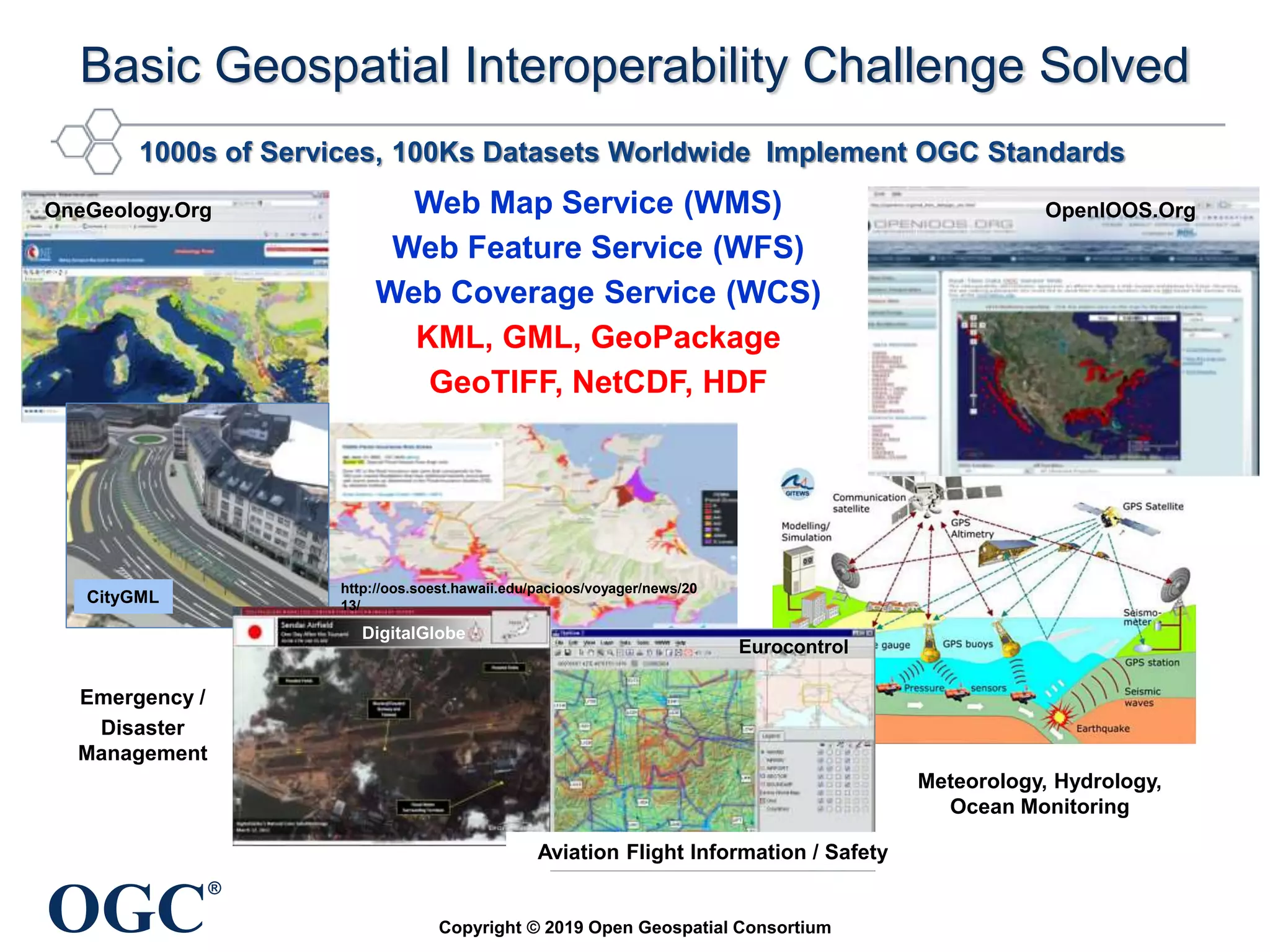
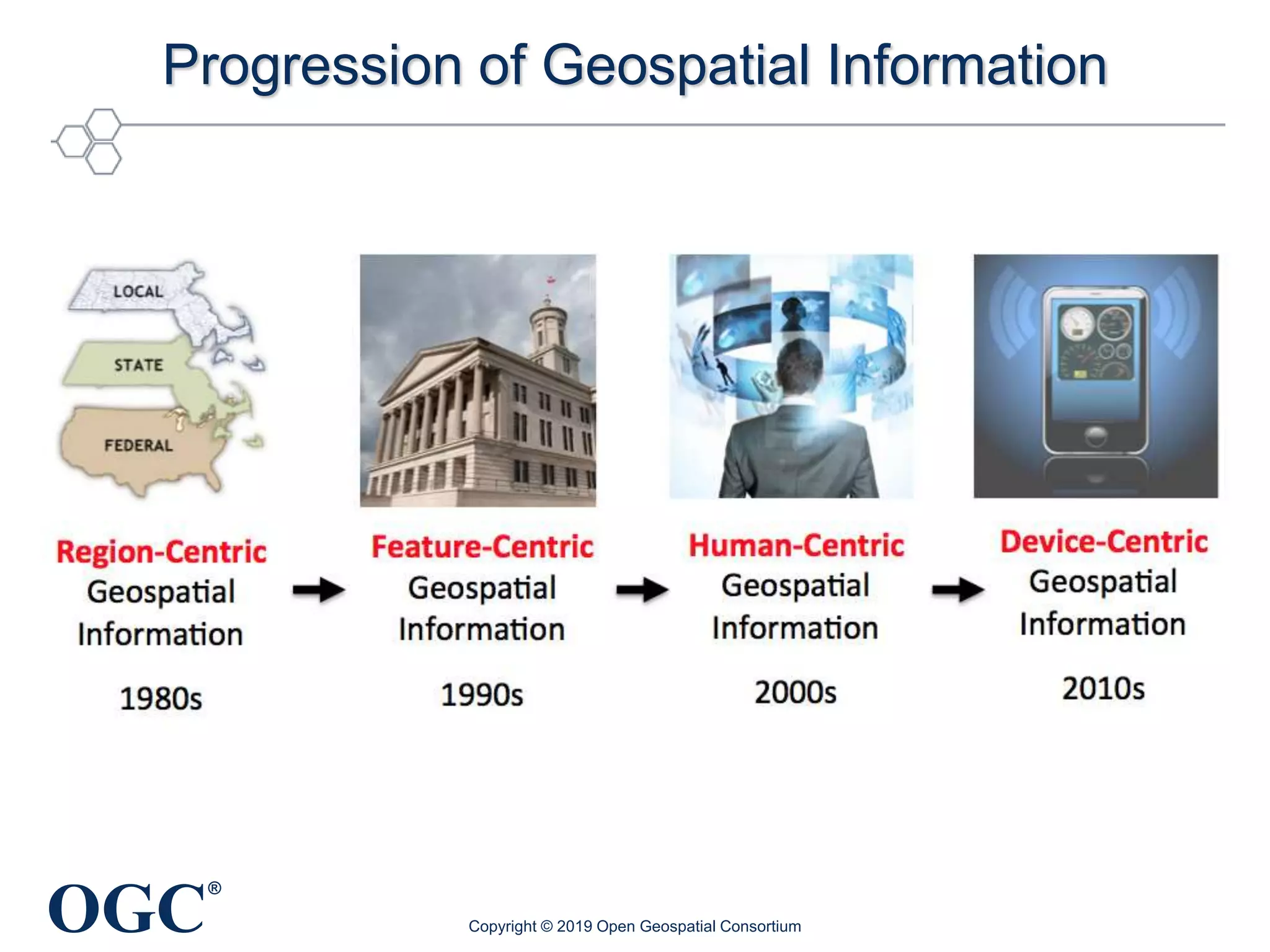
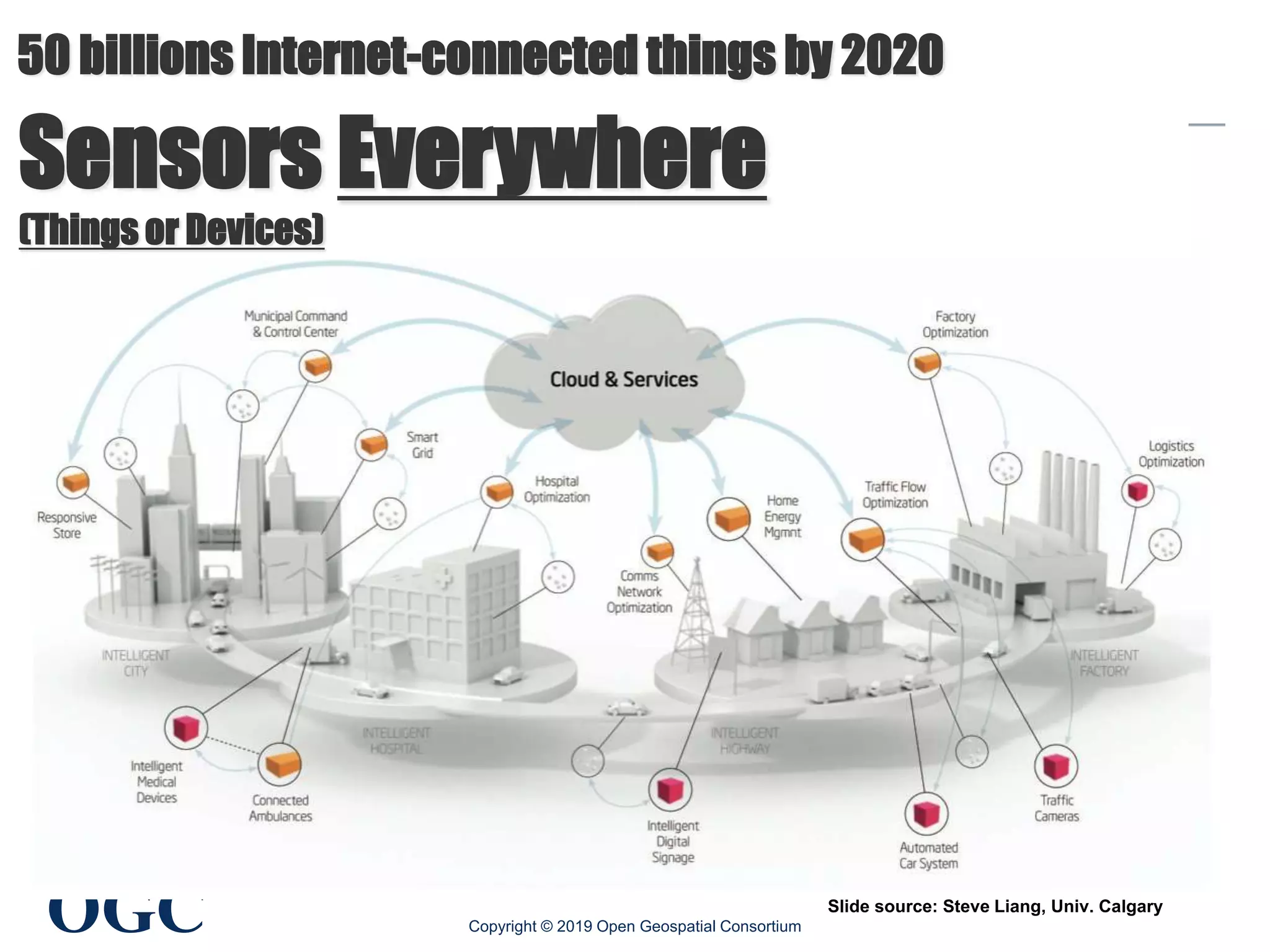
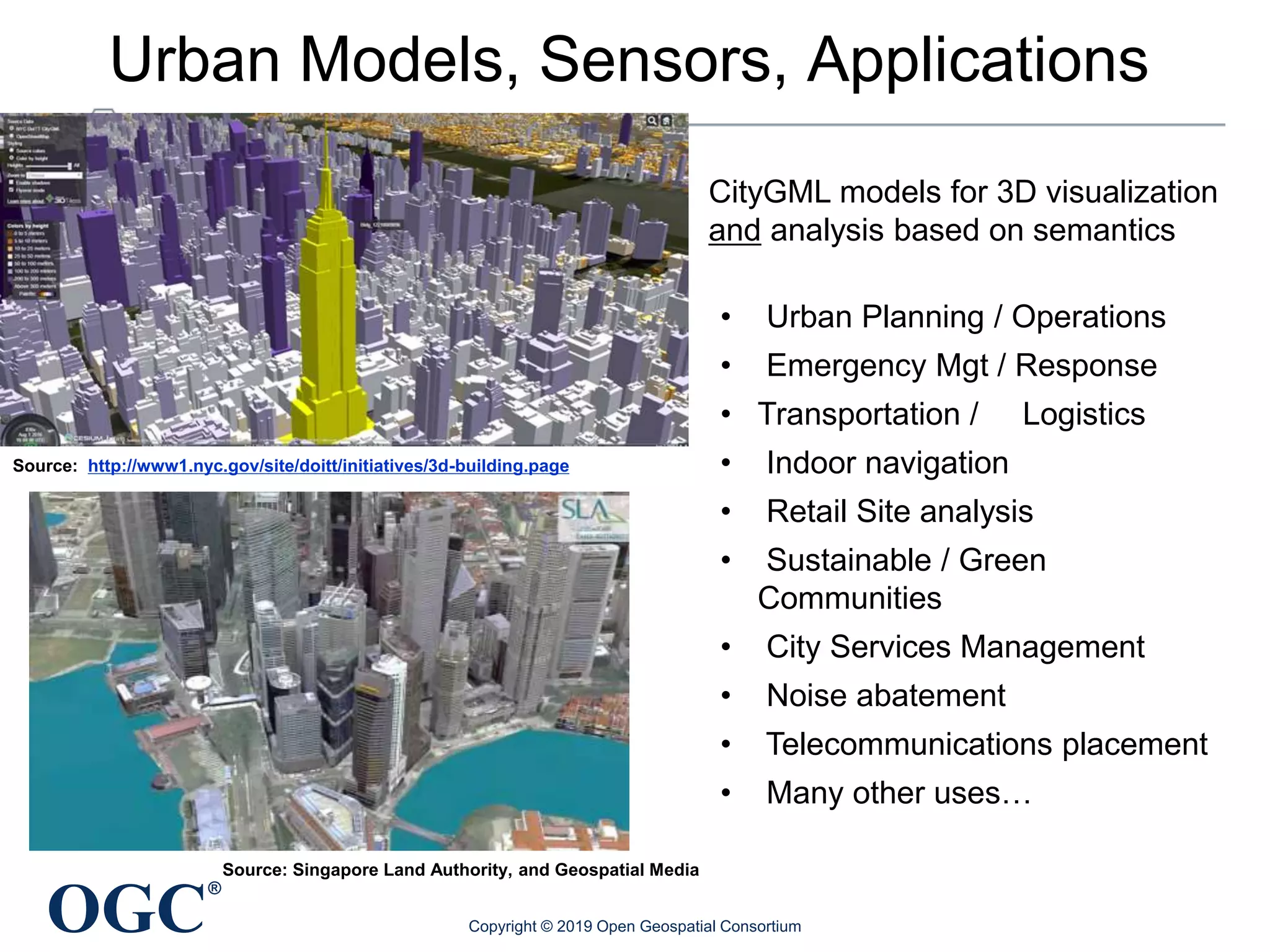
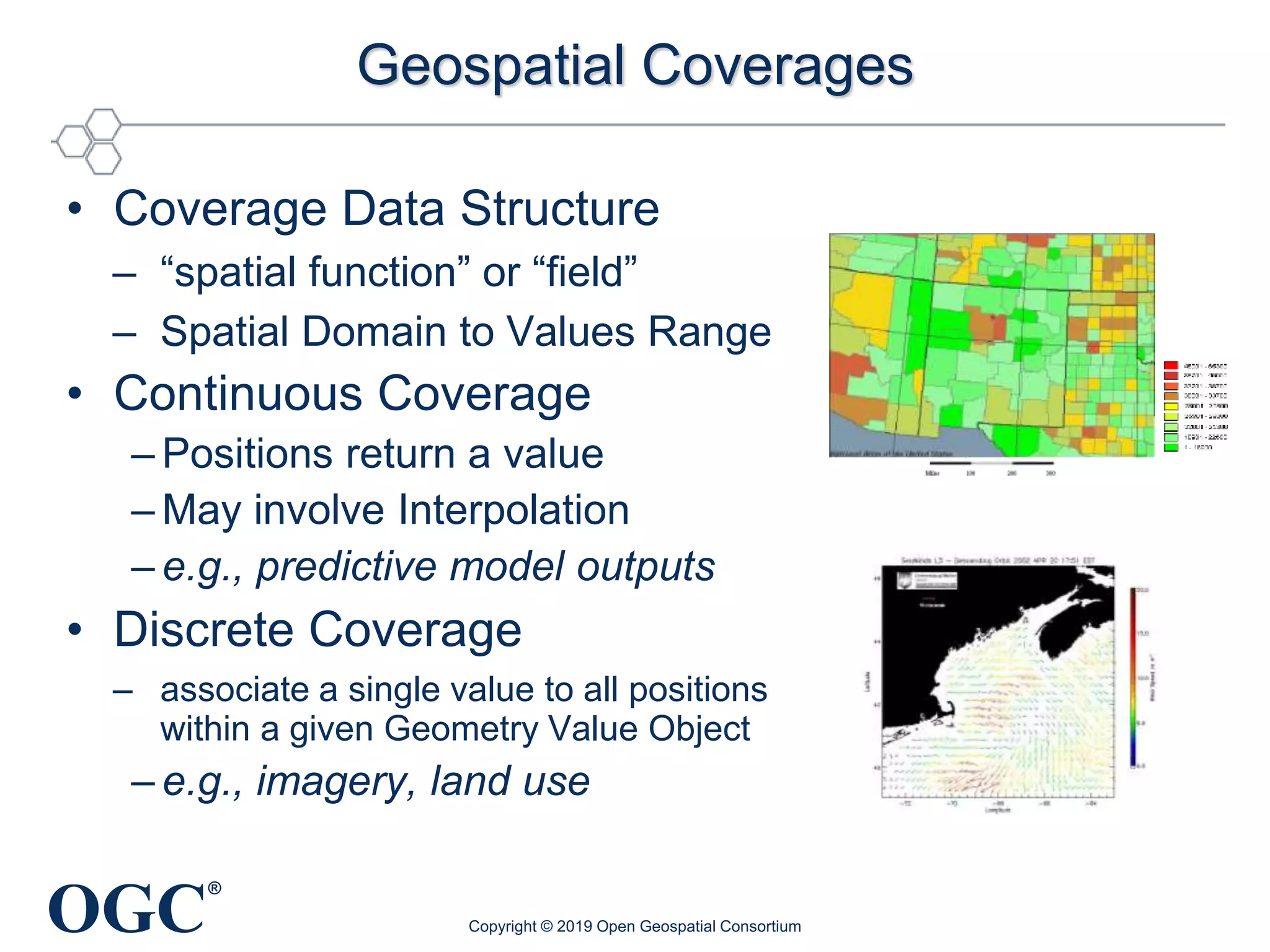
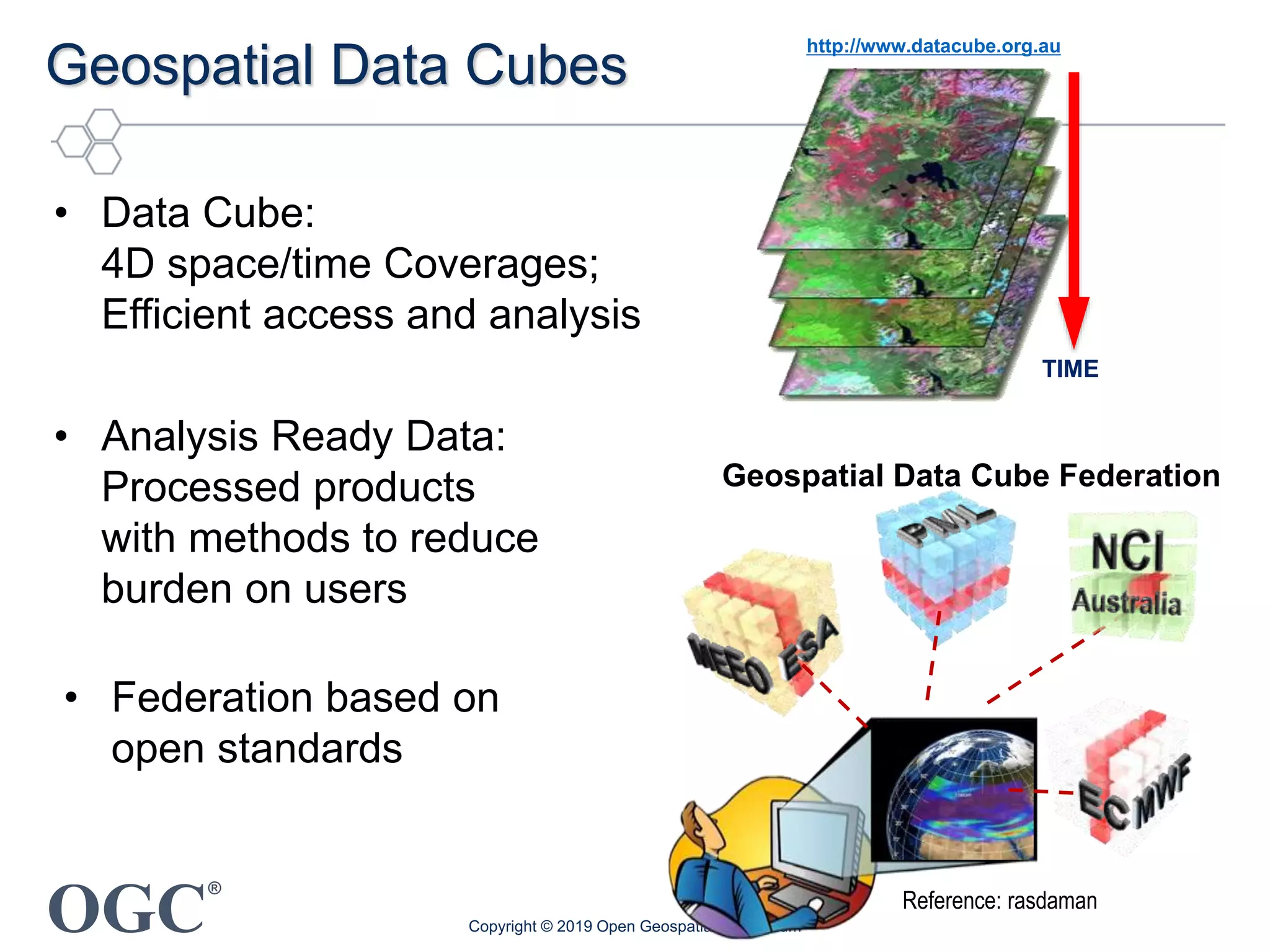
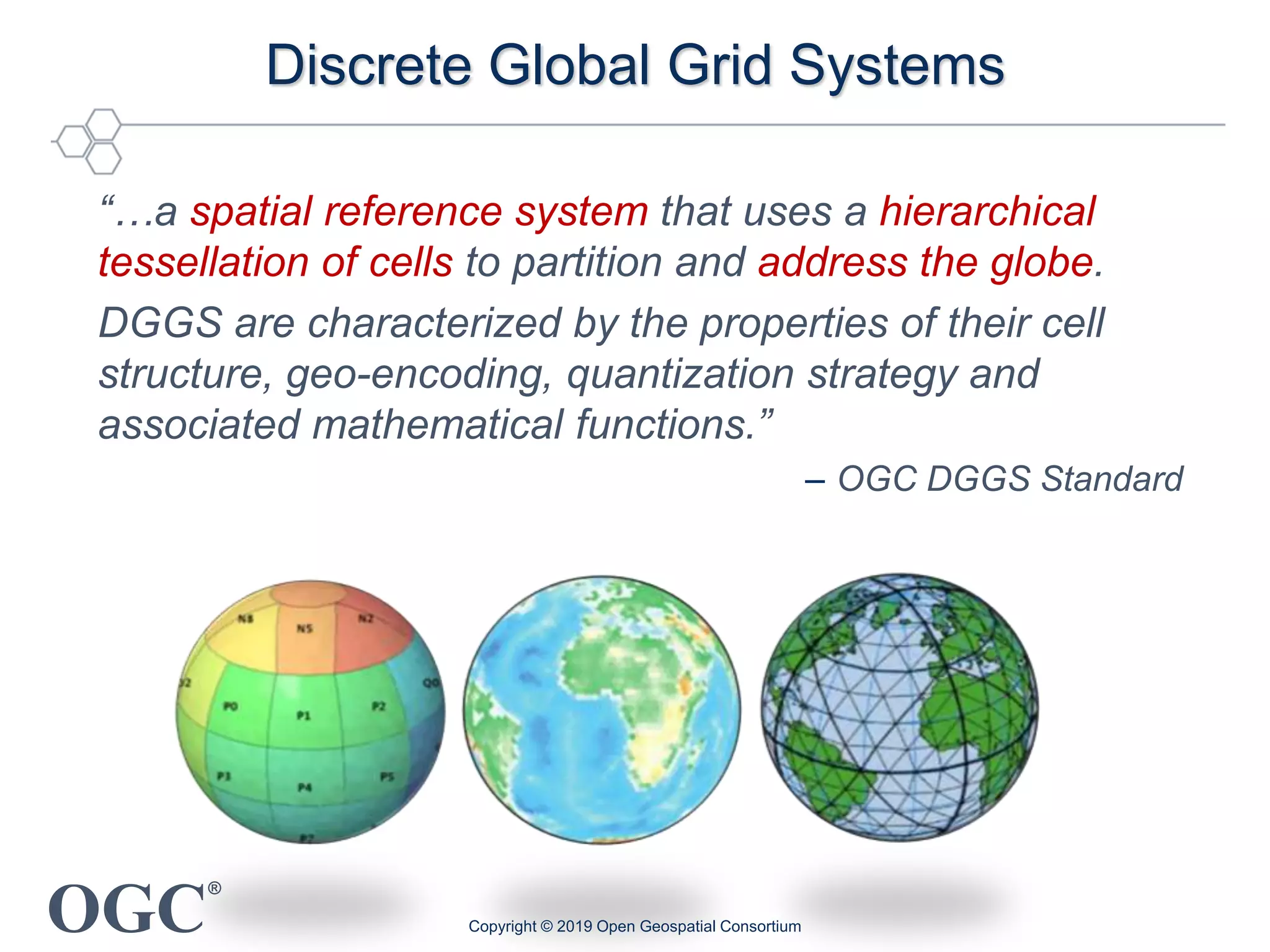
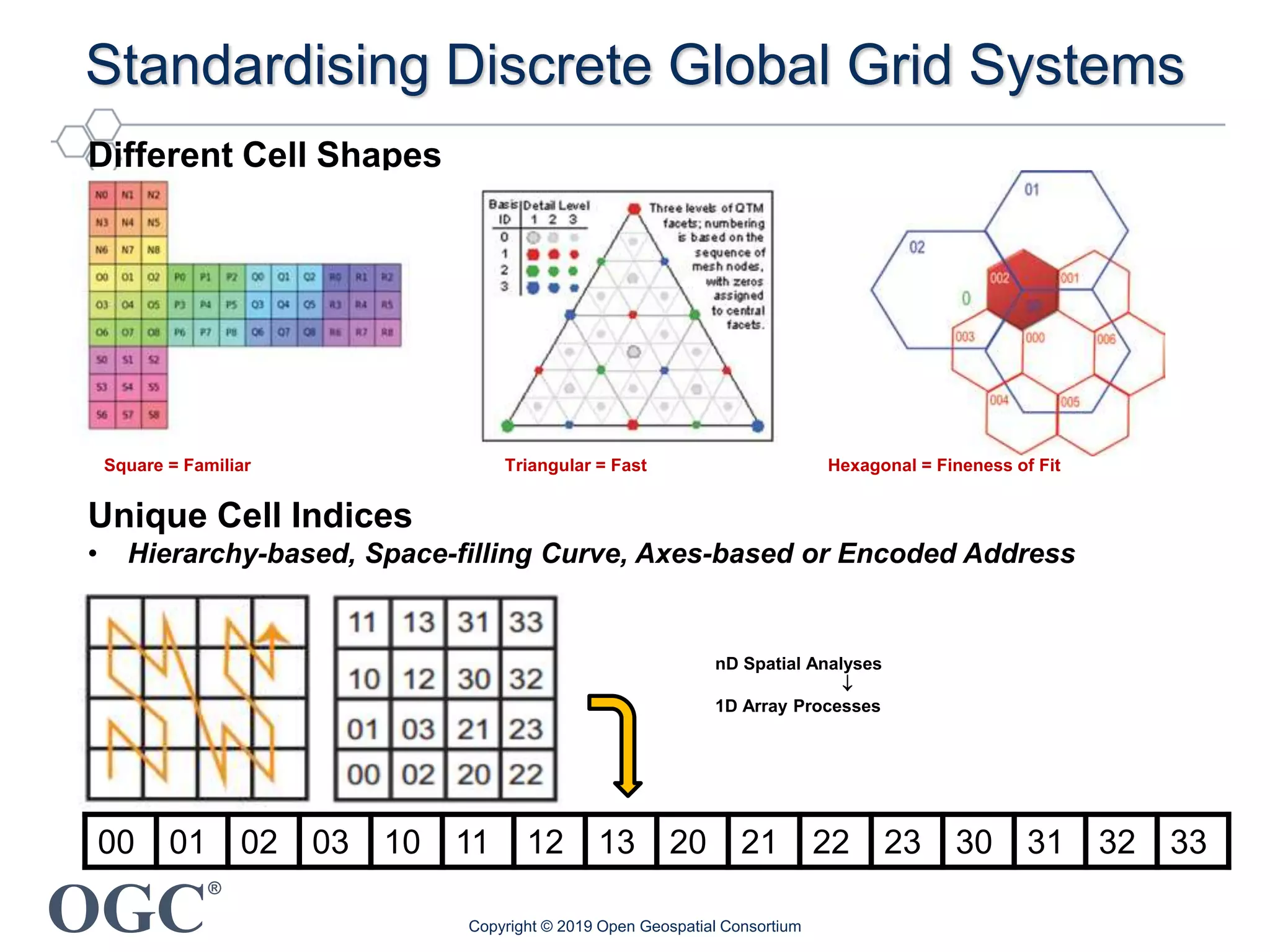
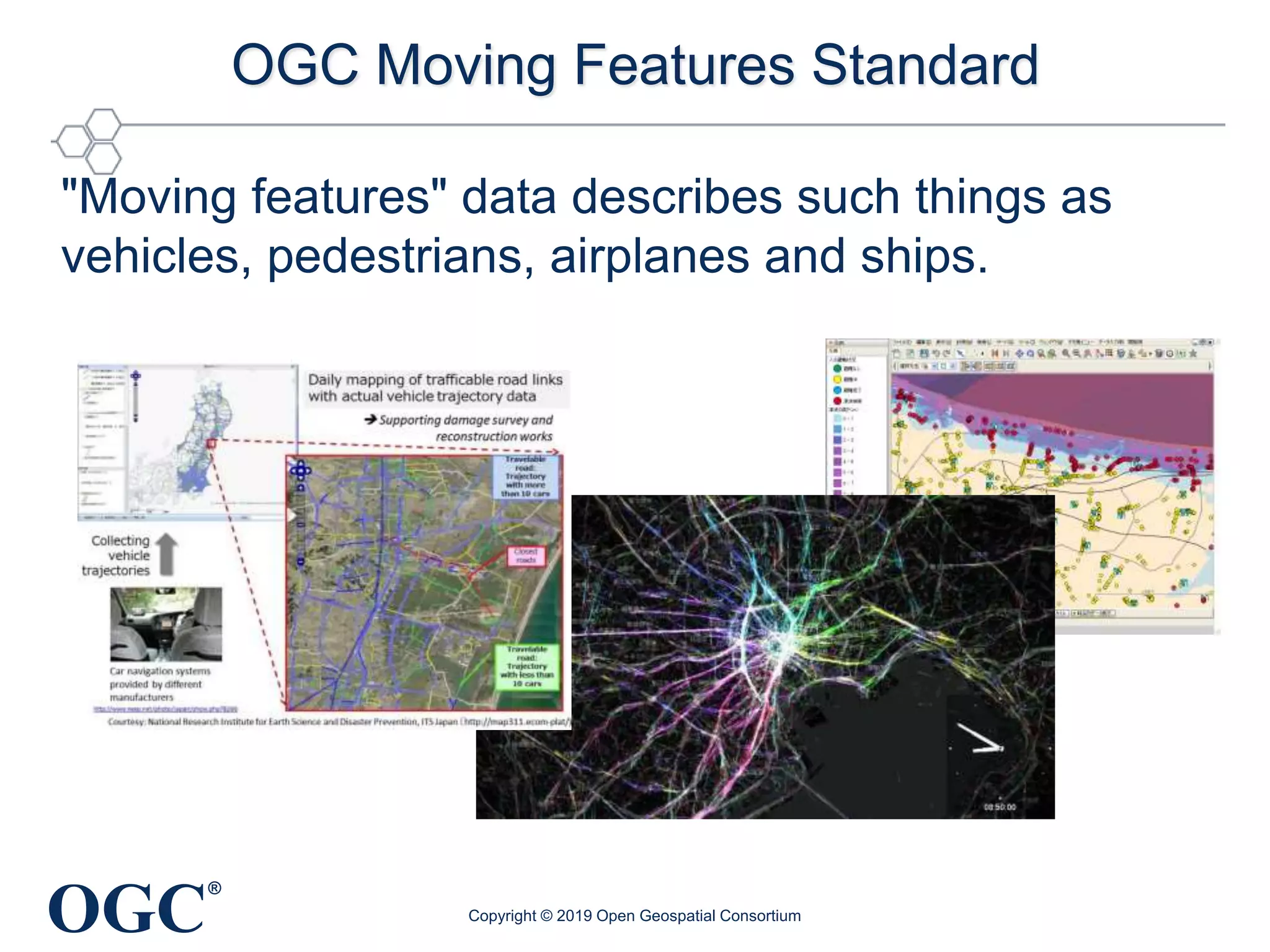
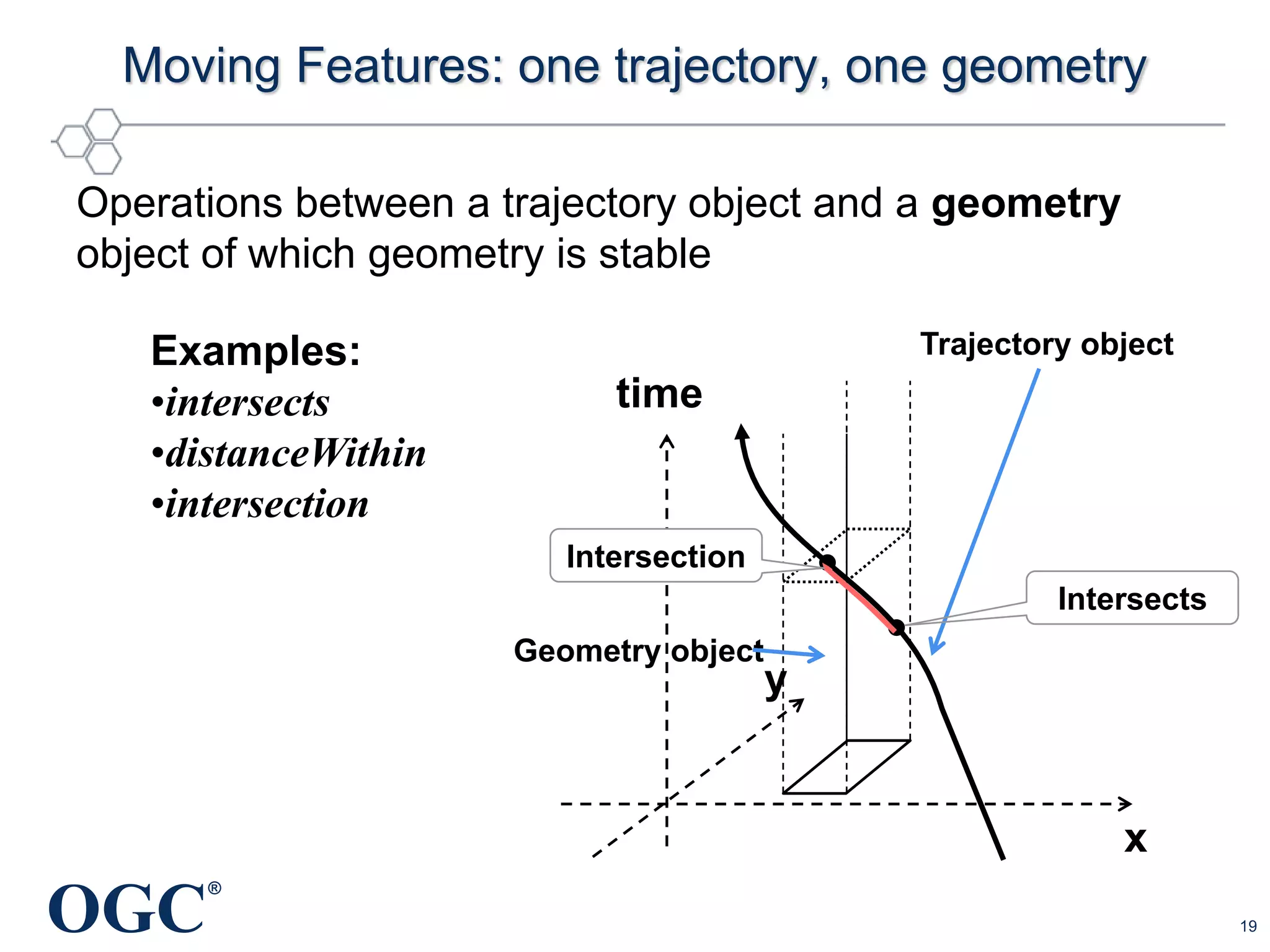
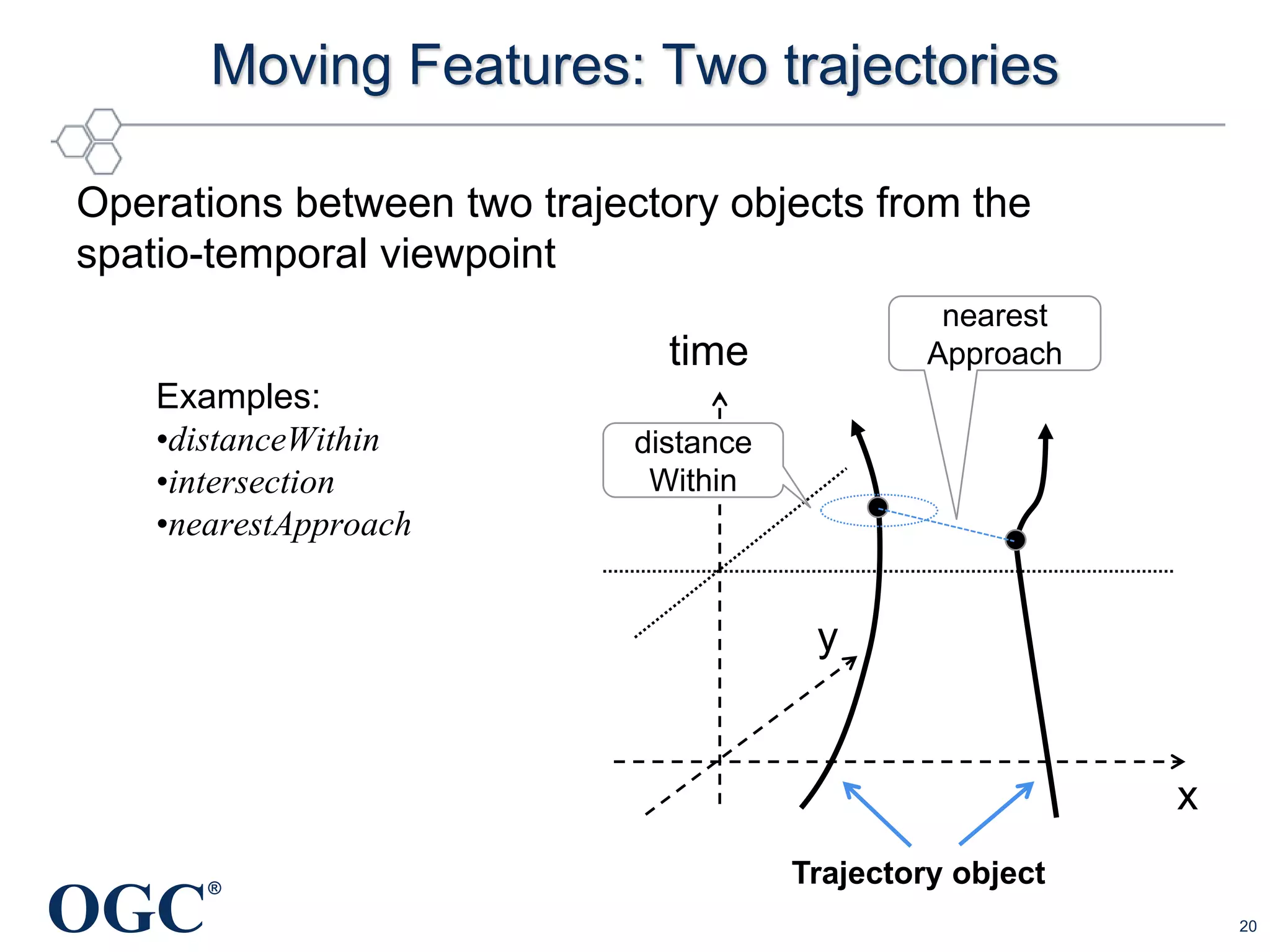
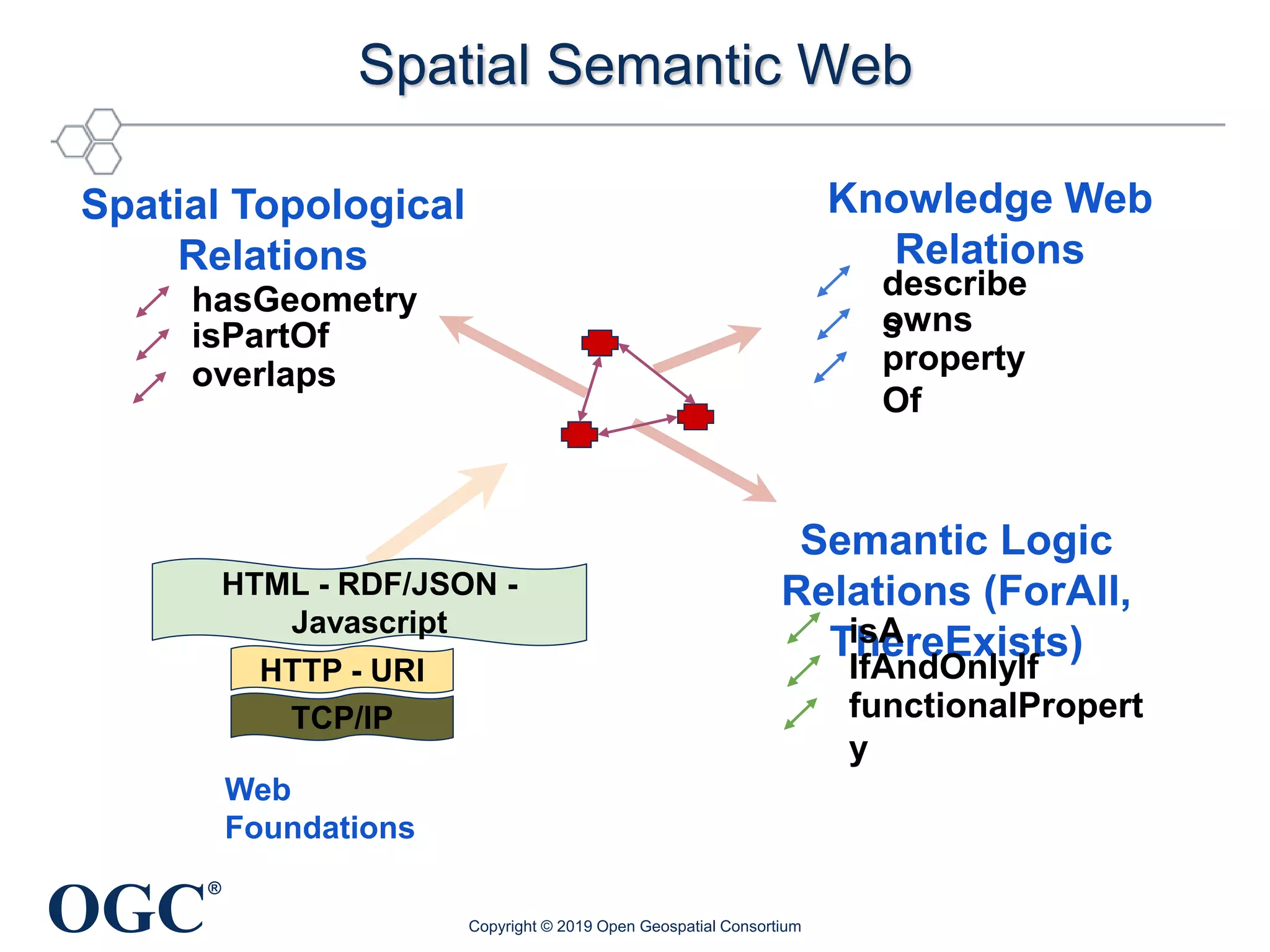
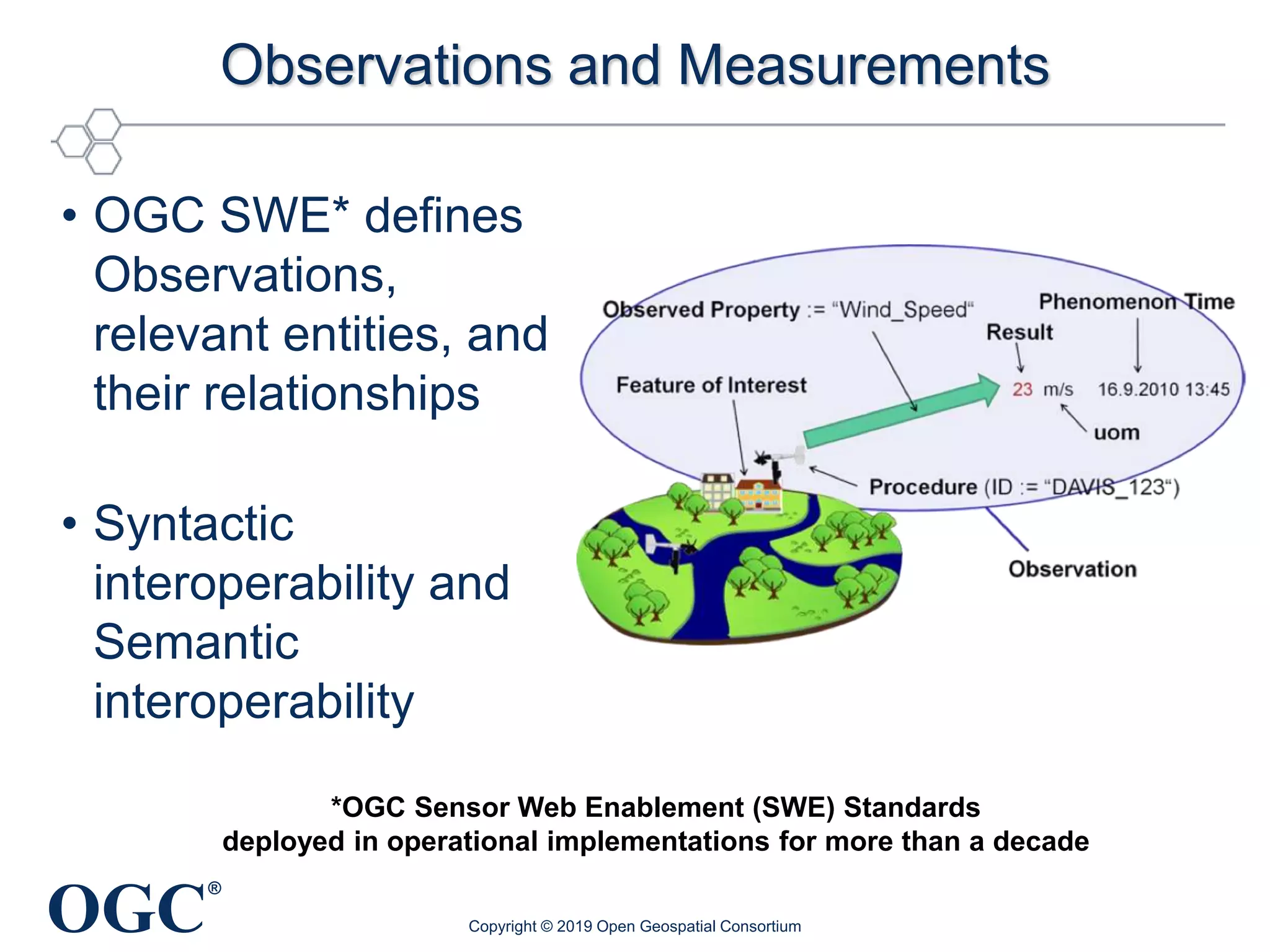
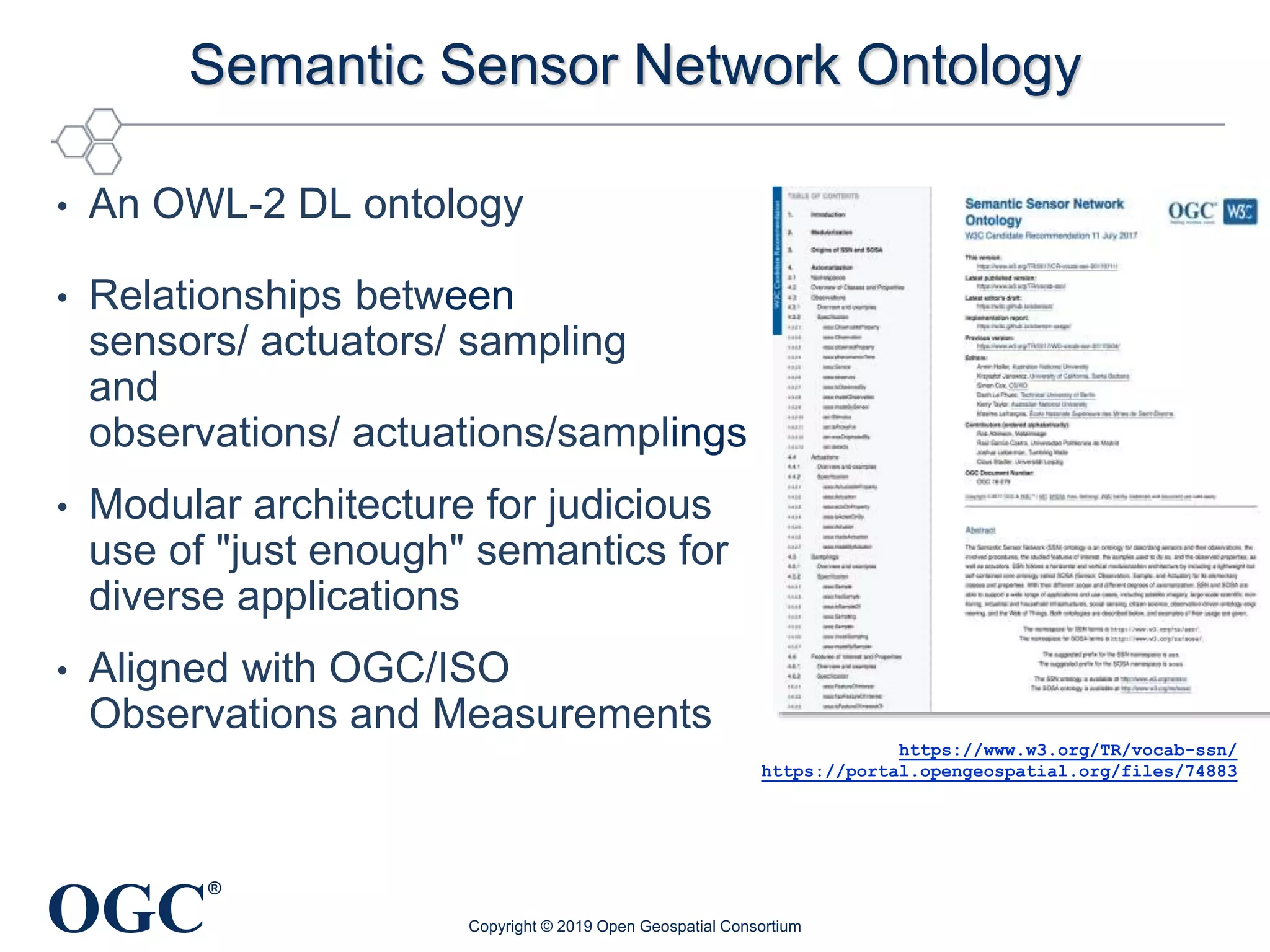
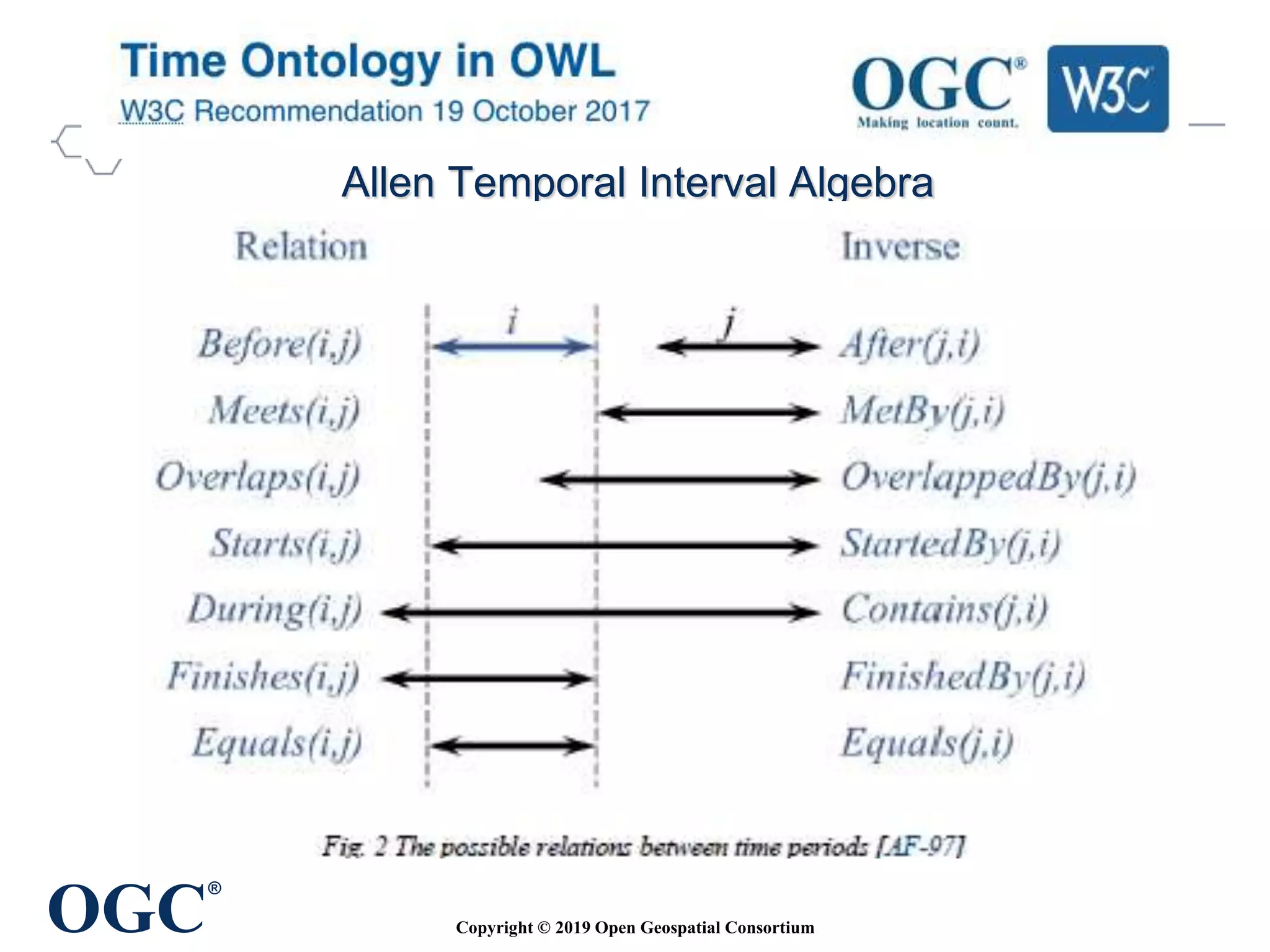
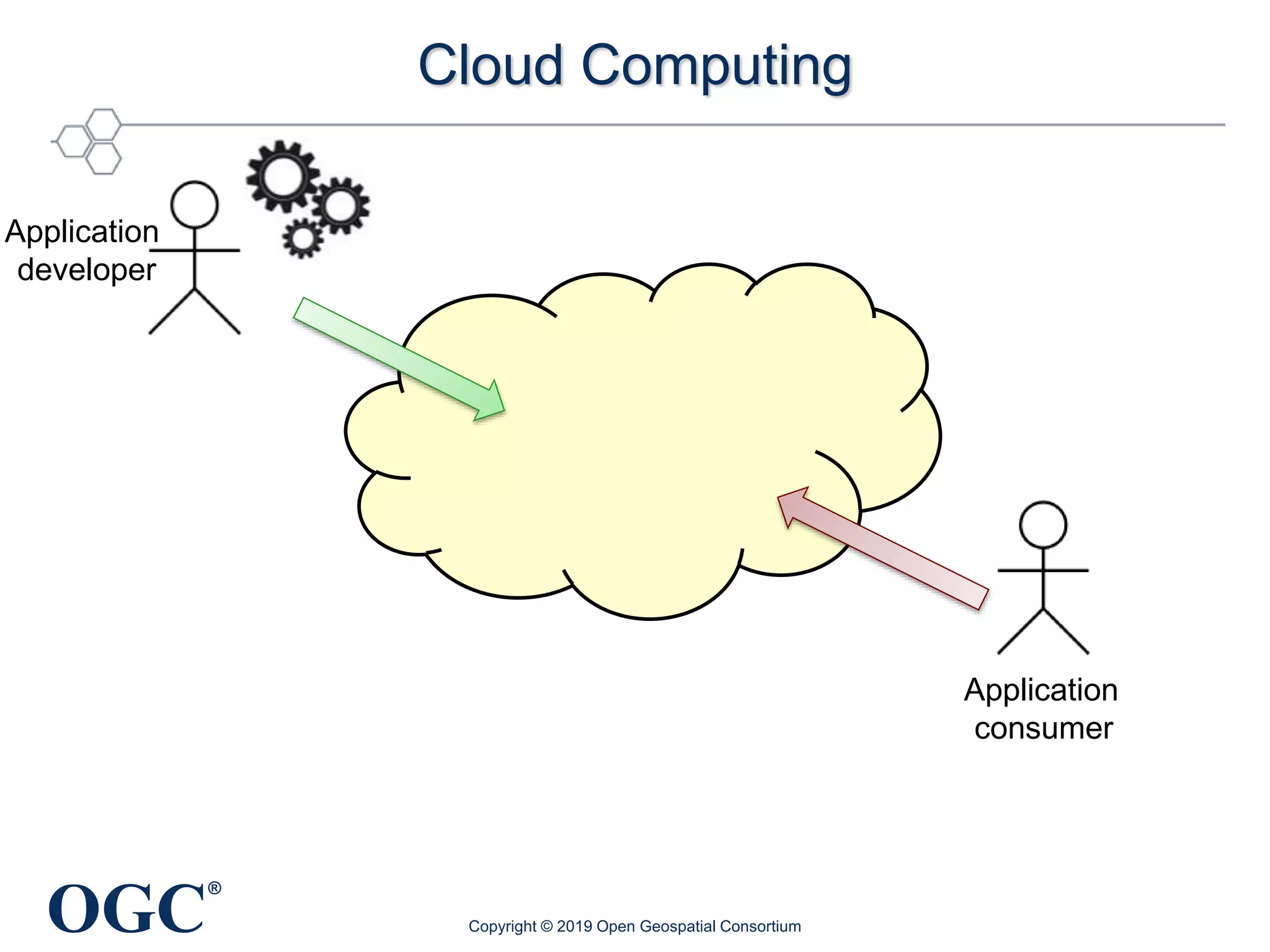
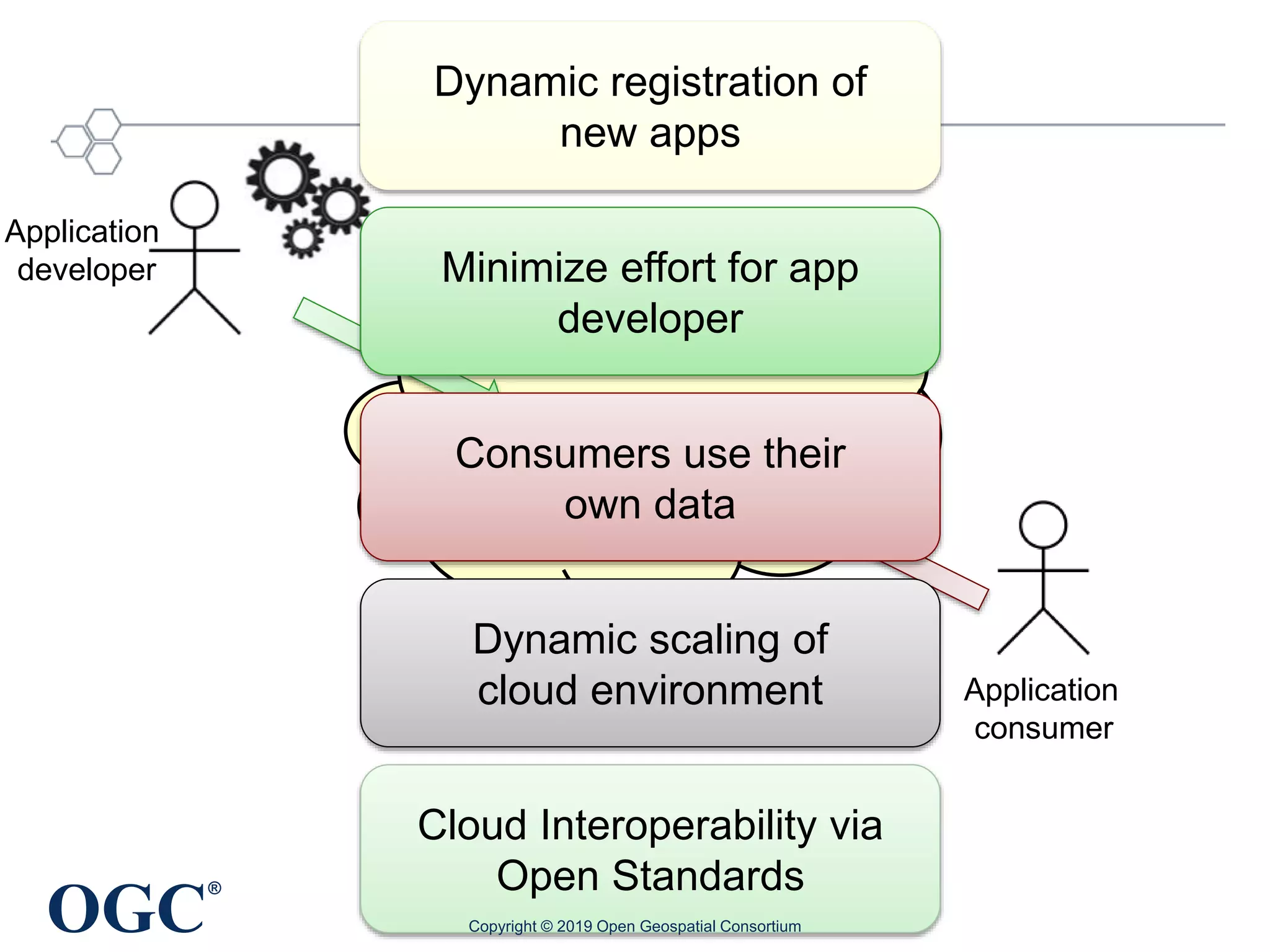
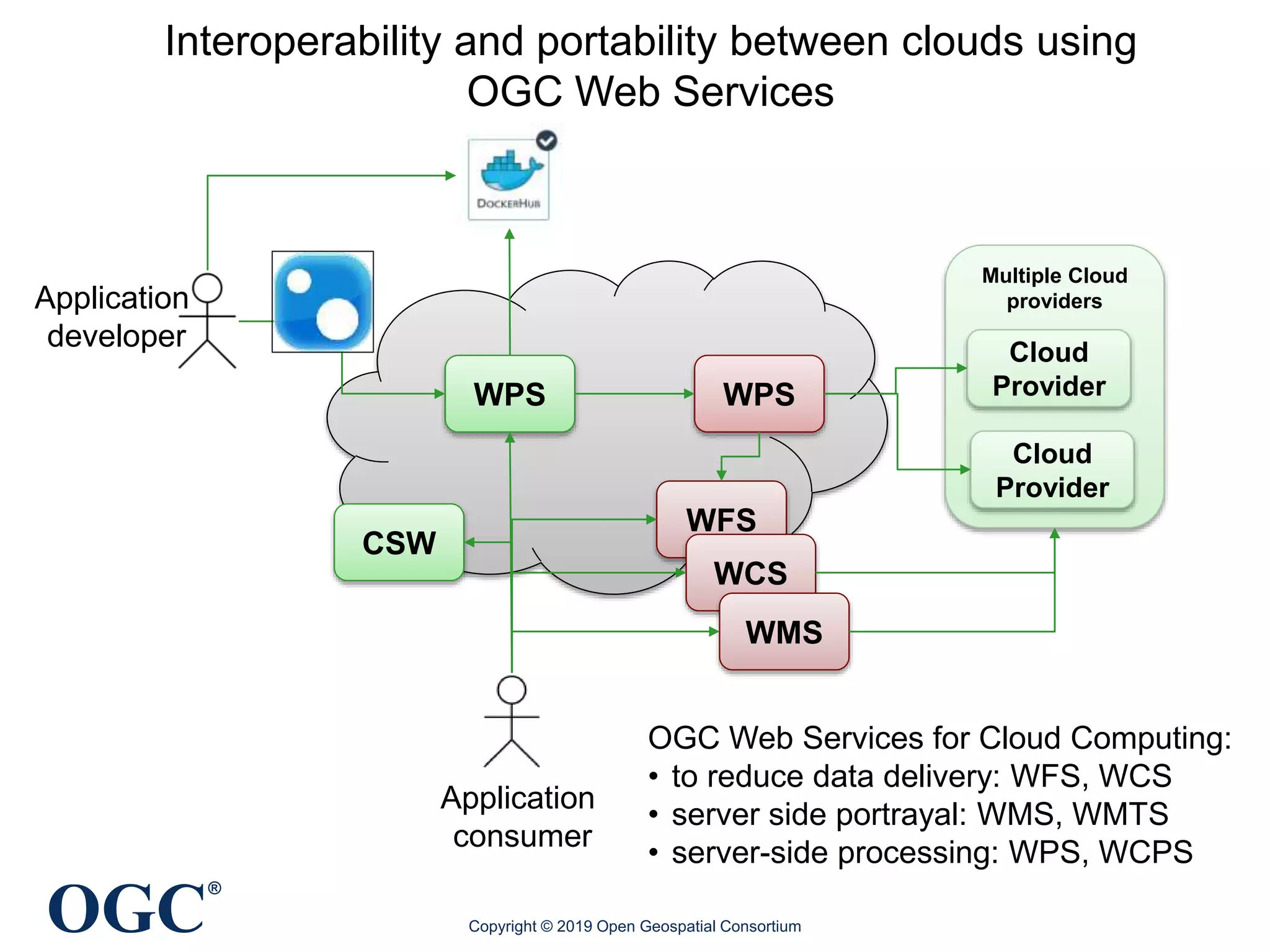
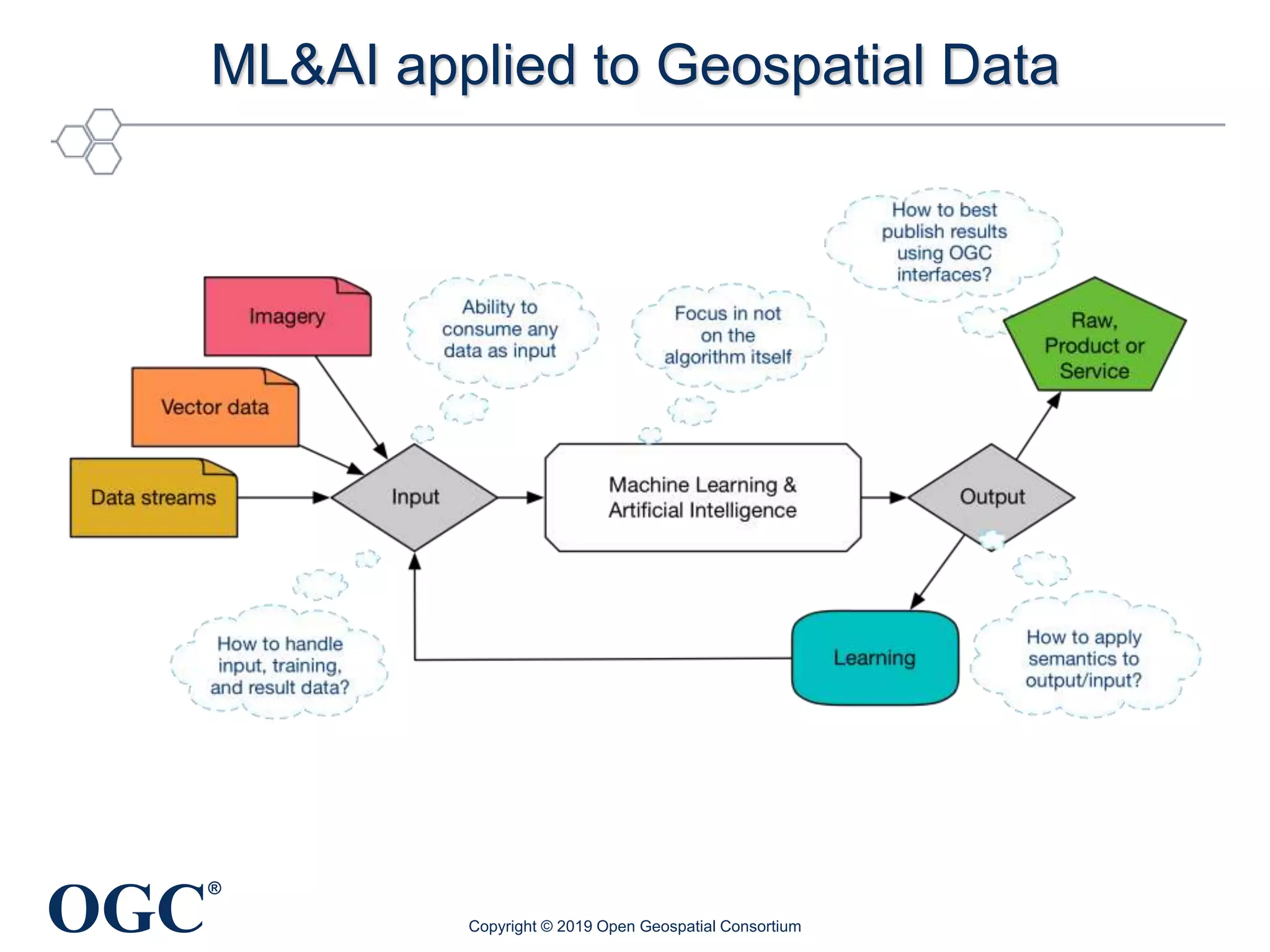
The document discusses the evolution and current state of geospatial data science, emphasizing the mission of the Open Geospatial Consortium to promote geospatial interoperability through global standards. It highlights the shift towards data-driven scientific methods supported by advanced computing, cloud services, and machine learning technologies, which enable efficient analysis and application of vast amounts of geospatial data. Additionally, the document outlines various applications of geospatial data in fields such as urban planning, disaster management, and environmental monitoring.