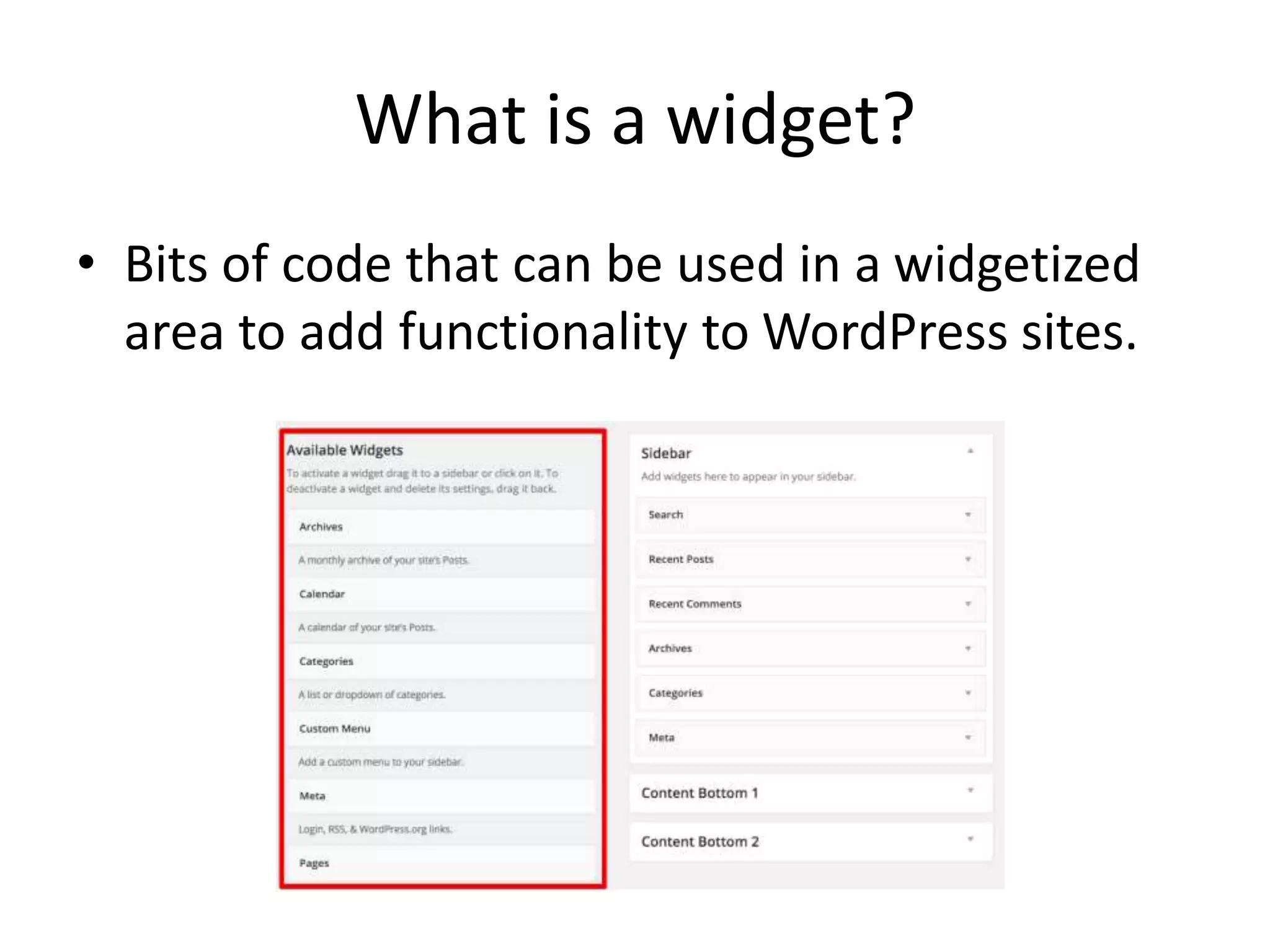
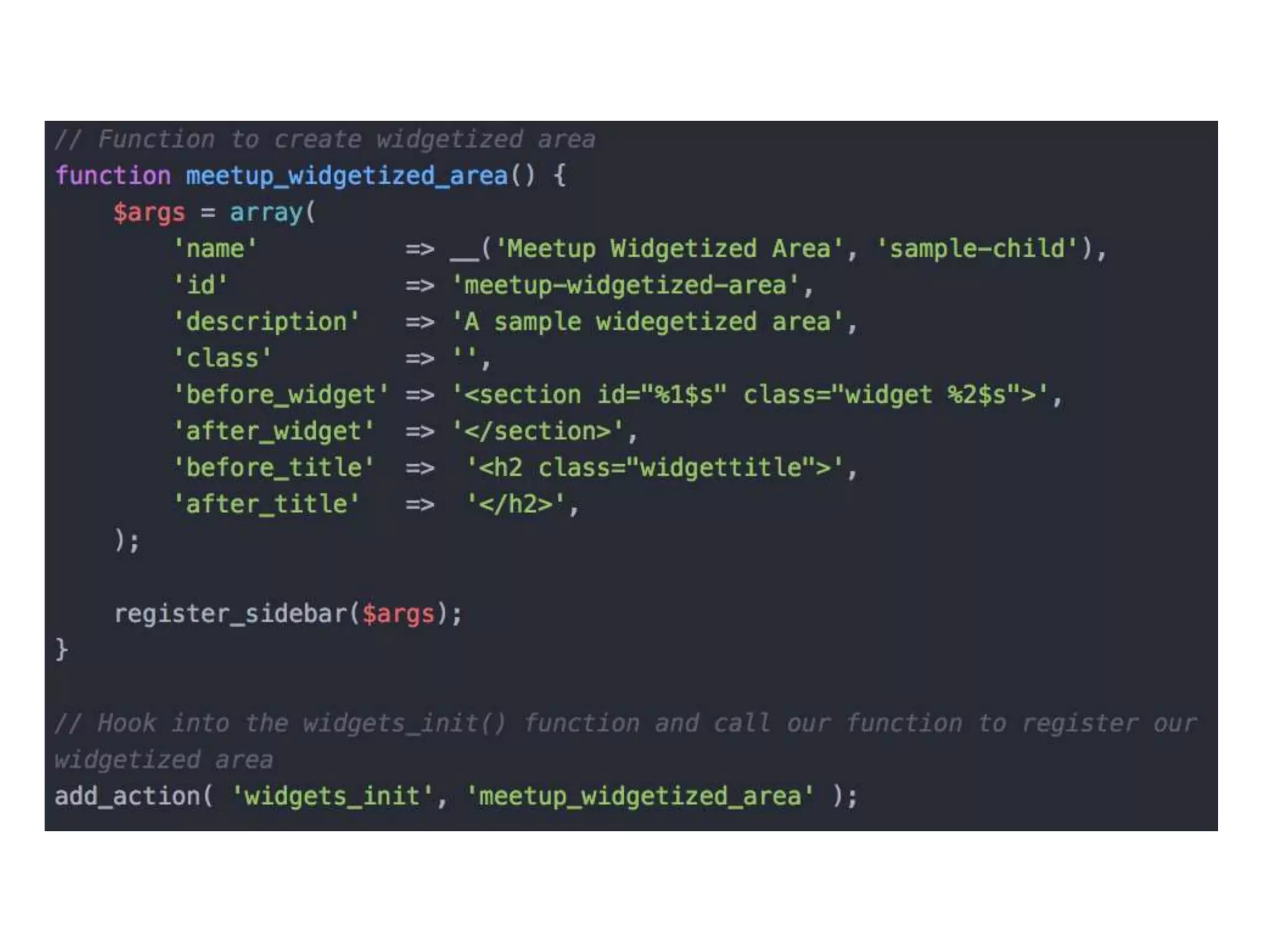
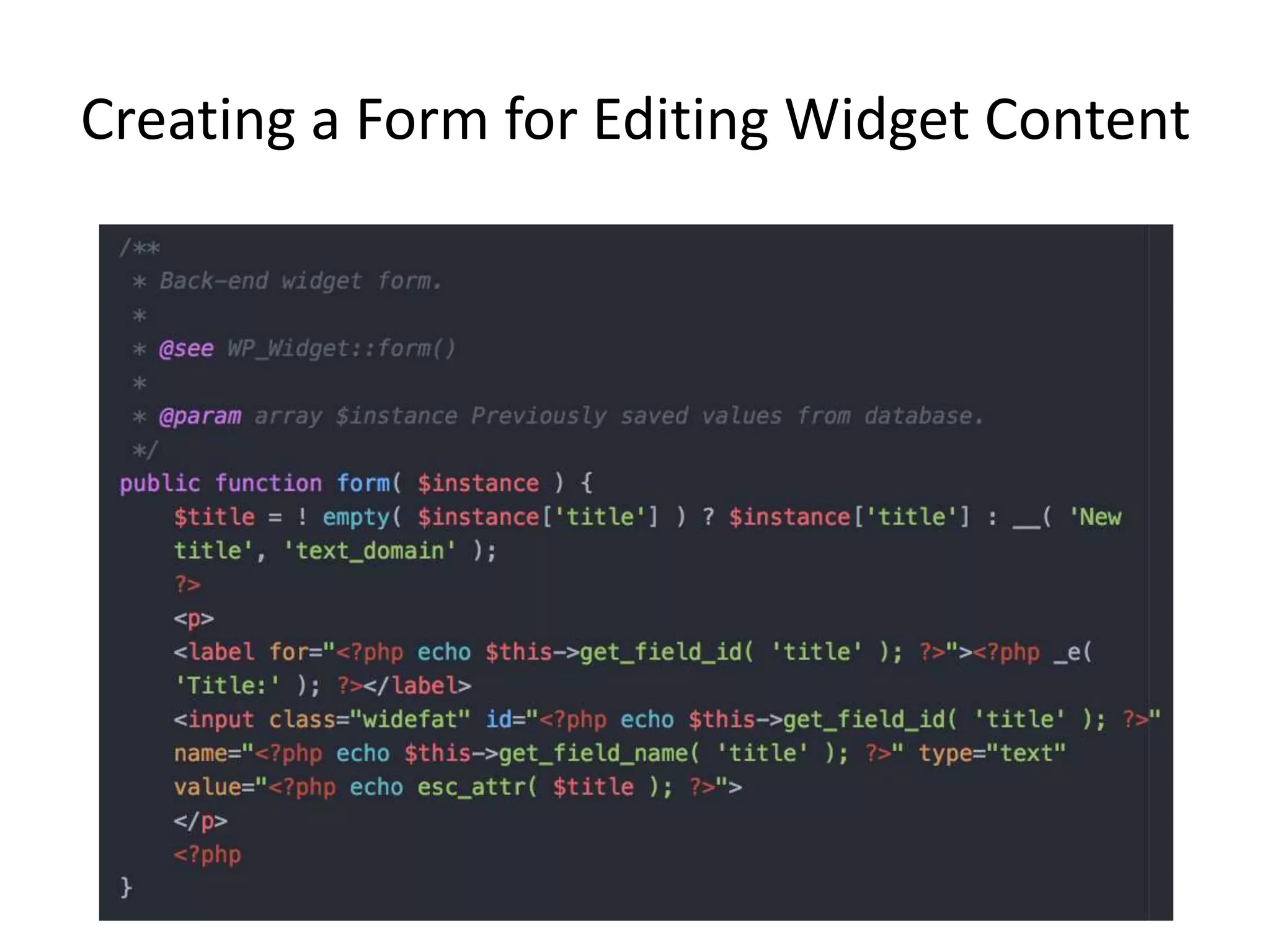
The document explains the concepts of sidebars and widgets in WordPress, highlighting their roles as areas for displaying additional information and functionality on a site. It details the process of registering and displaying widgetized areas using functions like register_sidebar() and dynamic_sidebar(), as well as how to create custom widgets by extending the wp_widget class. Additionally, the document outlines the methods for constructing, displaying, and saving widget content, ensuring proper integration within WordPress themes.