The document provides an overview of a workshop on creating single page web applications using JavaScript. The workshop will be conducted over 3 full days and cover building simple web pages with HTML and CSS, adding dynamic functionality with JavaScript, and developing a single page application using frameworks like Backbone.js. The first day will introduce HTML, DOM manipulation with JavaScript, and responsive design. The second day focuses on jQuery, AJAX, templates and CoffeeScript. The third day covers MVC principles, and building a single page app with Backbone.js and Underscore.js.







![Data Types
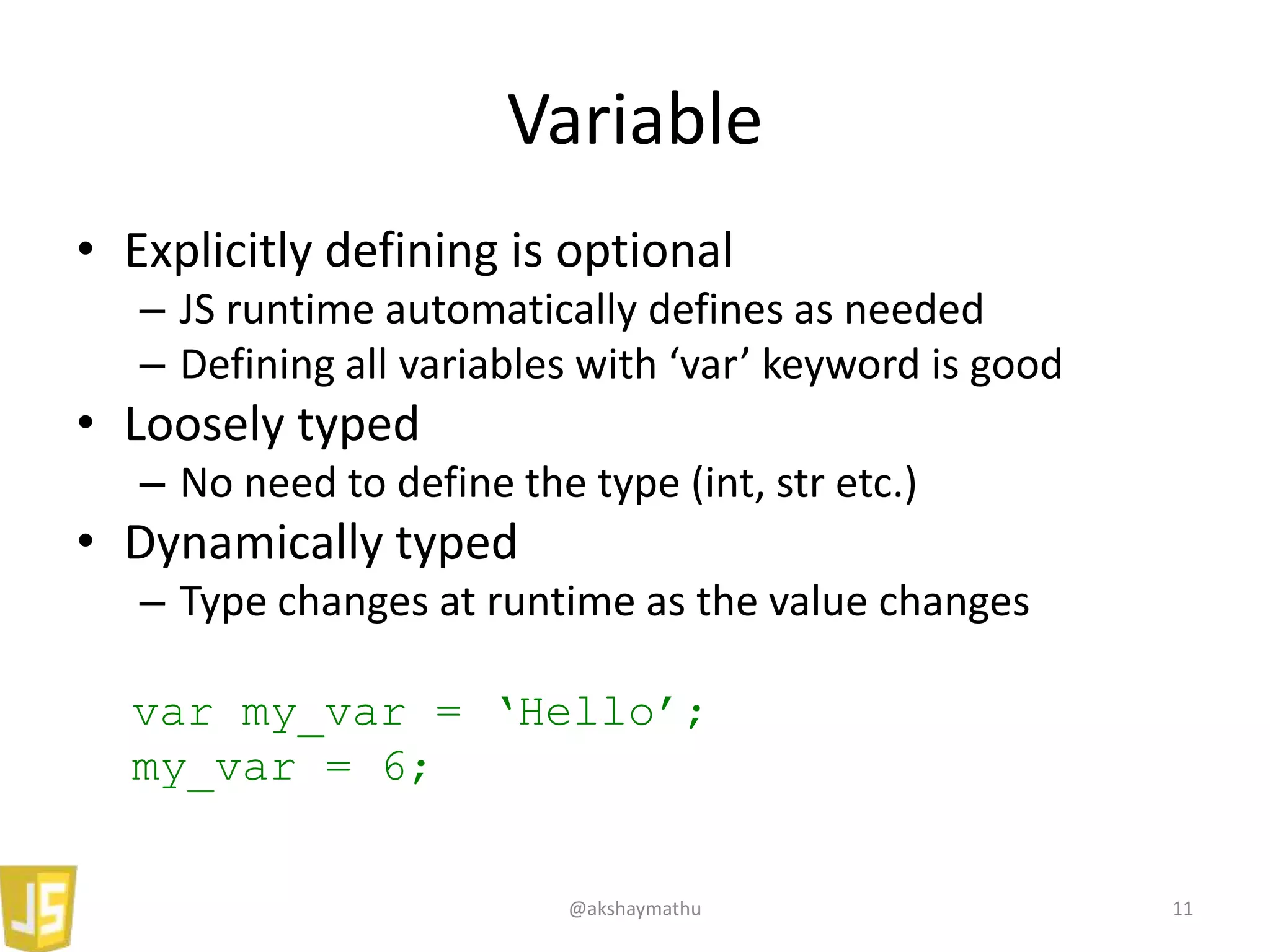
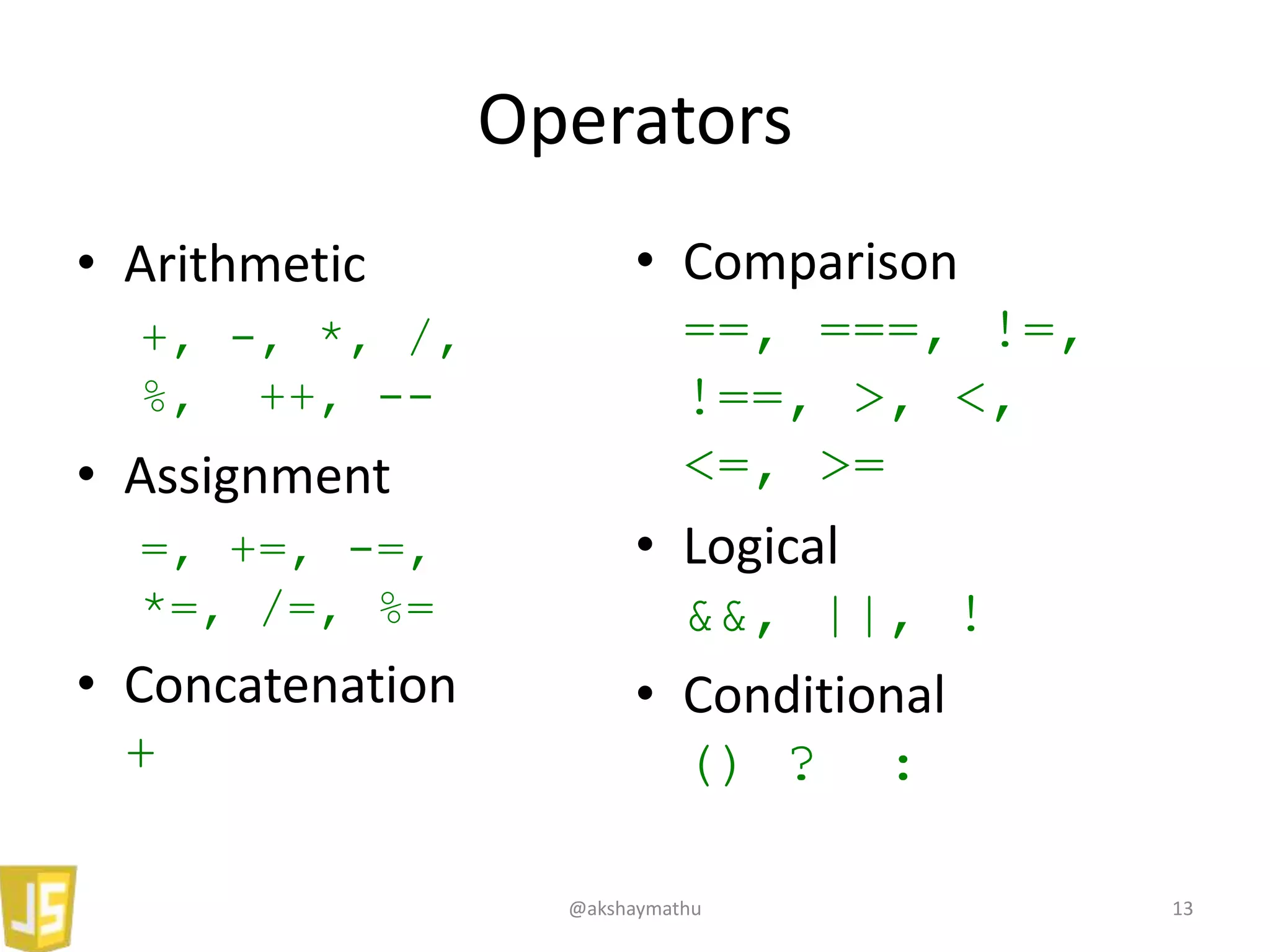
• String: “1”, “Hello! How are you”
• Number: 1, 2, 121.22
• Boolean: true, false
• Array: [1, “1”, false, {a: 10}]
• Object: {lang: “JS”, val: my_var}
• Null: null
• Undefined: undefined
• Functions: function(){}
• Date: Mon, 23 Sep 2013 12:18:54 GMT
typeof “1” // String
@akshaymathu 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js-basics-131002083305-phpapp02/75/Getting-Started-with-Javascript-12-2048.jpg)
![For Loop
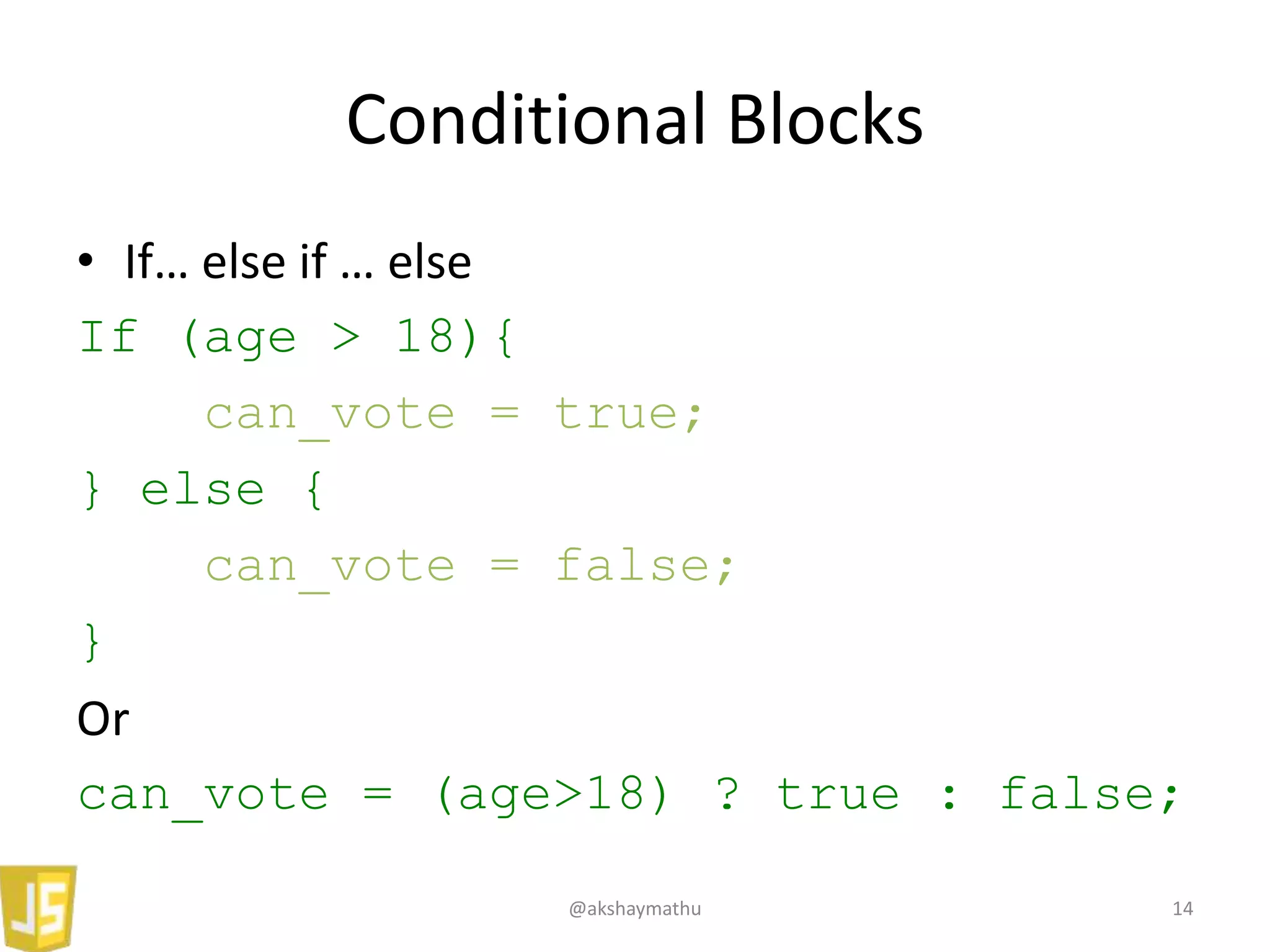
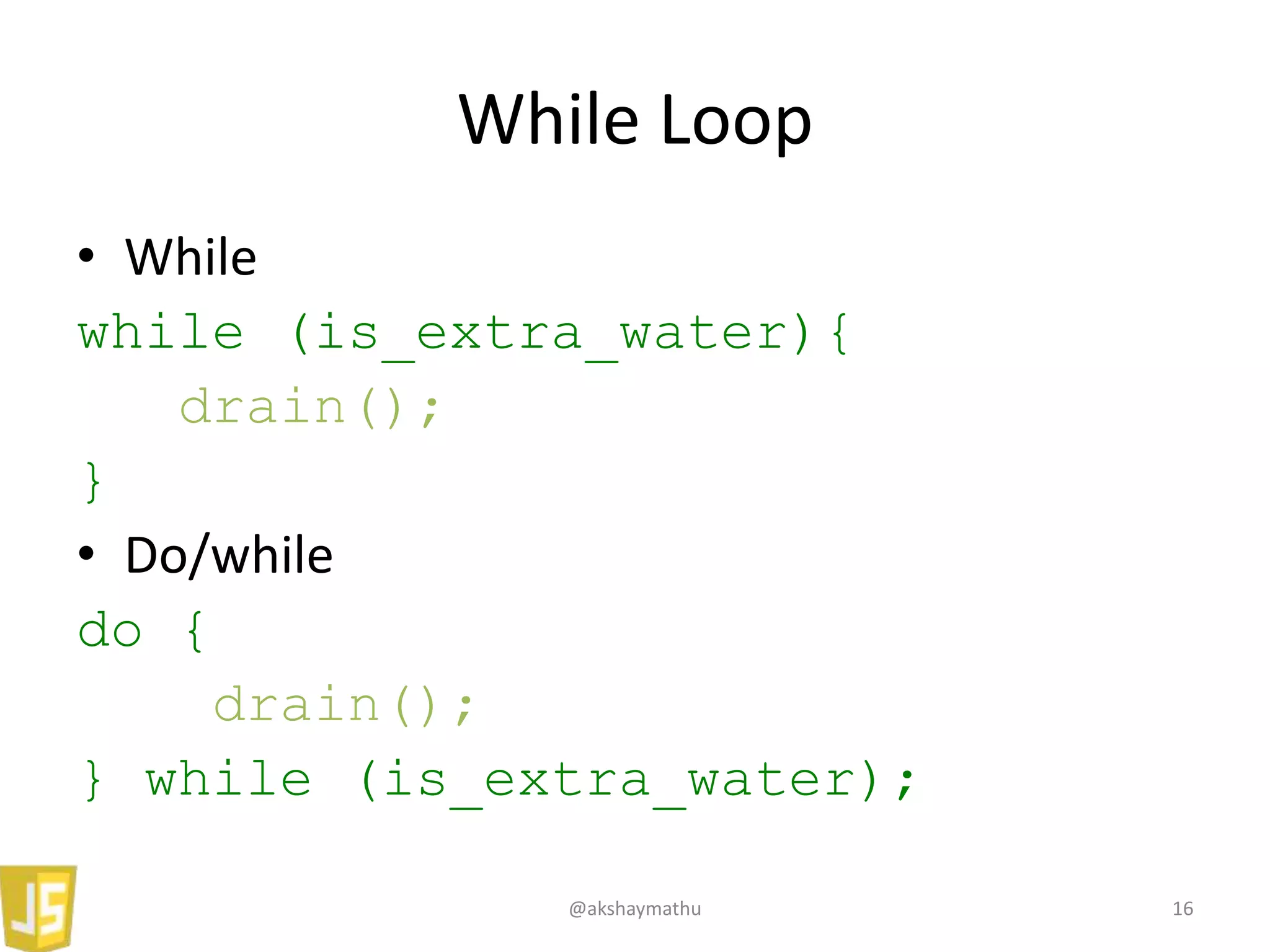
• For
for (i=0; i<array.length; i++){
console.log(array[i]);
}
• For/in
for (item in array){
console.log(item);
}
@akshaymathu 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js-basics-131002083305-phpapp02/75/Getting-Started-with-Javascript-15-2048.jpg)





![Objects
• Everything in JS is an object (instance)
“string”.length // 6
“str”.length.toFixed(2) // “3.00”
[„hell‟, „o!‟].join(„‟) // „hello!‟
• Custom objects can also be defined
@akshaymathu 28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js-basics-131002083305-phpapp02/75/Getting-Started-with-Javascript-28-2048.jpg)
![JSON
• Javascript Object has a key and a value
• Key is always string
• Value can be of any type
– Including another JSON object
A = {key1: value1, key2: value2};
or
A = new Object();
A[„key1‟] = value1;
A.key2 = value2;
@akshaymathu 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js-basics-131002083305-phpapp02/75/Getting-Started-with-Javascript-29-2048.jpg)