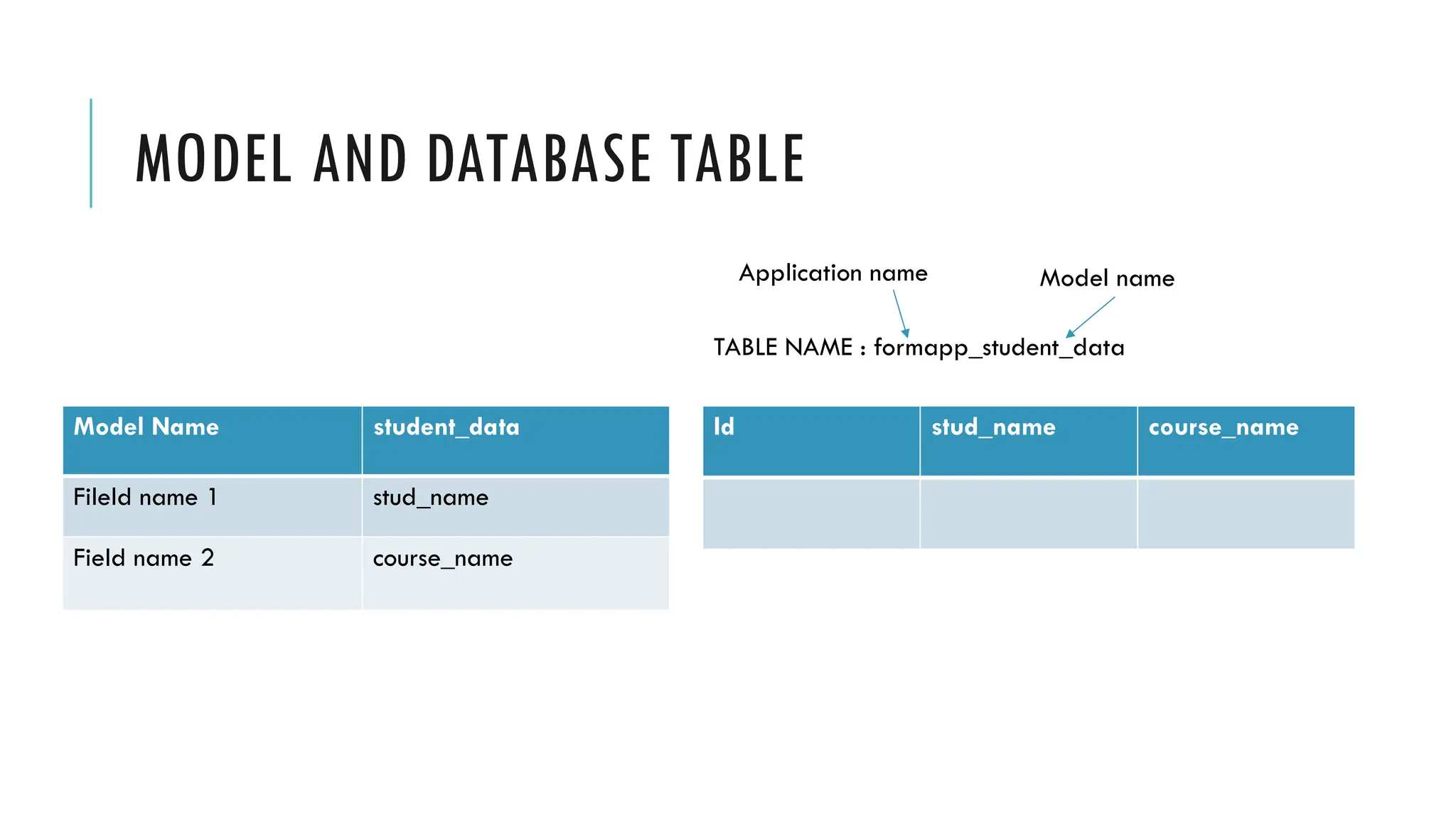
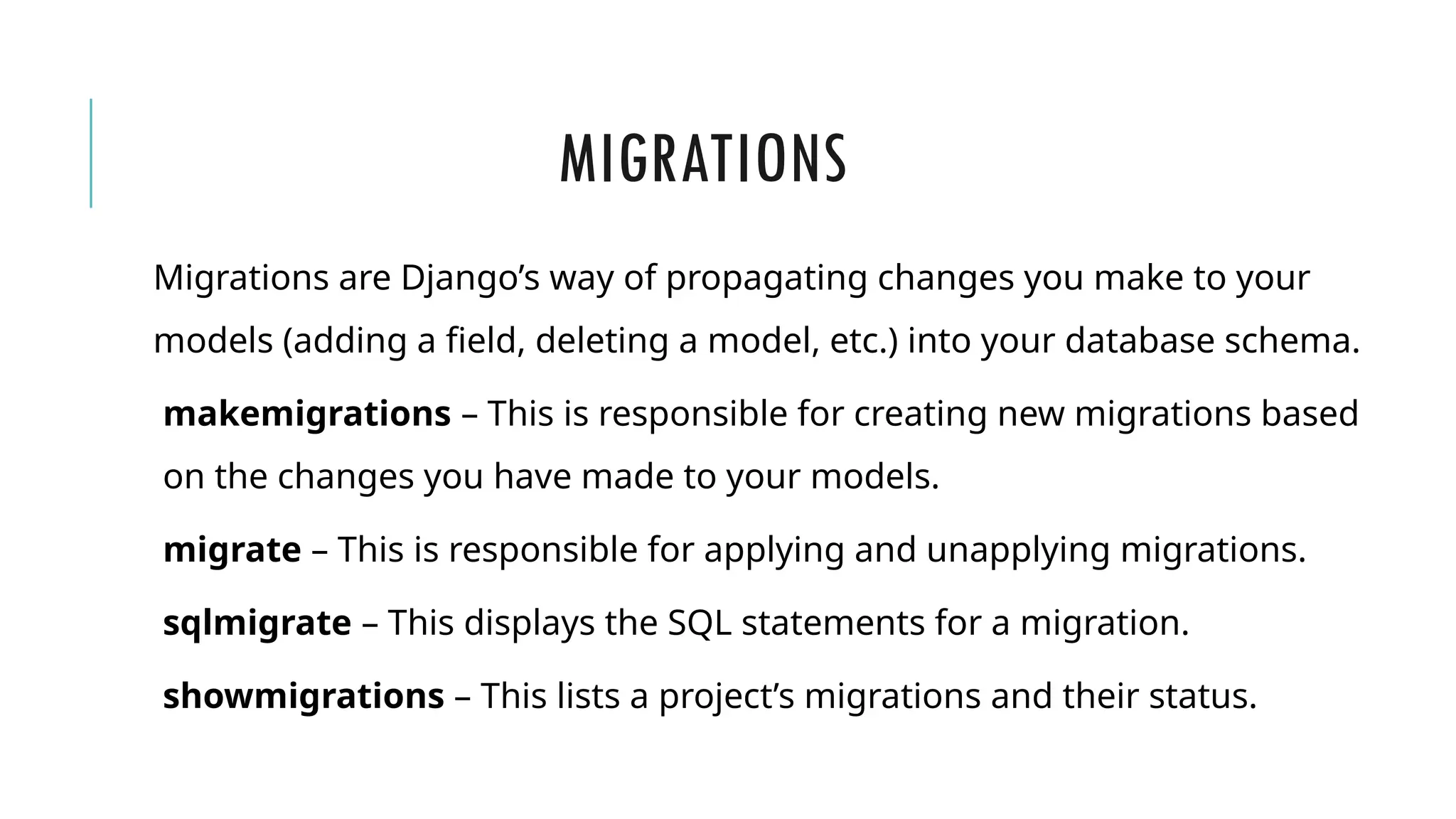
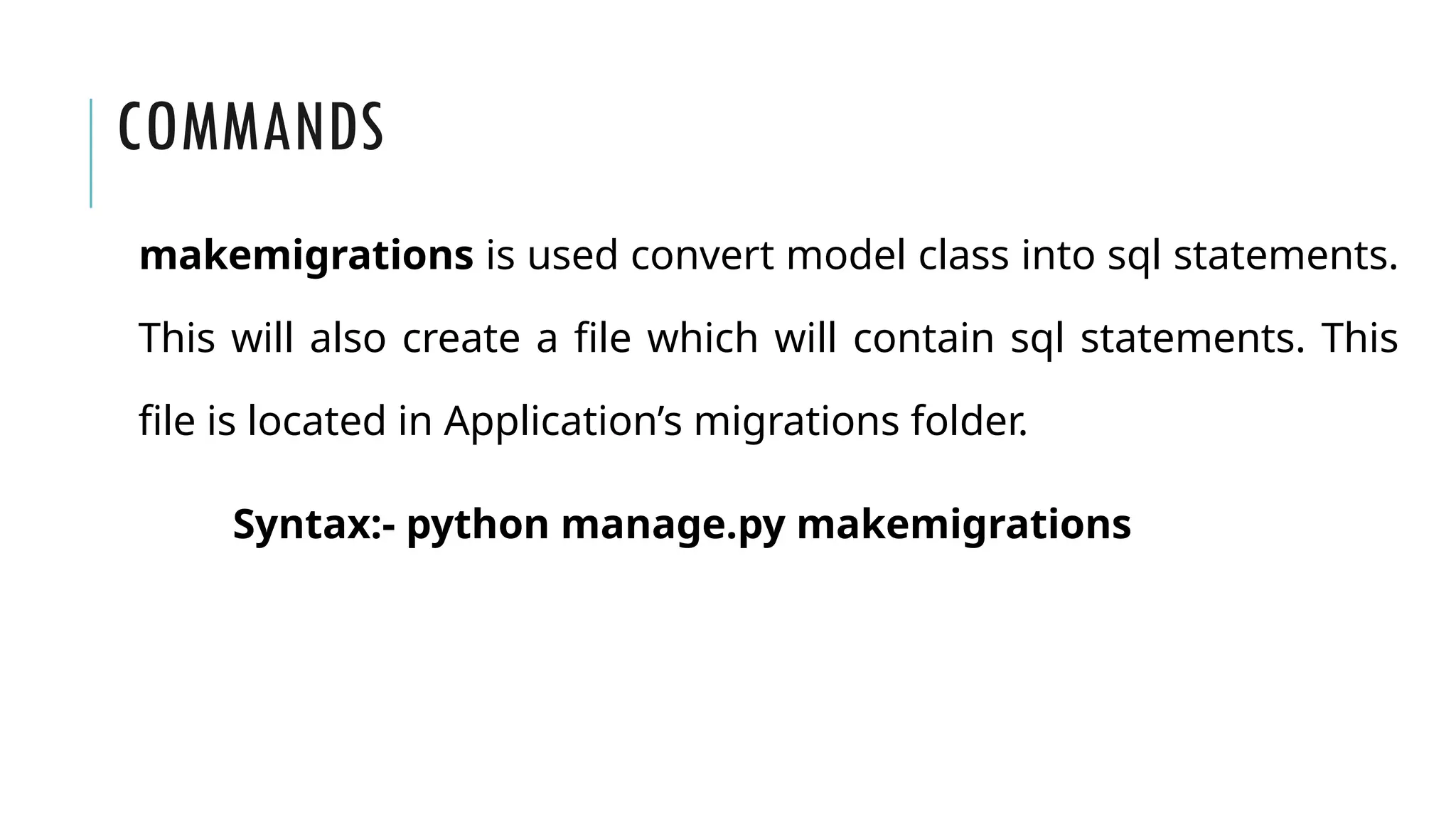
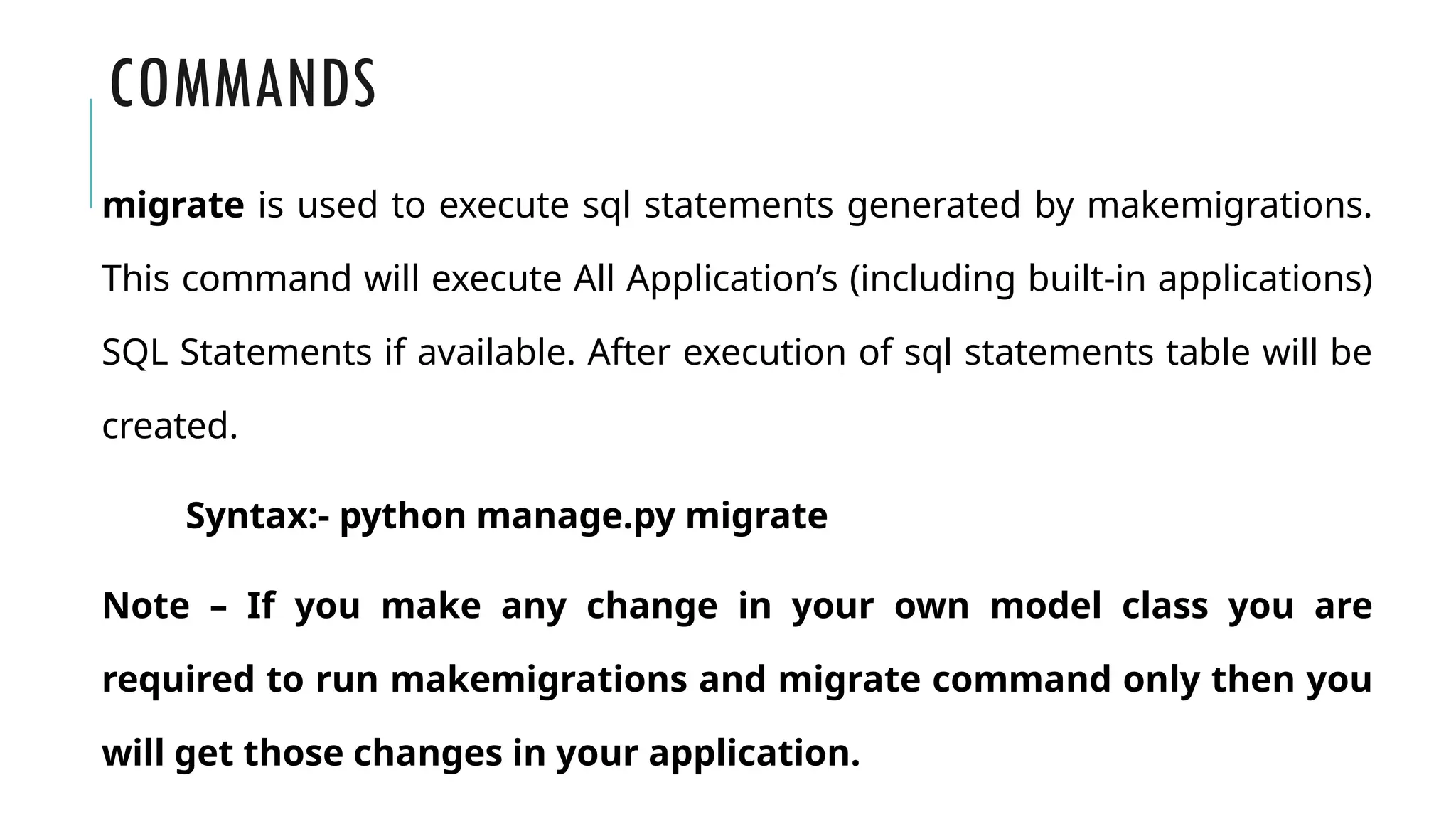
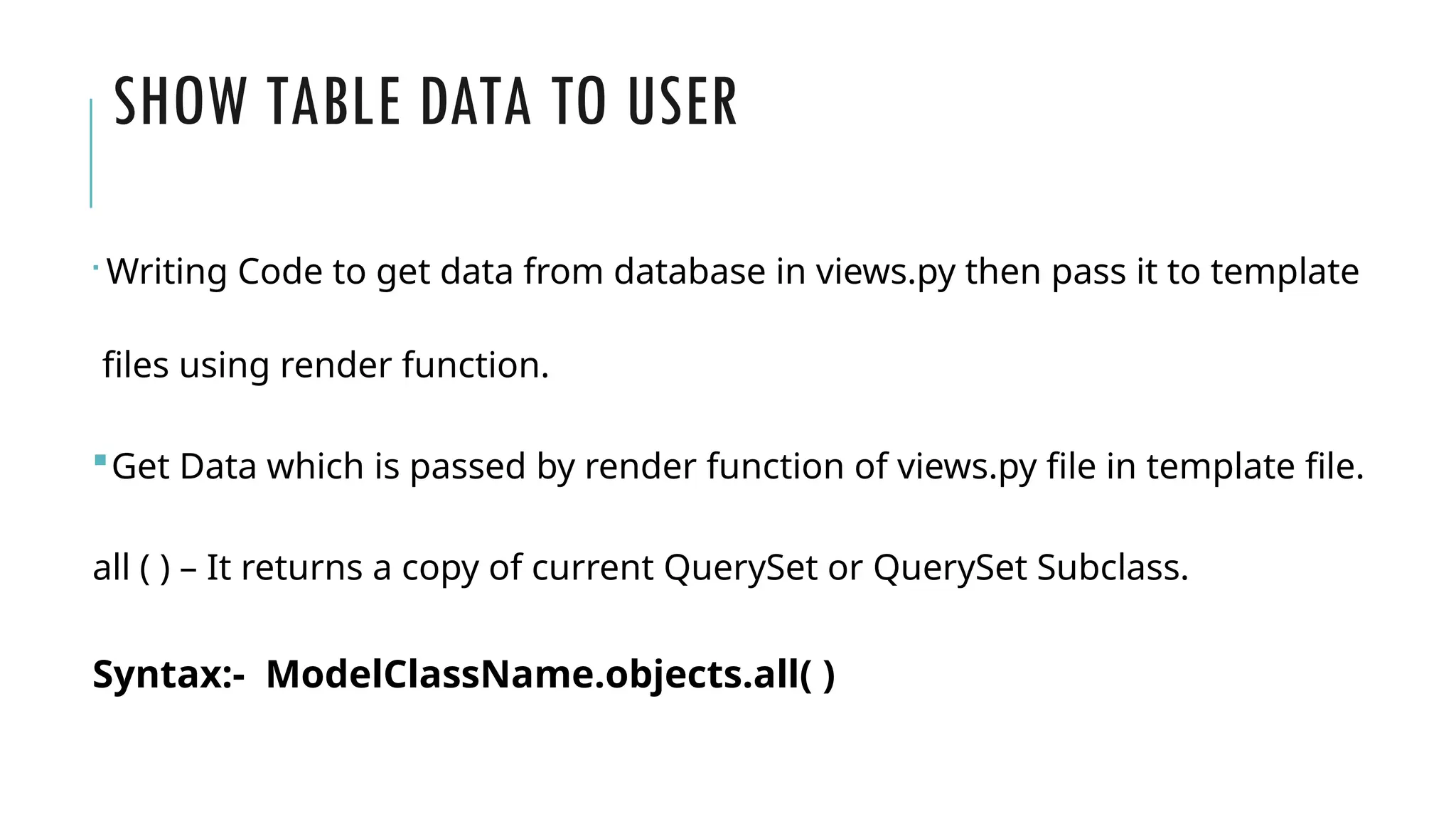
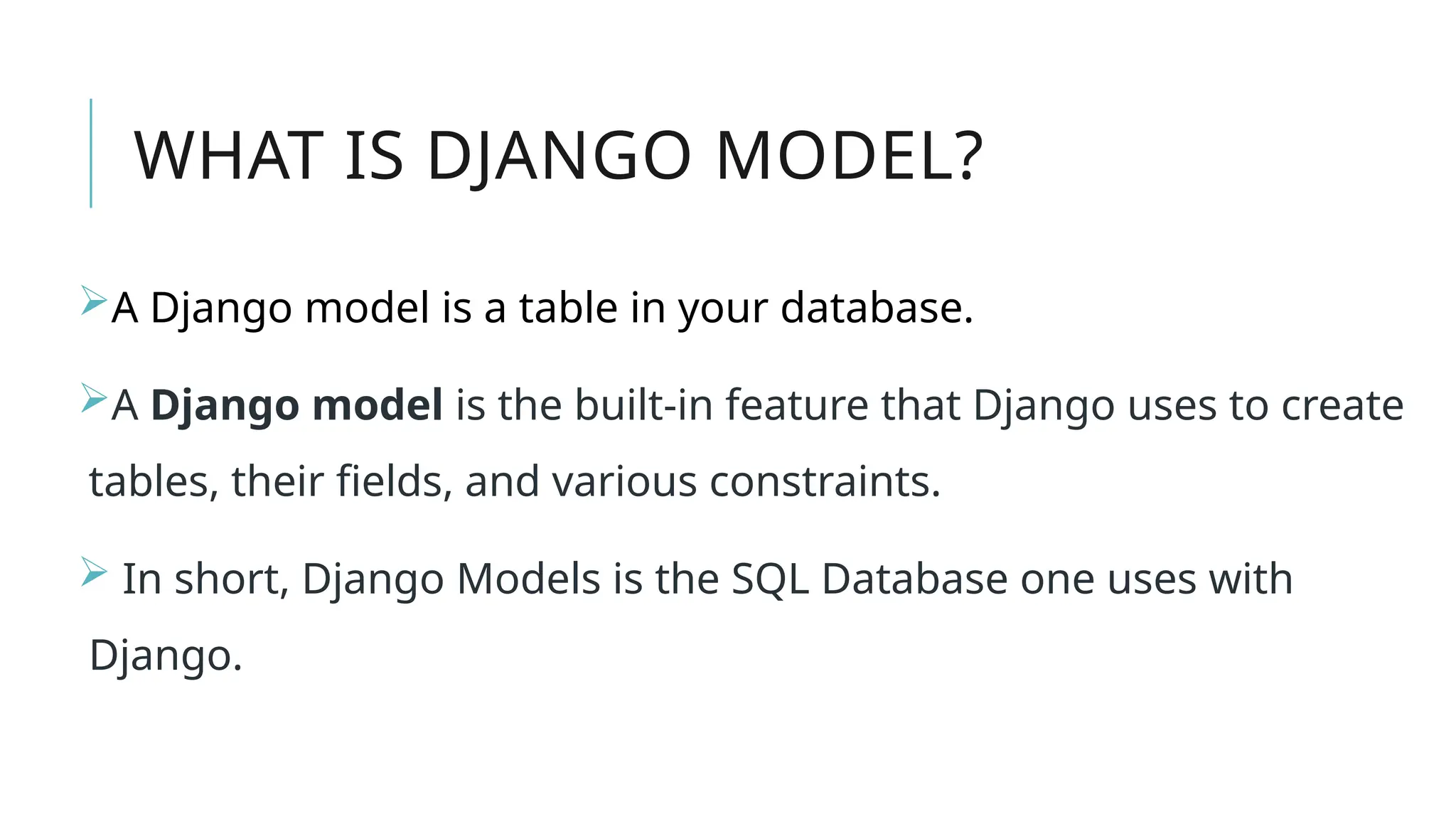
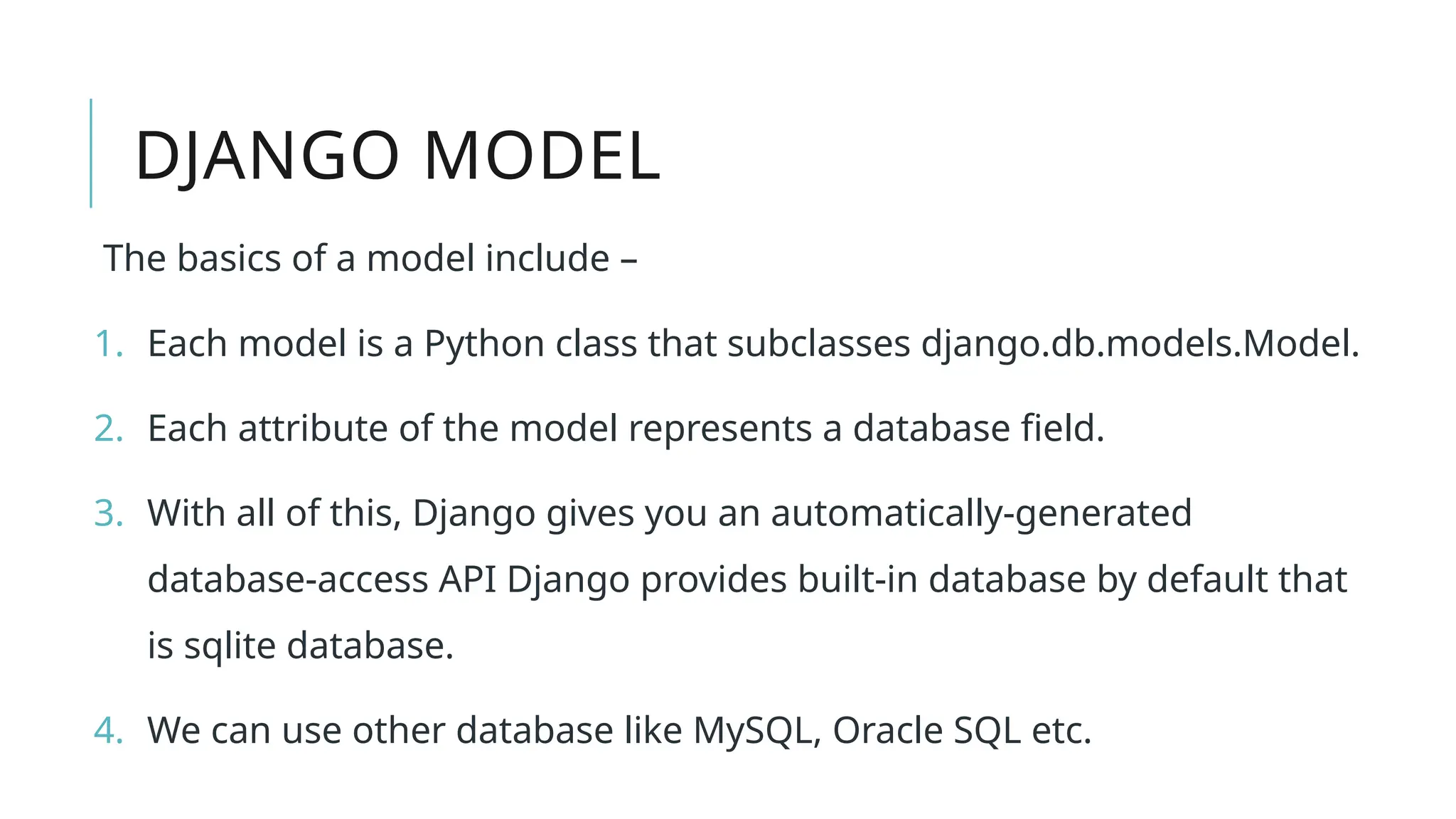
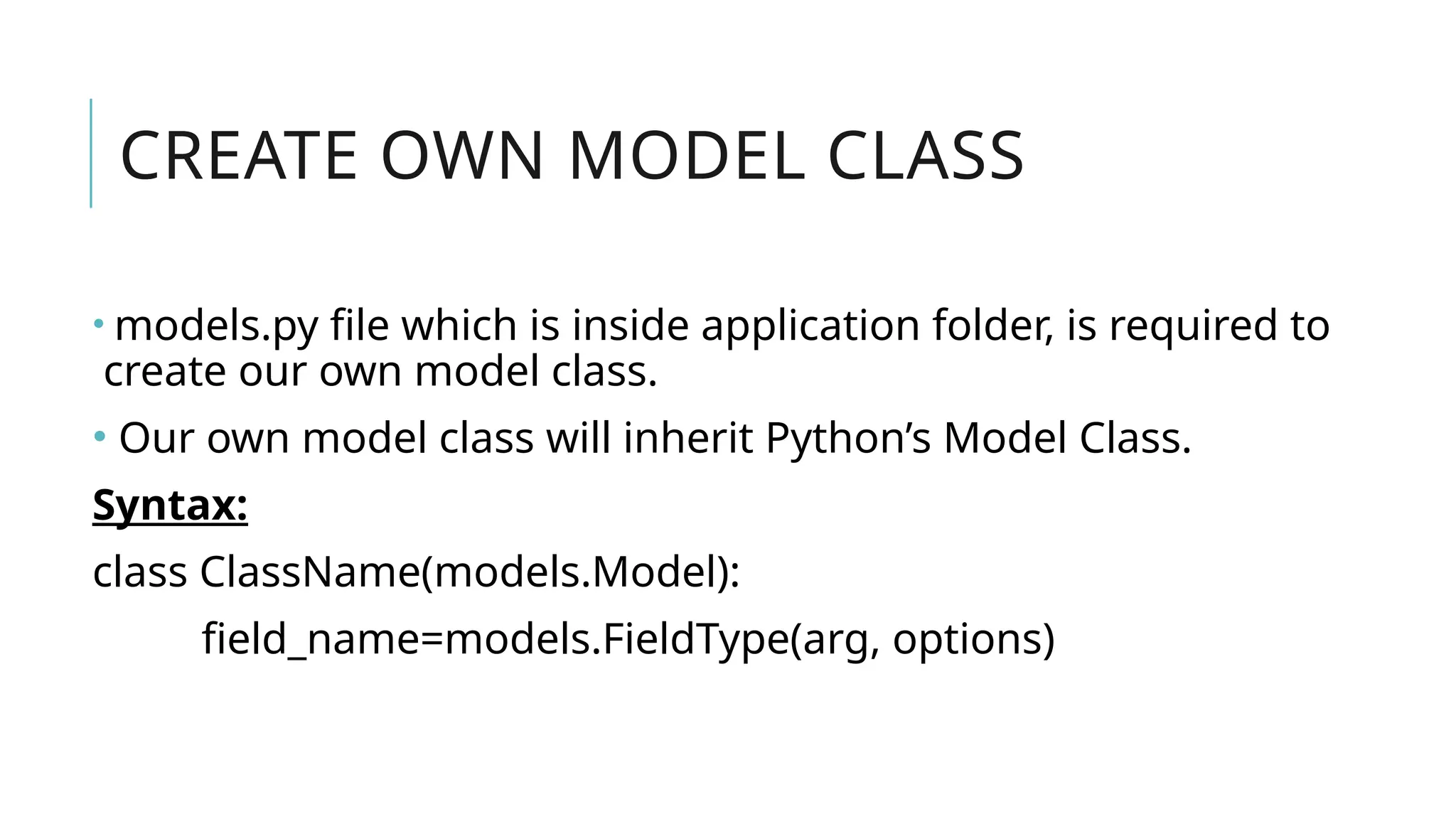
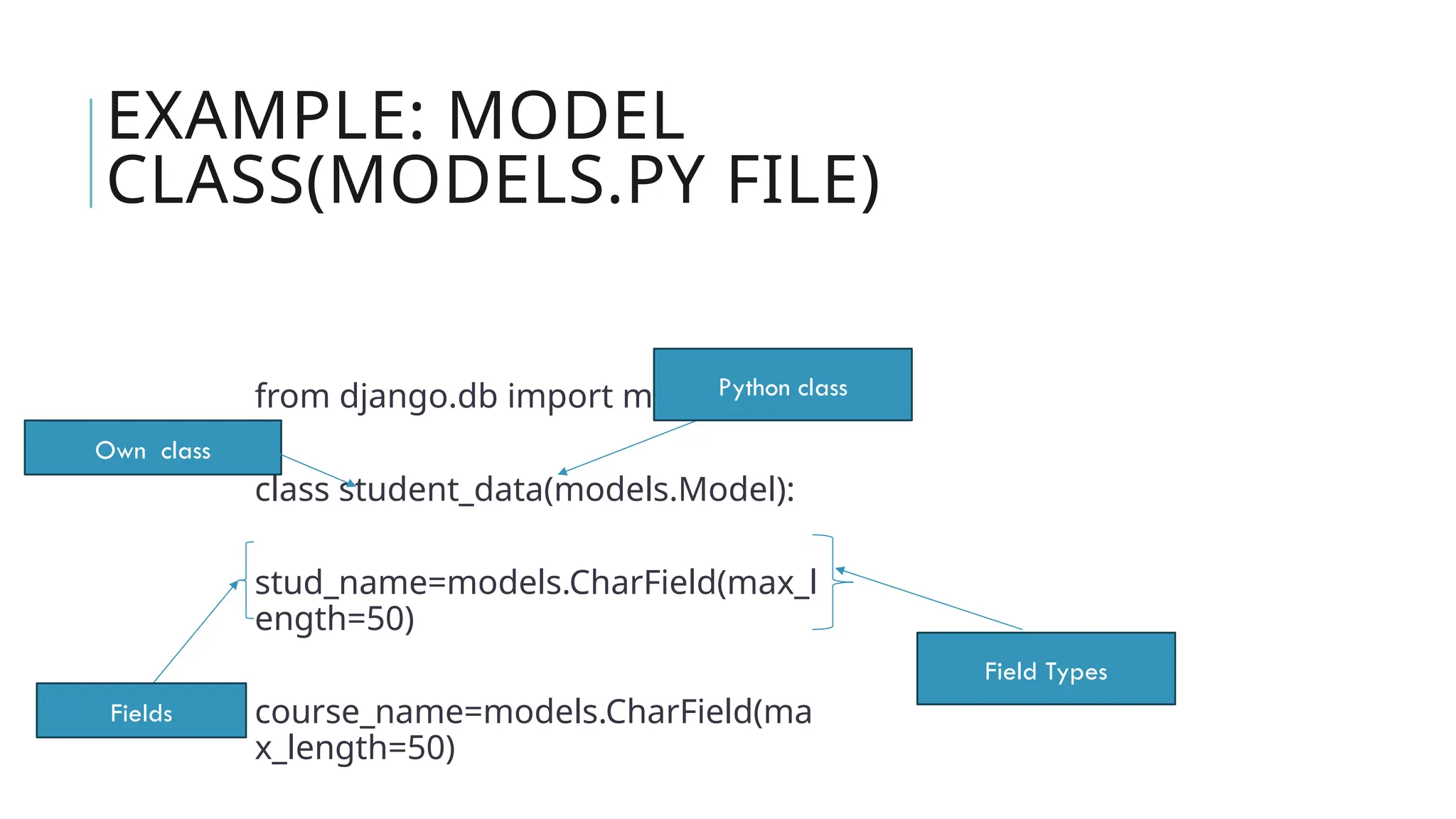
A Django model is a table in a database, created using a Python class that inherits from django.db.models.Model. Each model’s attributes represent database fields, and the built-in database access API helps manage these tables. To apply changes to models, commands like makemigrations and migrate are used, ensuring that model modifications reflect in the database schema.


![HOW TO USE MODELS
Once you have defined your models, you need to tell Django you’re going to use
those models.
•Open settings.py file
•Write app name which contains models.py file in INSTALLED_APPS = [ ]
•Open Terminal
•Run python manage.py makemigrations
•Run python manage.py migrate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modelintroduction-241121083923-f4f1d291/75/Django-model-create-a-table-in-django-web-framework-7-2048.jpg)