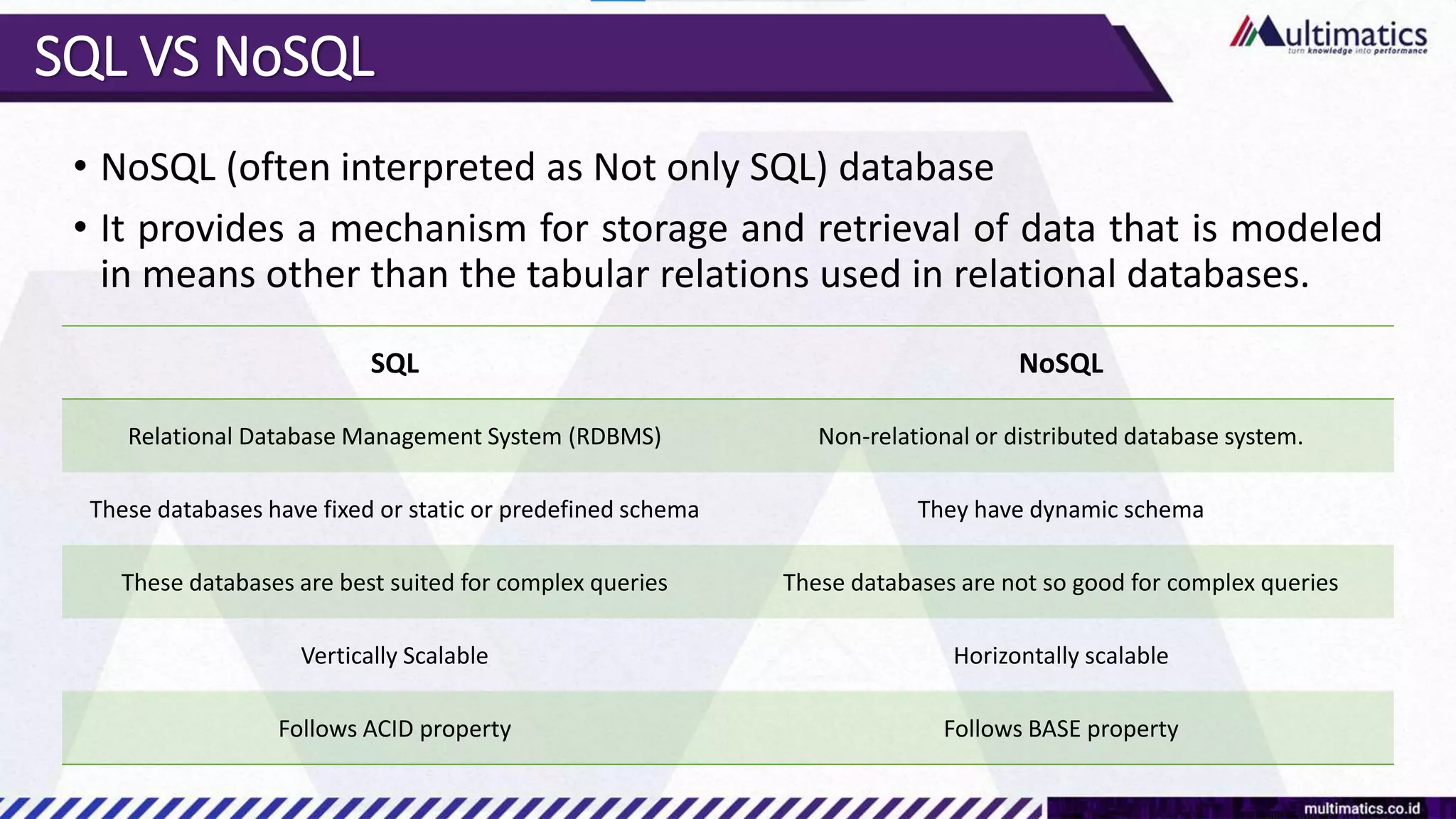
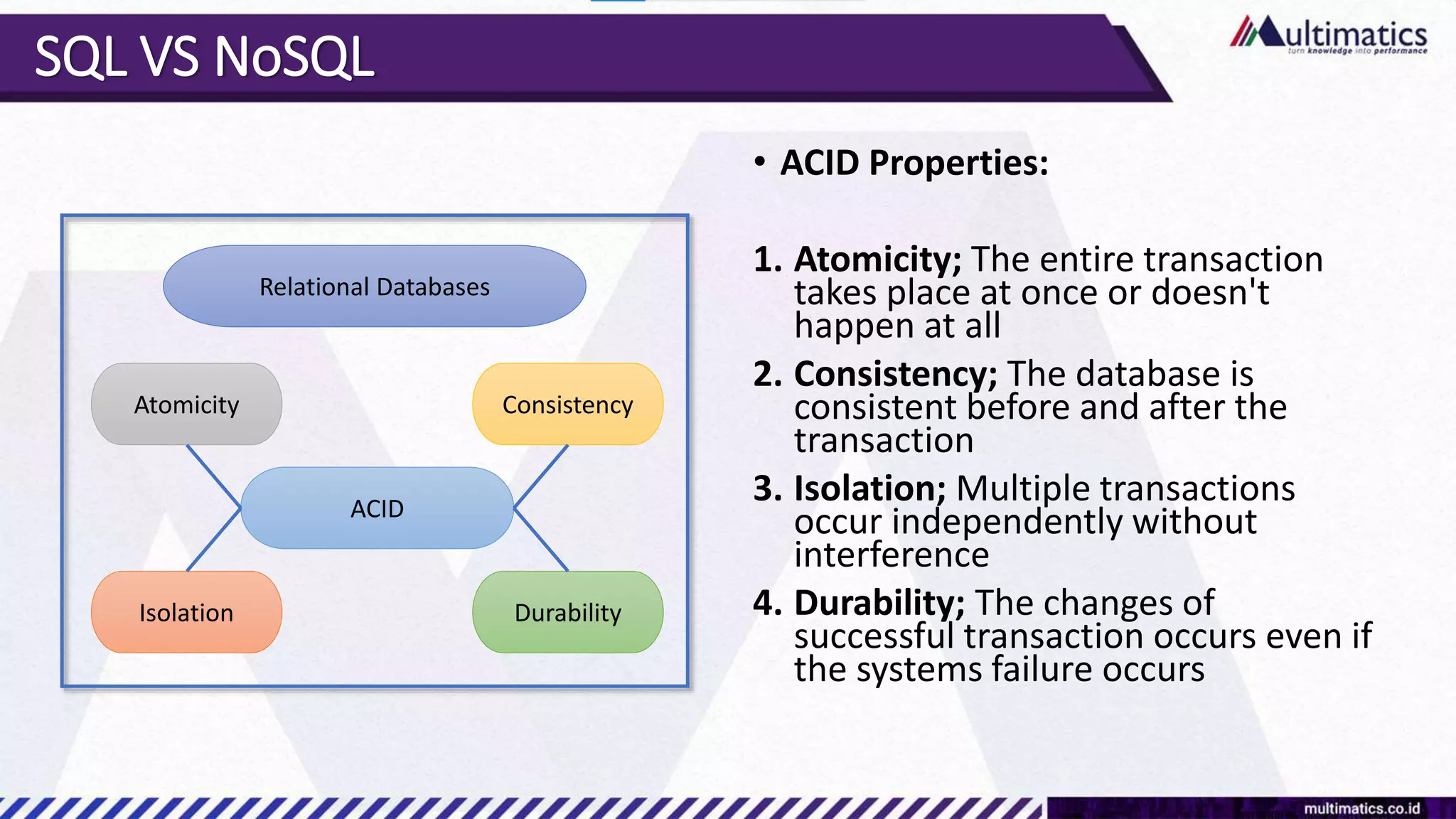
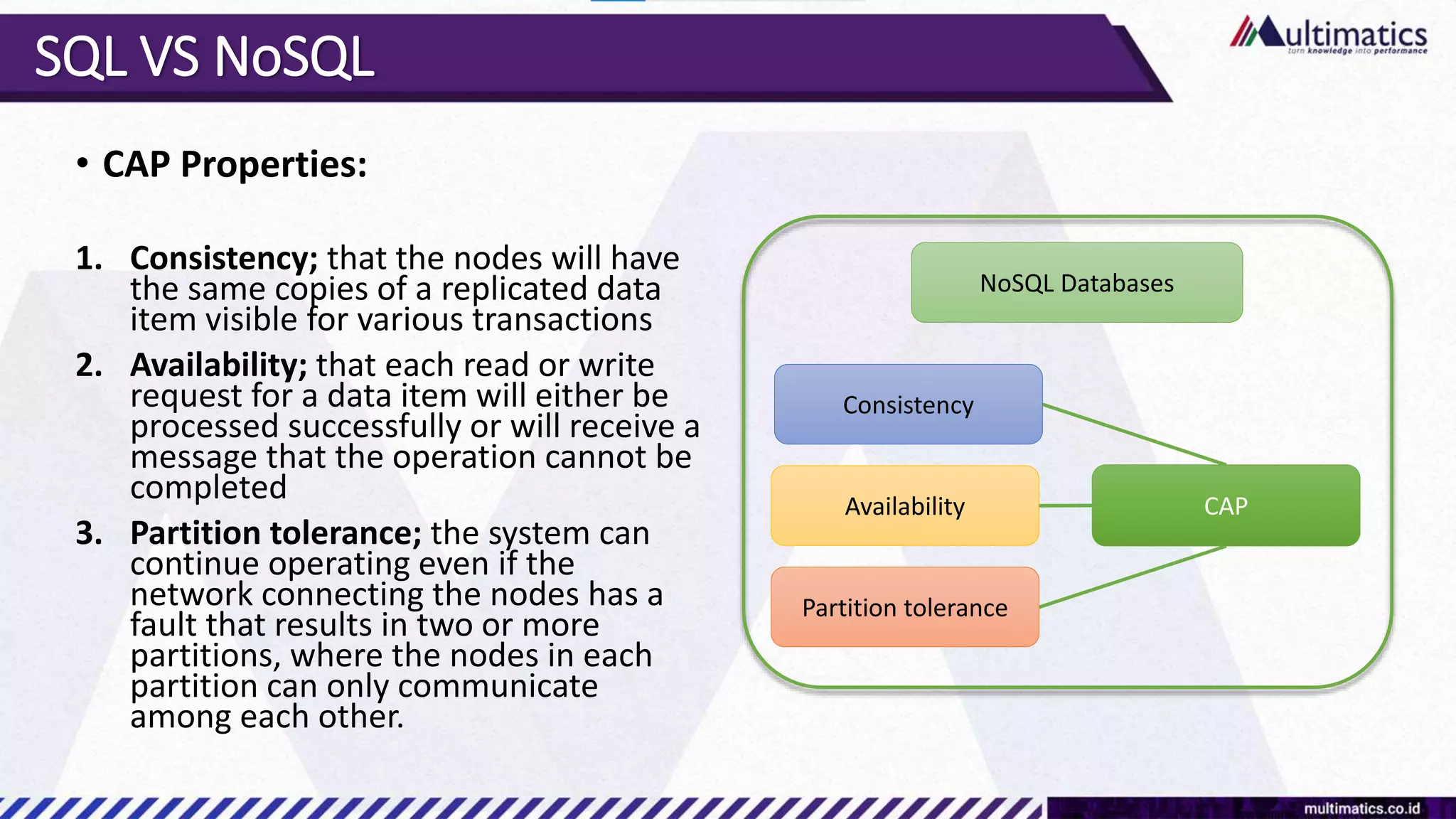
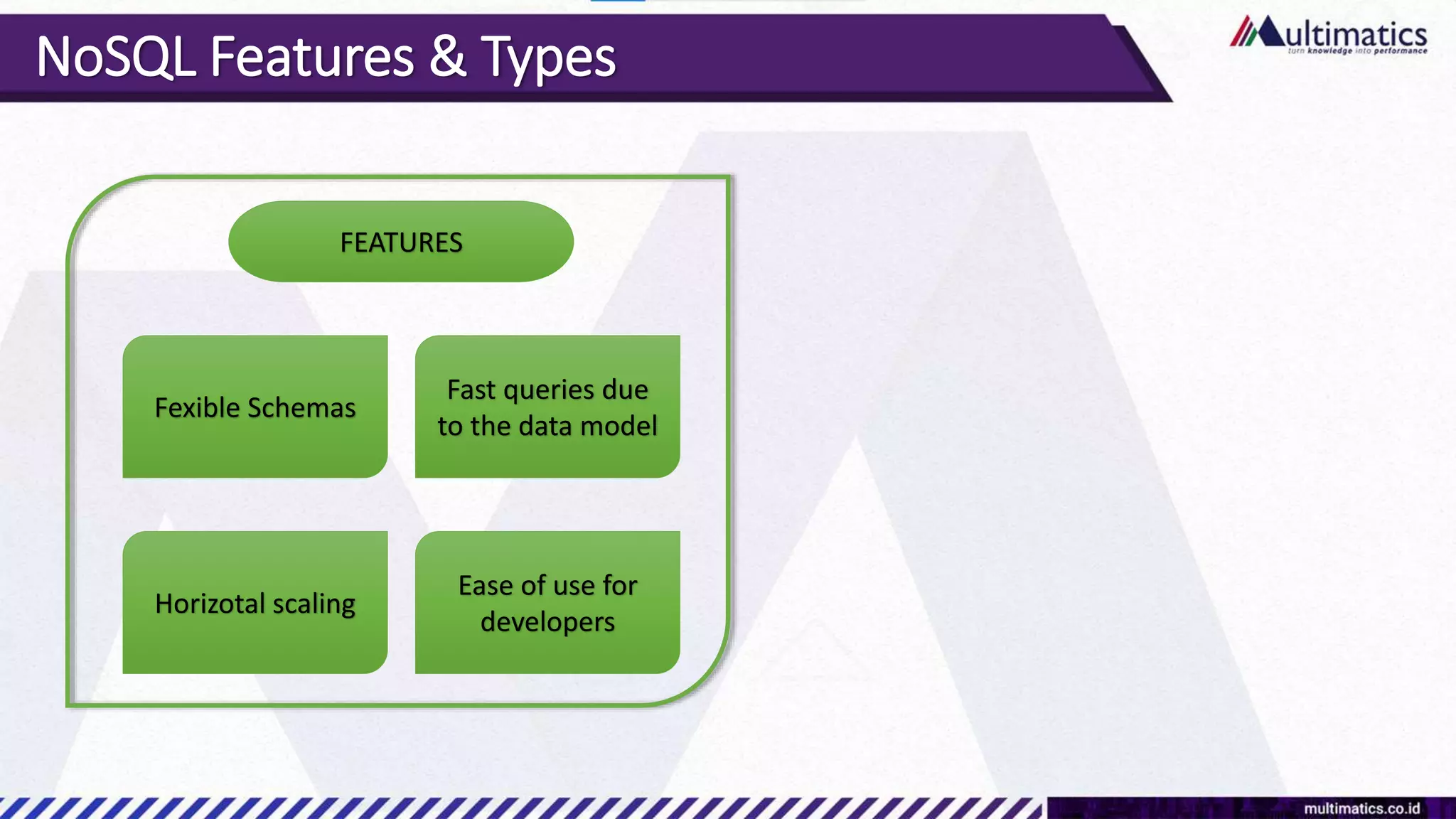
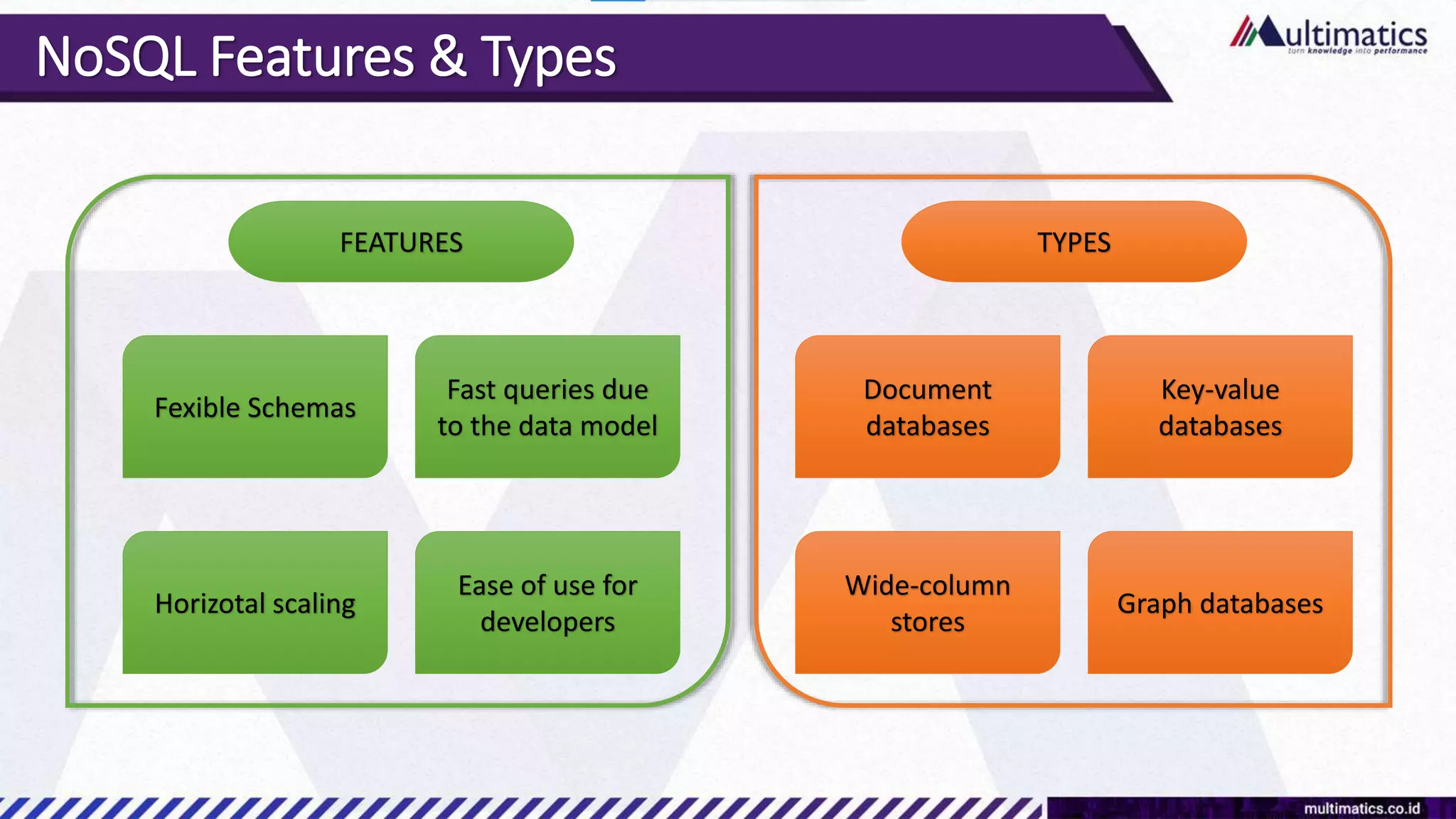
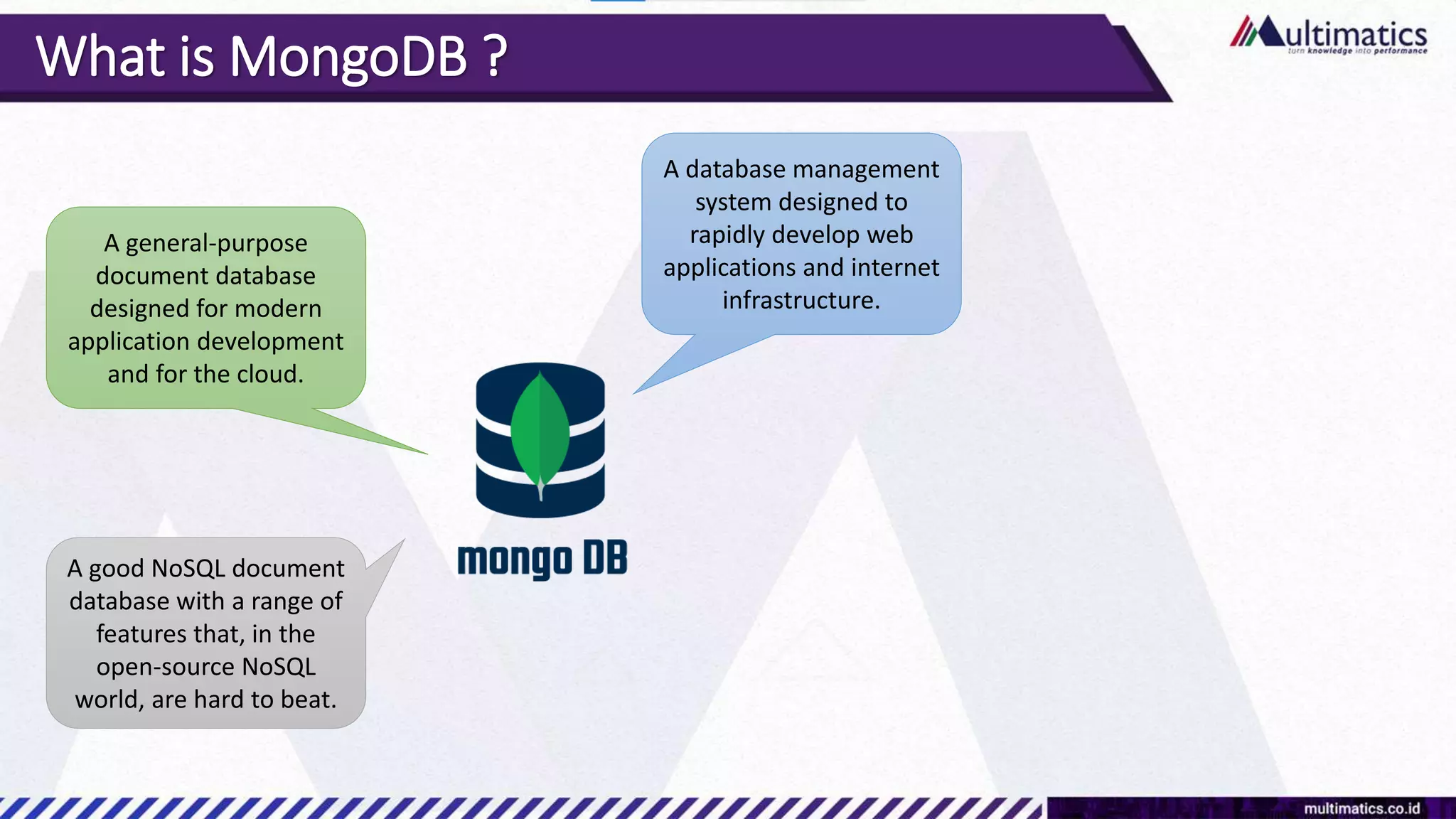
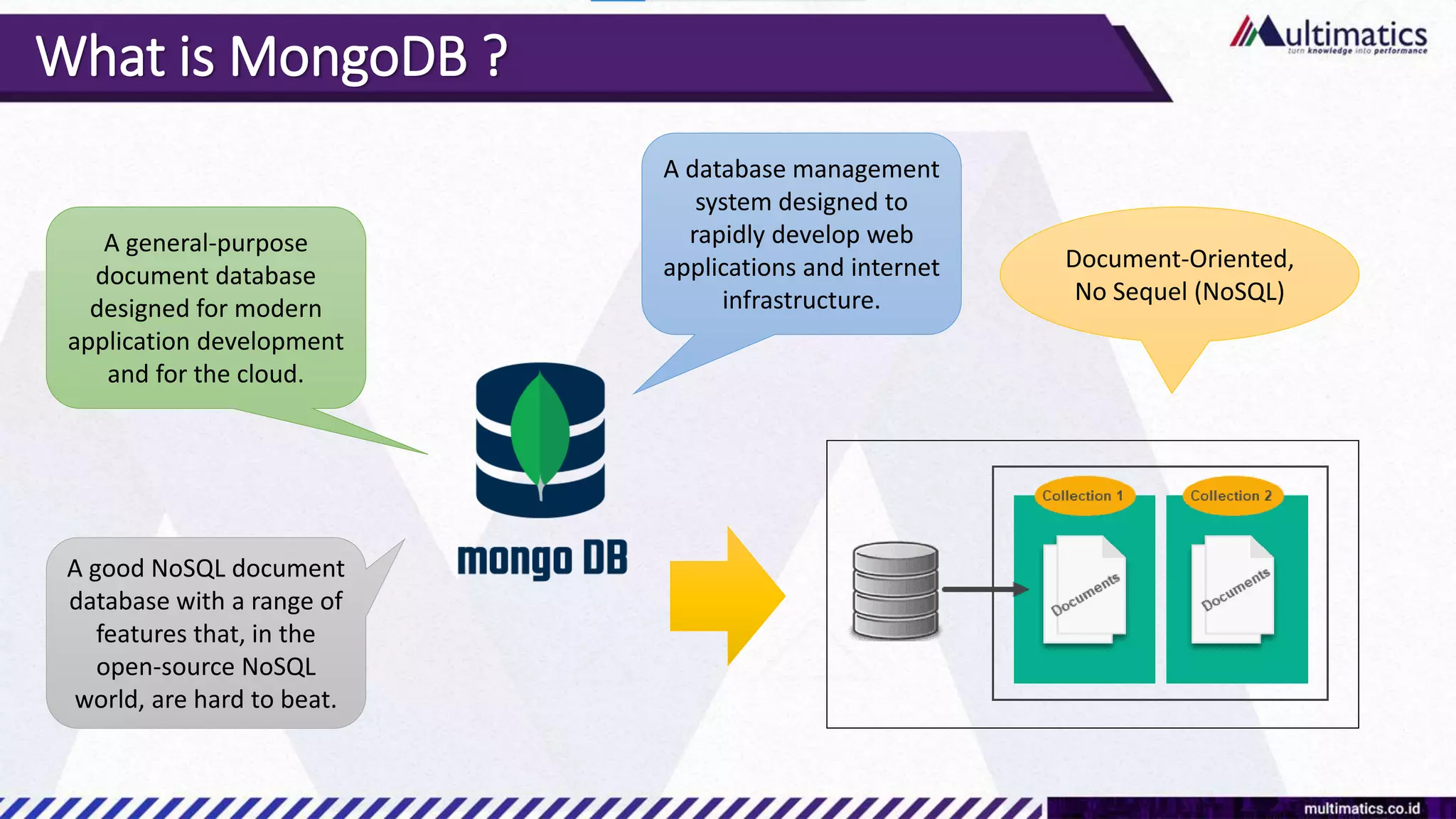
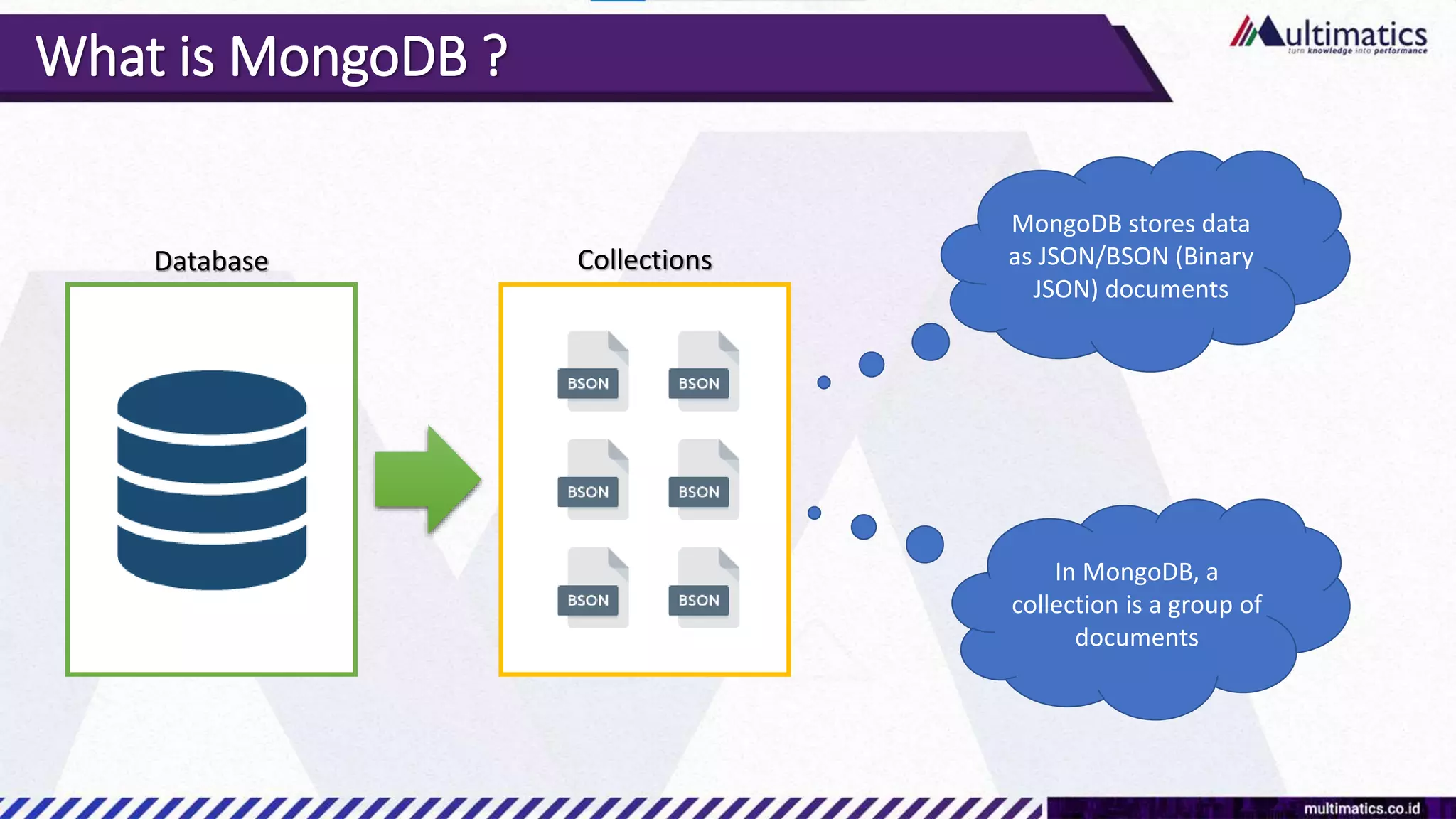
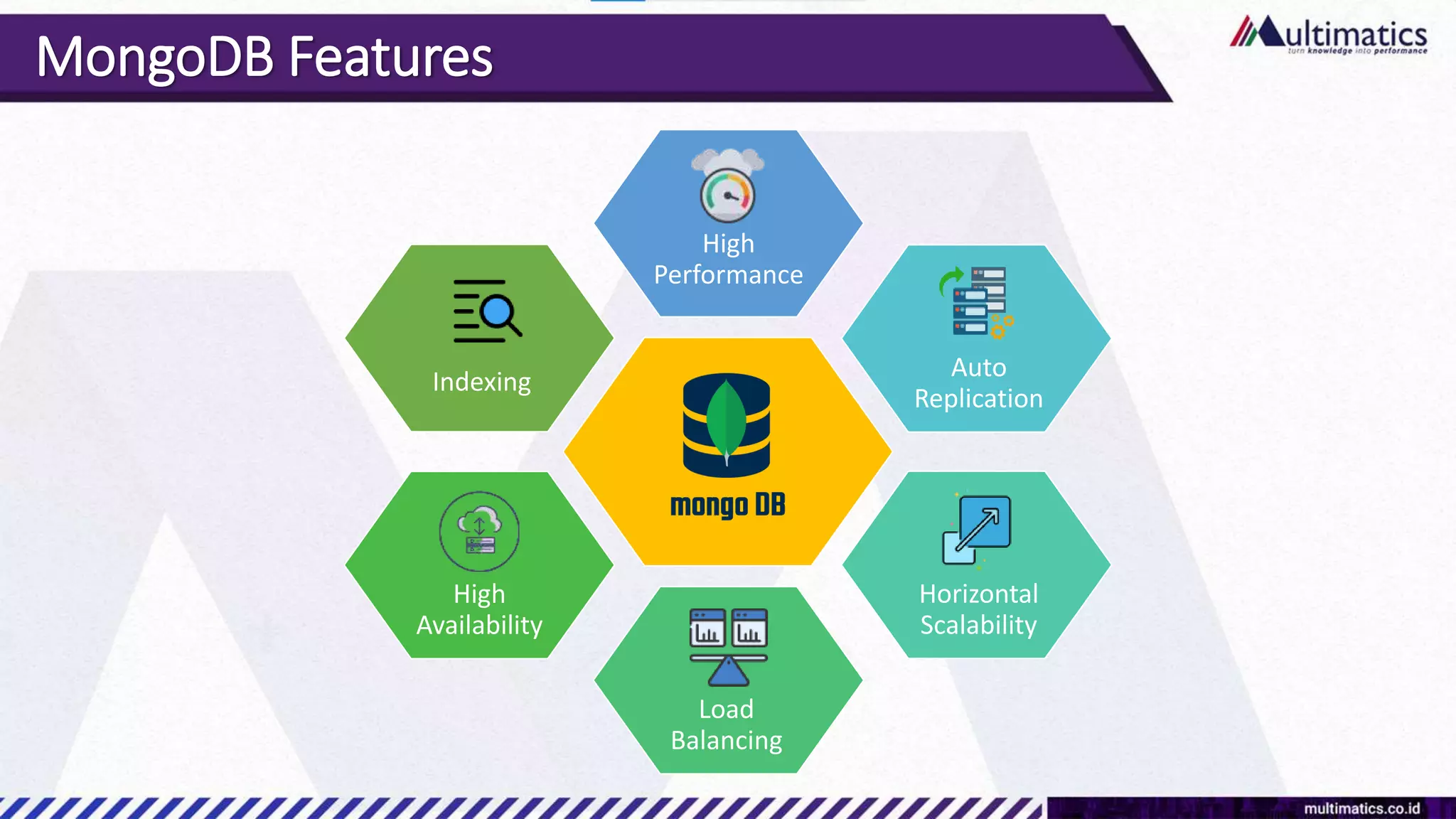
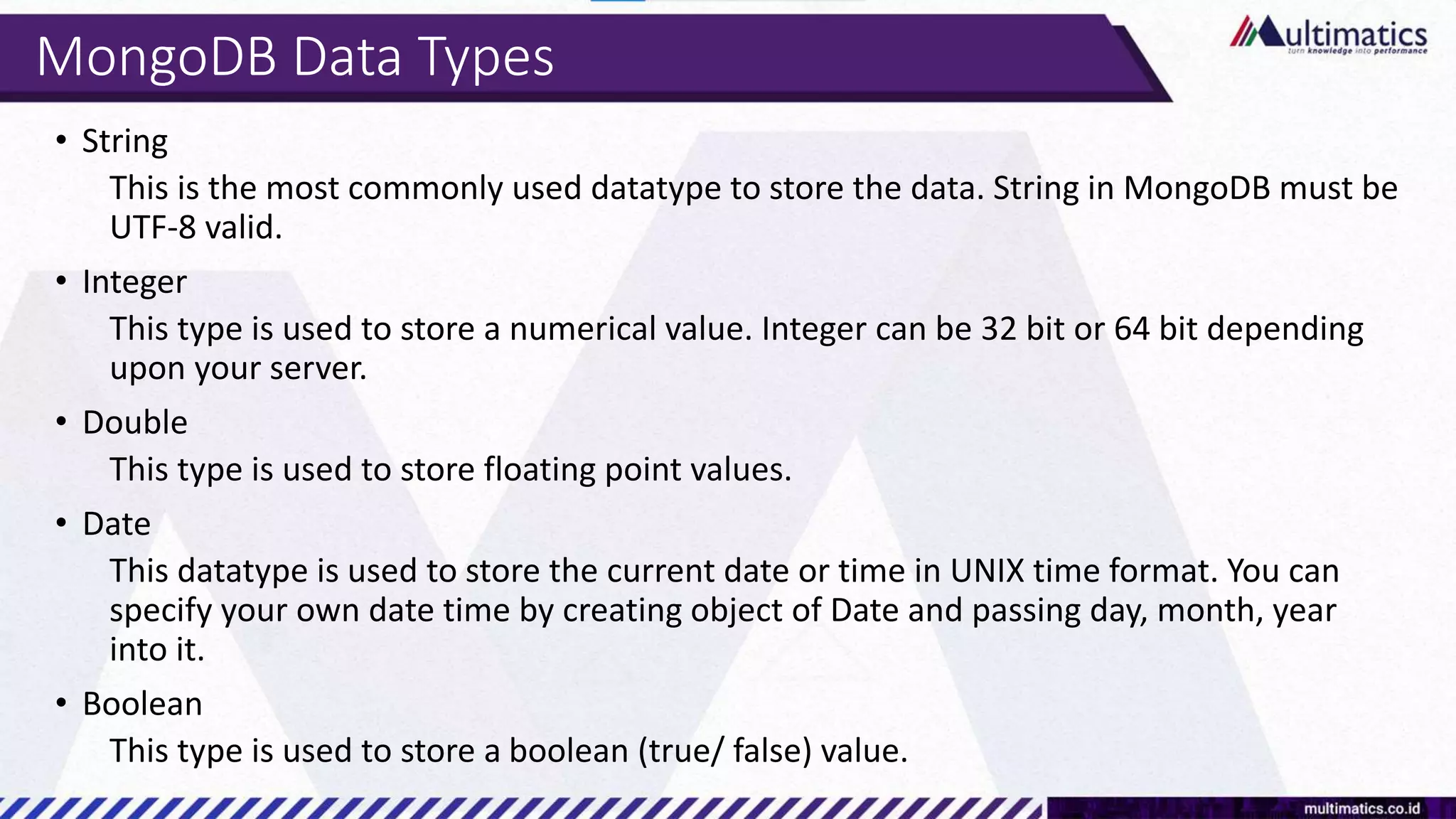
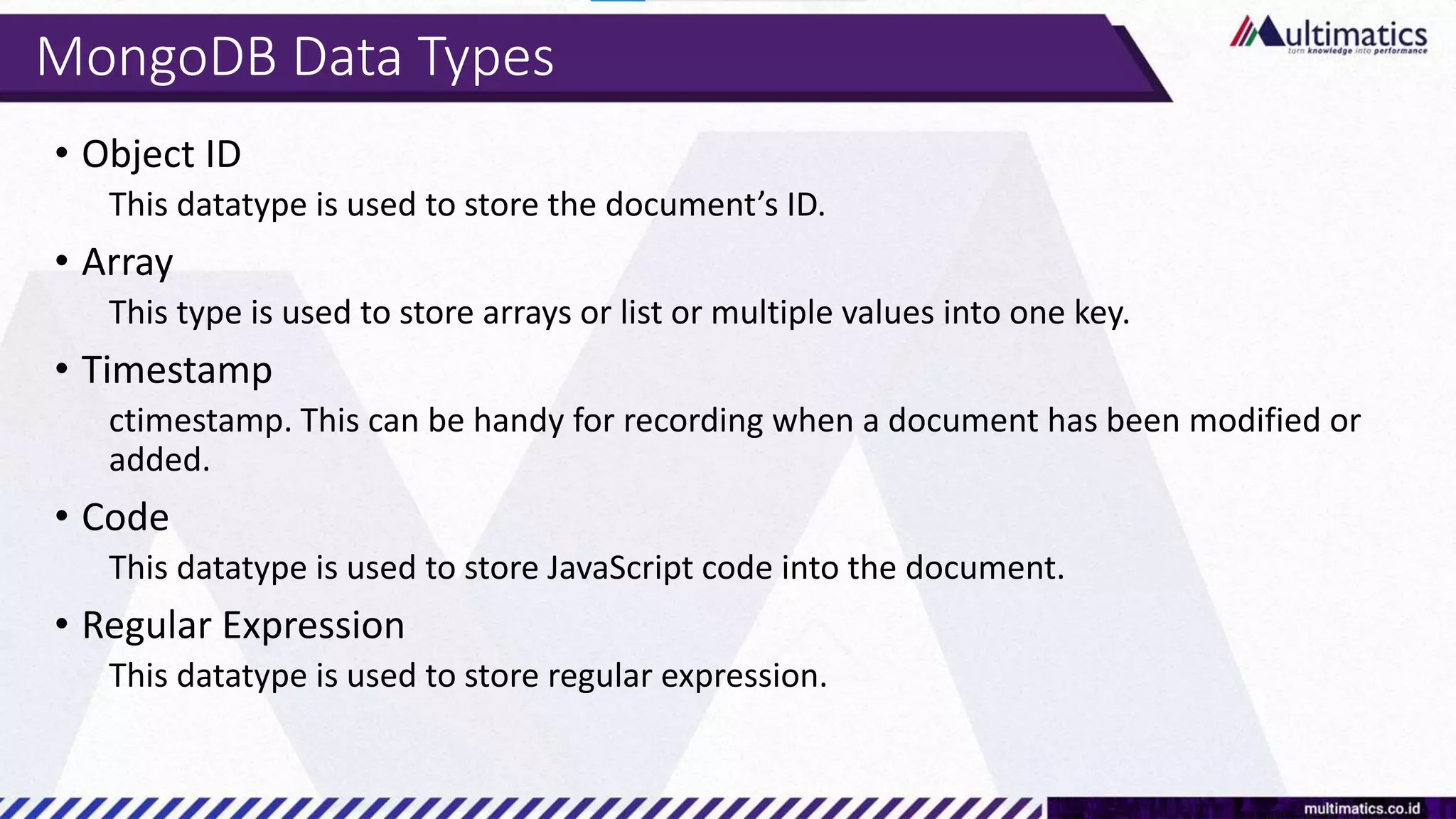
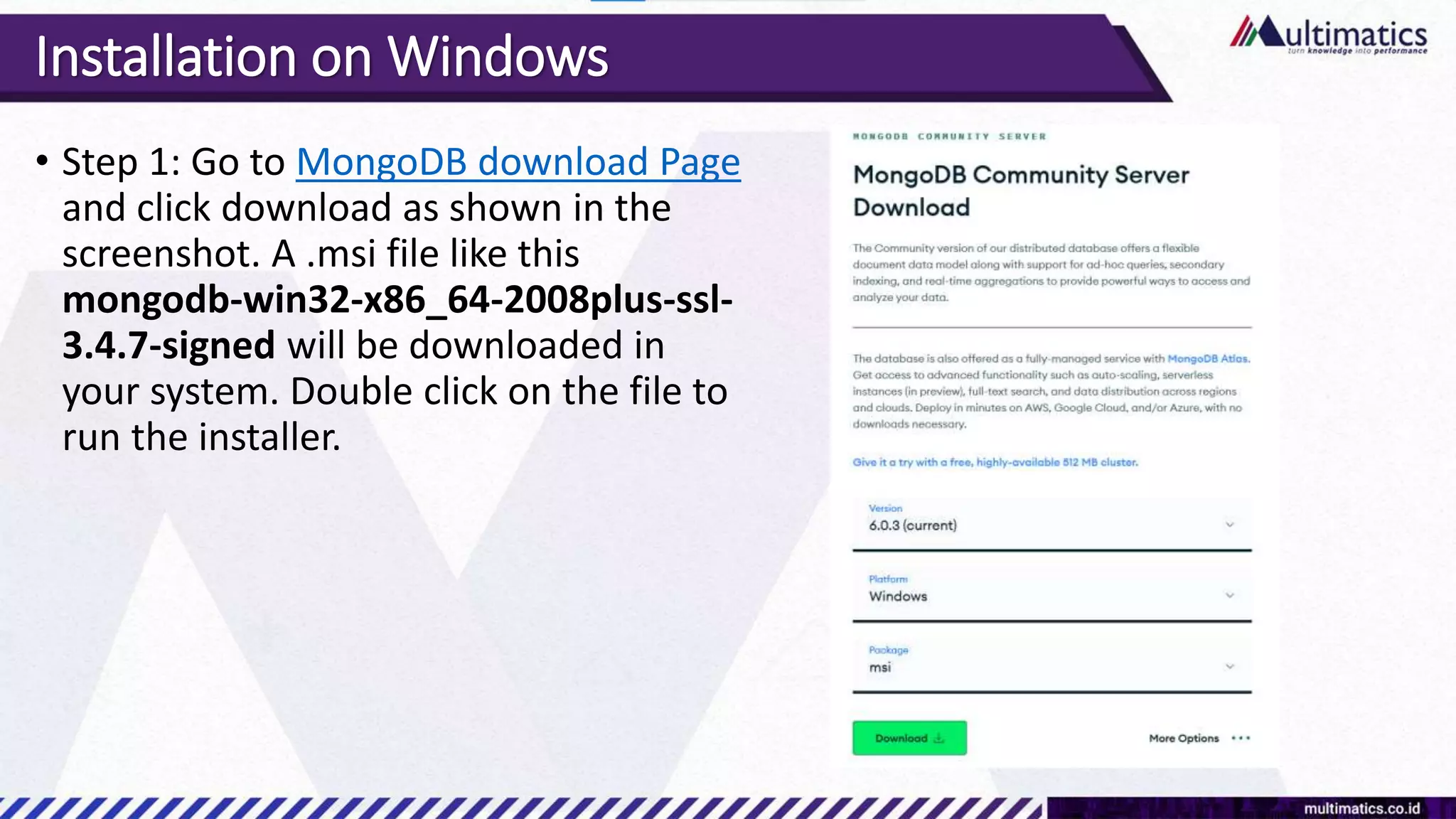
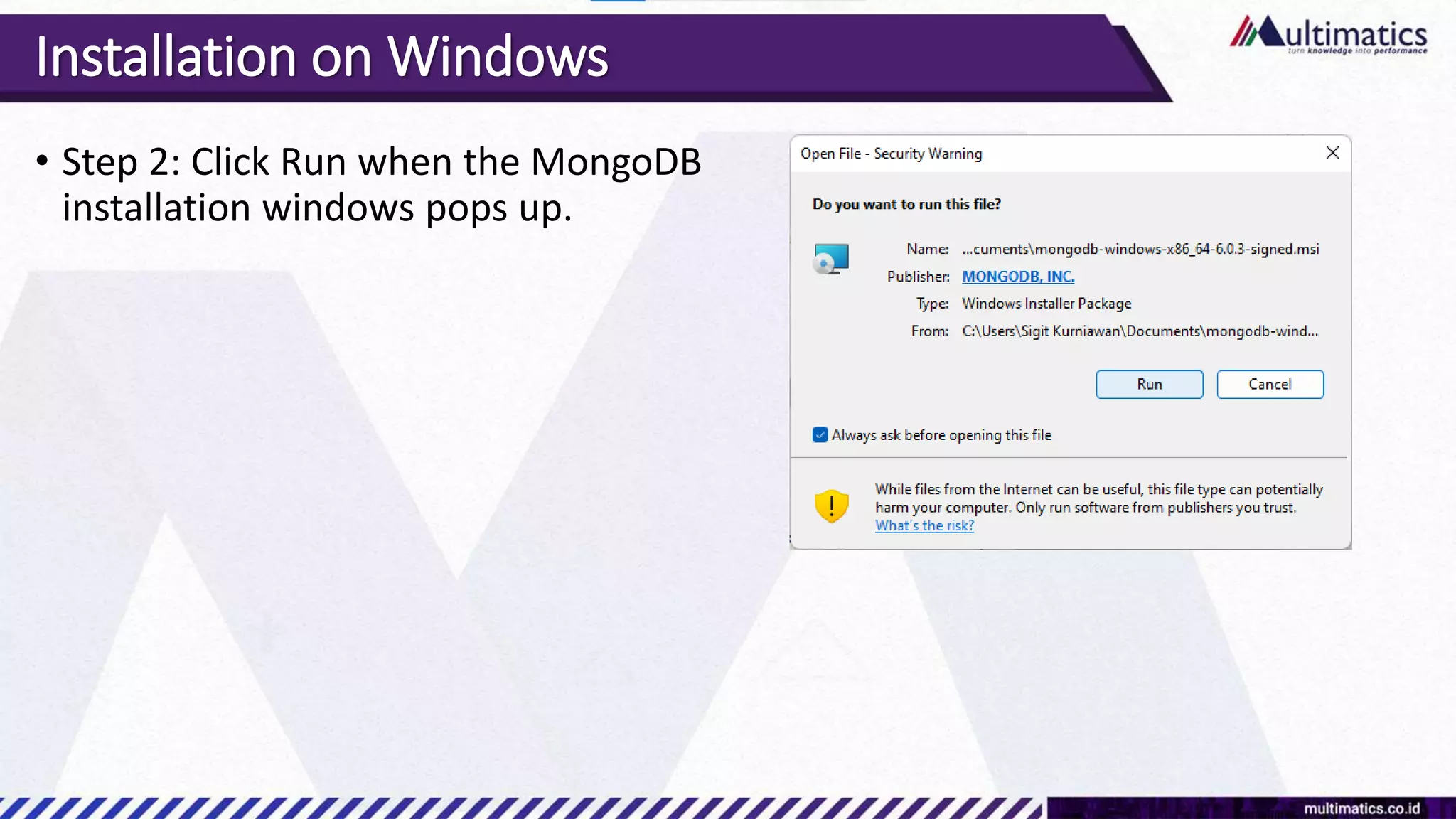
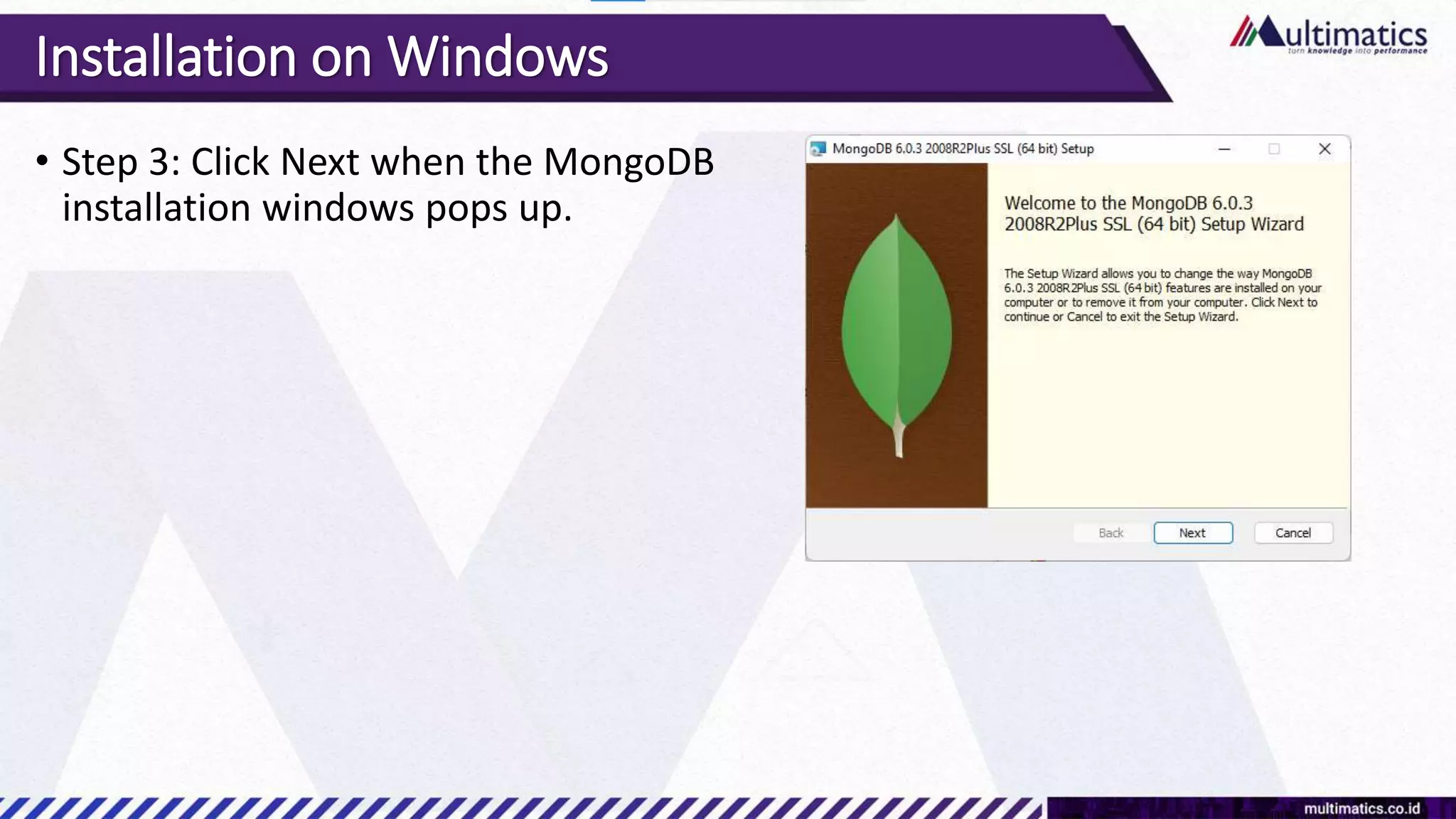
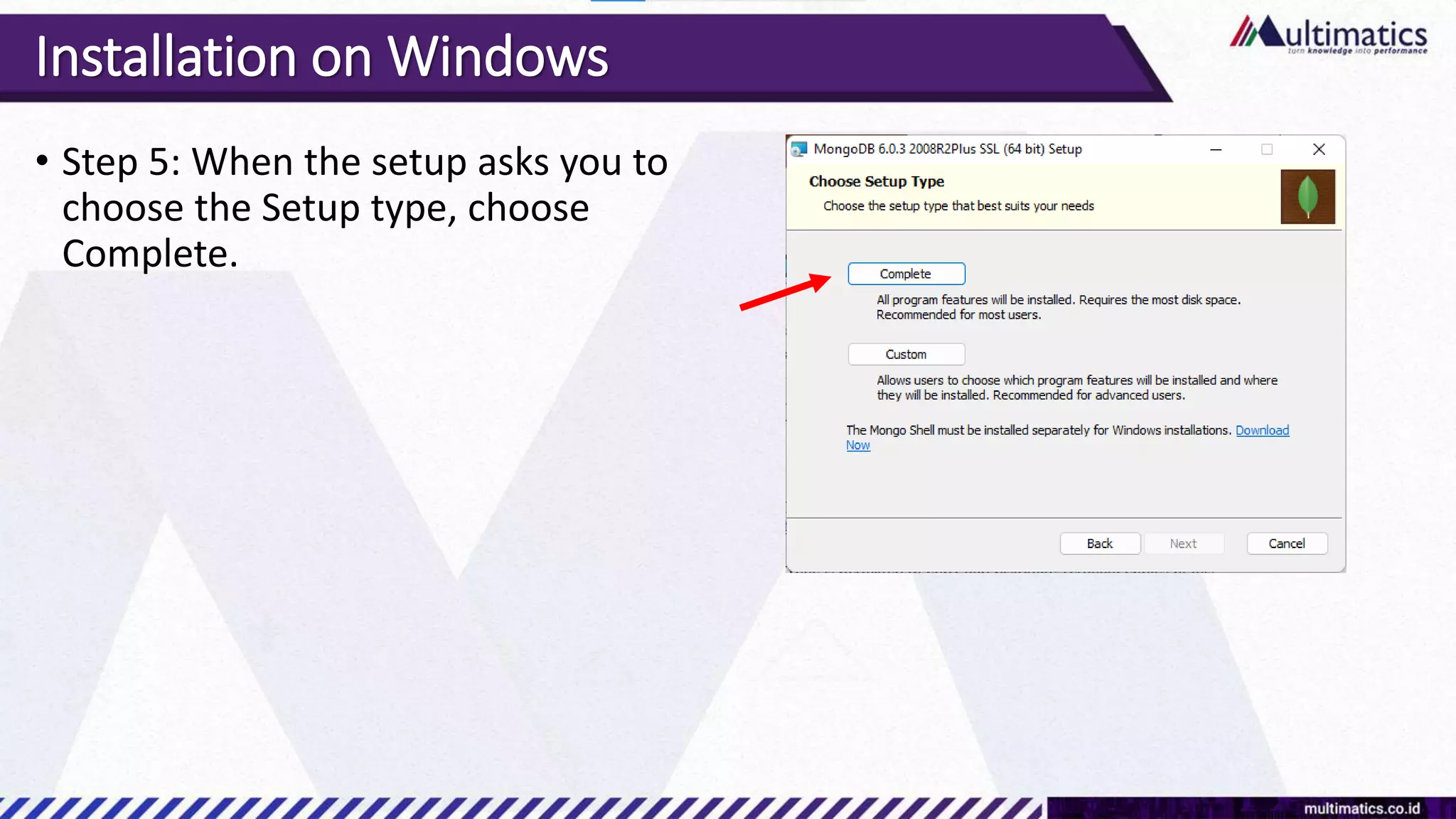
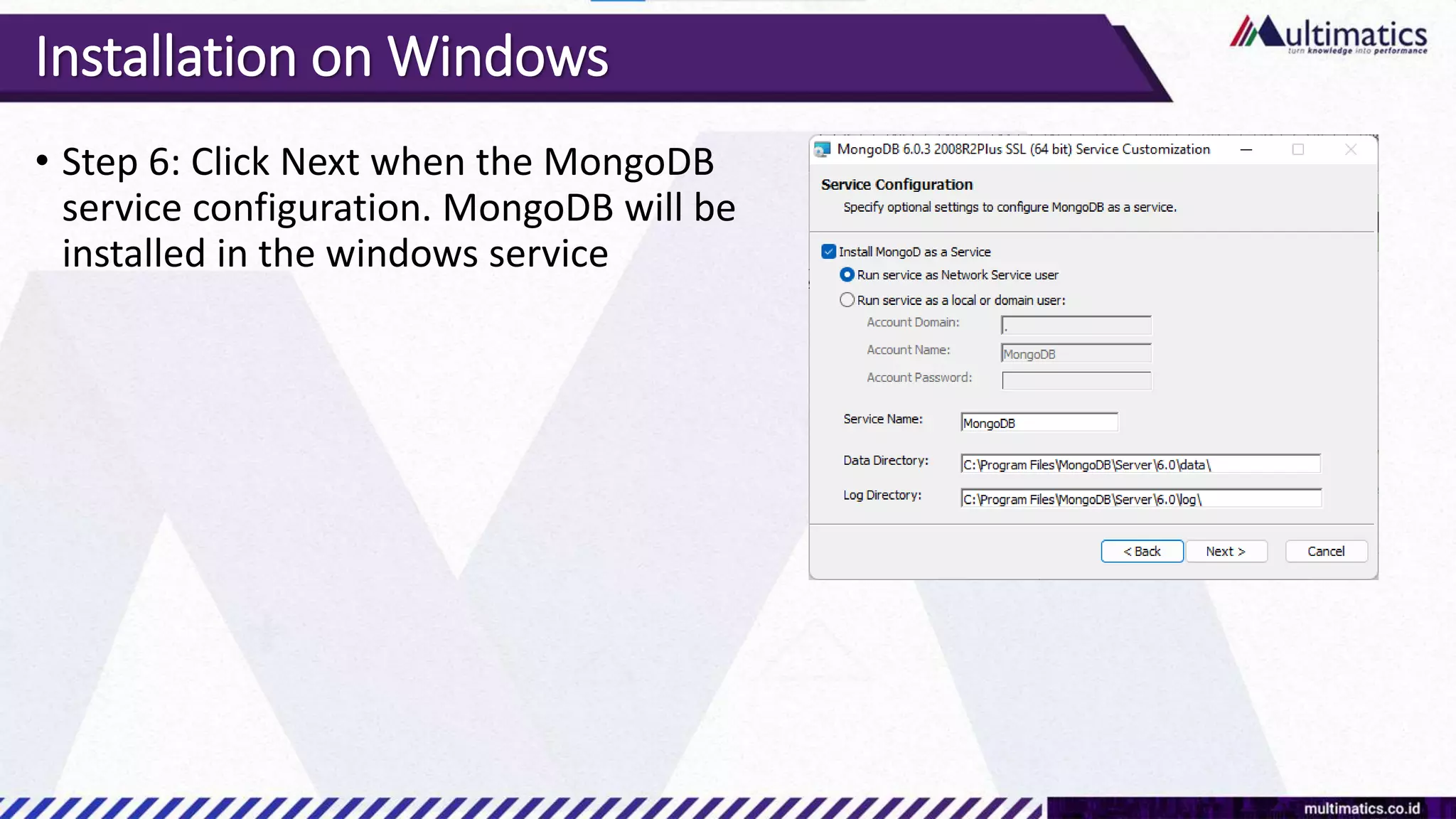
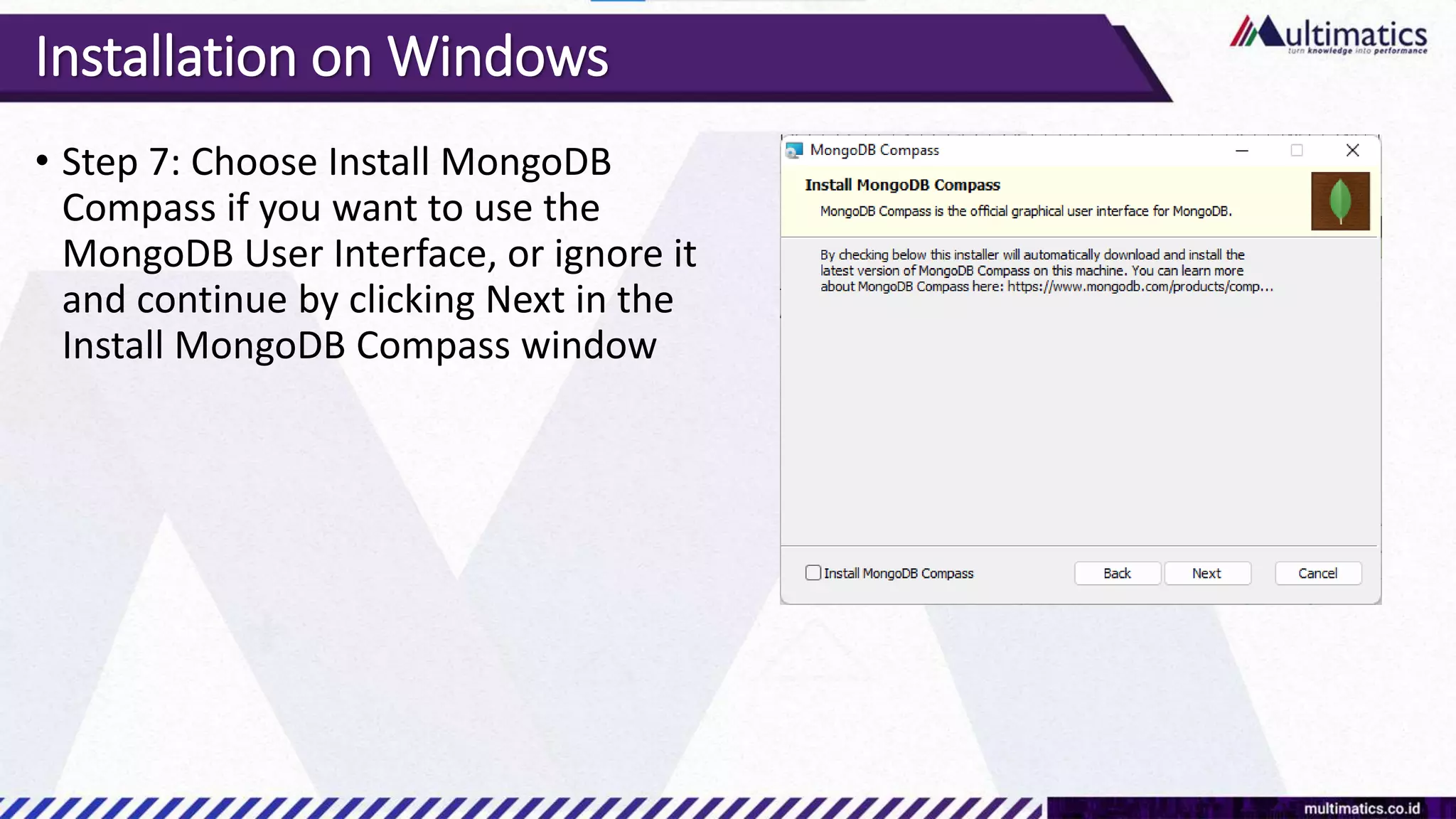
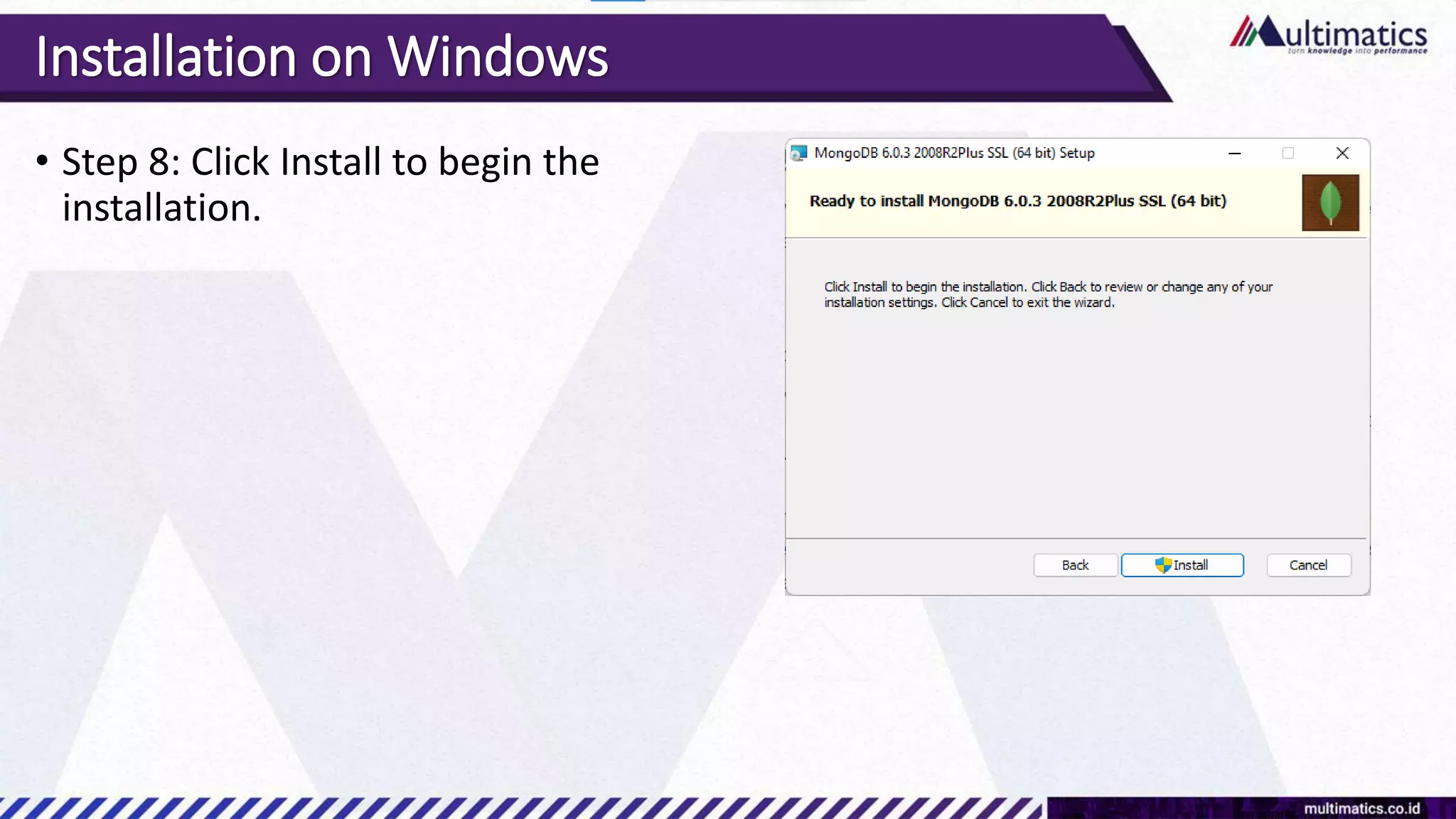
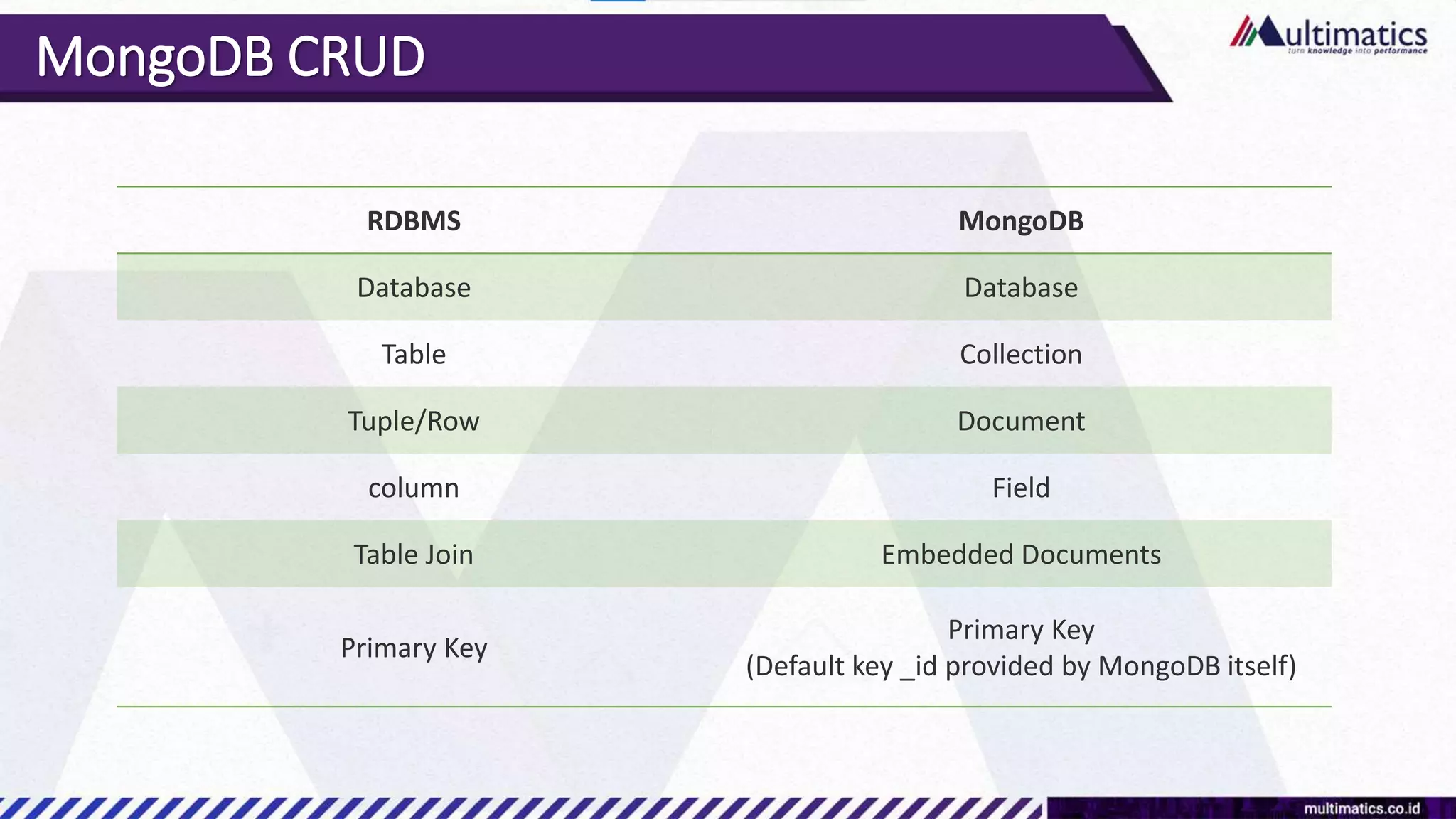
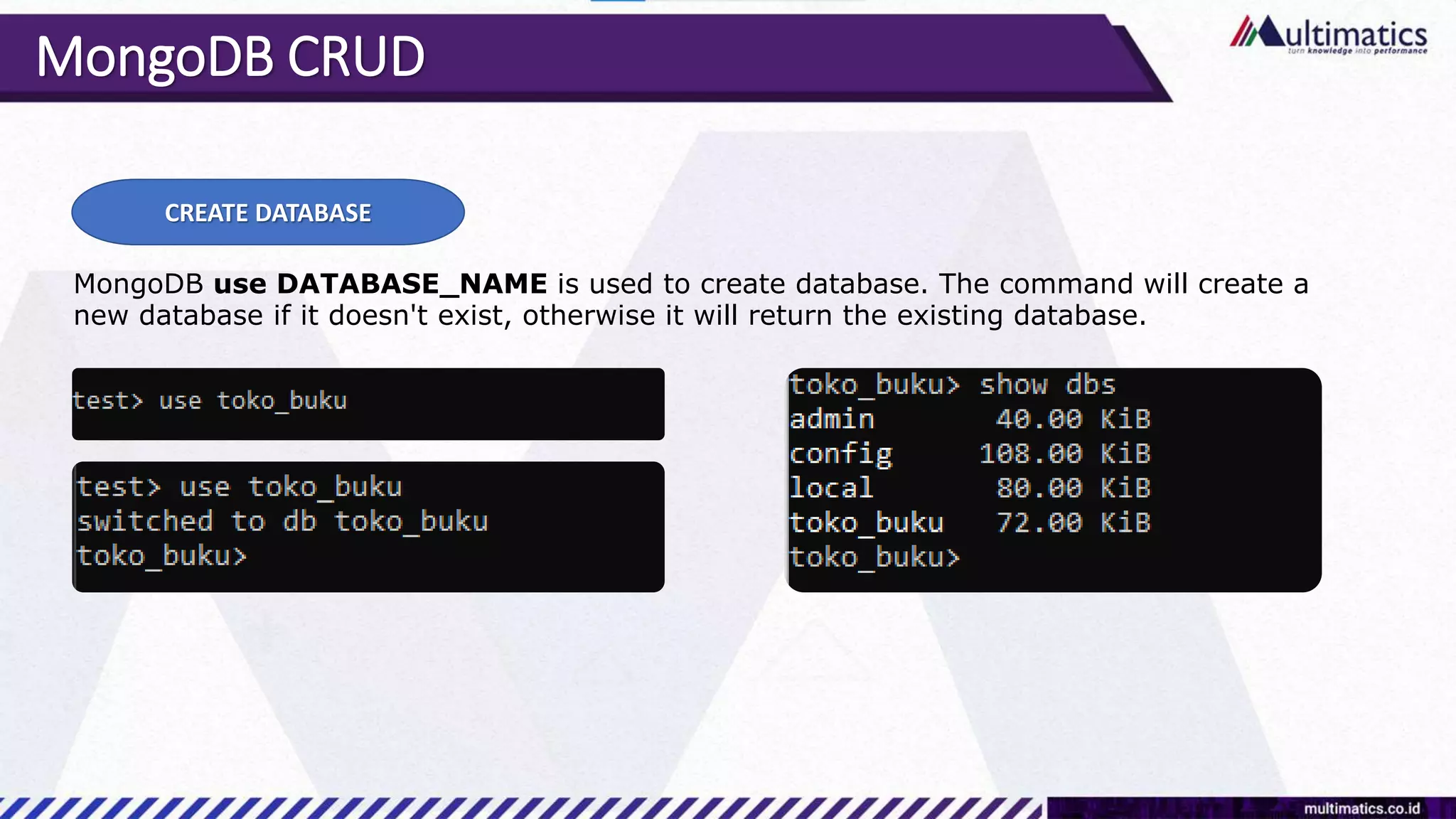
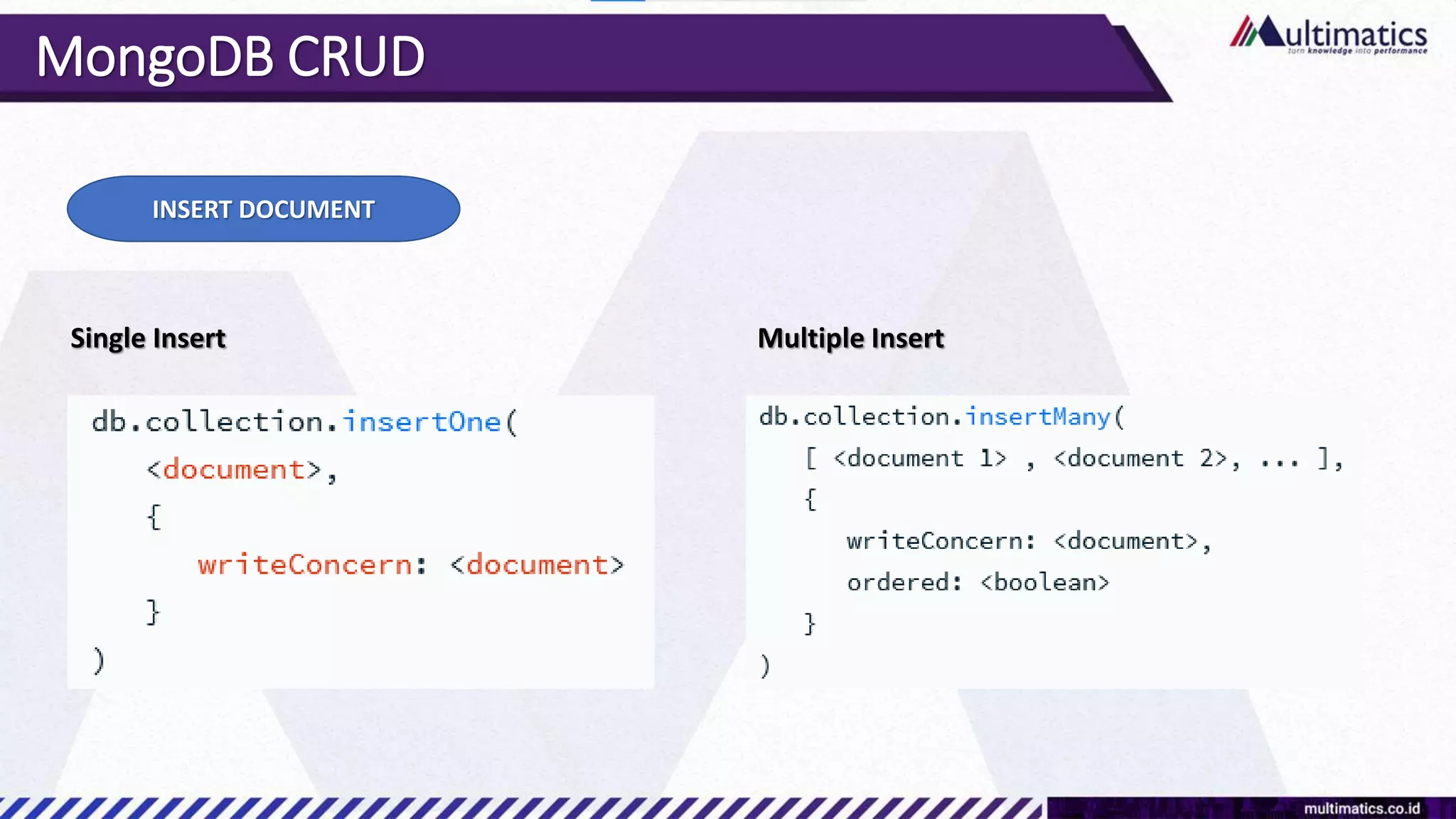
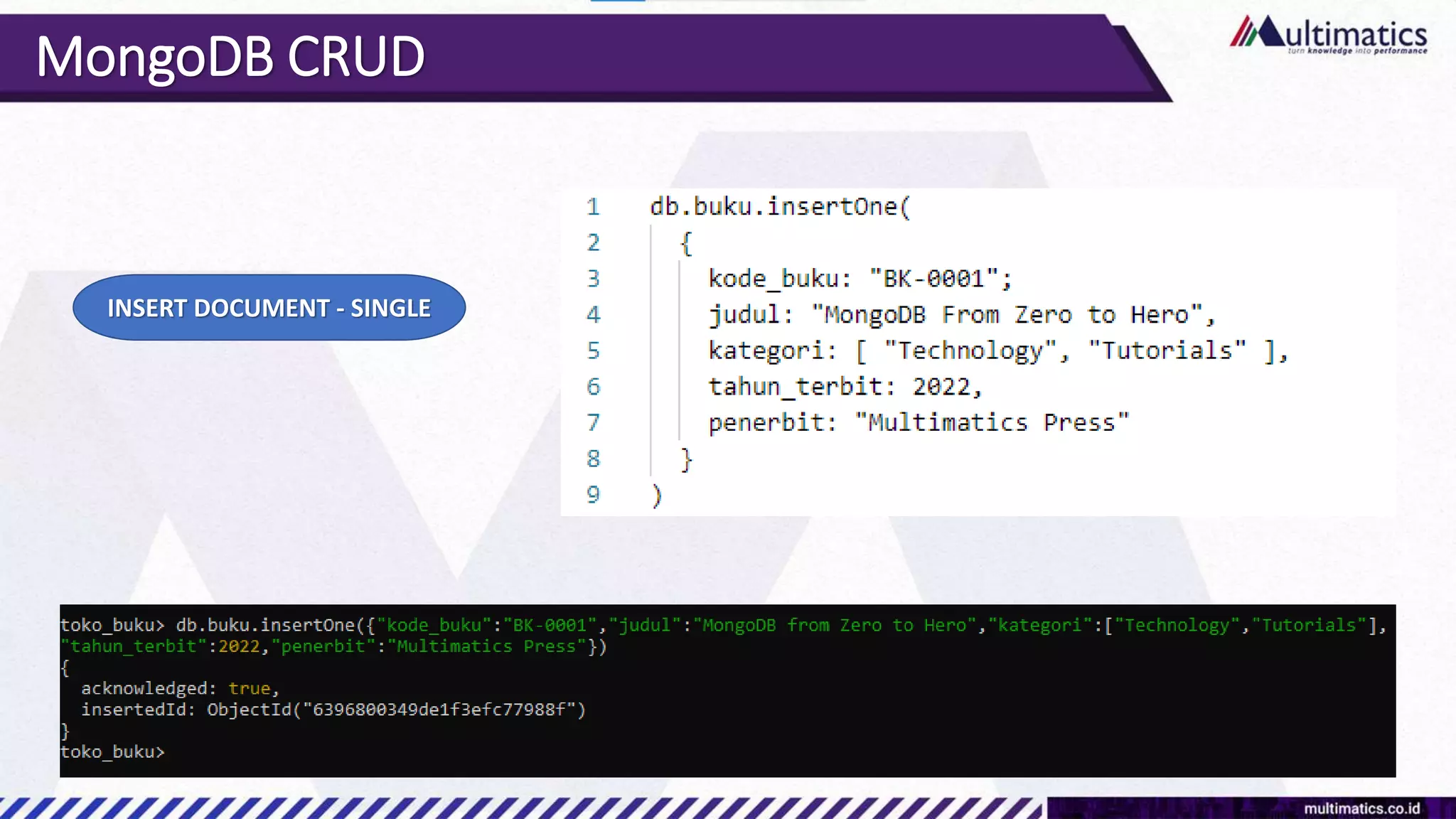
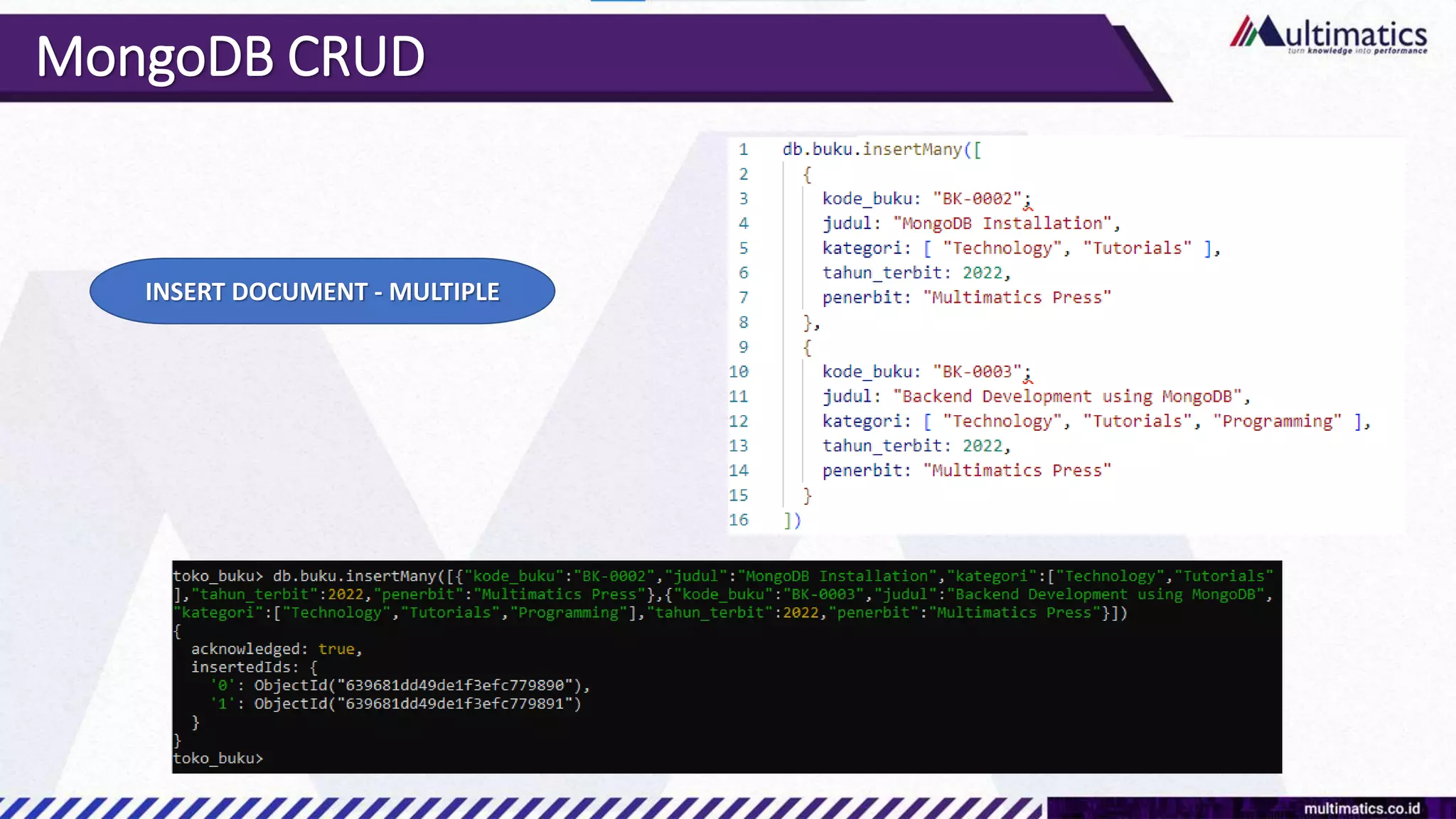
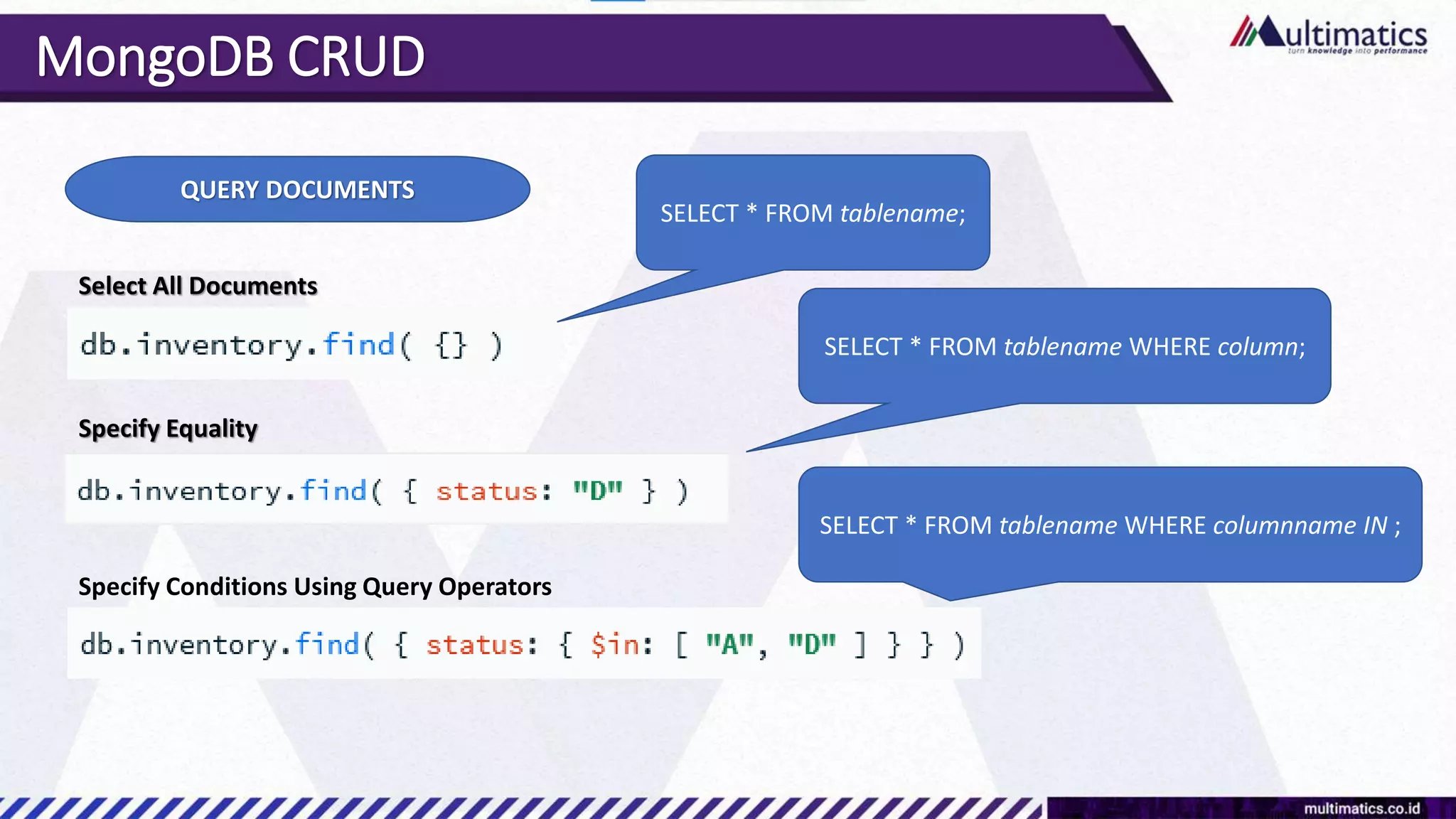
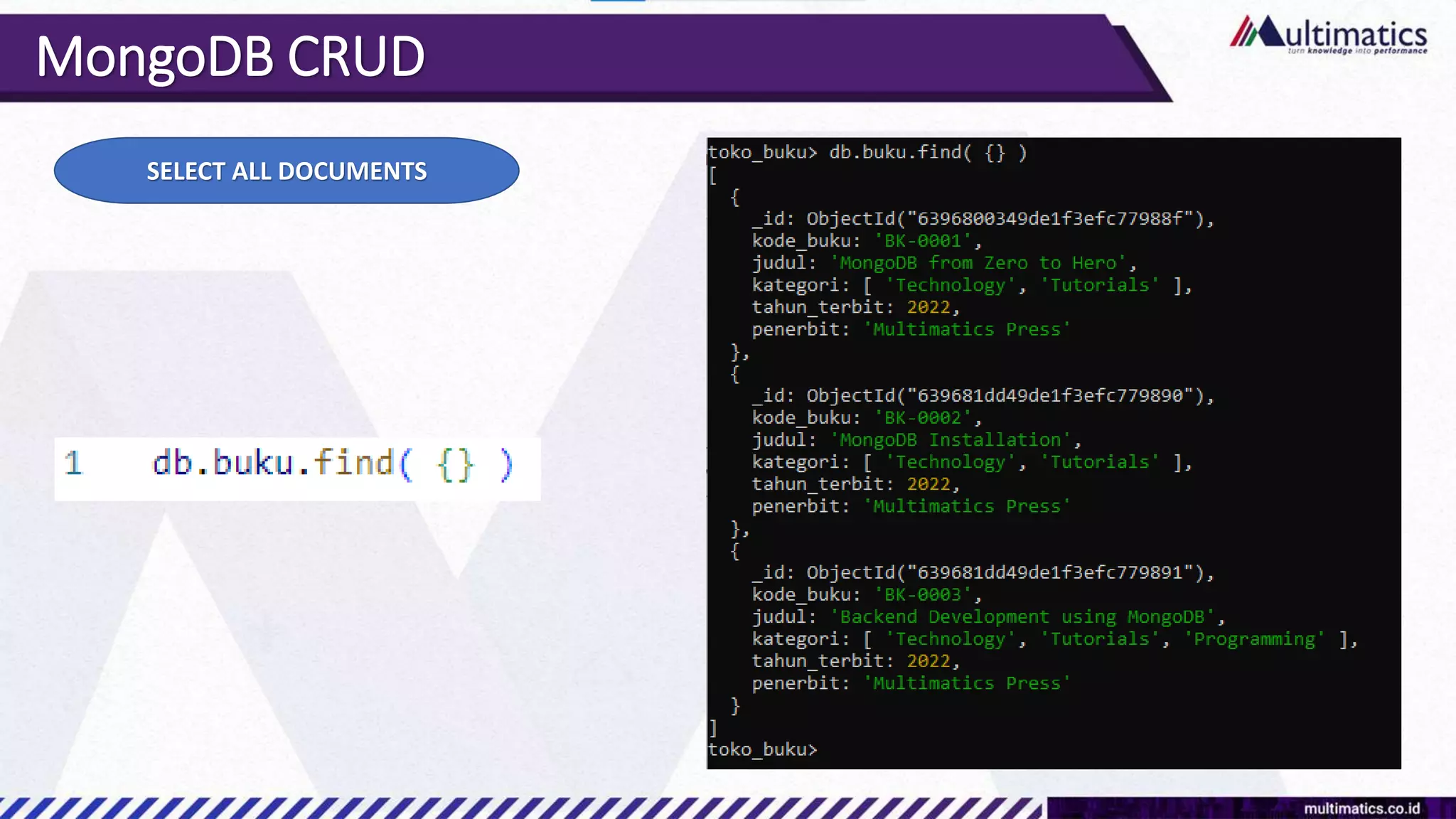
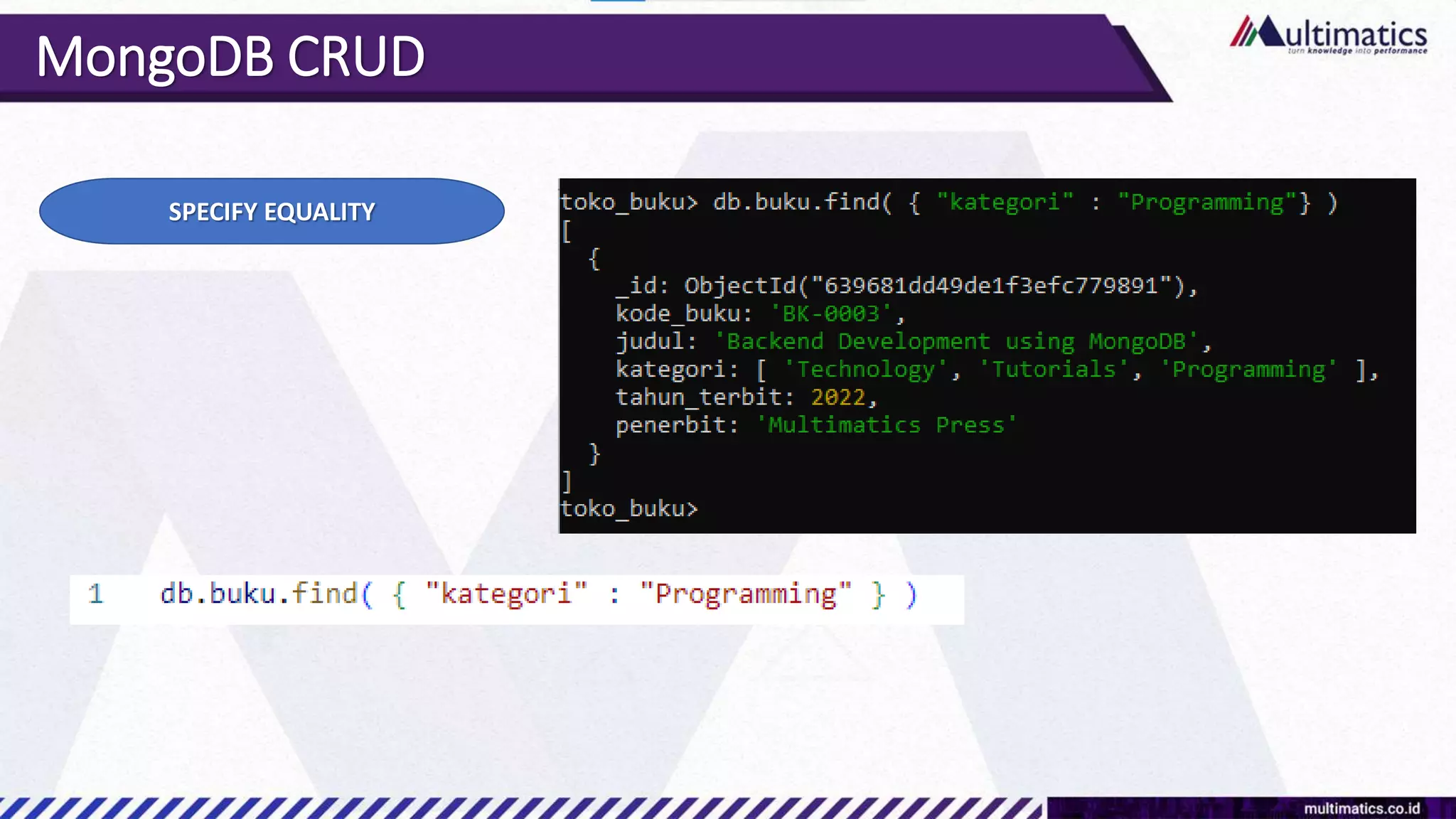
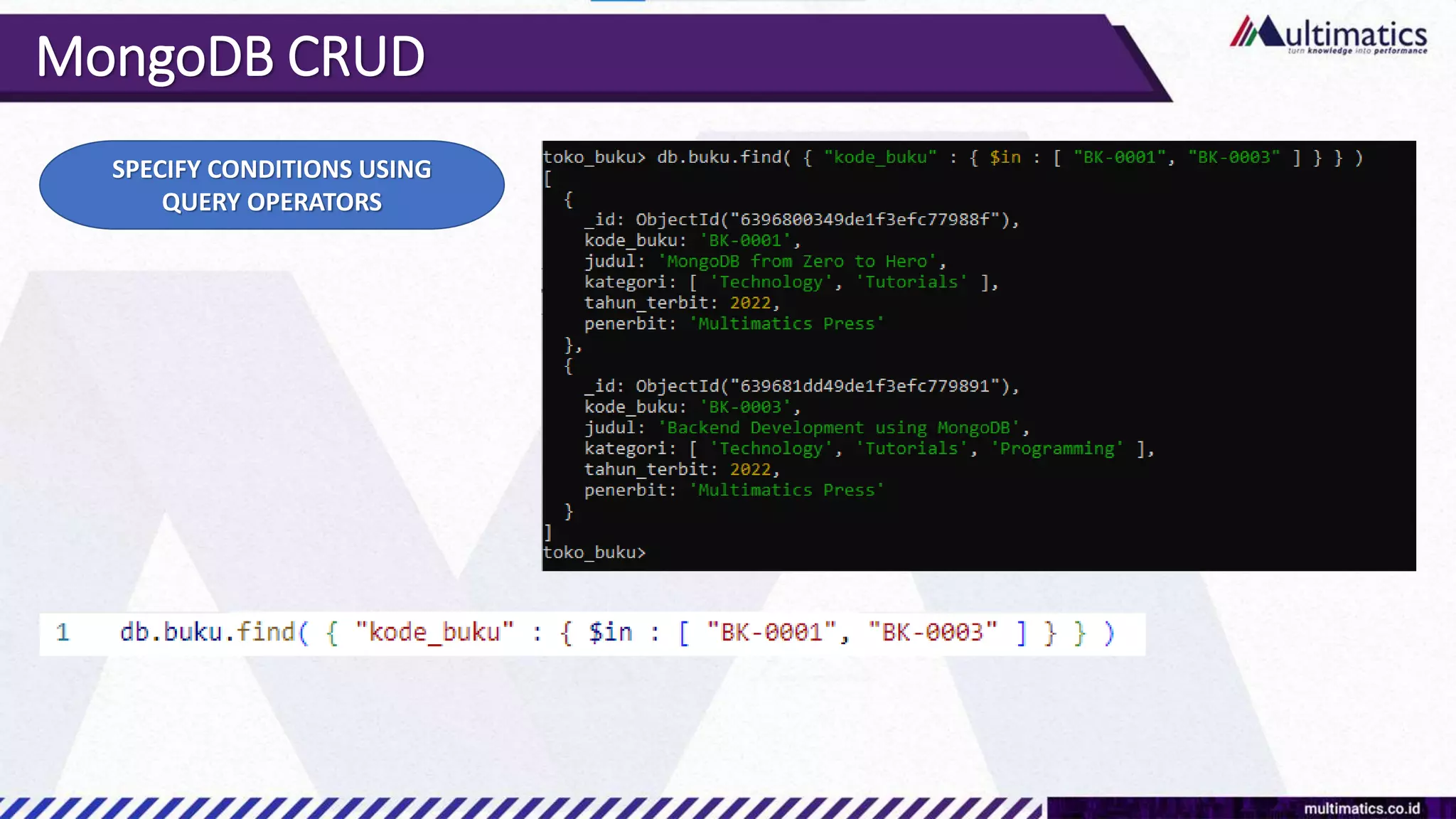
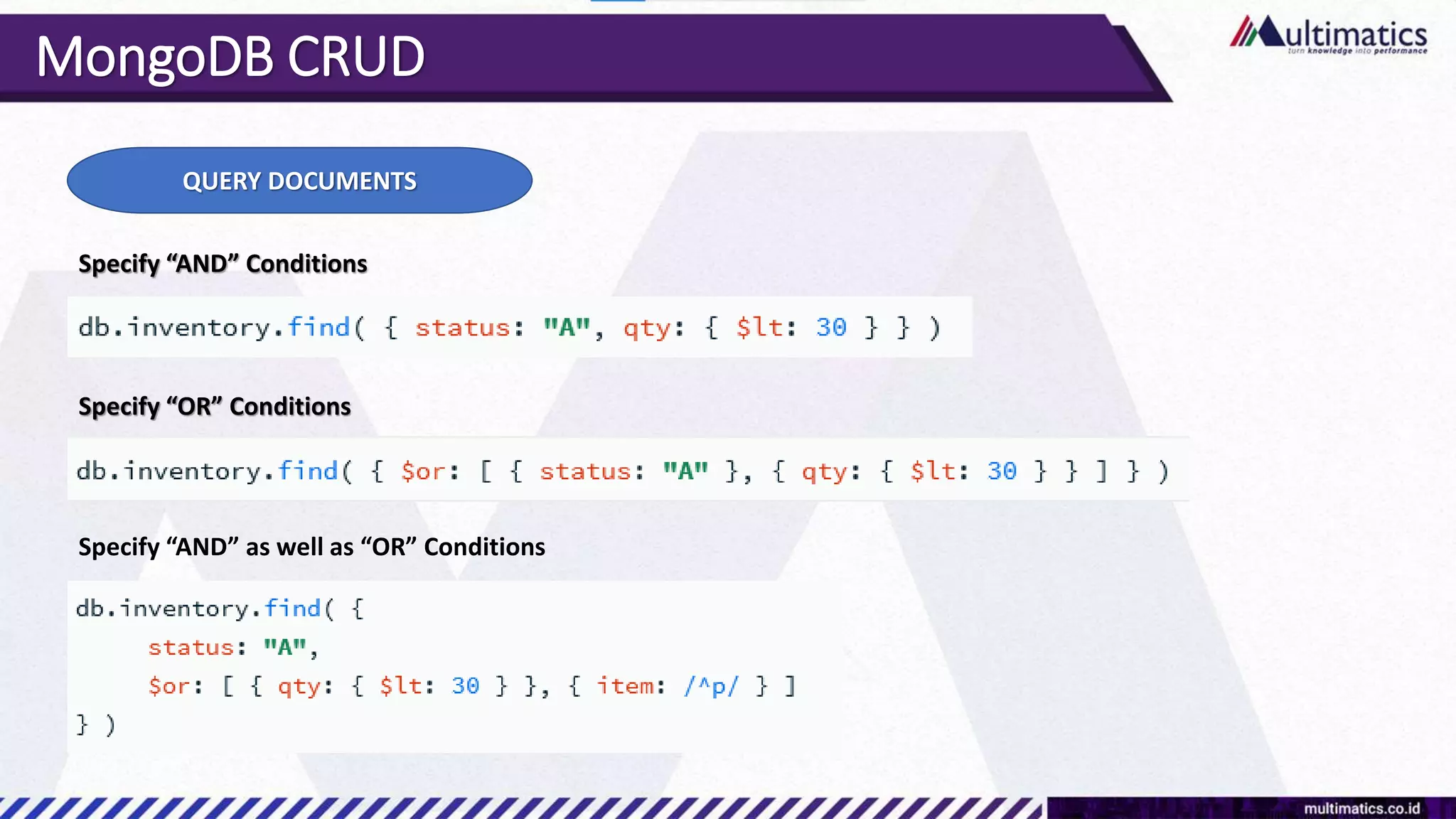
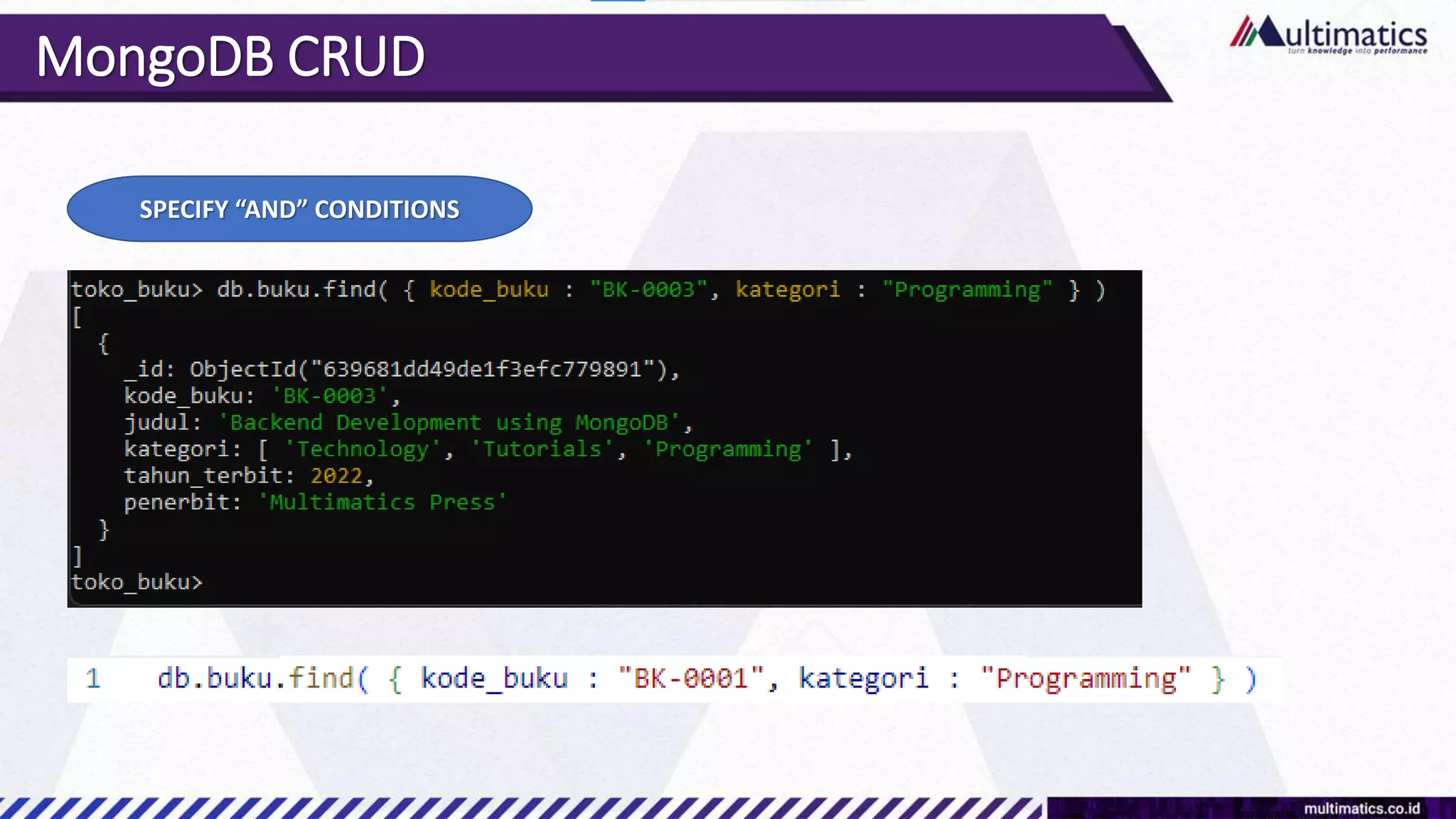
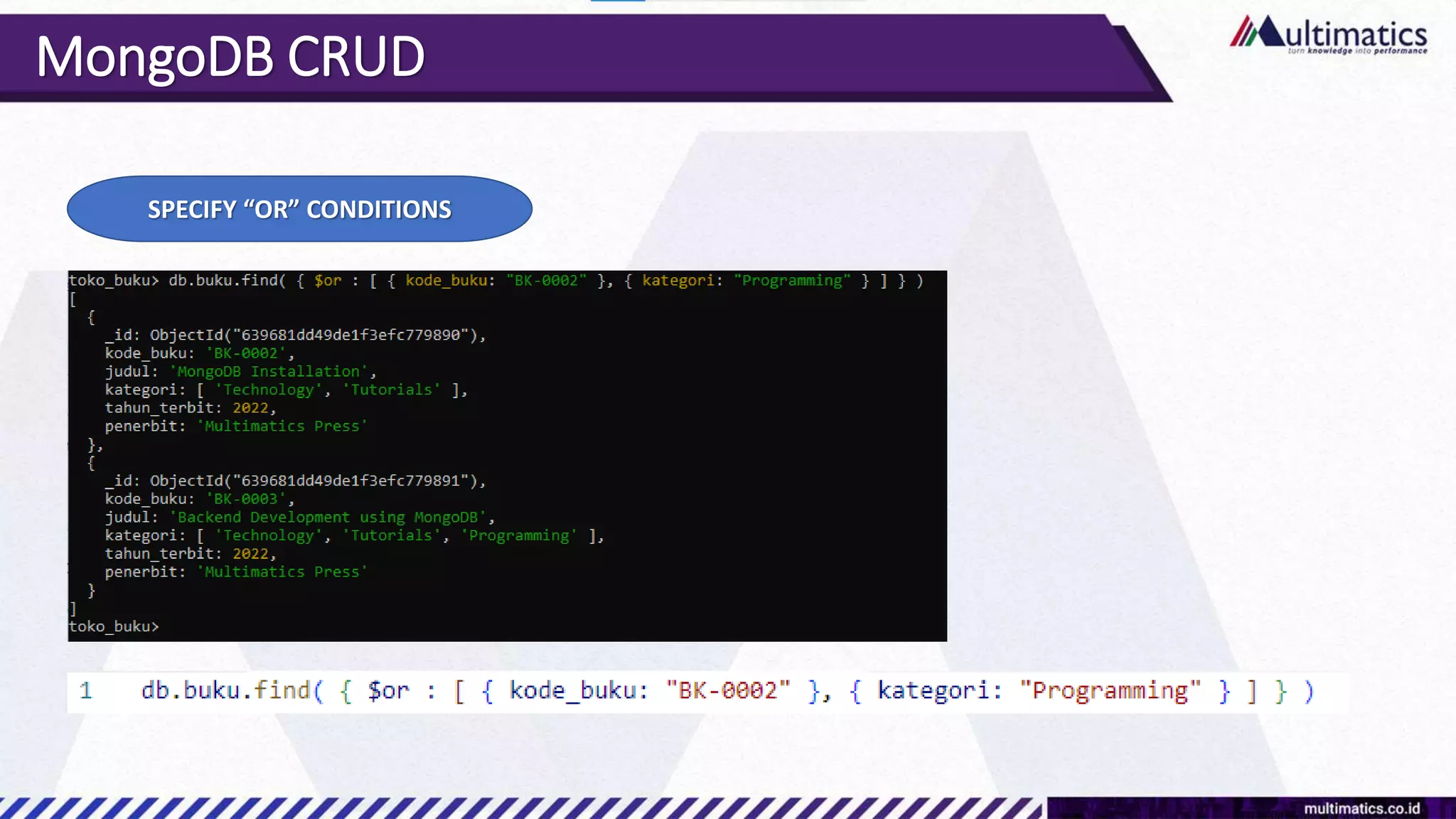
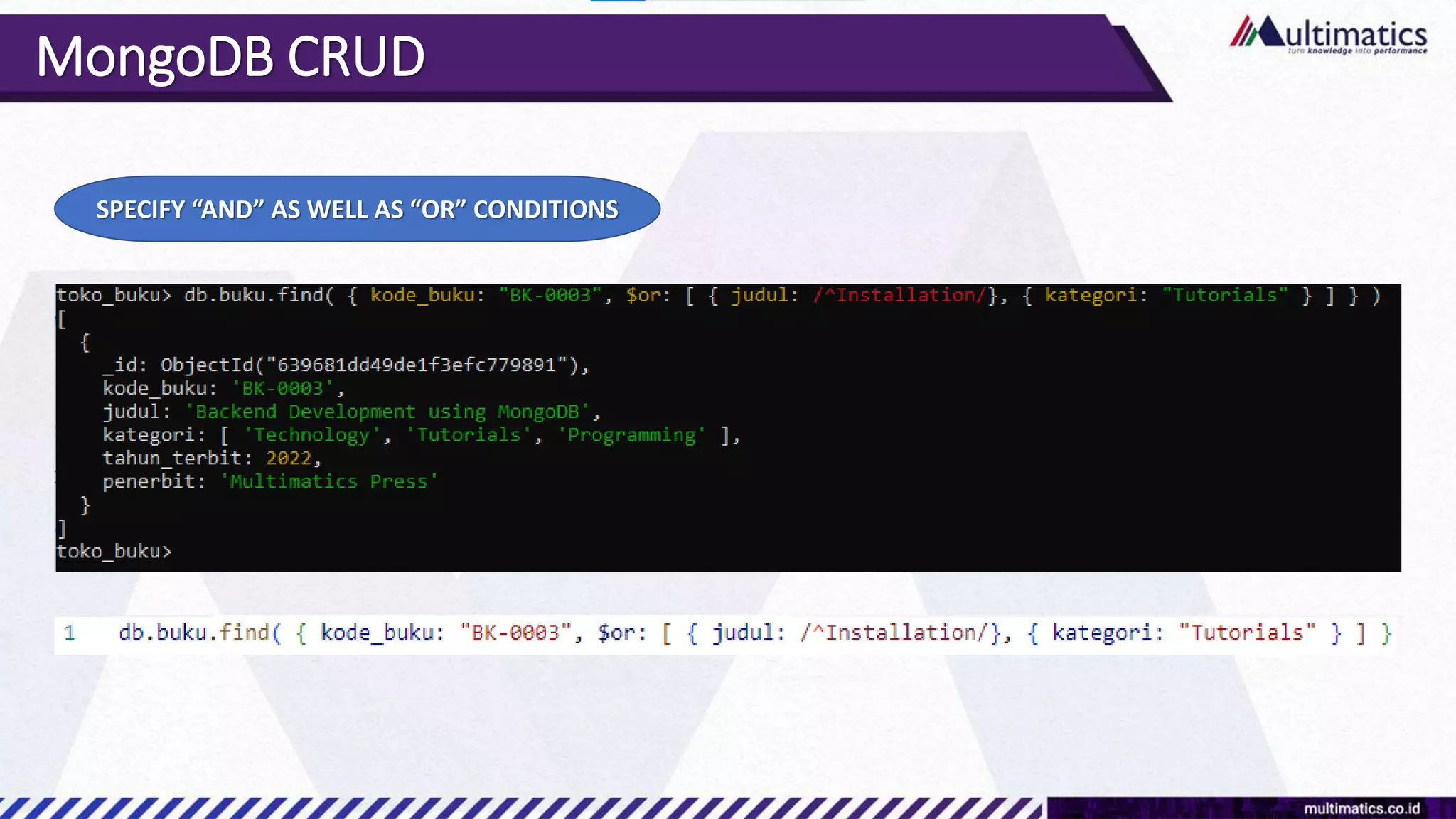
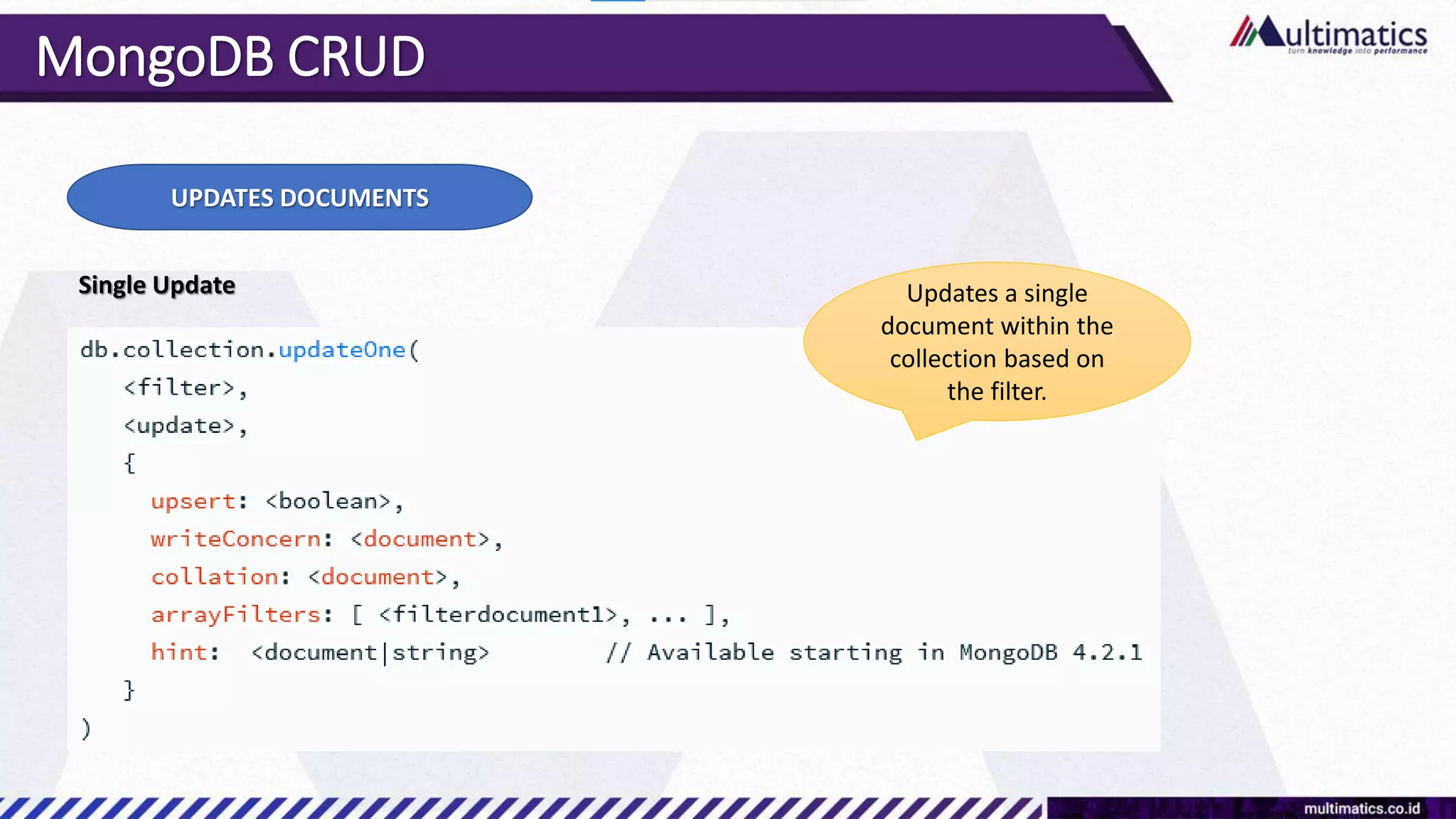
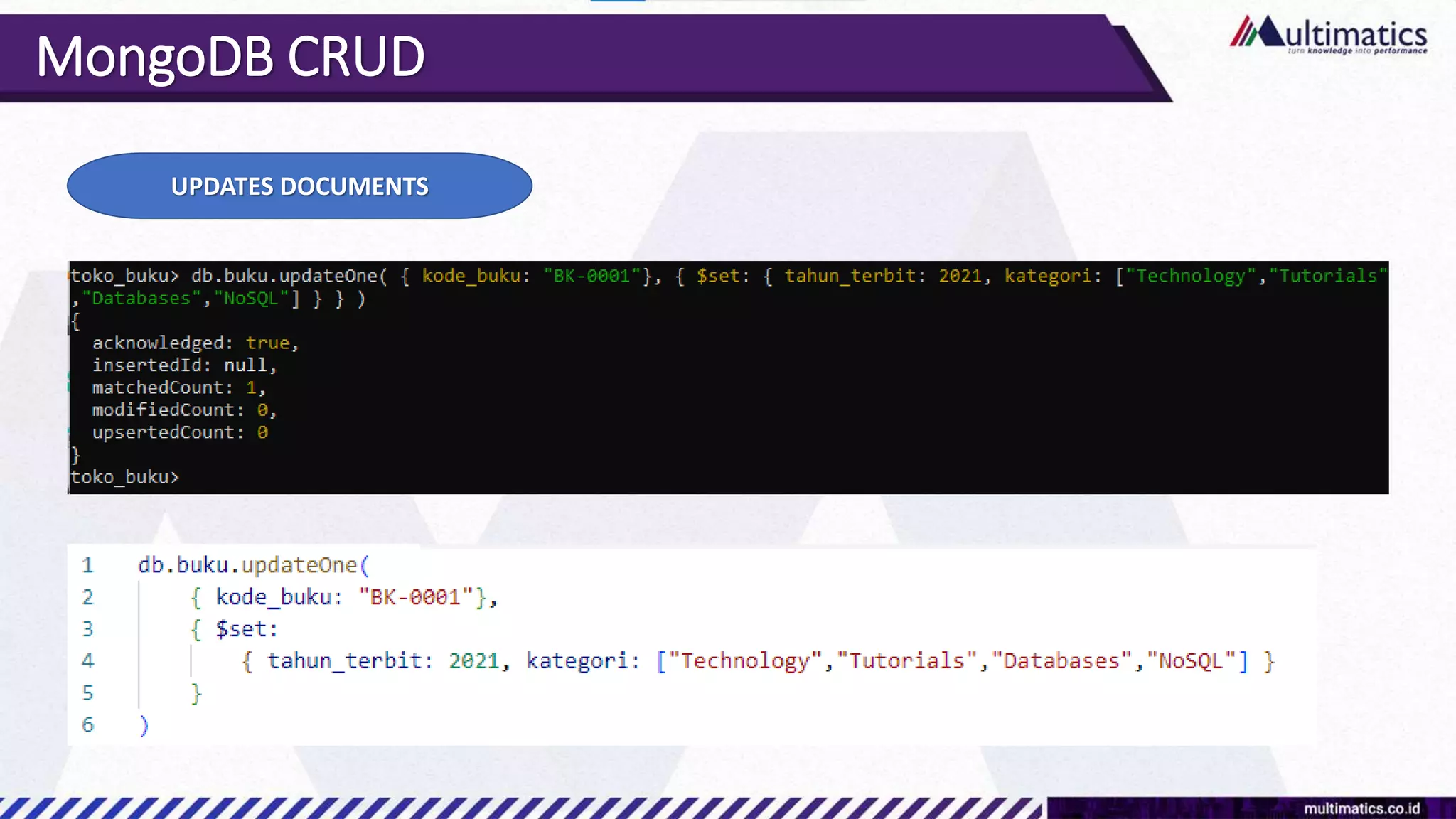
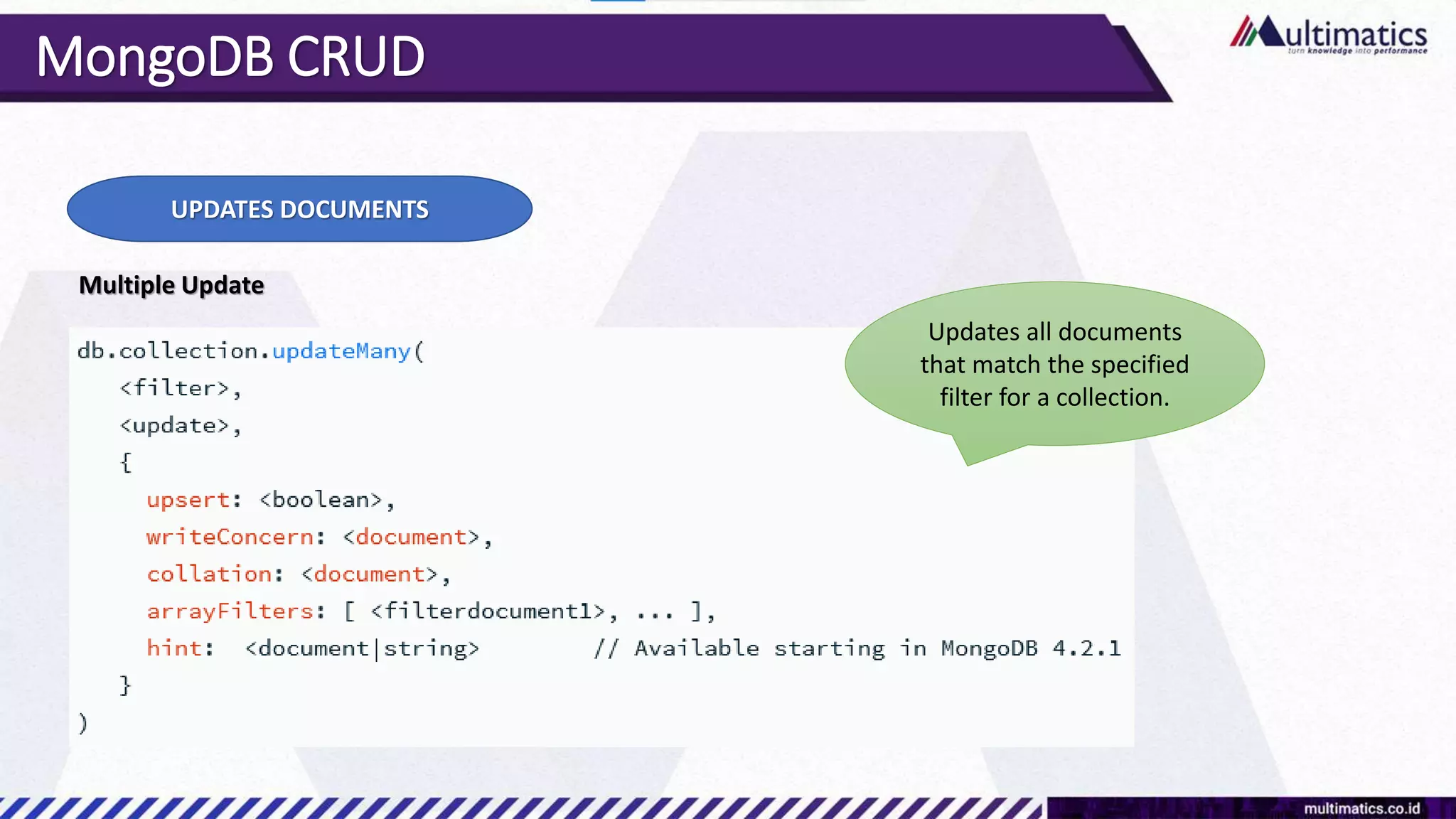
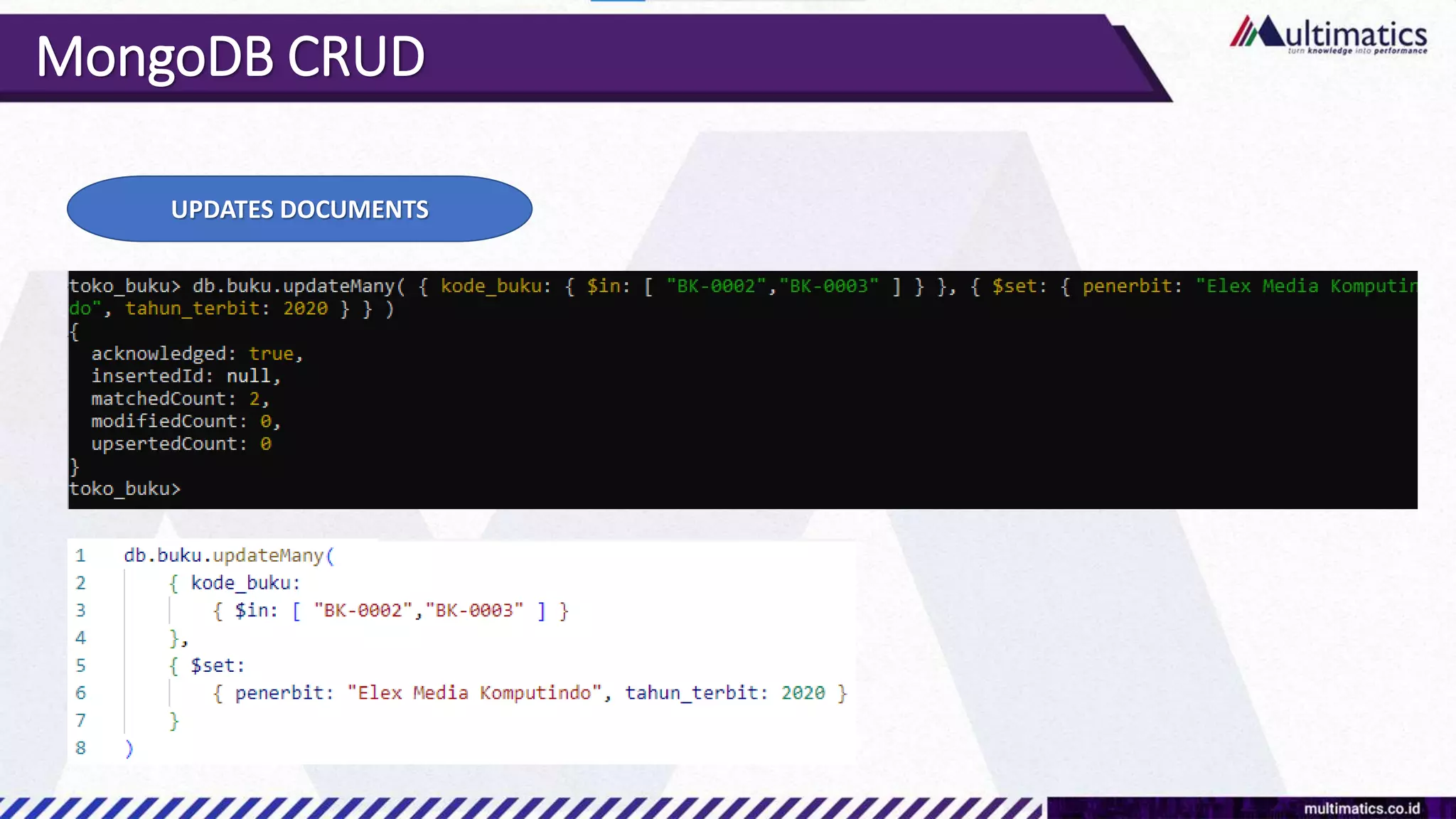
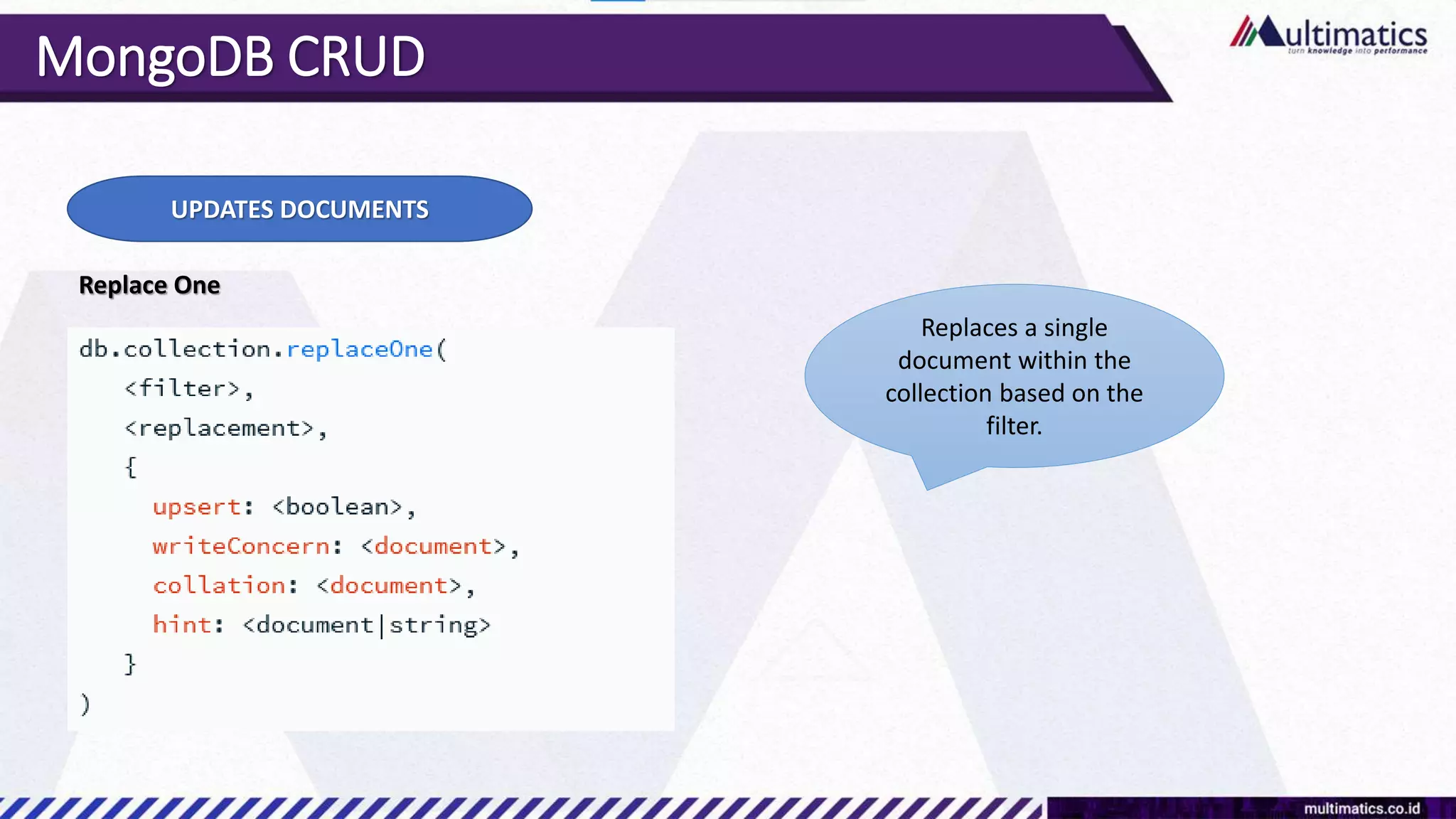
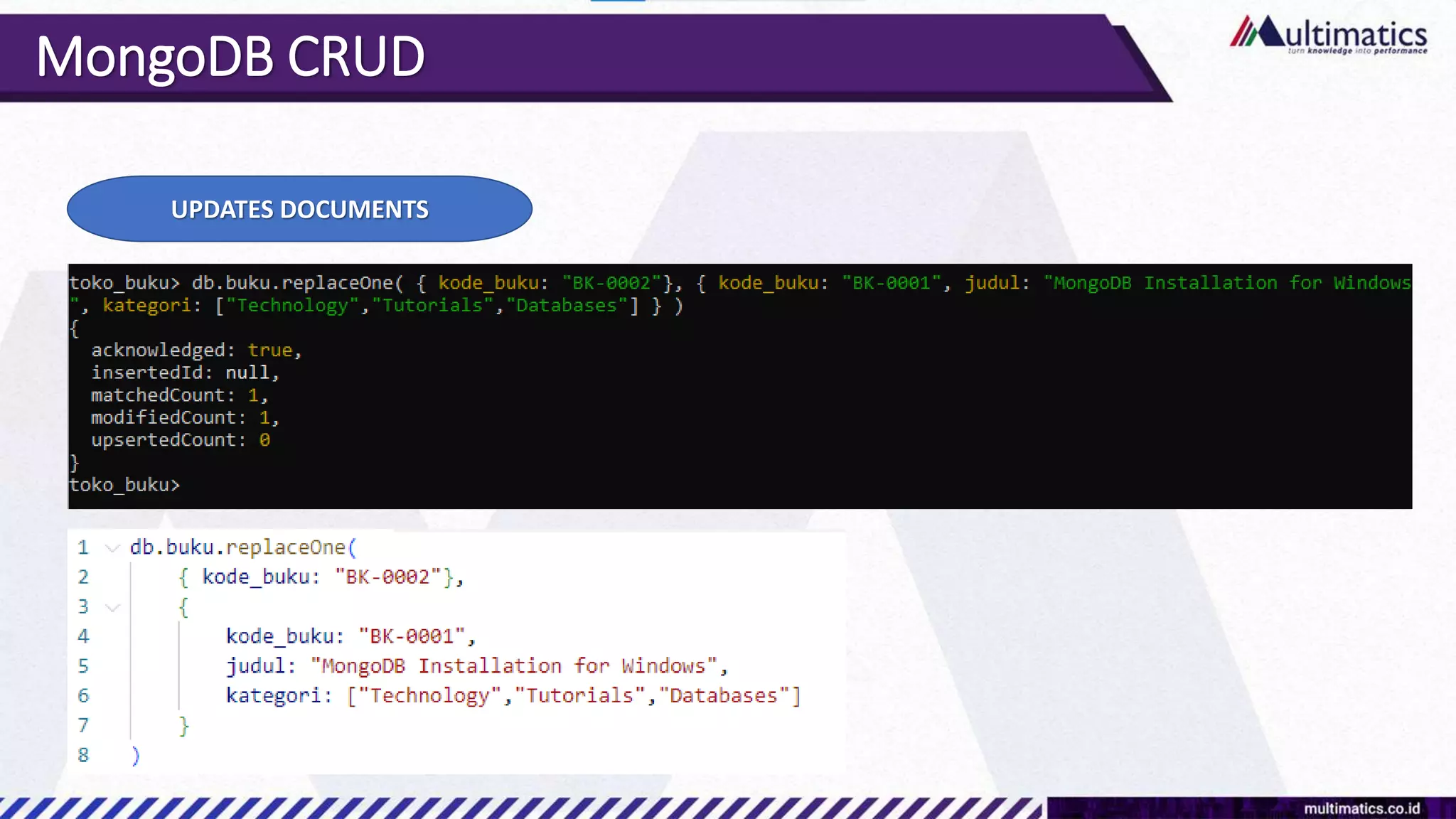
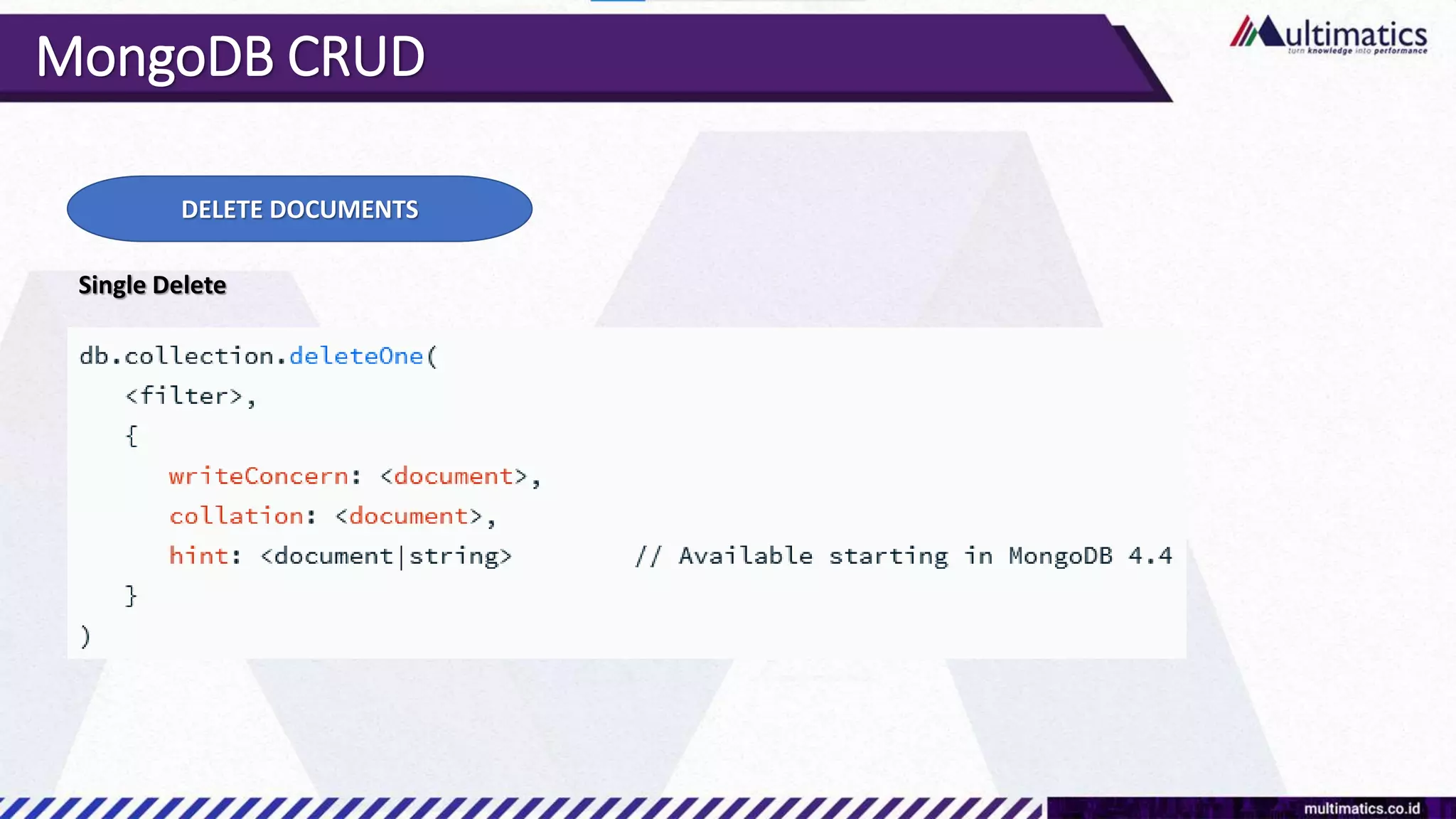
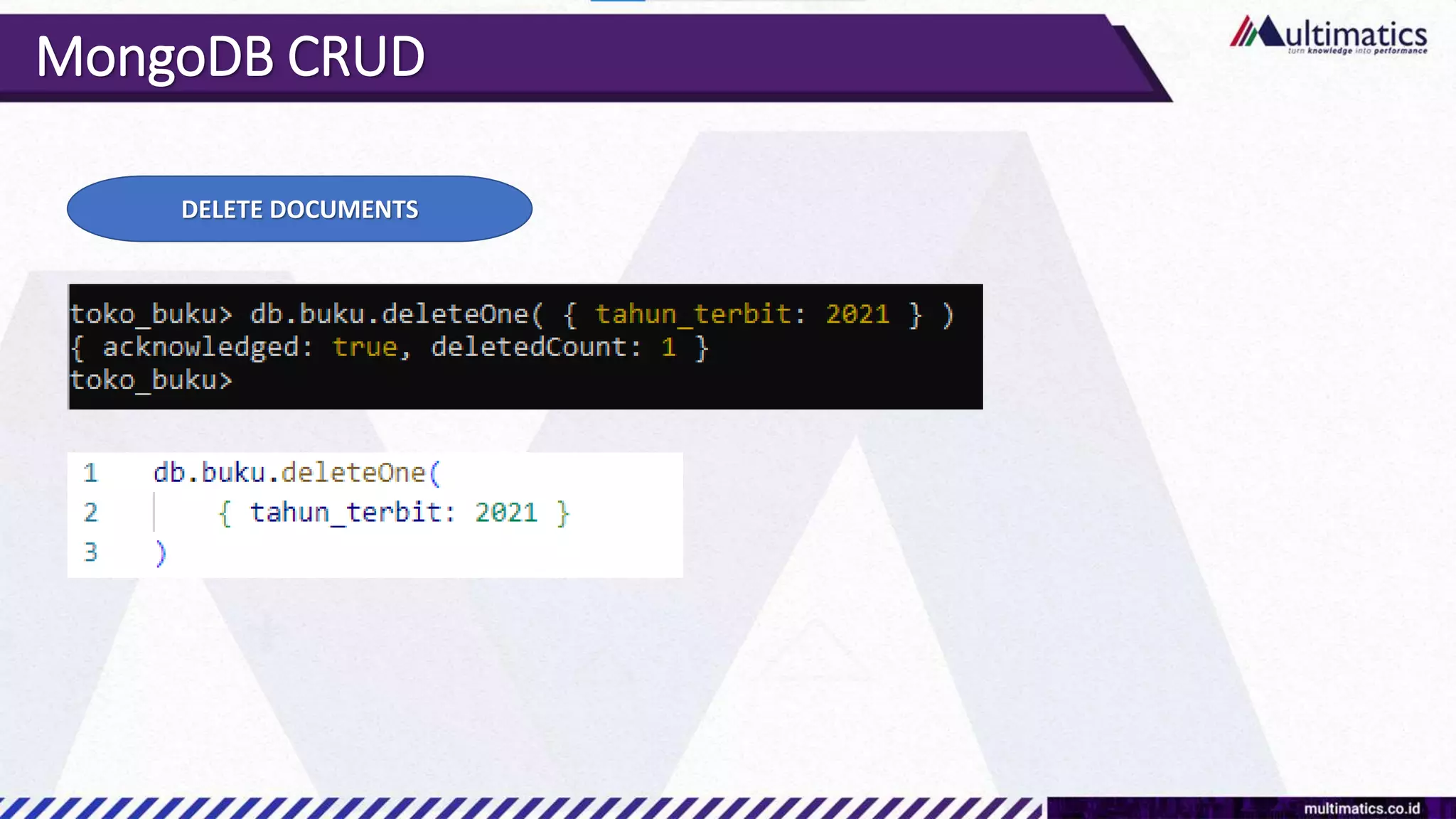
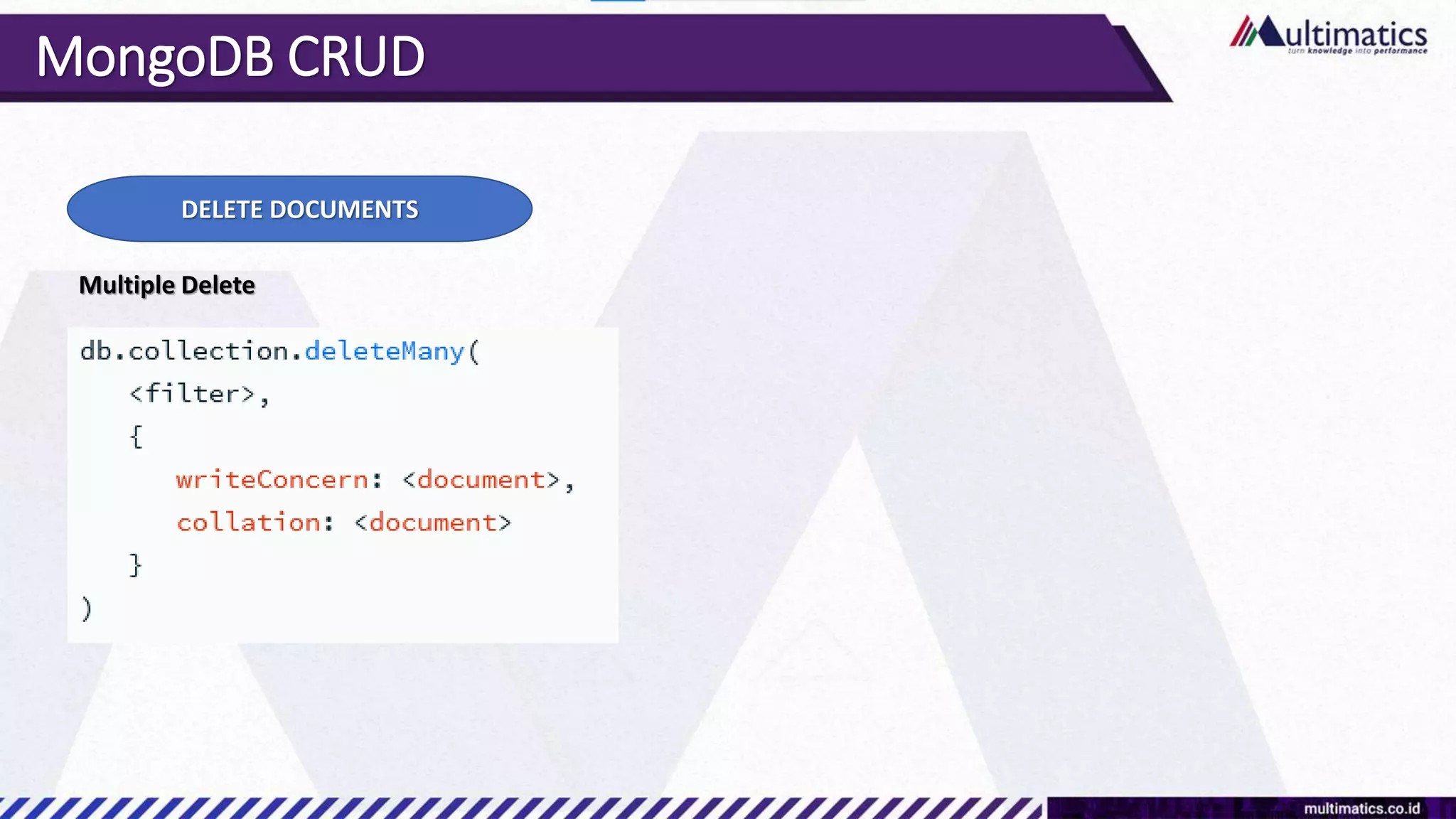
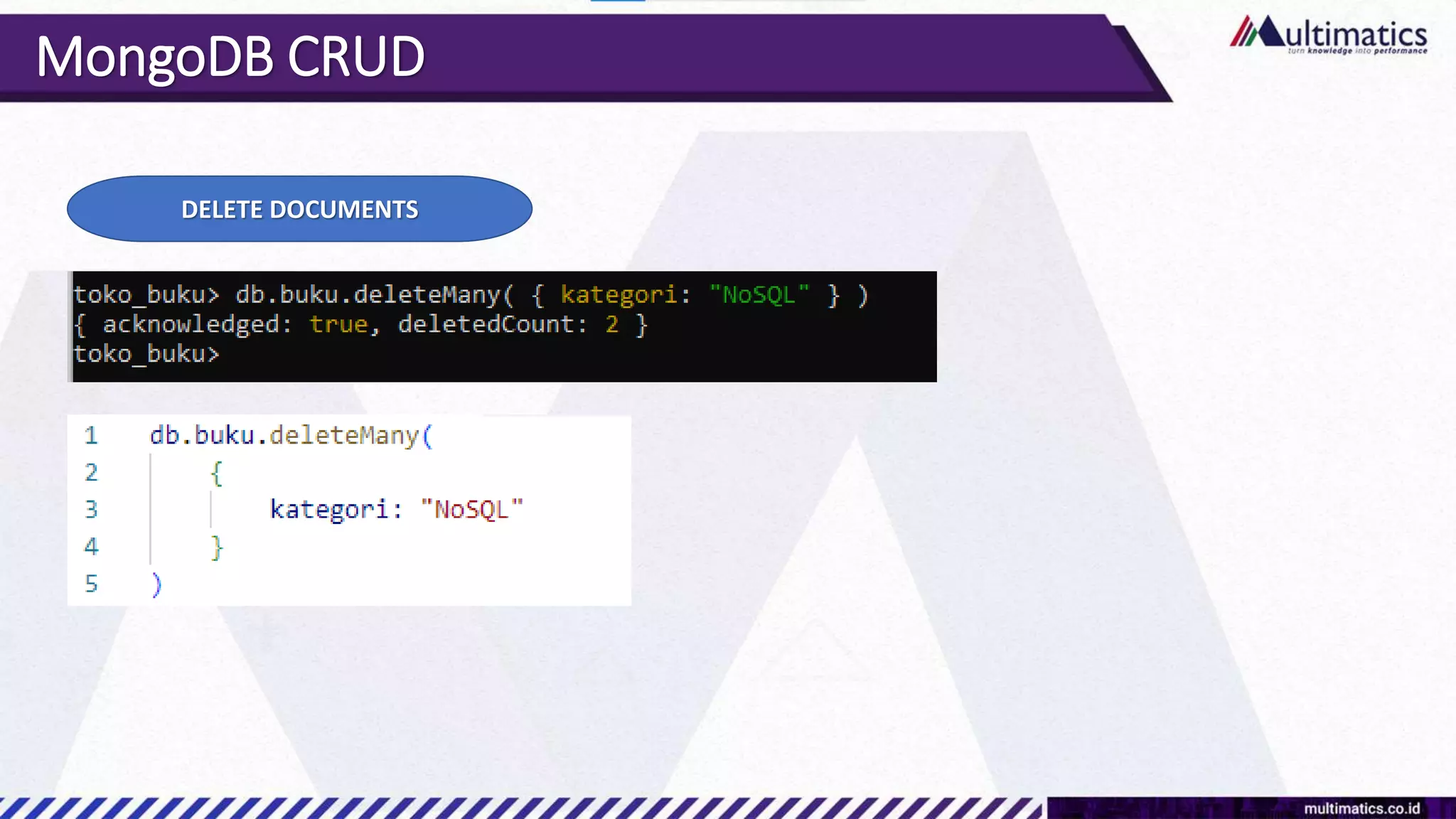
Sigit Kurniawan discusses MongoDB and provides an overview of key concepts. The document covers SQL vs NoSQL, MongoDB features, data types, installation on Windows, and CRUD operations. MongoDB is a document database designed for scalability and flexible schemas. It uses dynamic schemas and is horizontally scalable.