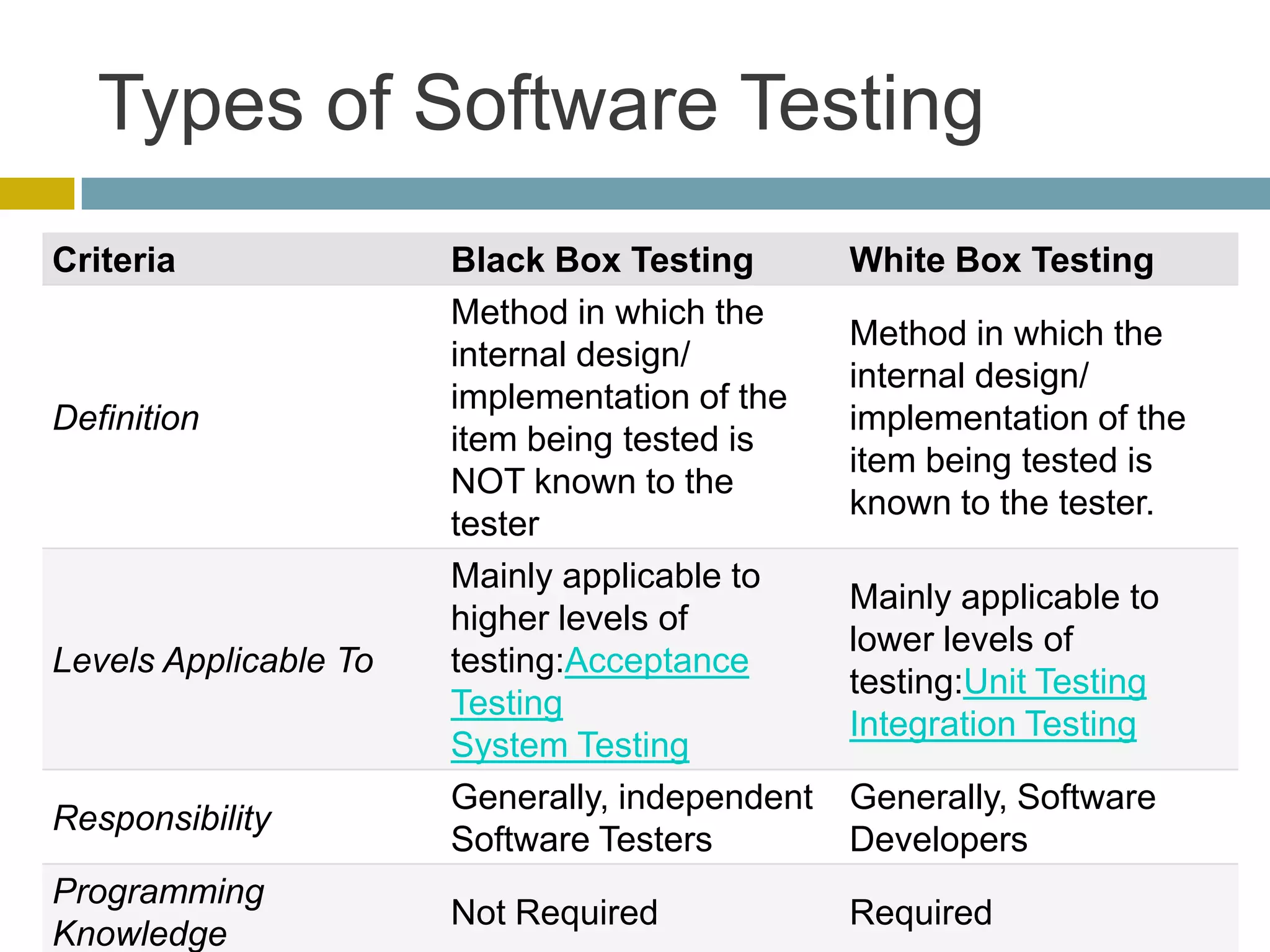
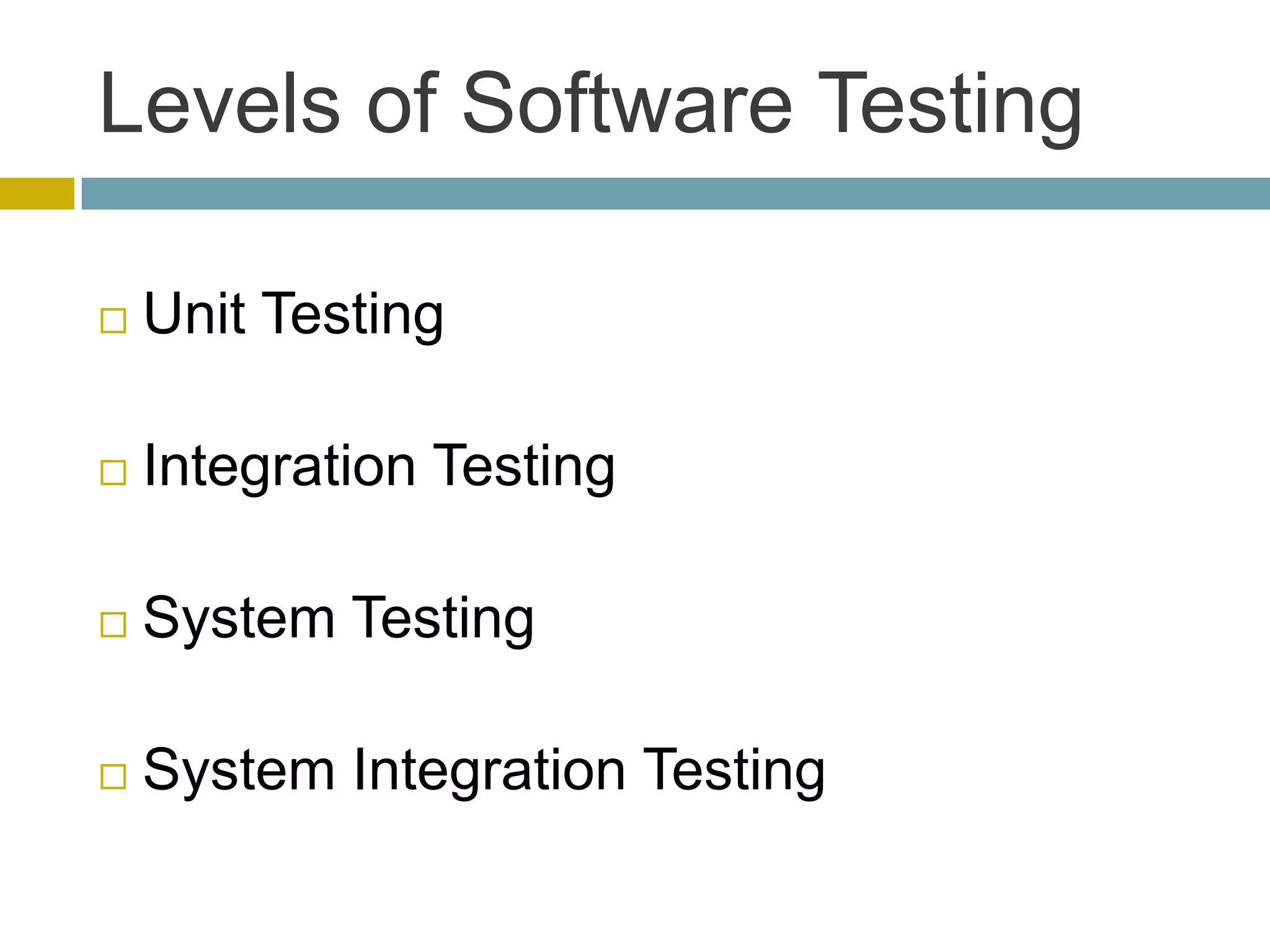
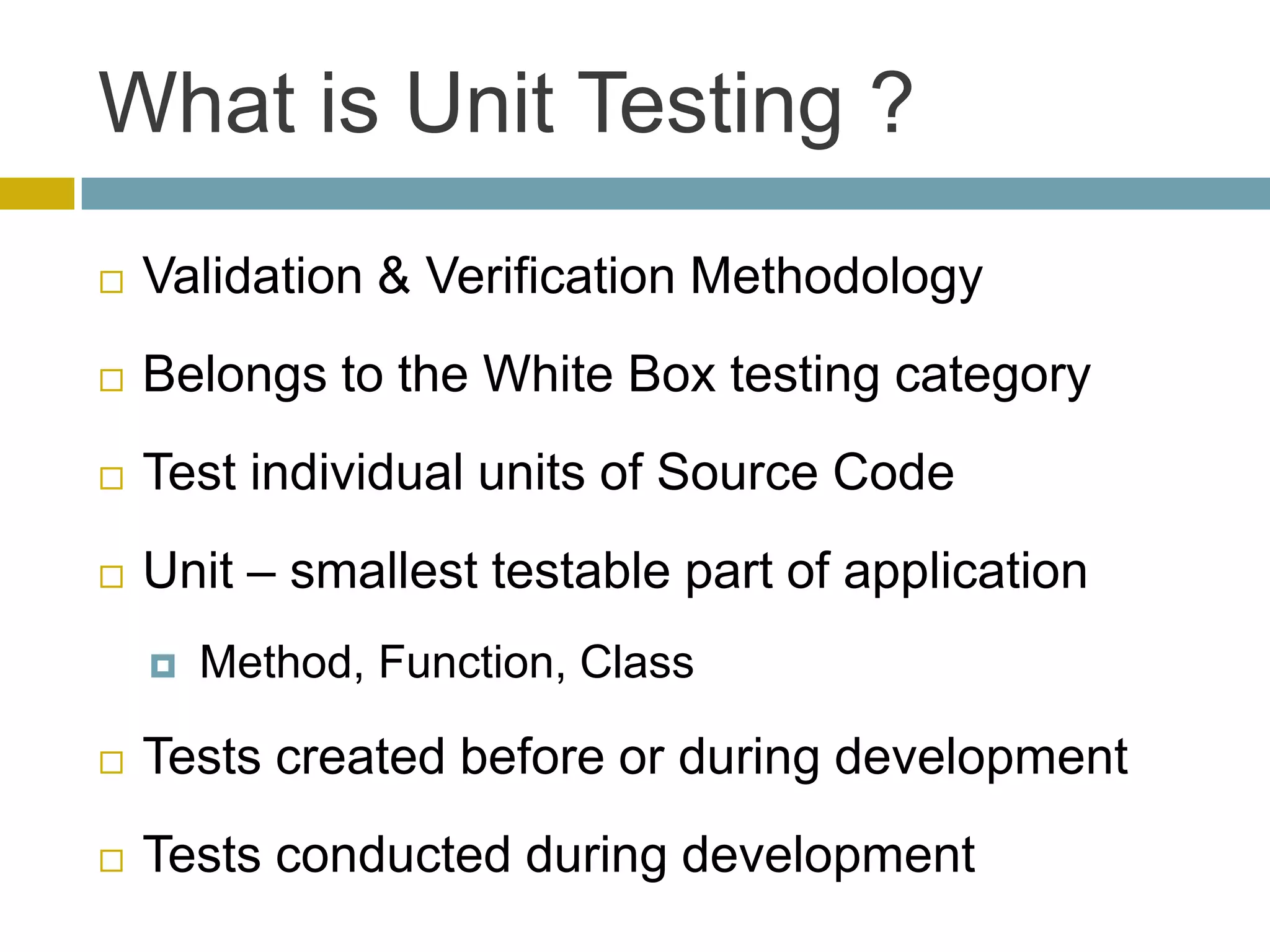
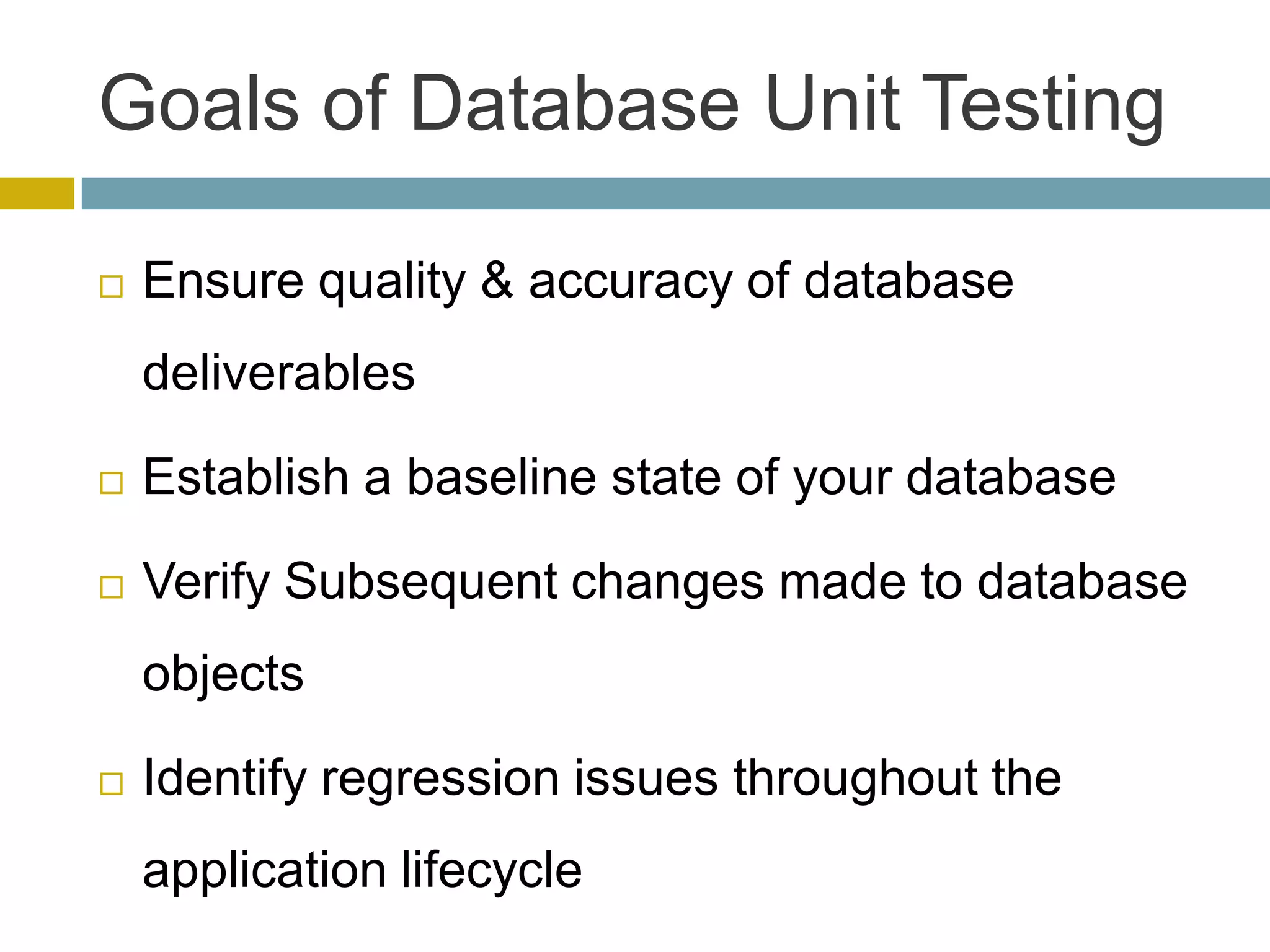
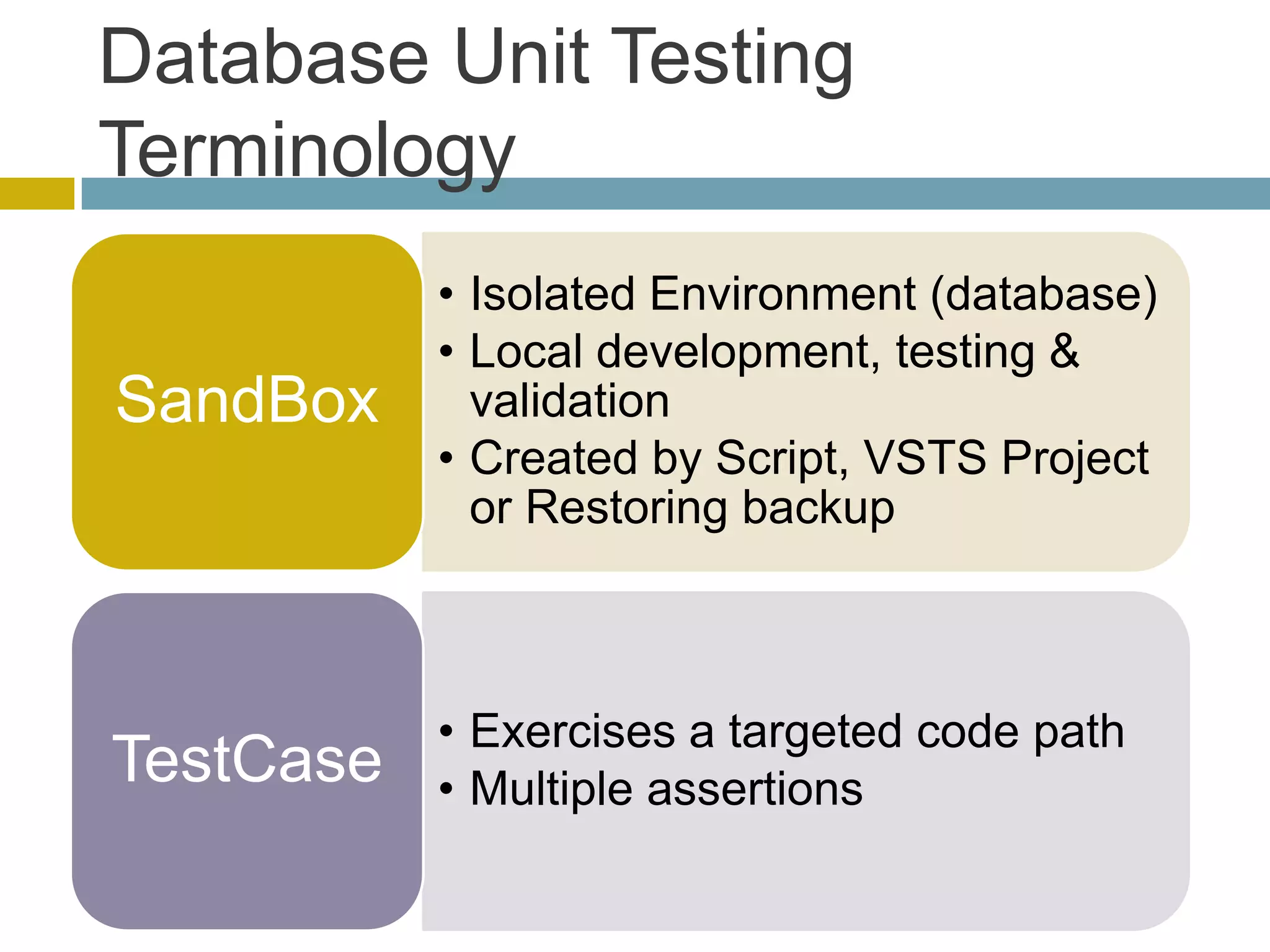
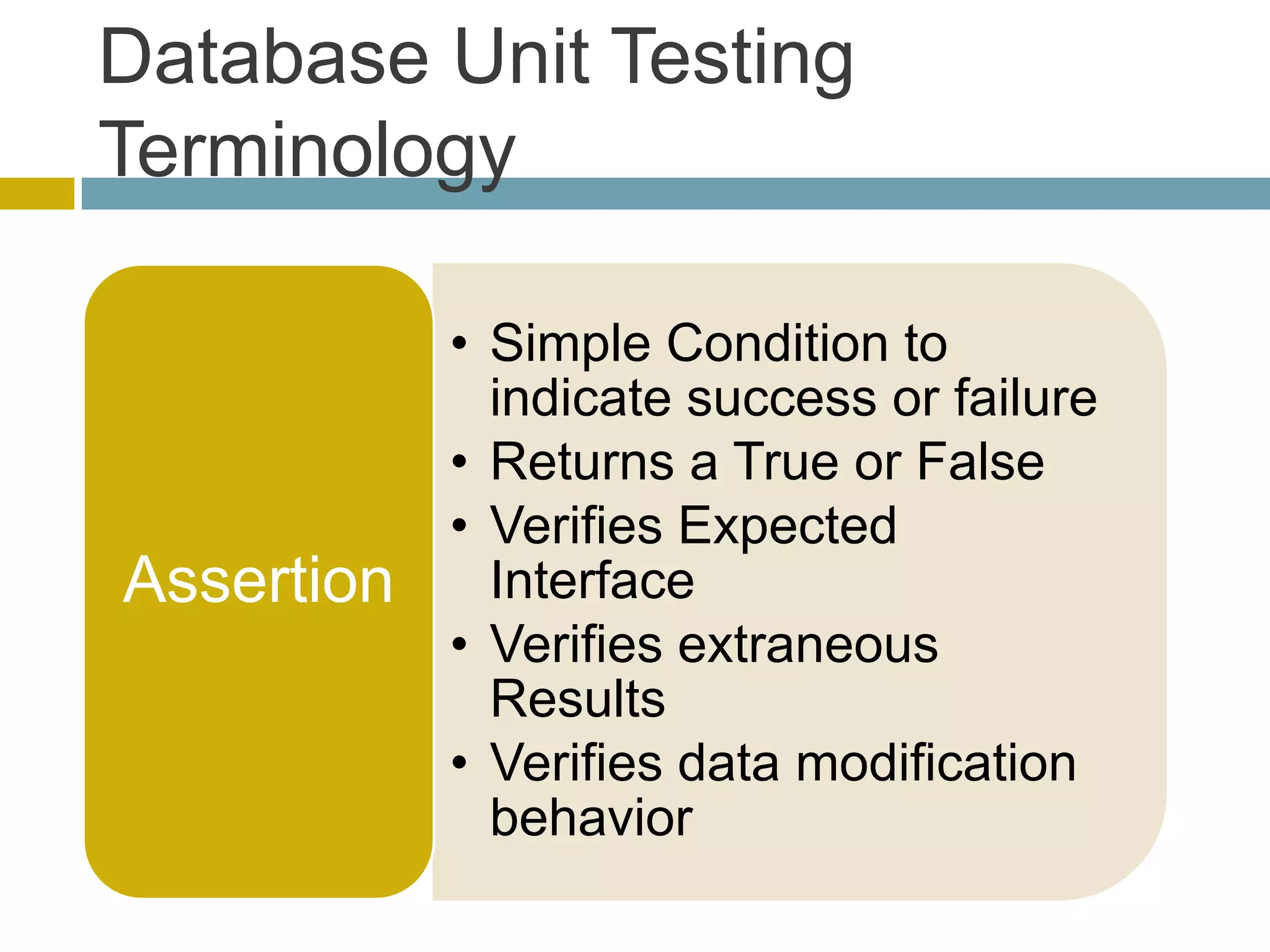
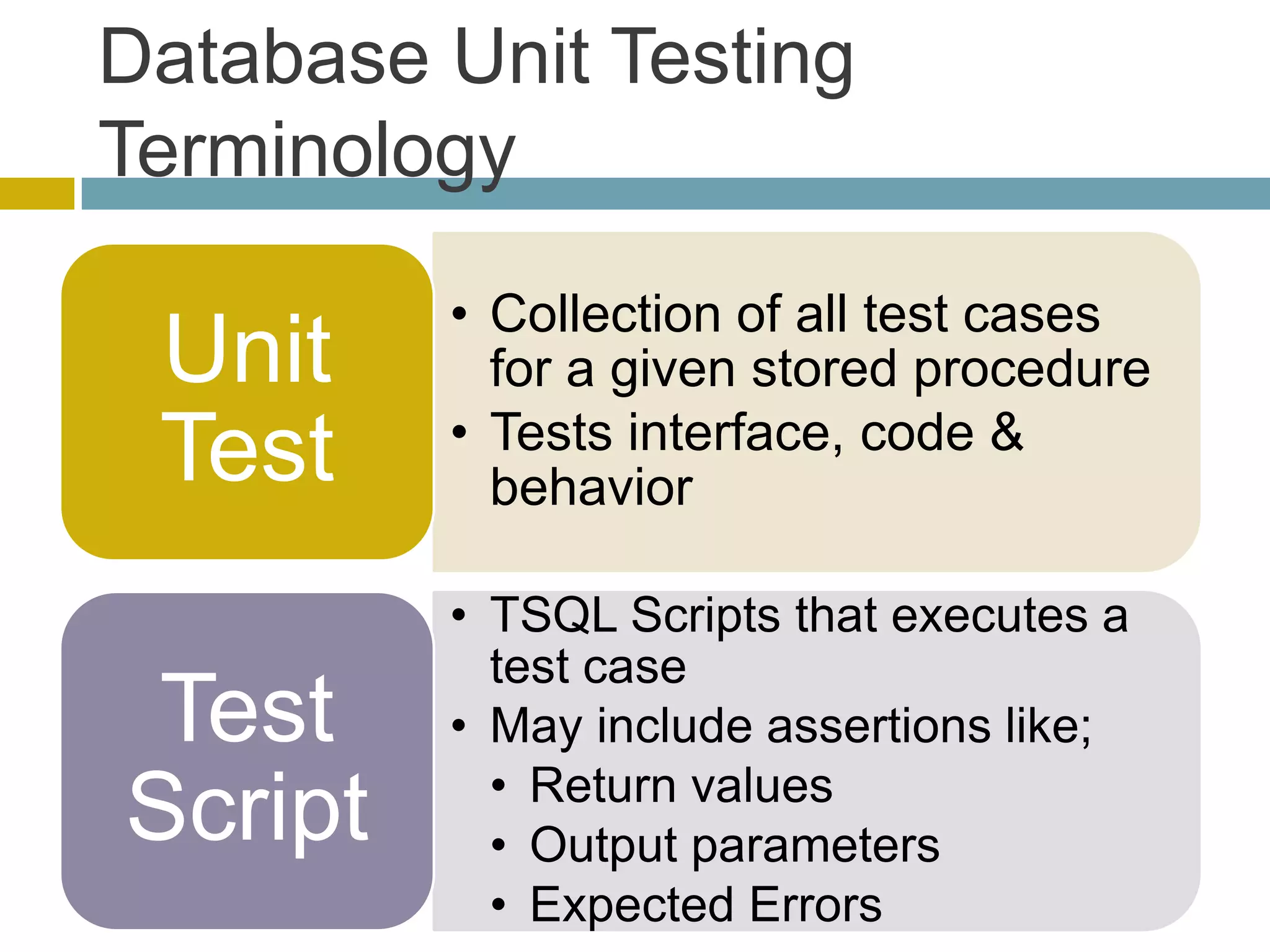
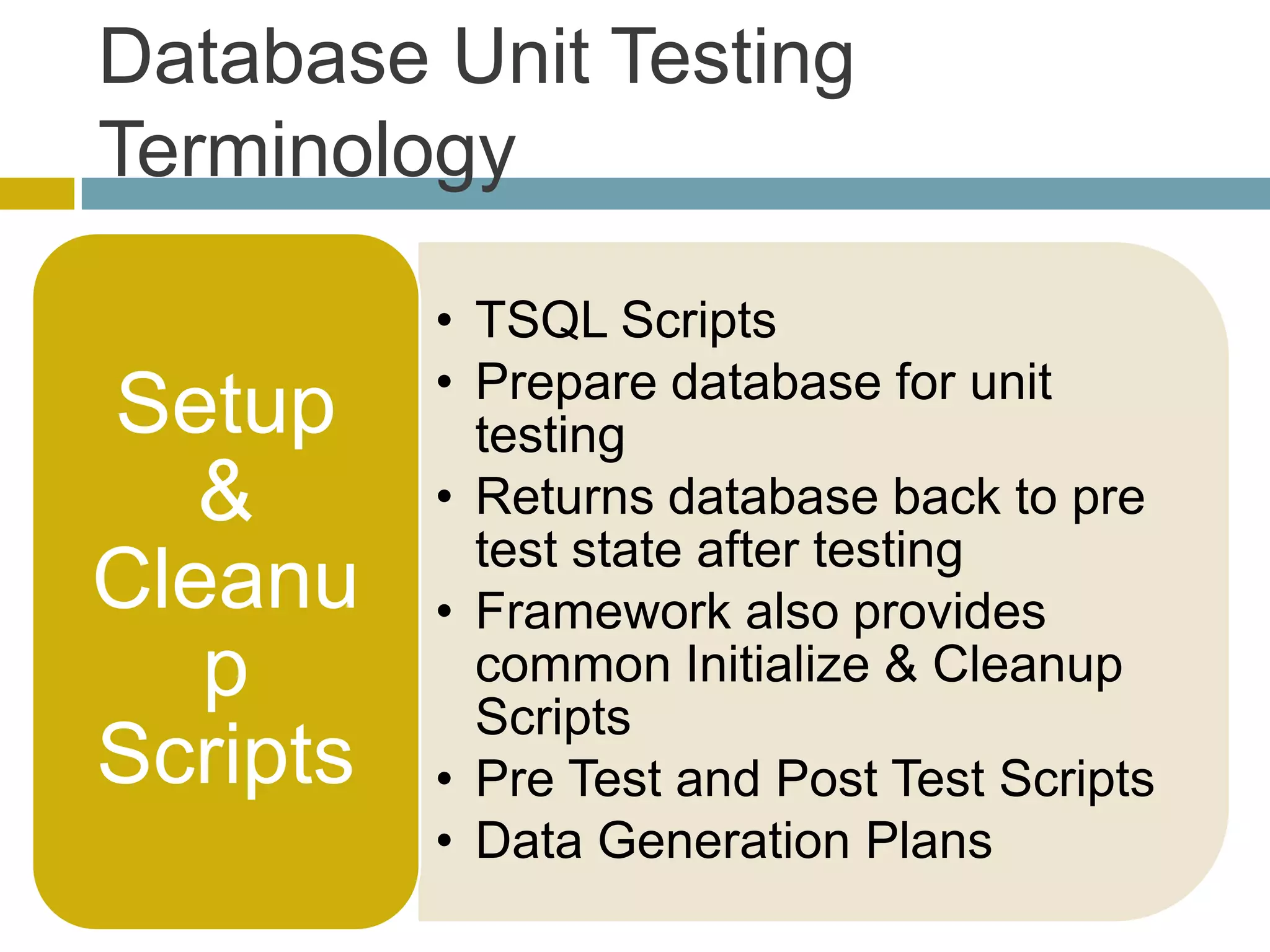
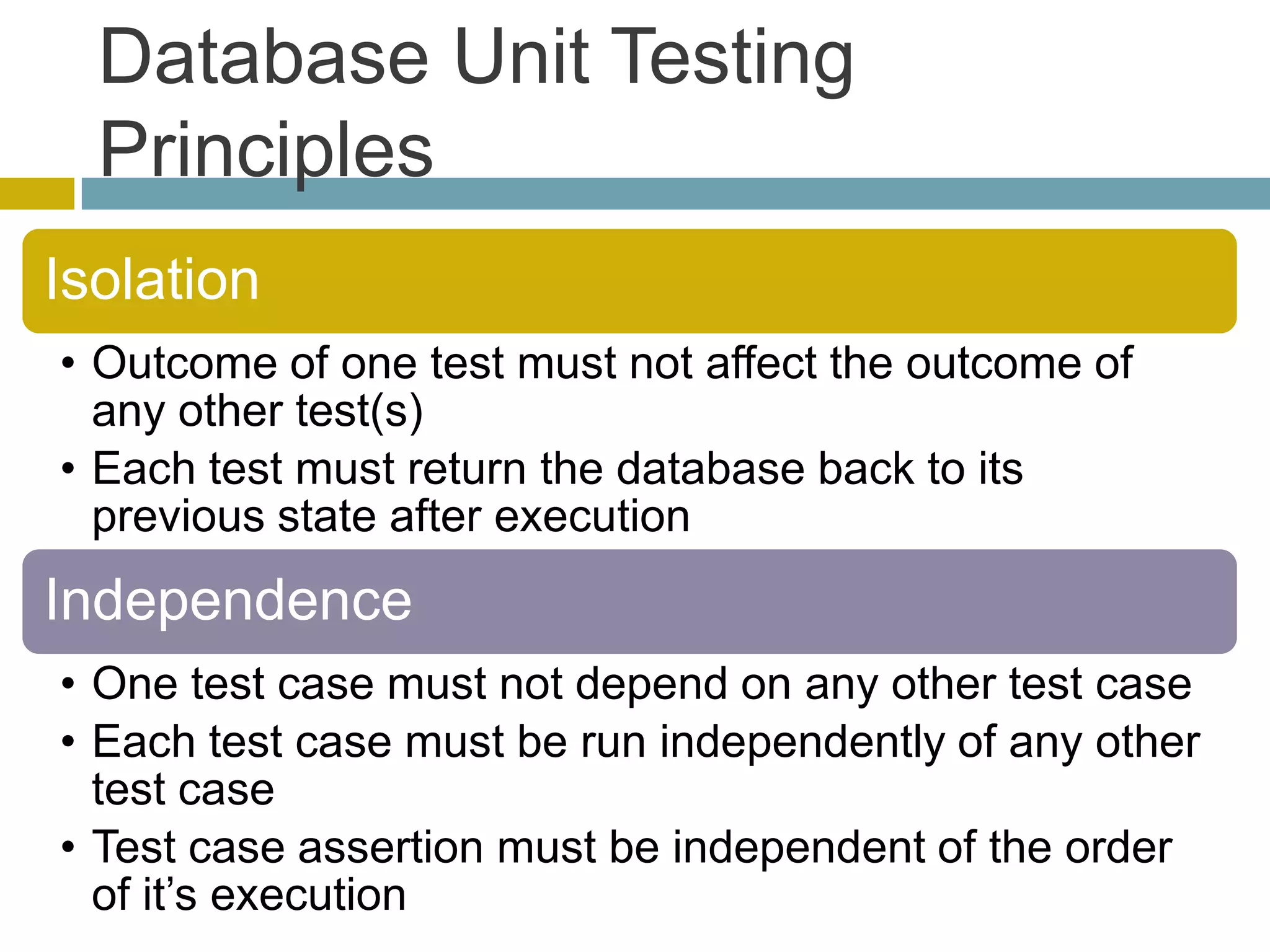
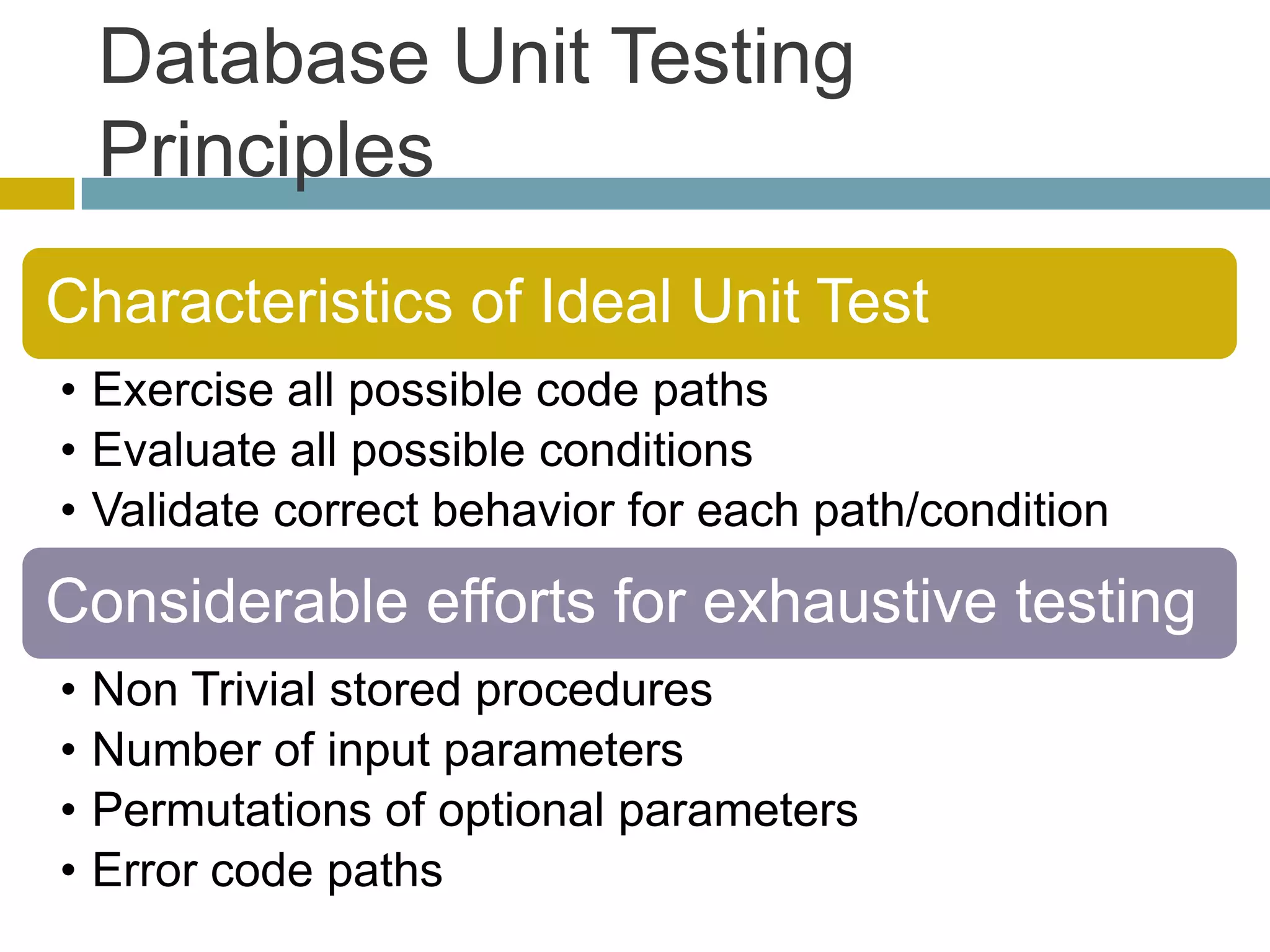
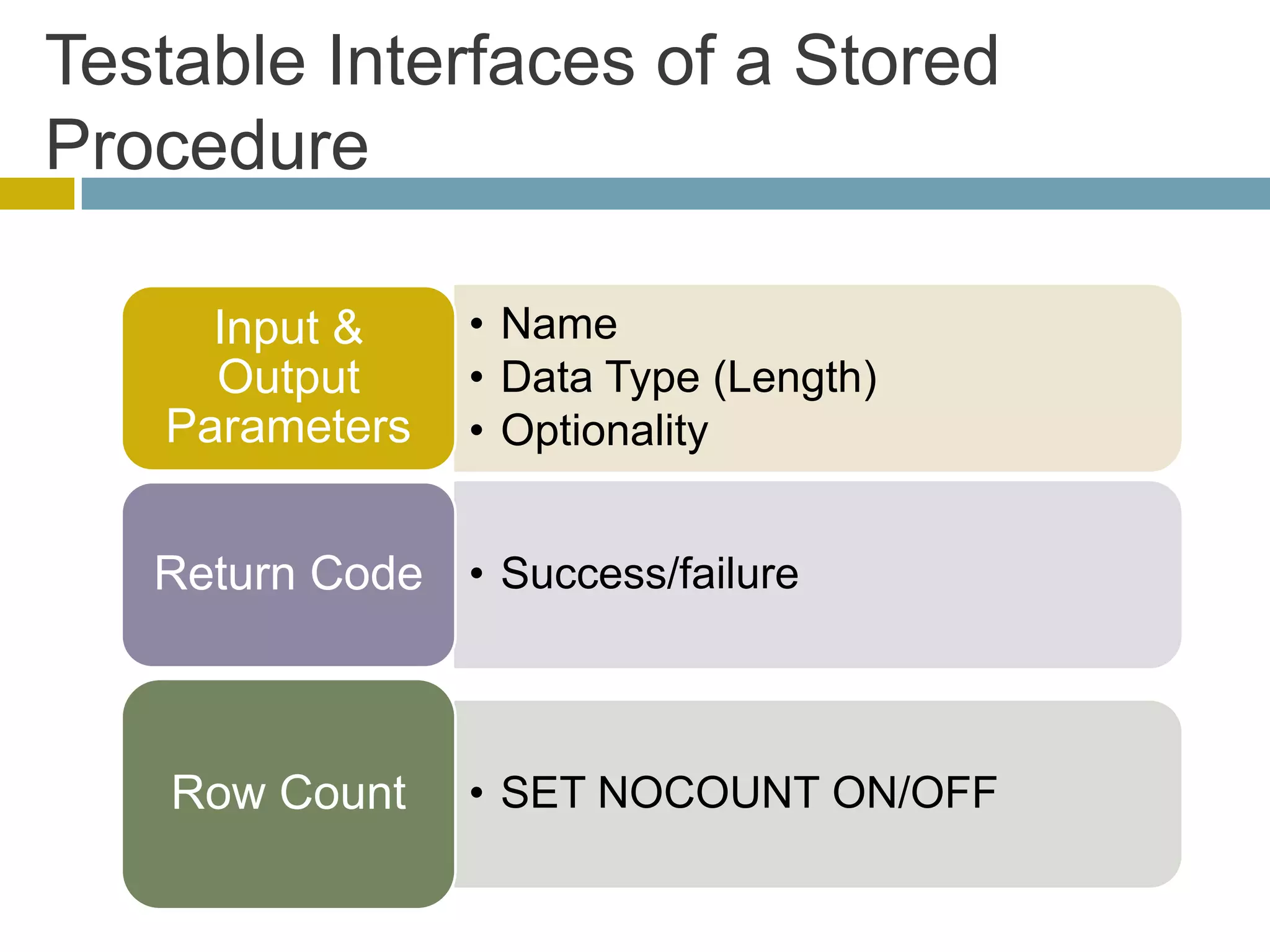
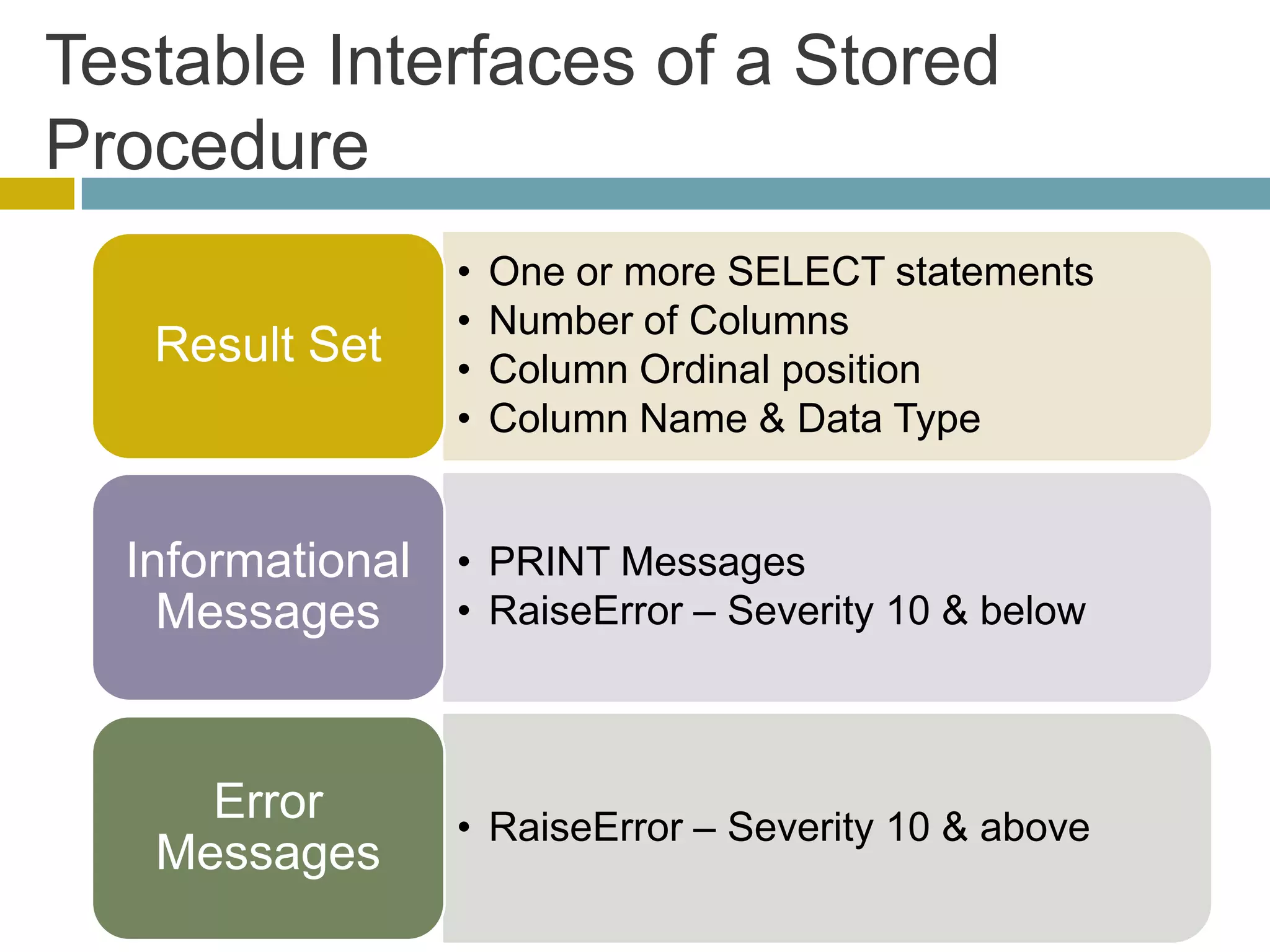
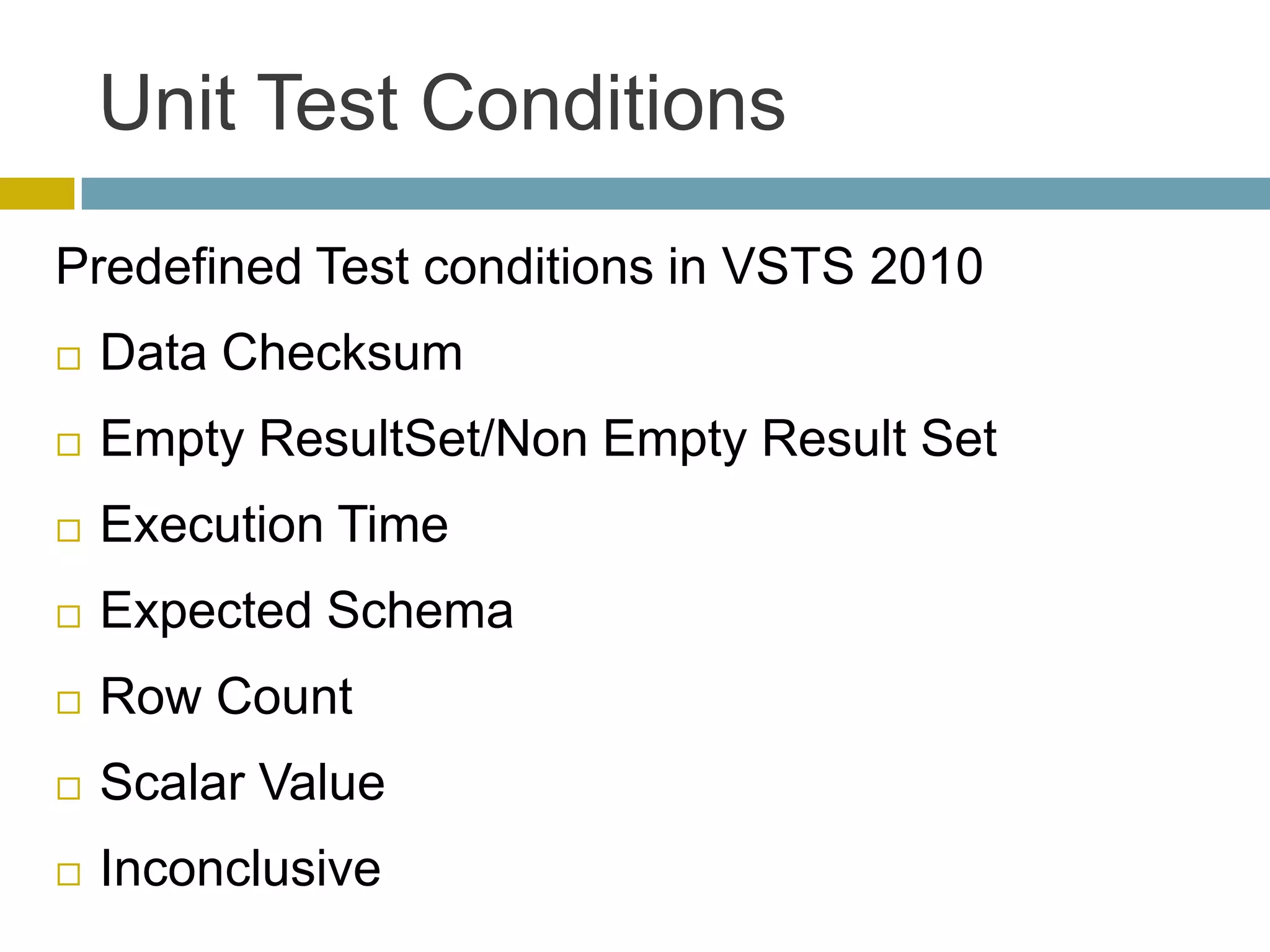
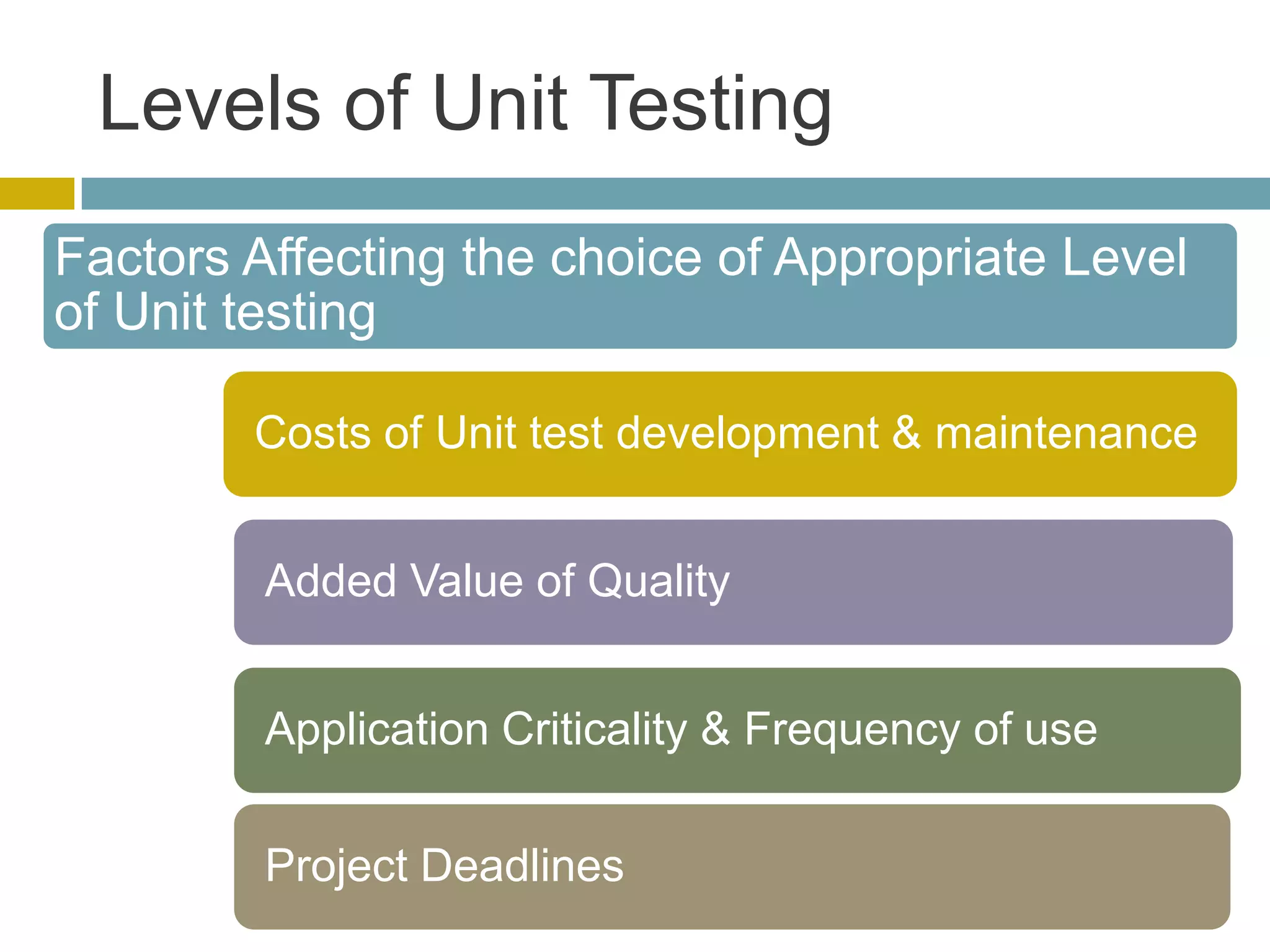
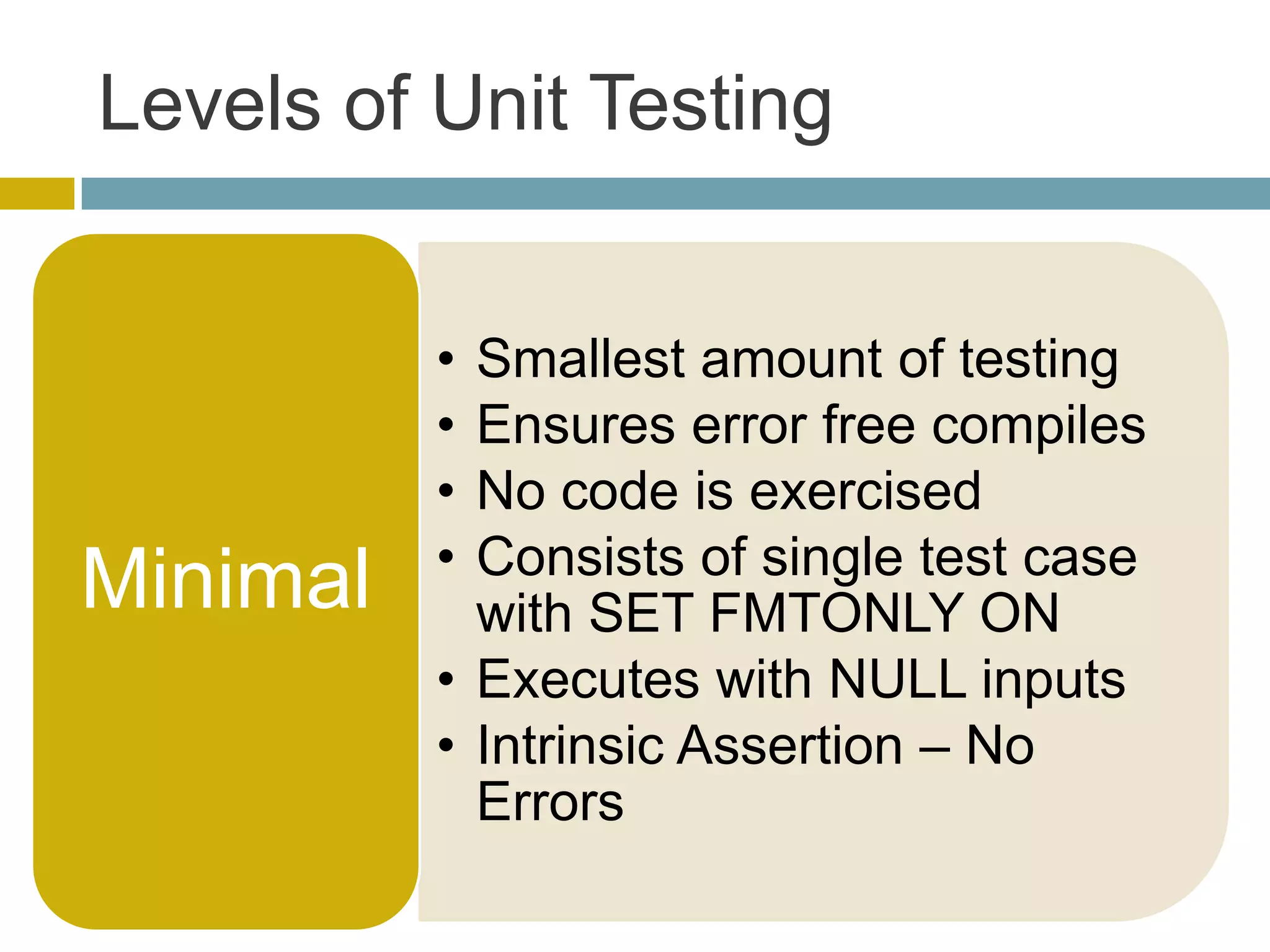
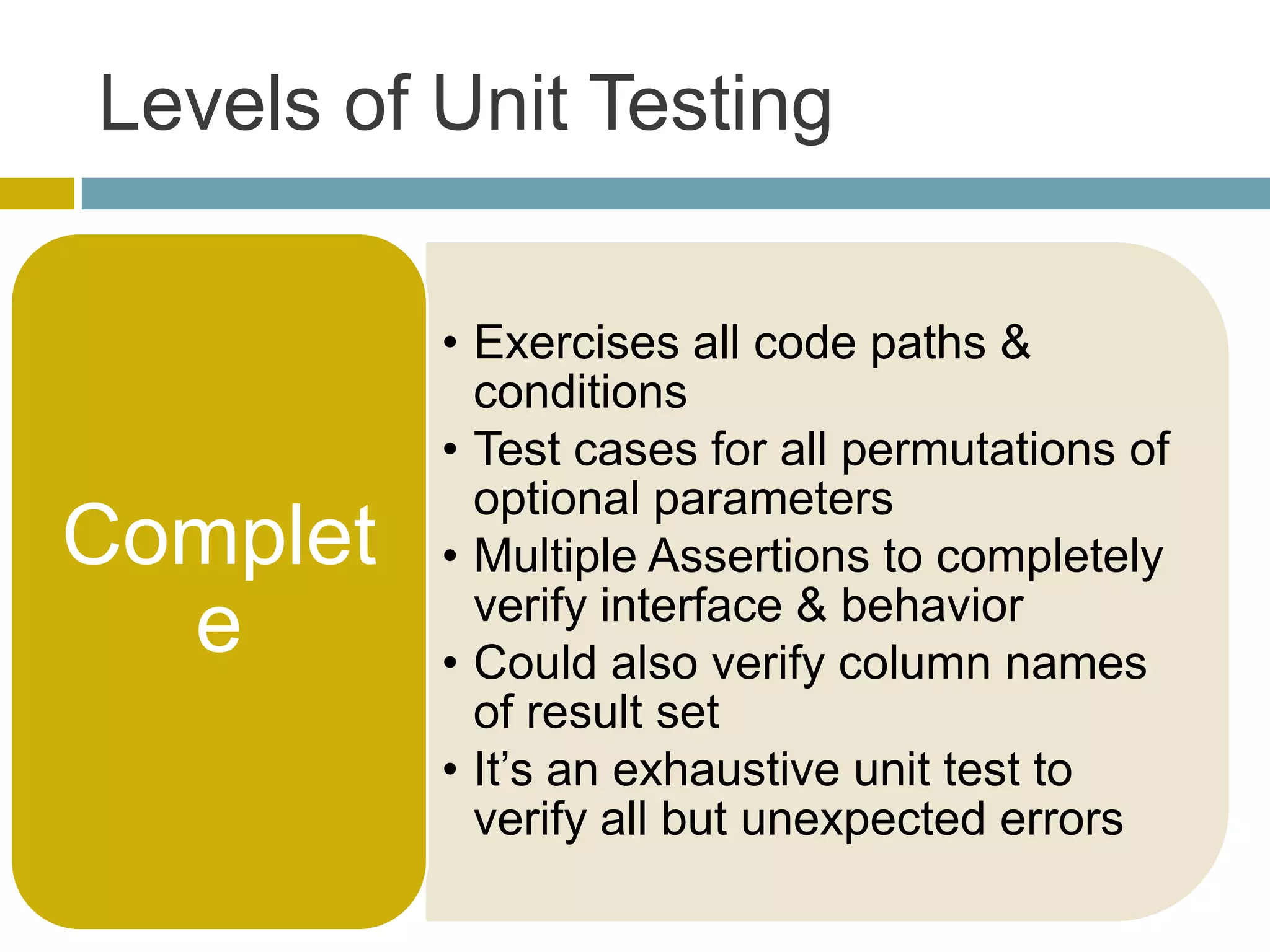
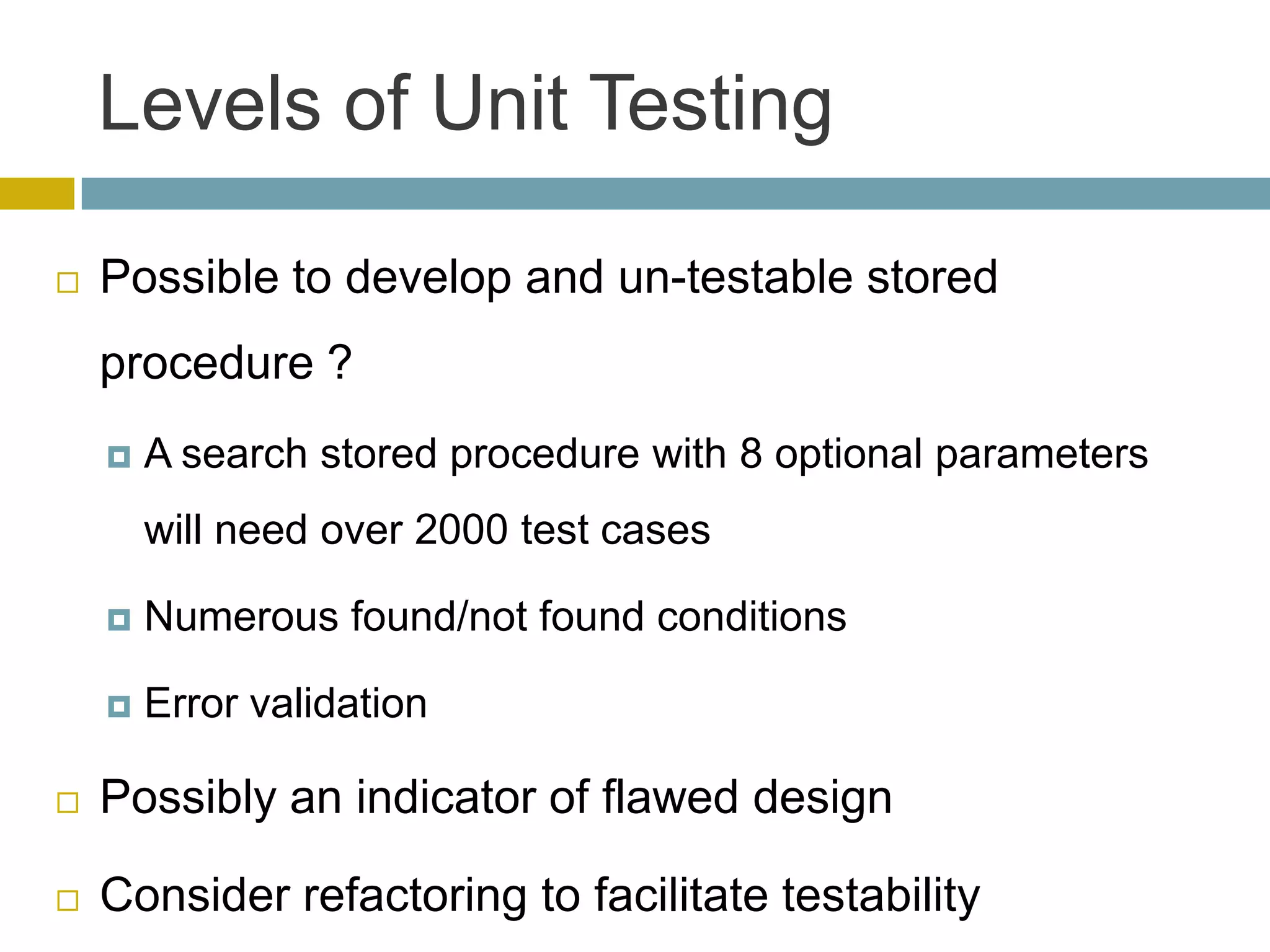
This document discusses database unit testing using Visual Studio Team System (VSTS). It begins with an overview of software testing basics and unit testing principles. It then covers database unit testing terminology, principles of isolation and independence, and testable interfaces of stored procedures. The document outlines different levels of unit testing and factors to consider. It demonstrates implementing database unit testing in VSTS 2010 and new features in VSTS 2012. The goal is to show how VSTS can be used to test database code and improve quality.