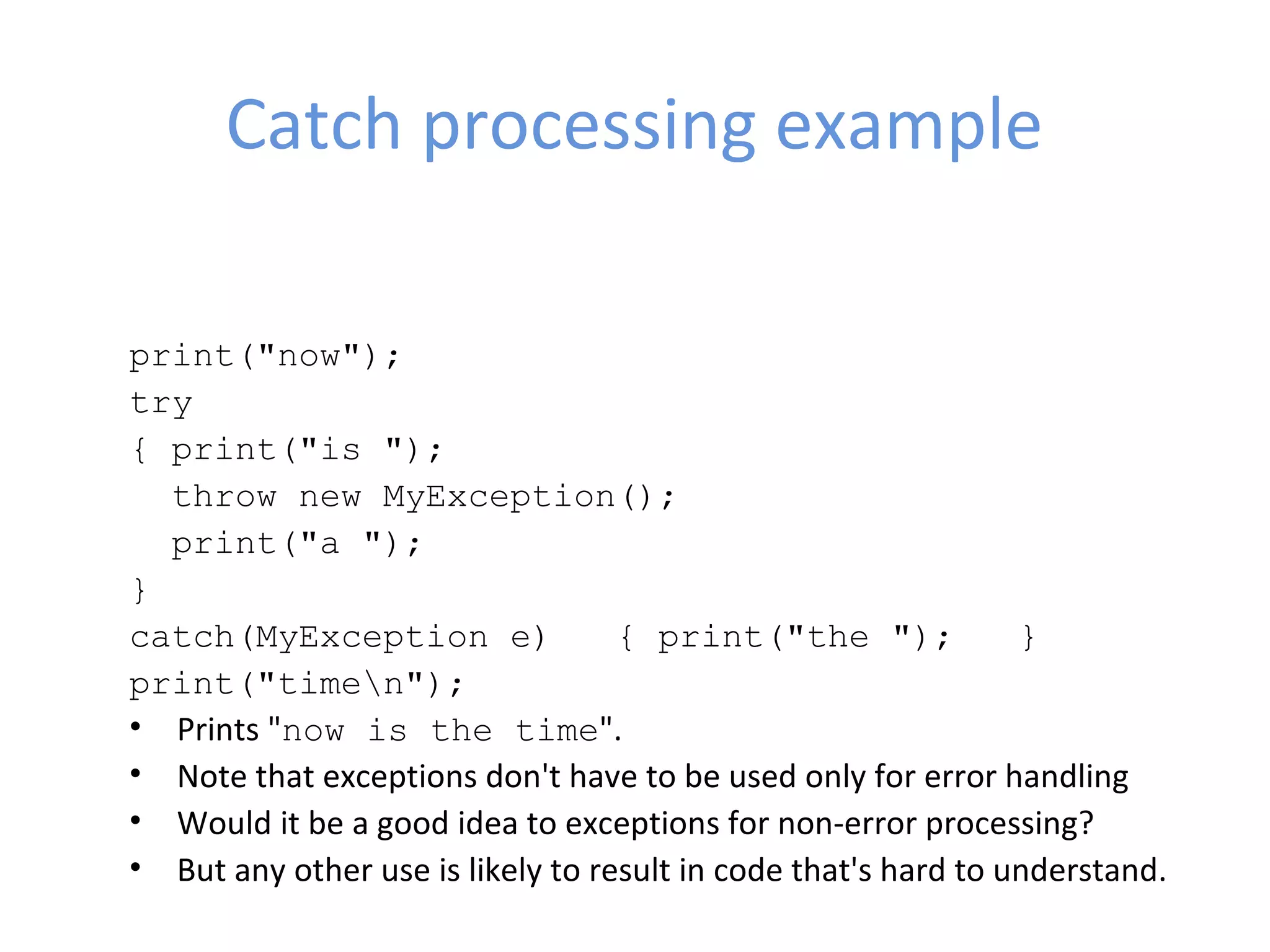
Exceptions in Java allow errors to be handled separately from main program logic. Exceptions break normal program flow and can be caught and handled in catch blocks. There are checked exceptions that must be caught or declared as thrown, and unchecked exceptions like RuntimeException that do not require handling. Finally blocks are always executed to cleanup resources whether an exception occurs or not.