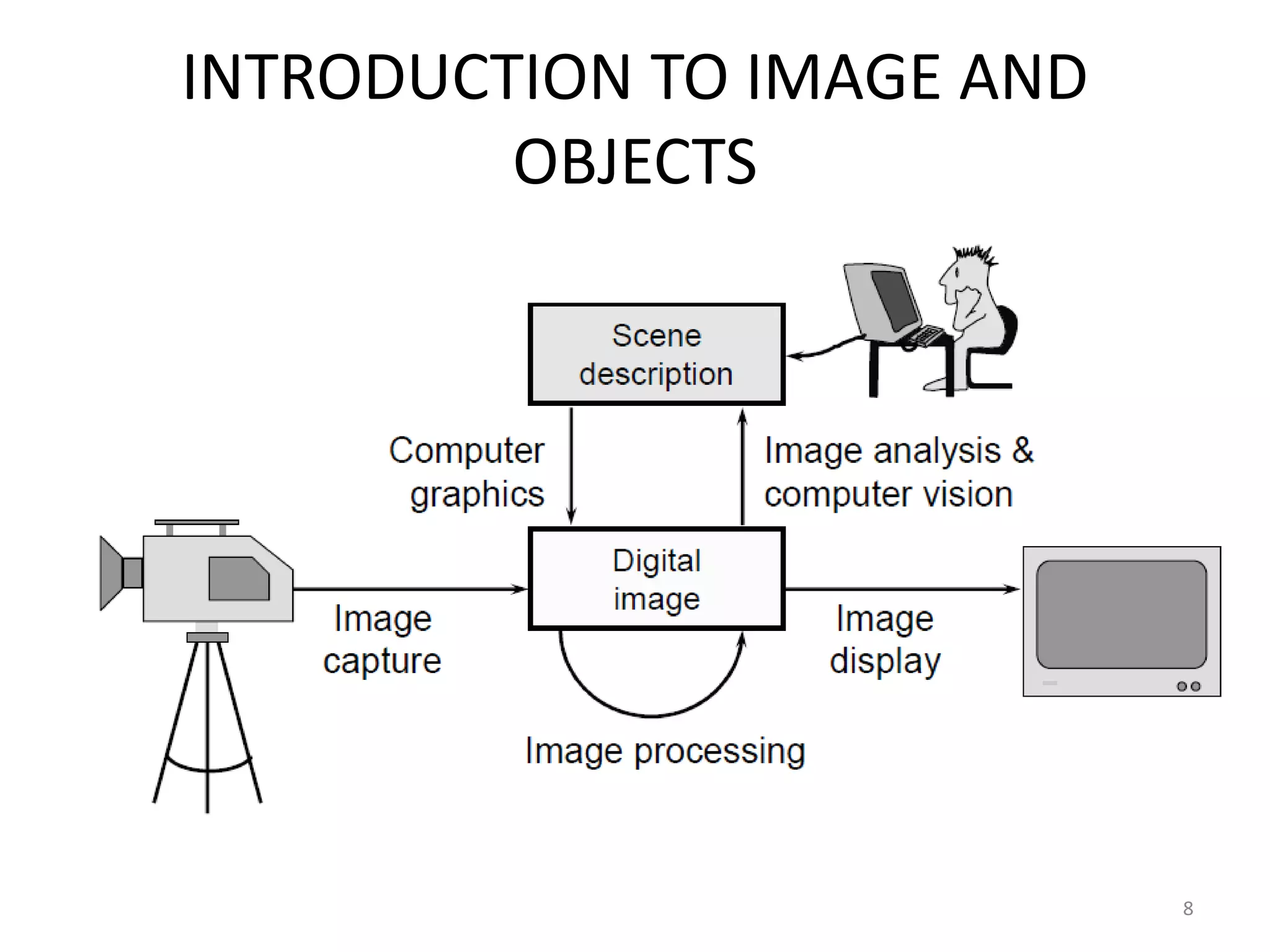
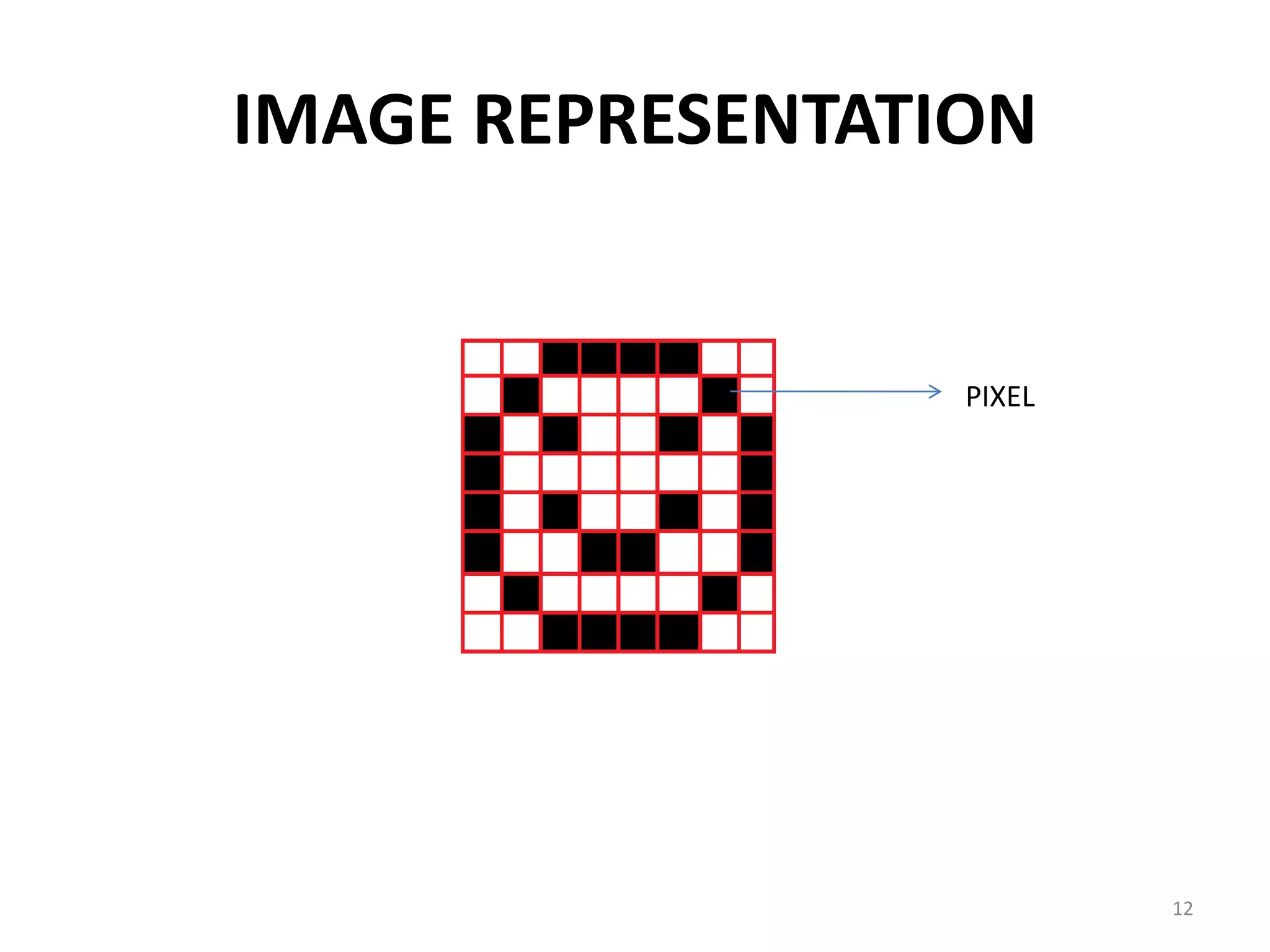
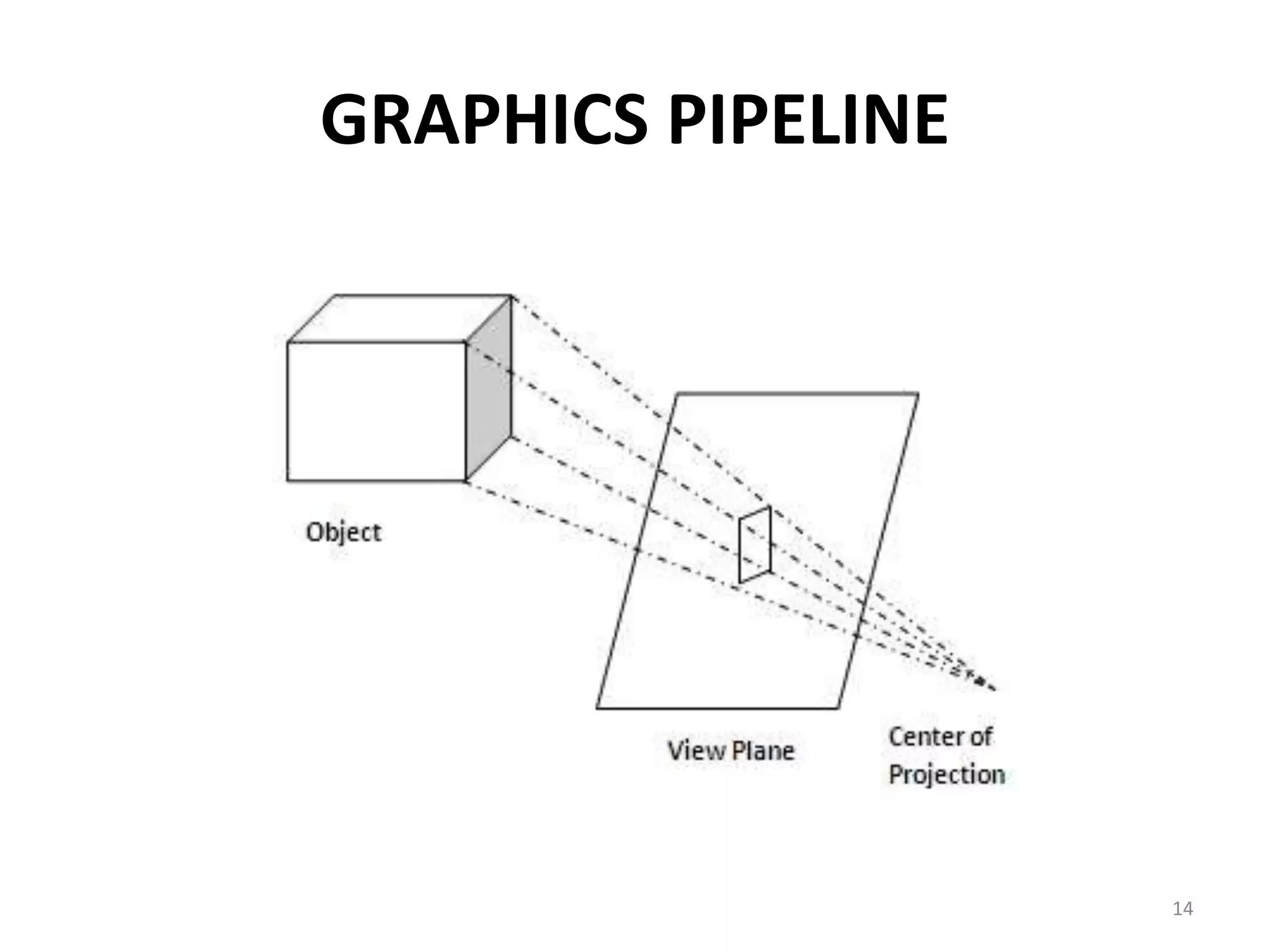
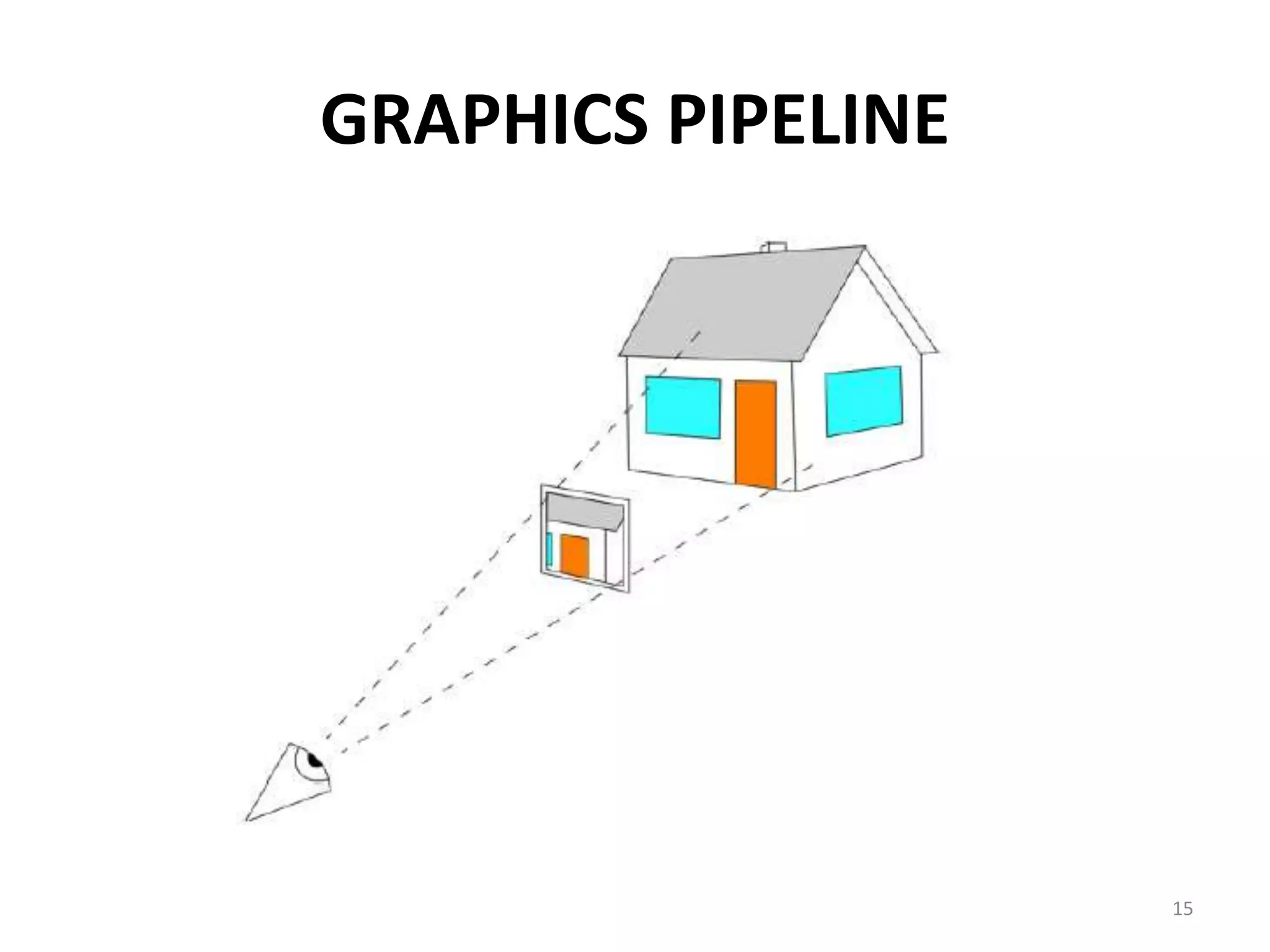
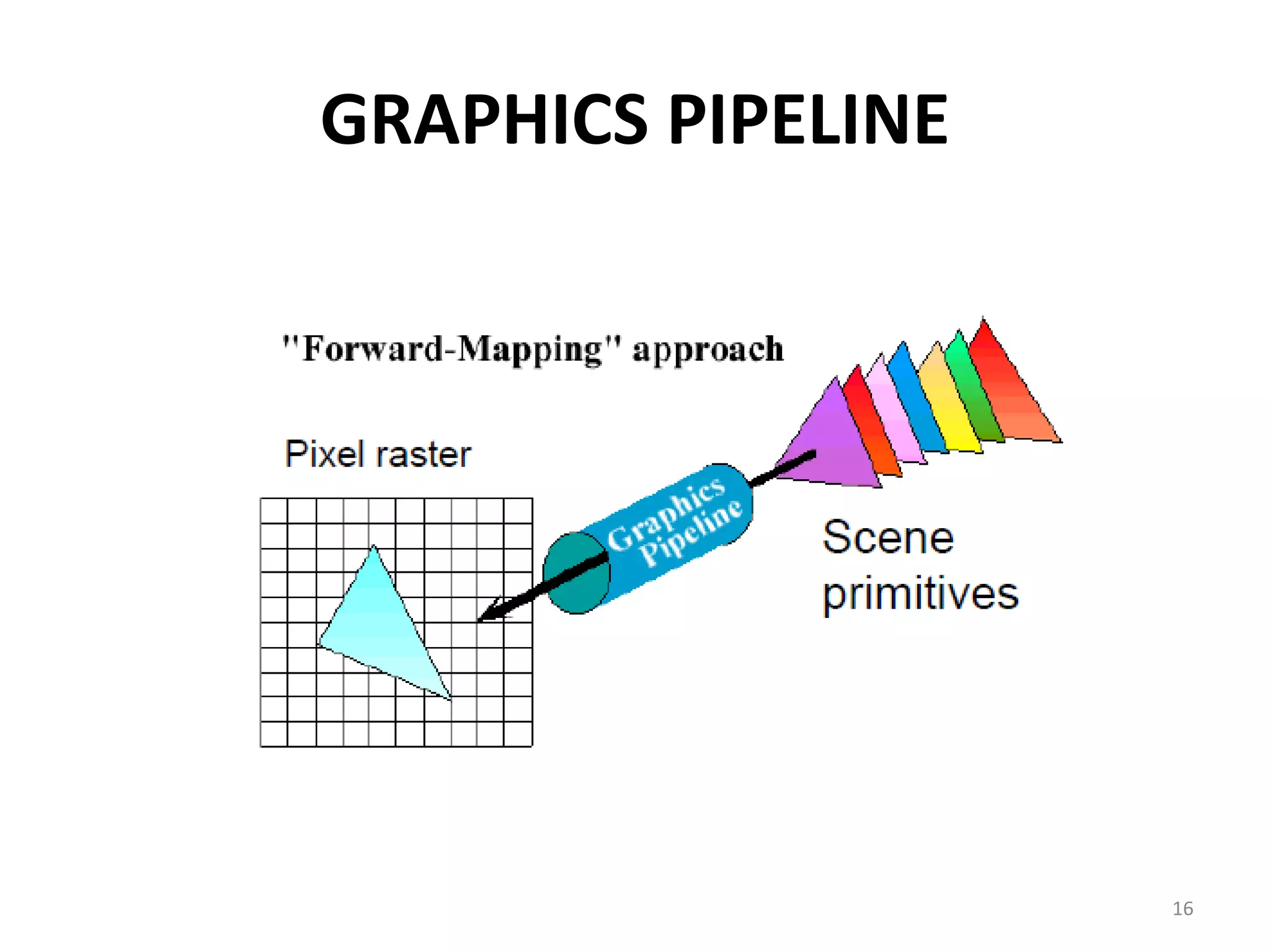
Computer graphics involves the creation and manipulation of images through programming. There are four major operations in computer graphics: imaging, modeling, rendering, and animation. Computer graphics is used in many applications including computer-aided design, presentation graphics, computer art, entertainment, education and training, visualization, image processing, and graphical user interfaces.