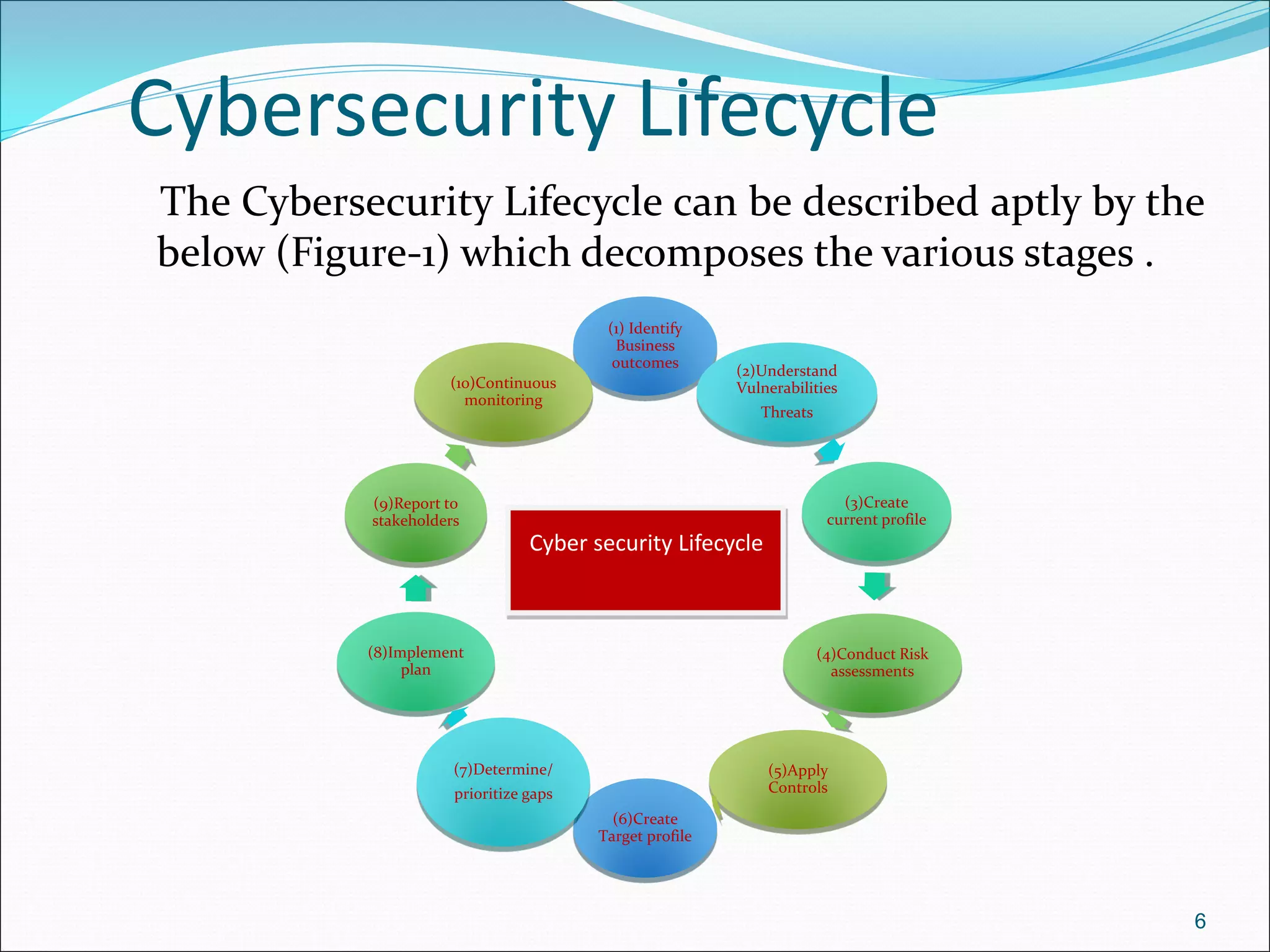
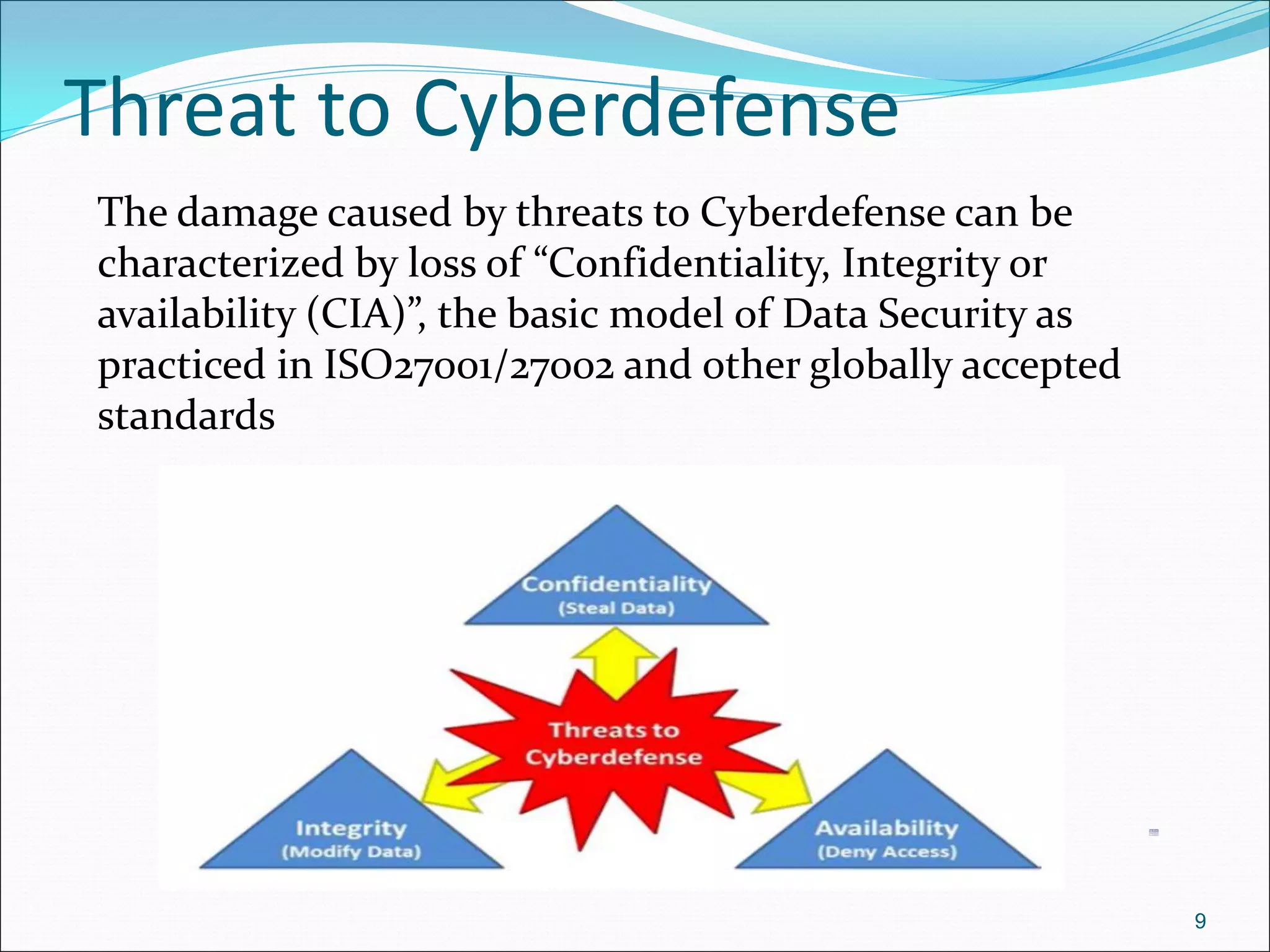
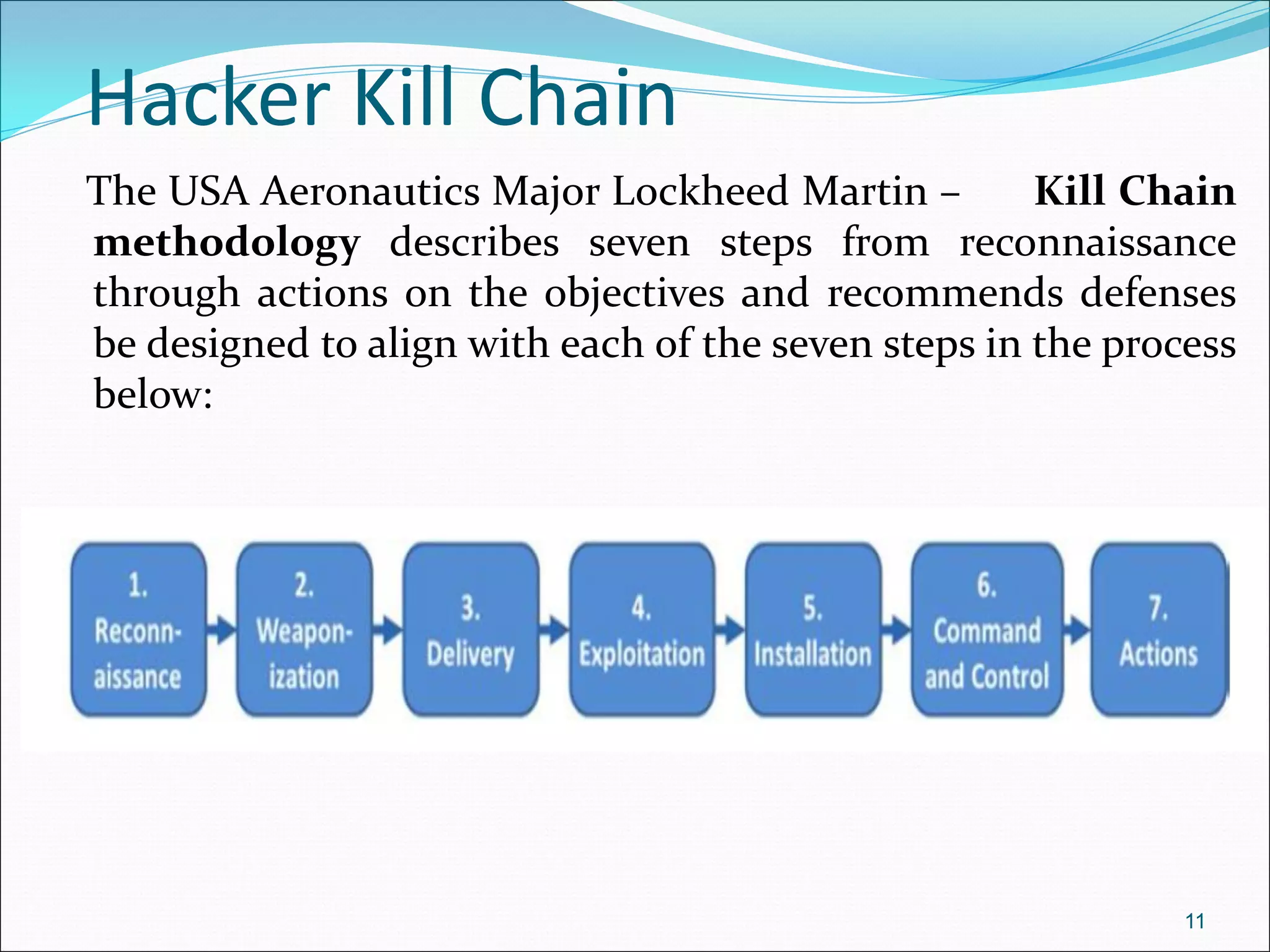
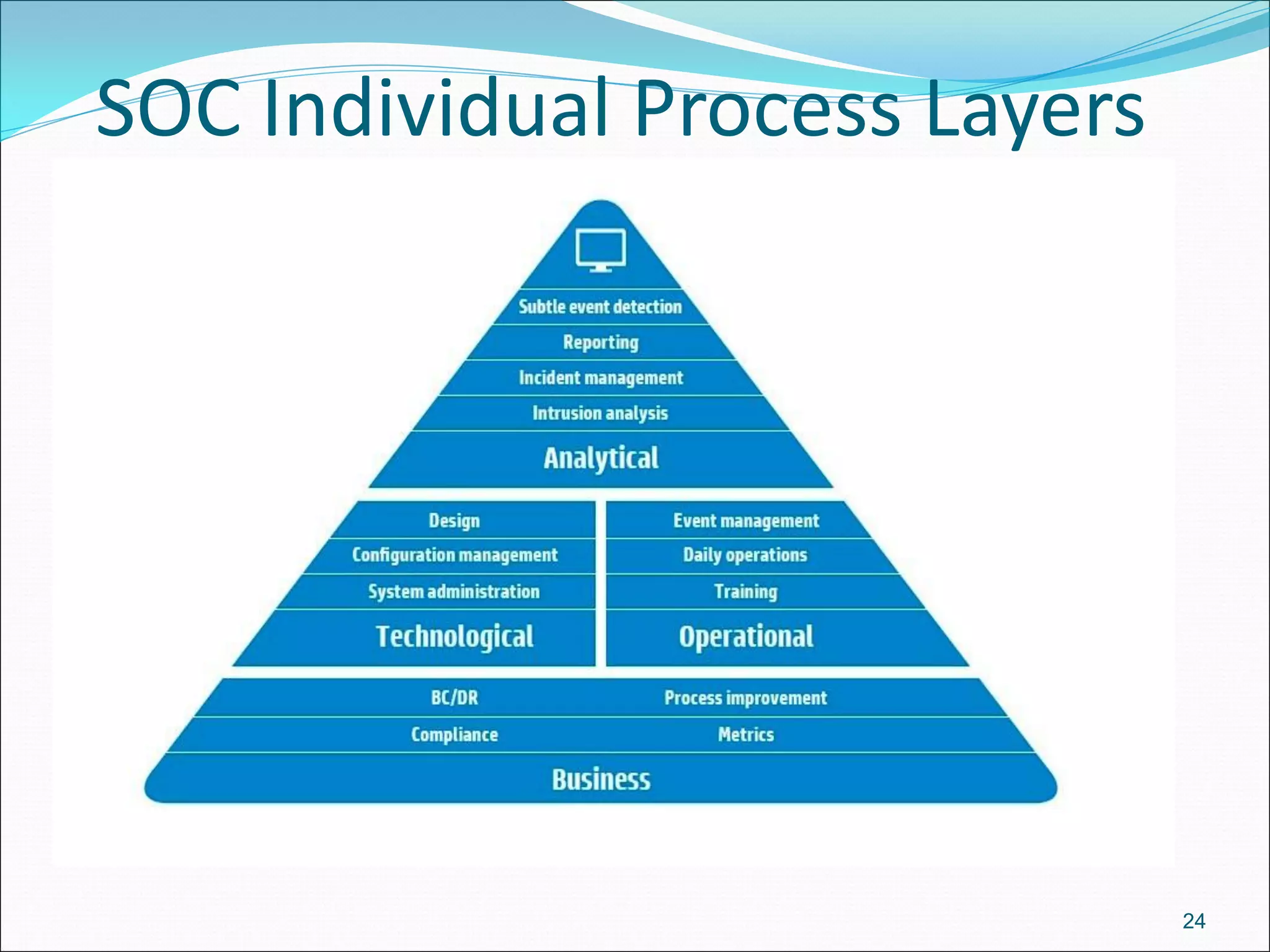
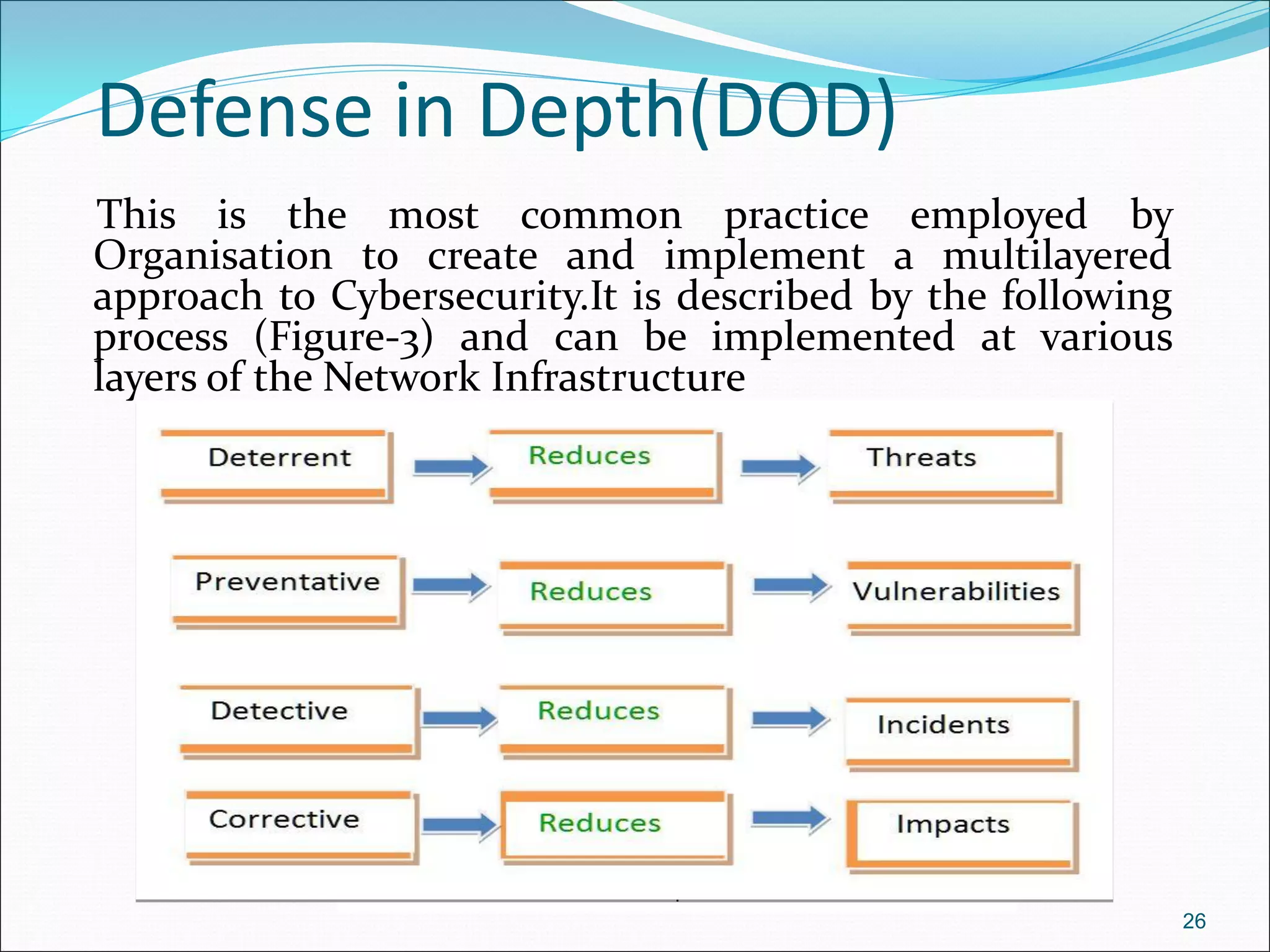
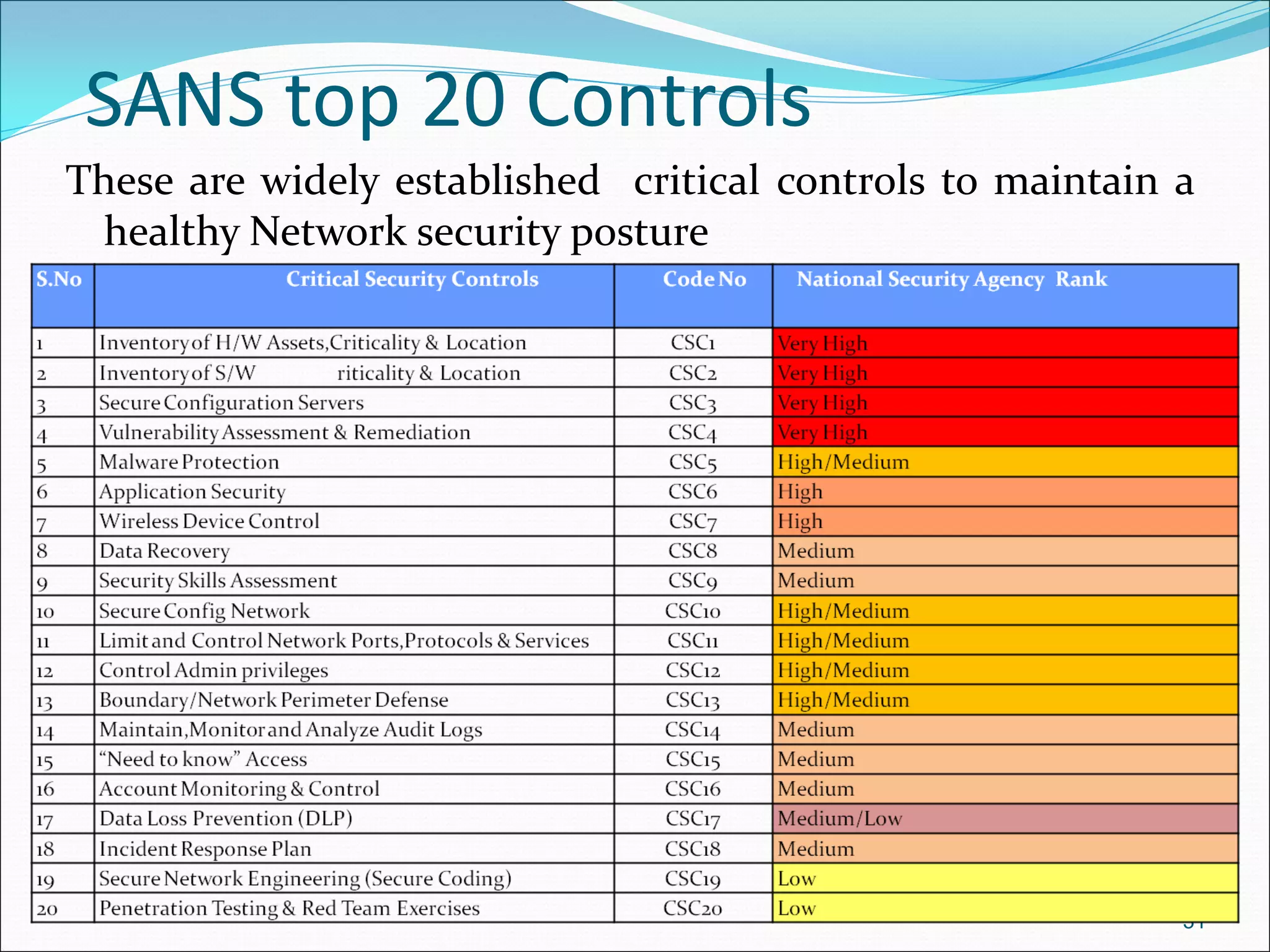
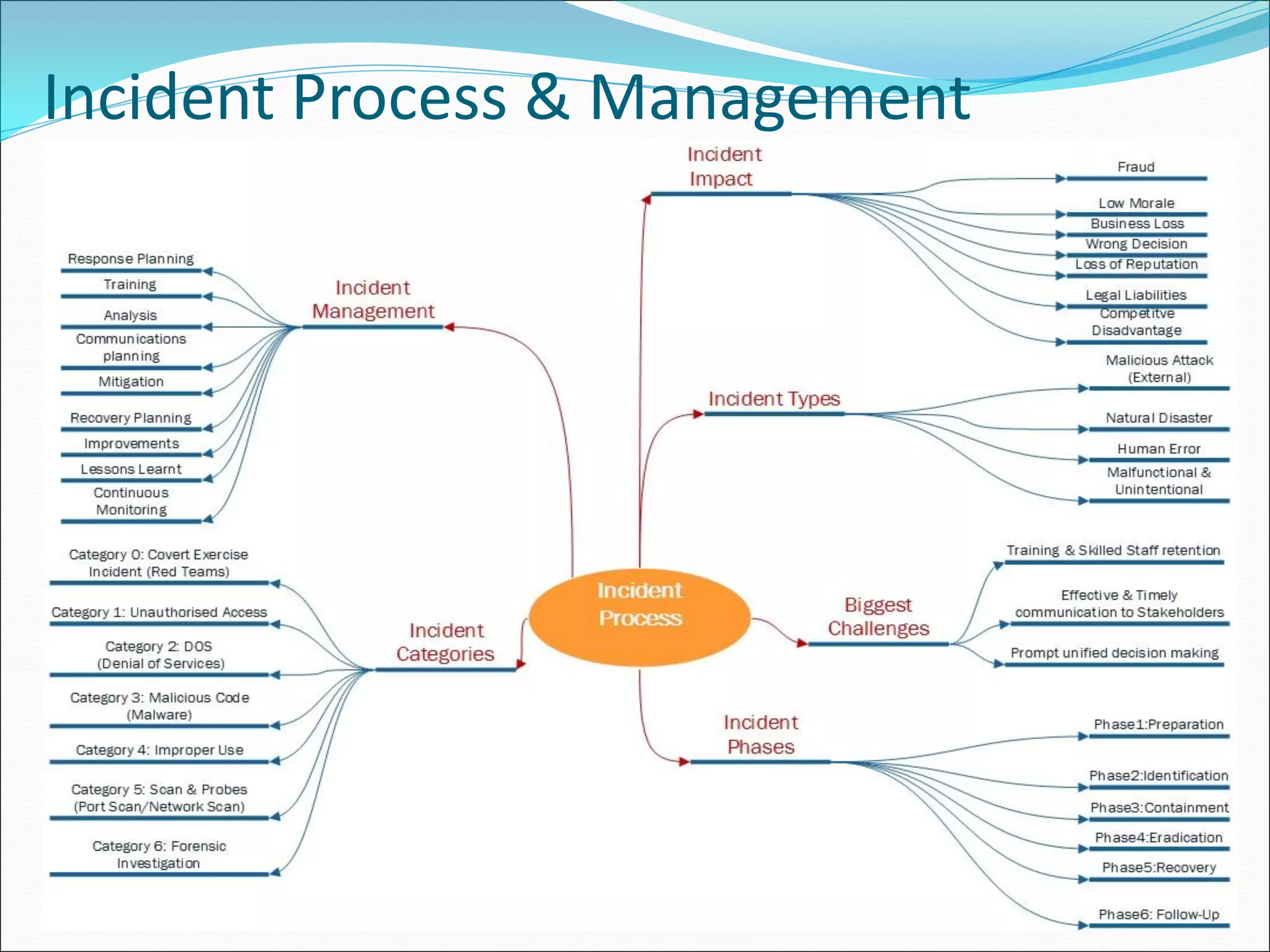
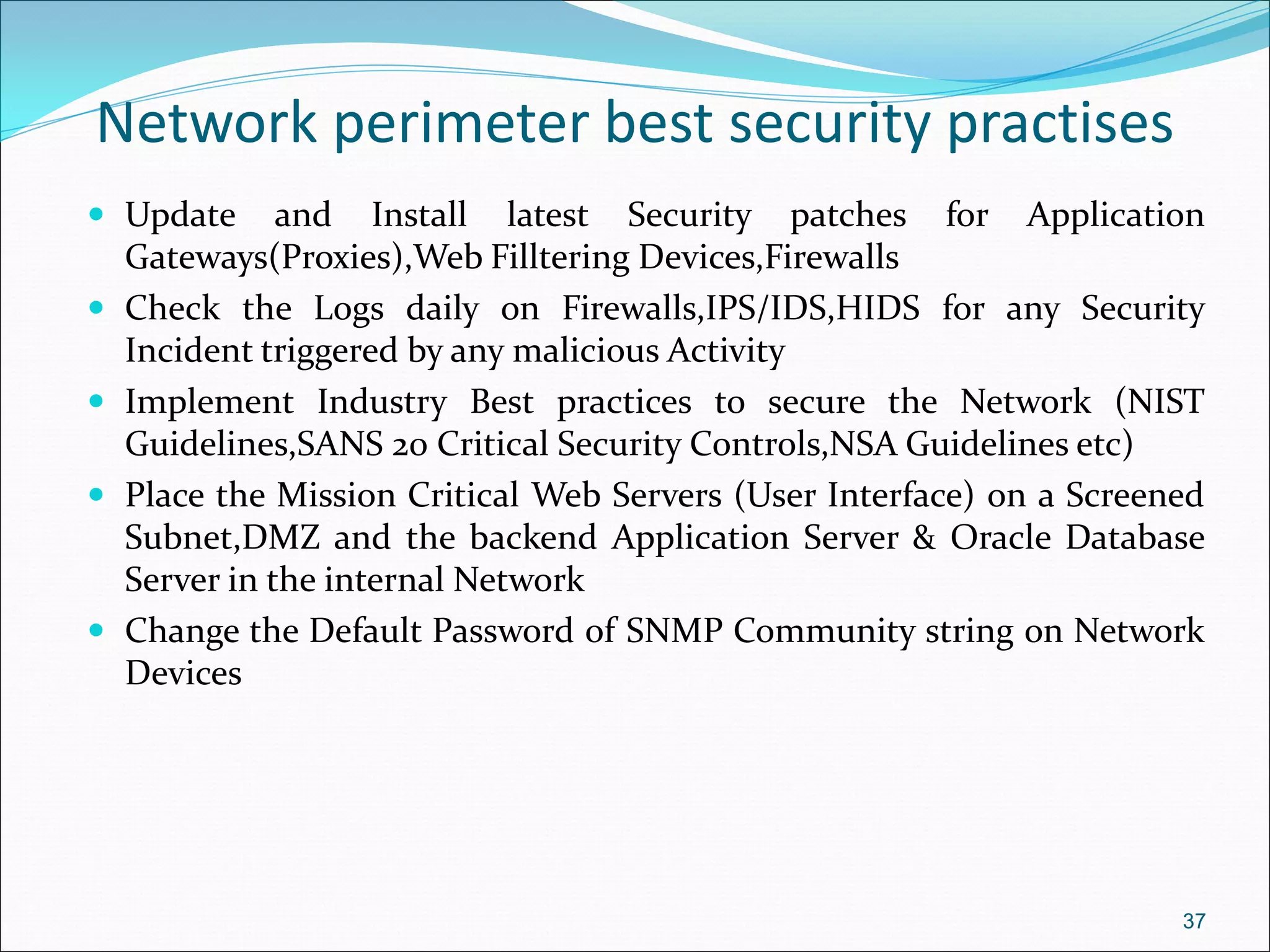
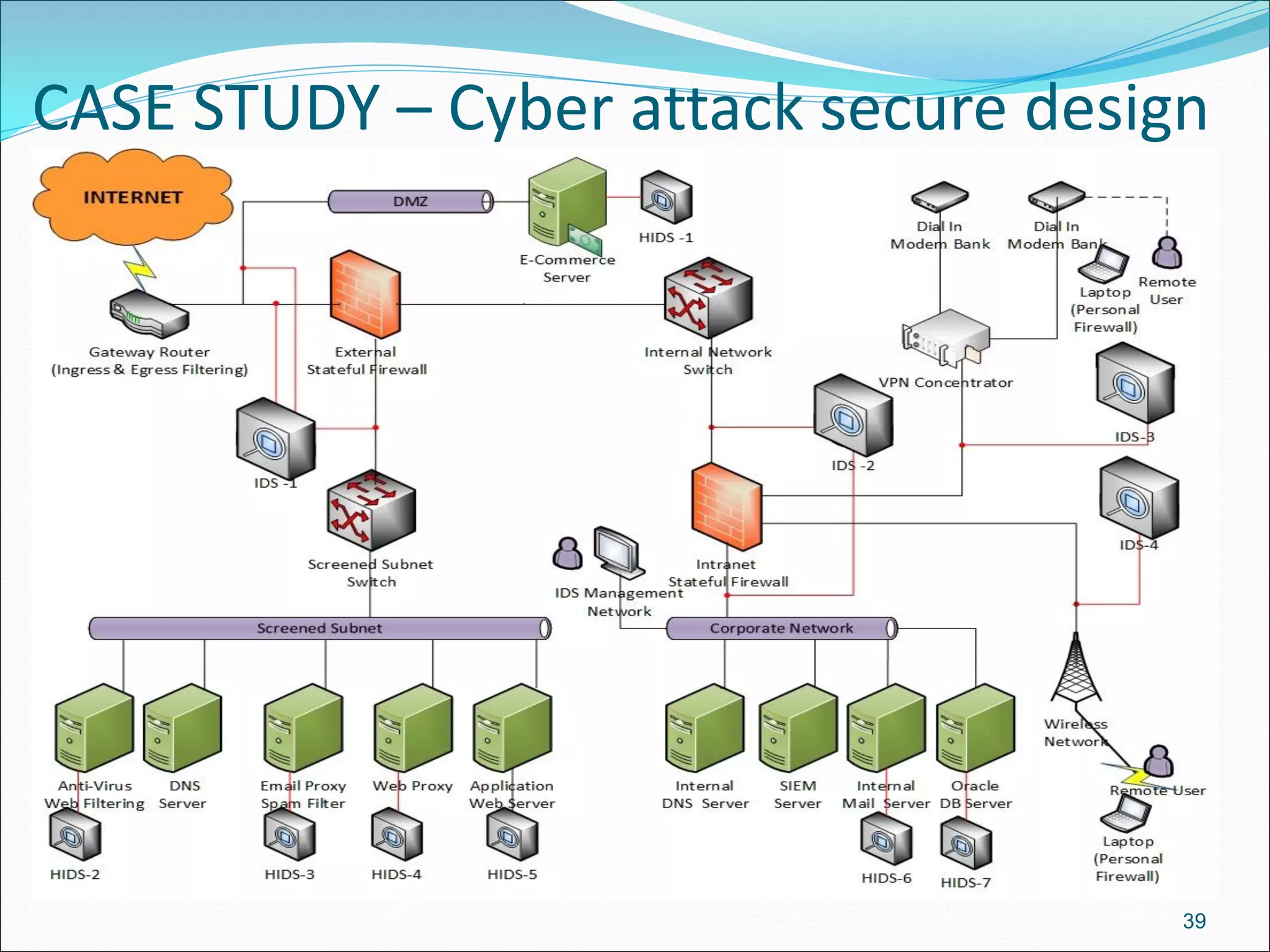
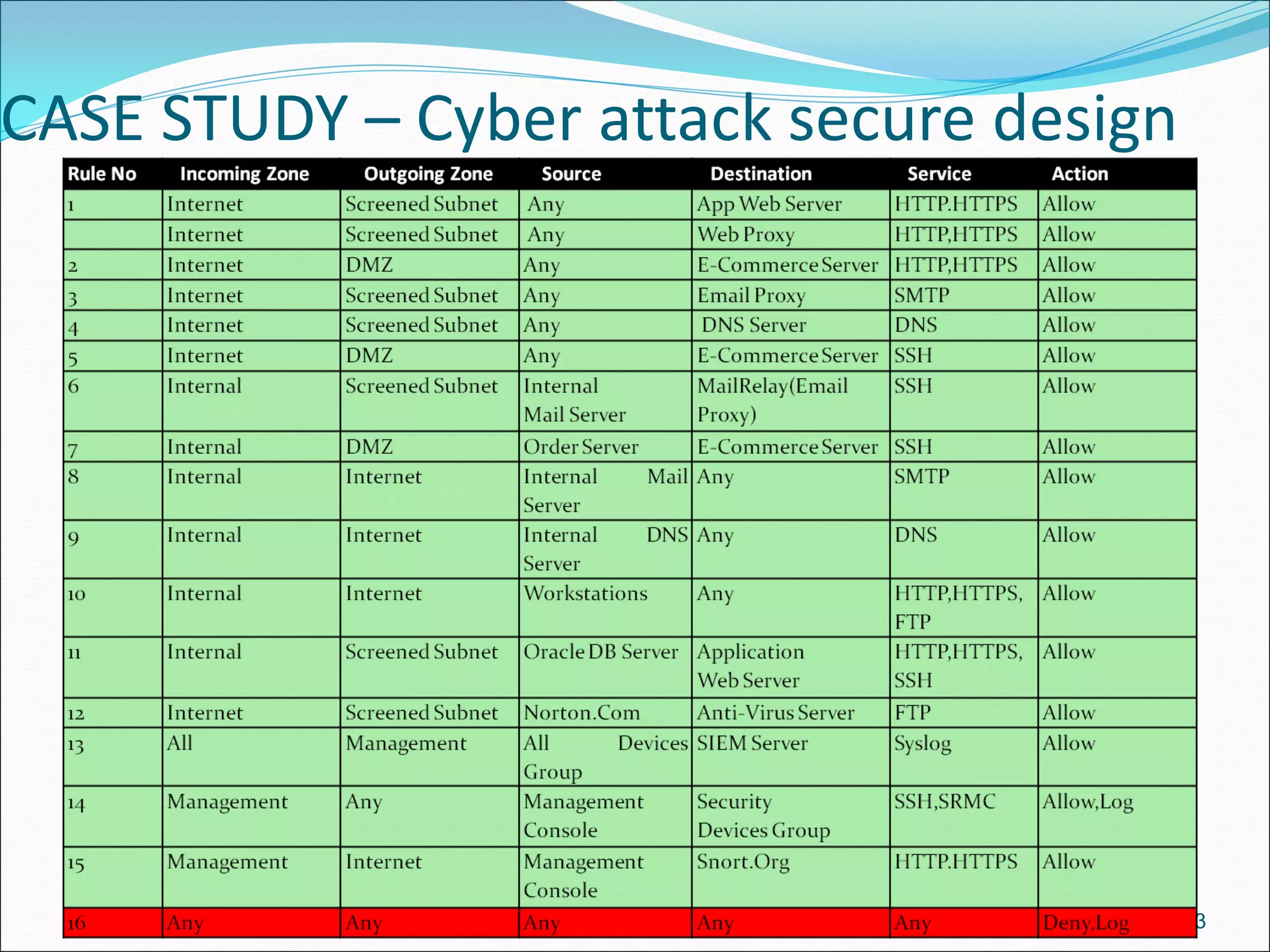
The document presents a comprehensive overview of cybersecurity concepts, frameworks, and best practices essential for protecting entities against global cyber threats. It outlines key cybersecurity standards such as NIST and ISO, discusses the hacker kill chain methodology, and emphasizes the importance of continuous monitoring and implementing robust security measures within organizations. Additionally, it highlights operational processes, recommended guidelines, and the critical role of a Security Operations Center (SOC) in maintaining a strong cybersecurity posture.