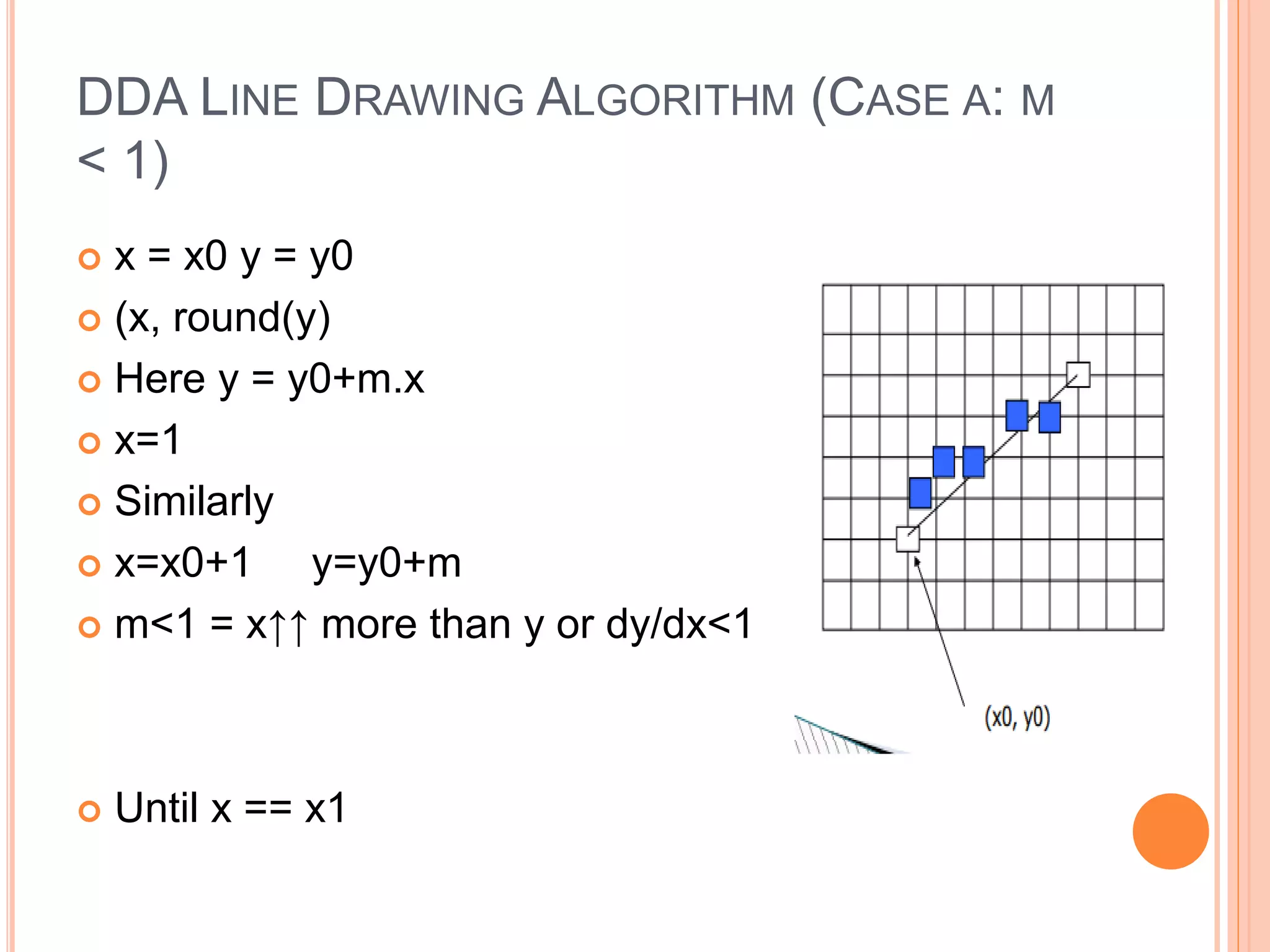
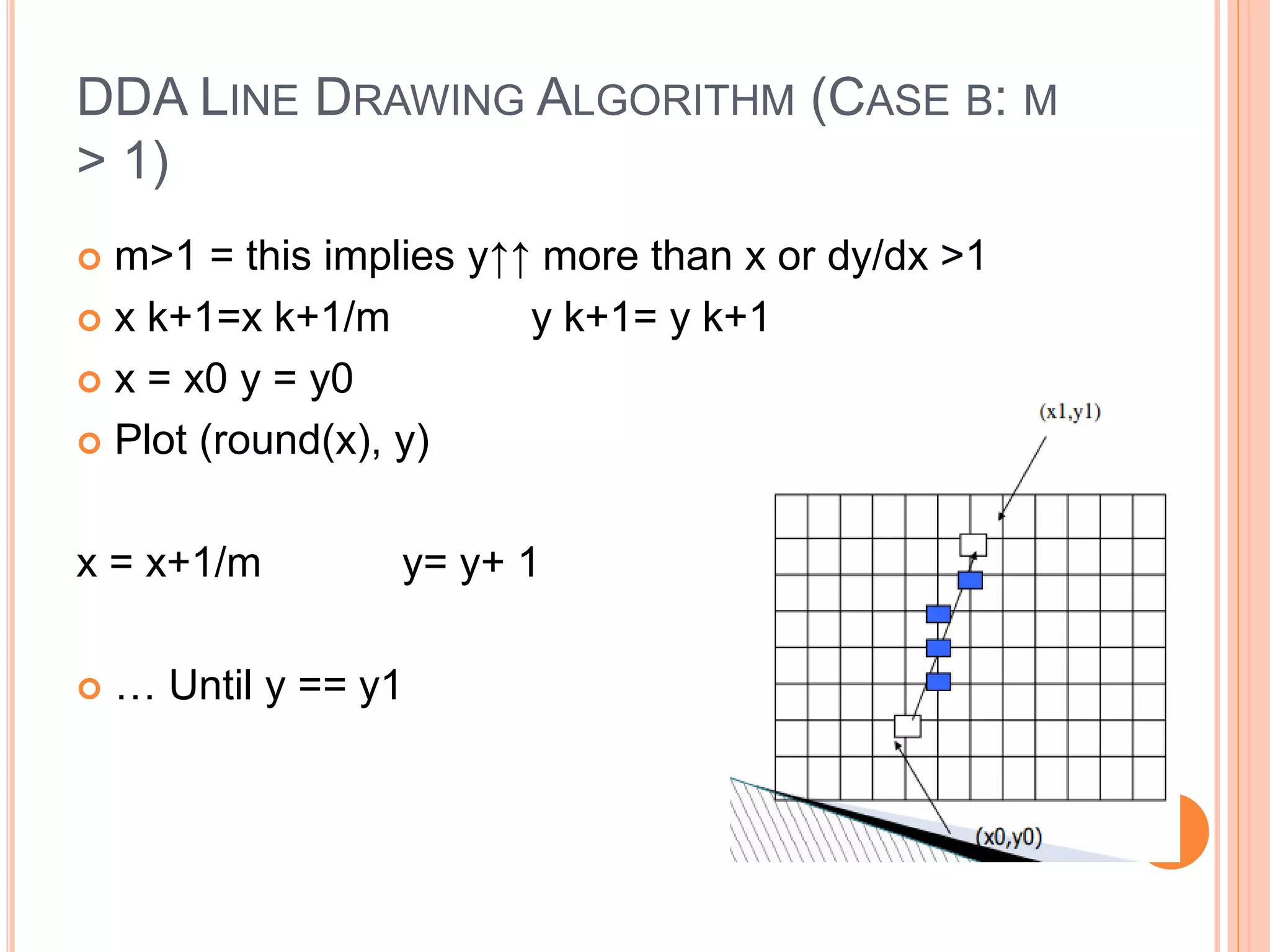
This document discusses the Digital Differential Analyzer (DDA) algorithm, which is a basic line drawing algorithm used in computer graphics. The DDA algorithm uses slope-intercept form (y=mx+b) to incrementally calculate pixel positions along the line between two points. It handles cases where the slope is less than or greater than 1 by incrementing either the x or y coordinate by 1 at each step. The DDA algorithm is simple to implement but requires floating point calculations and has orientation dependency issues.



![(DDA) ALGORITHM
Walk through the line, starting at (x0,y0)
Constrain x, y increments to values in [0,1] range
Case a: x is incrementing faster (m < 1)
Step in x=1 increments, compute and round y
Case b: y is incrementing faster (m > 1)
Step in y=1 increments, compute and round x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ddaalgorithm-180520071316/75/Dda-algorithm-5-2048.jpg)