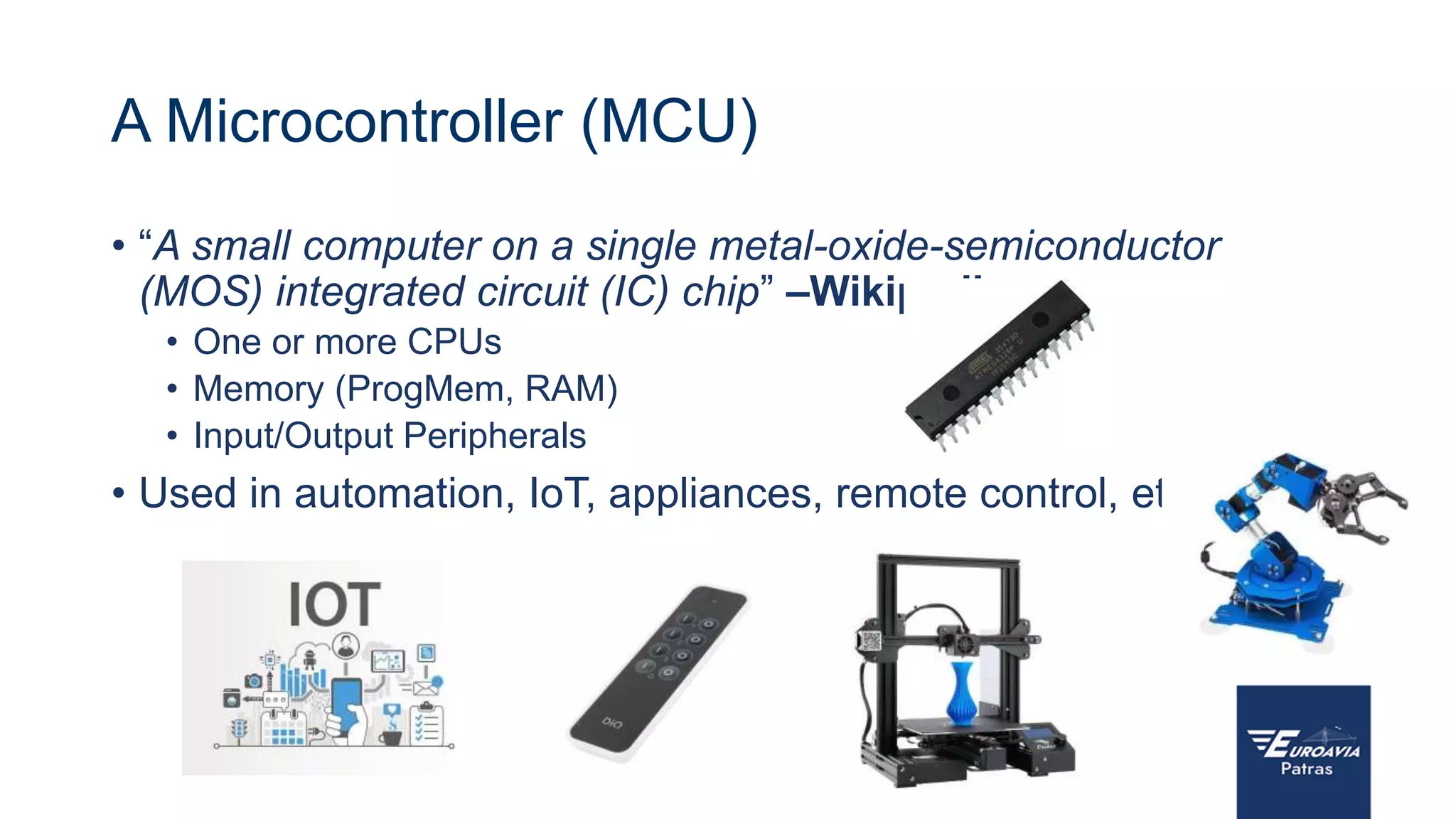
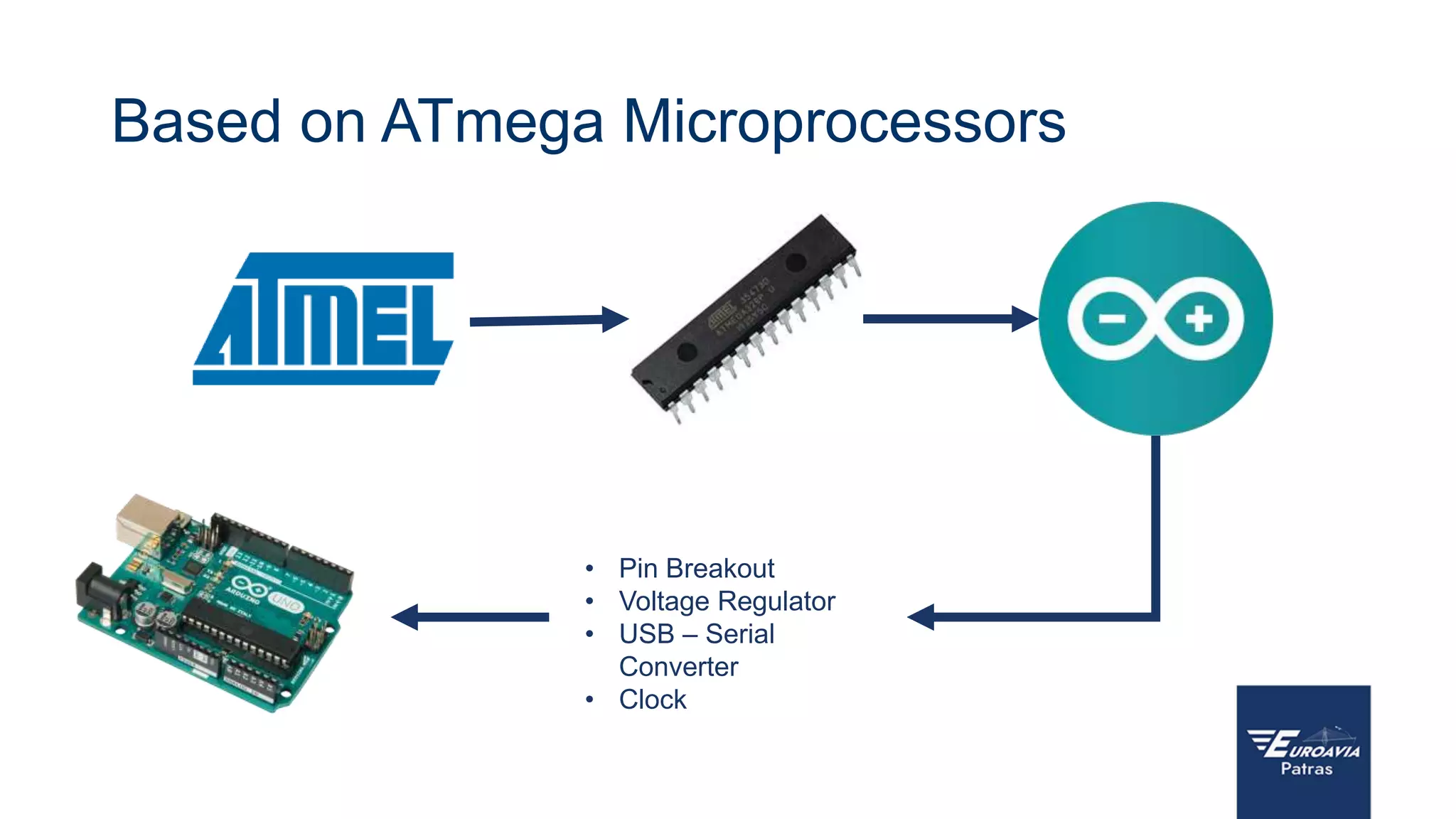
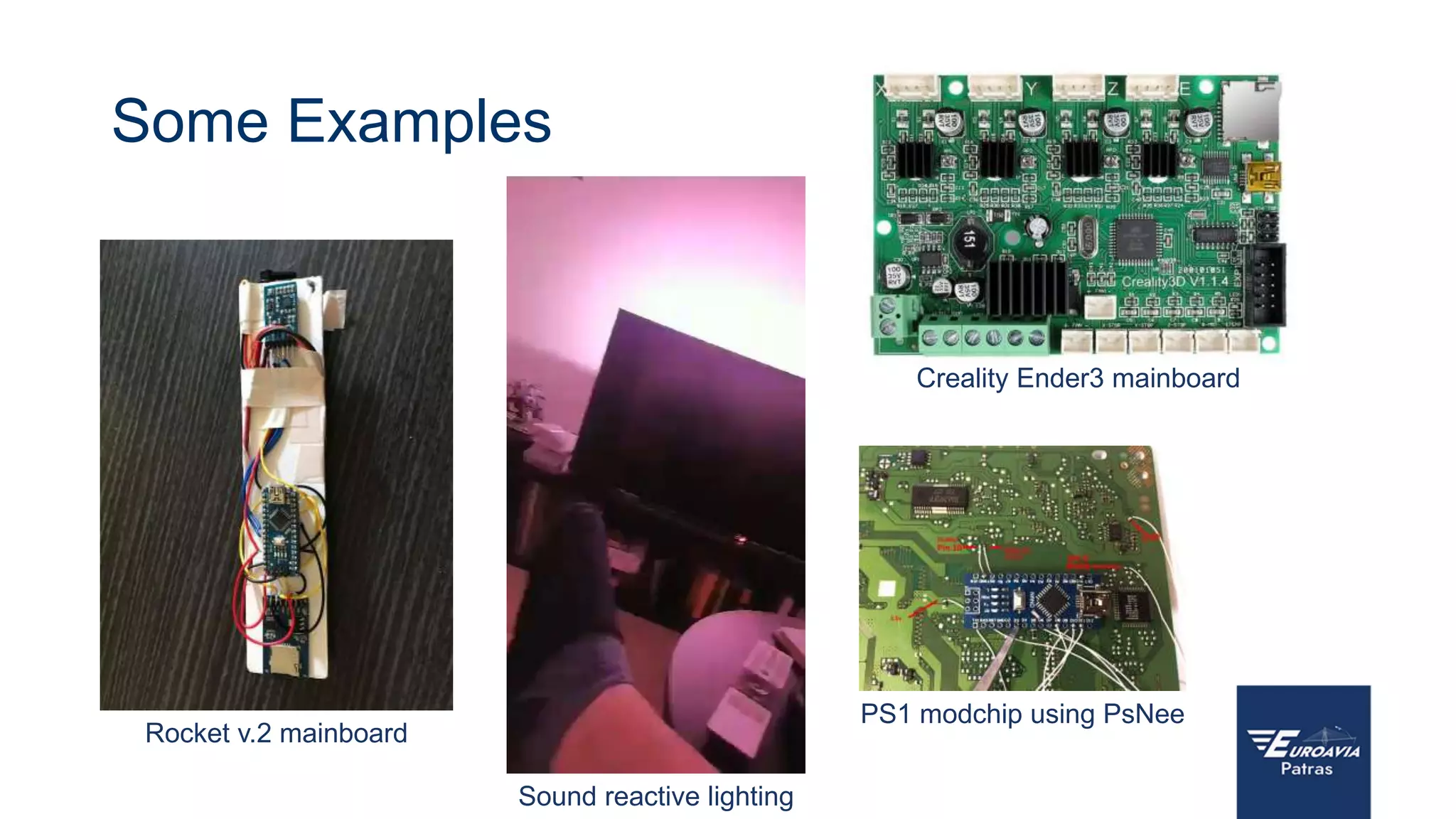
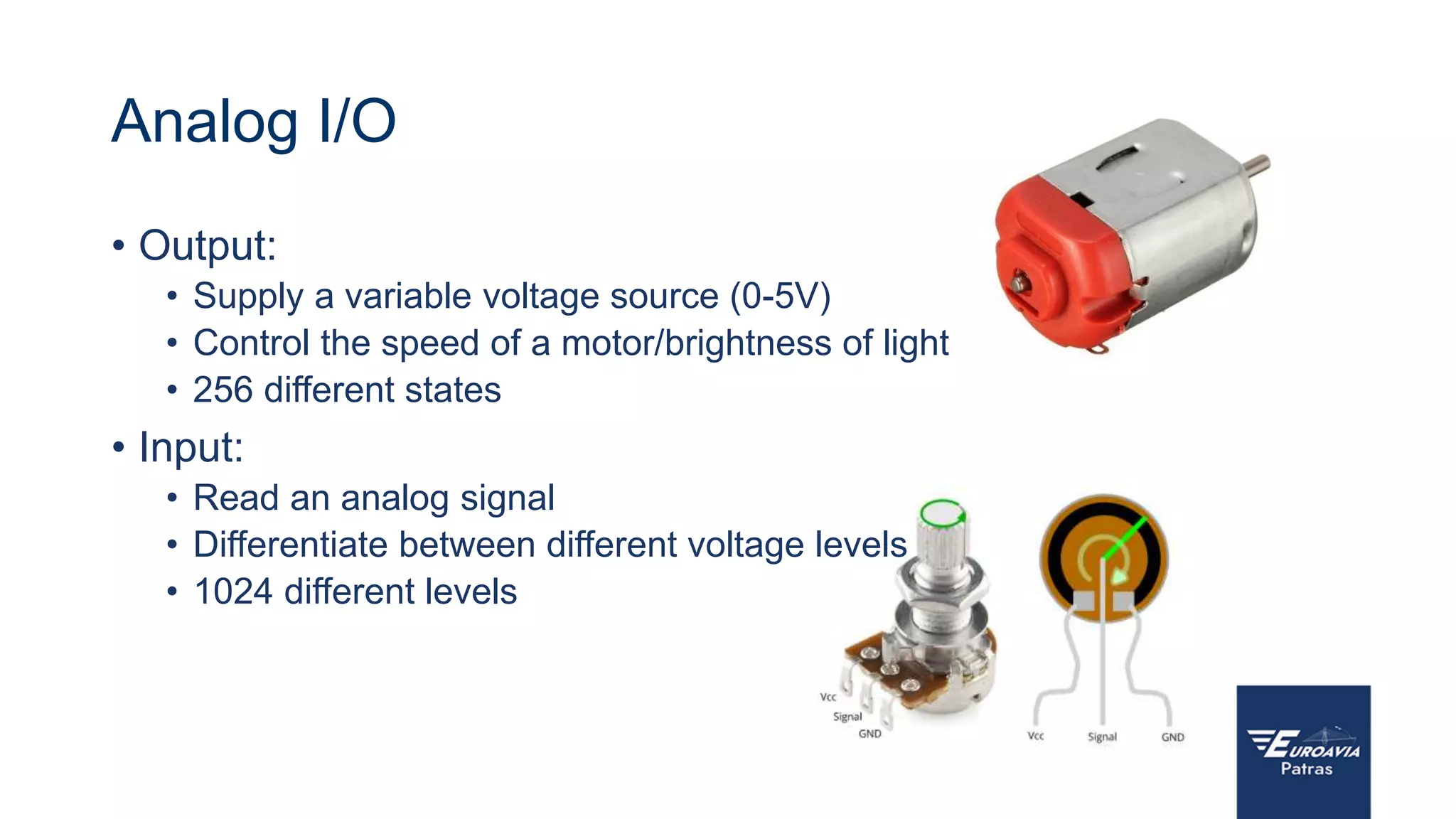
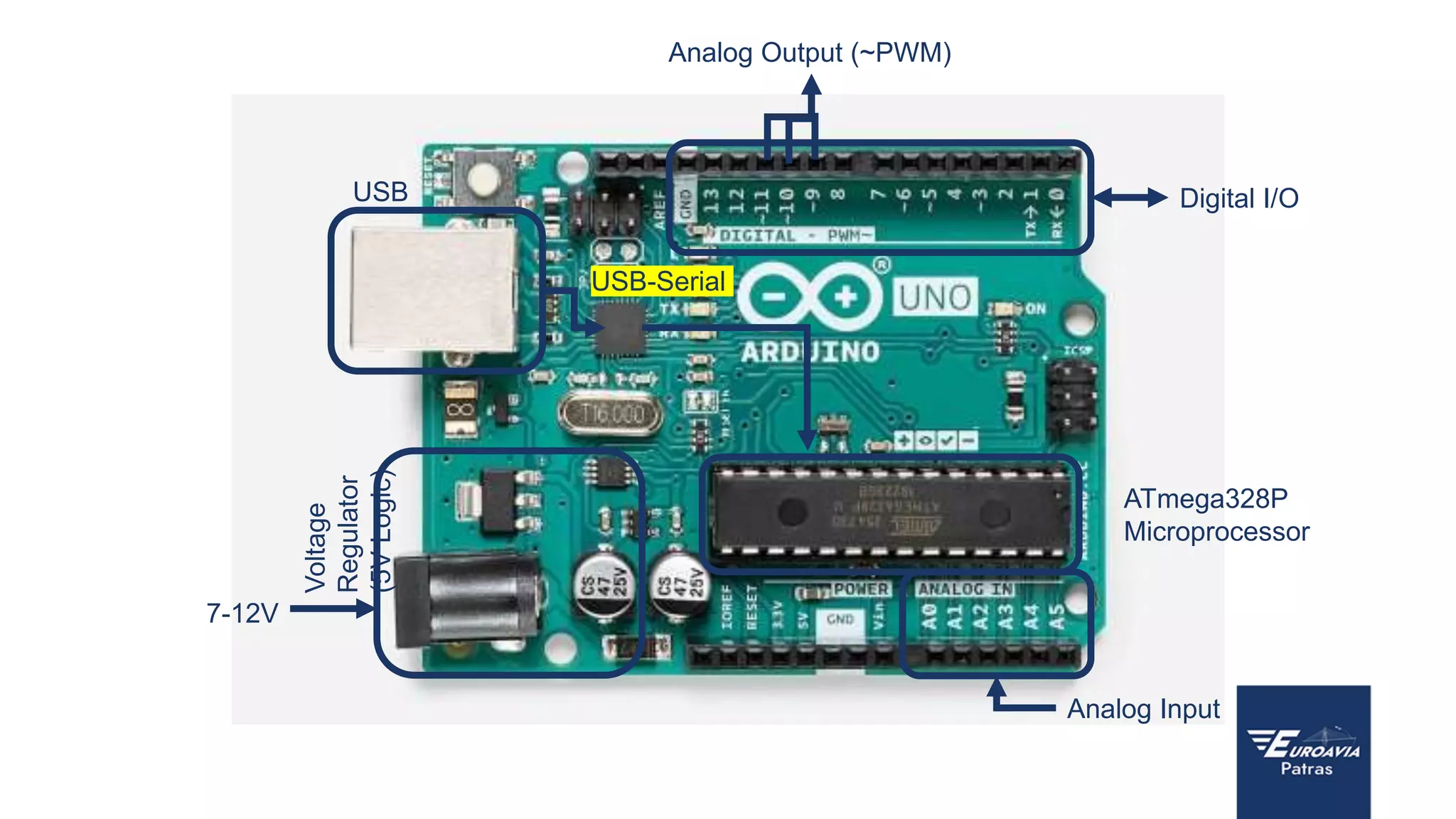
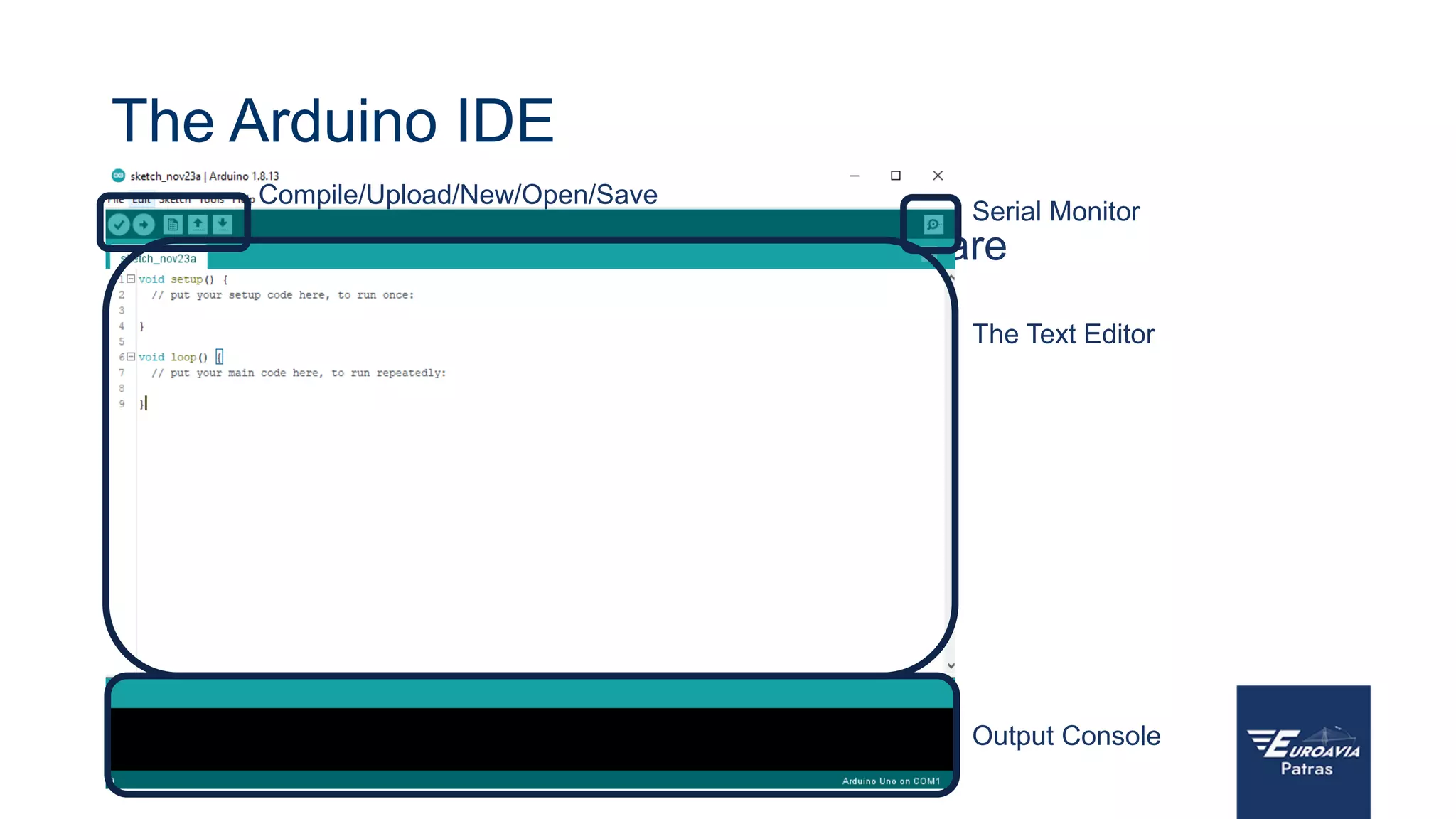
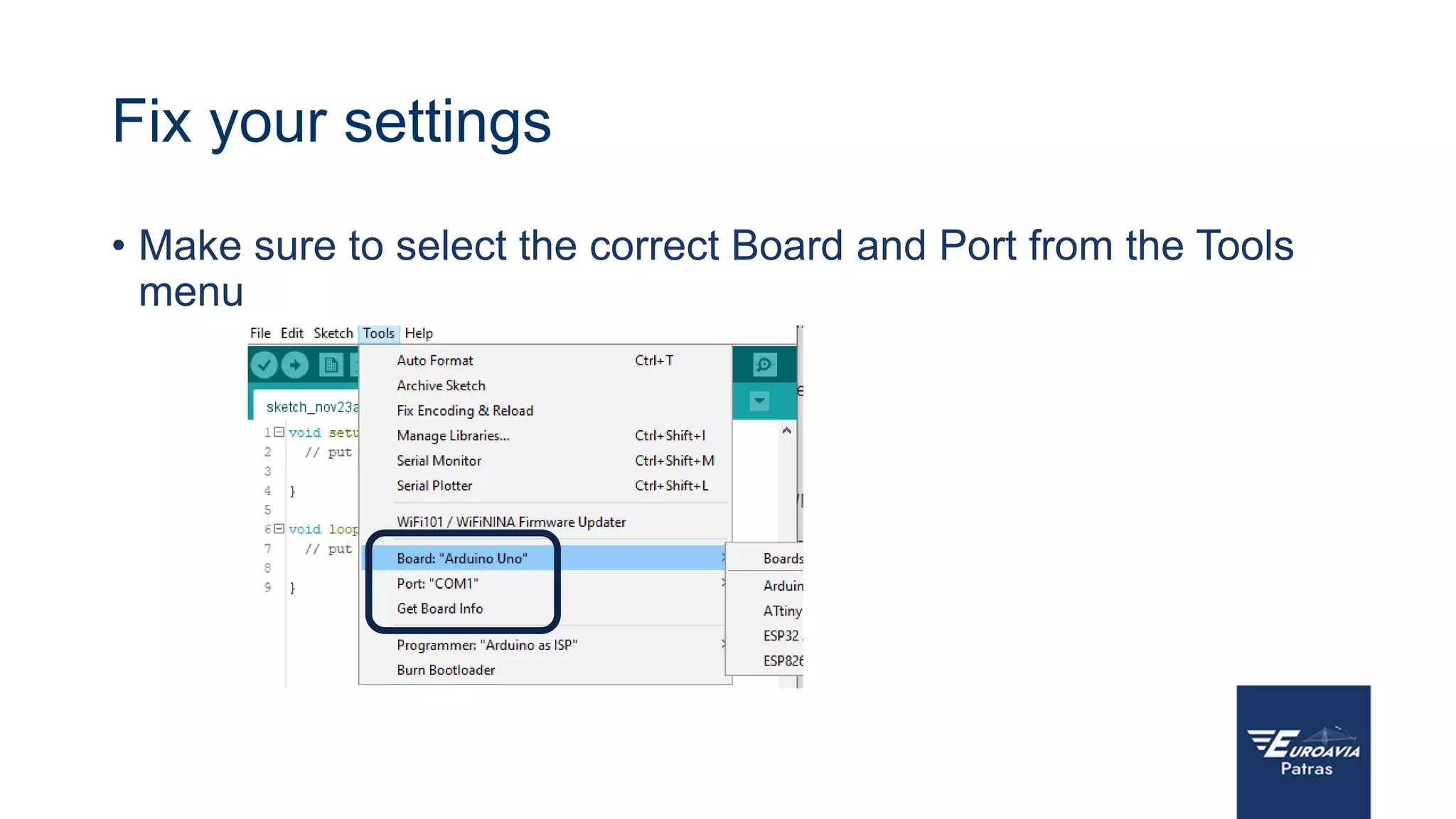
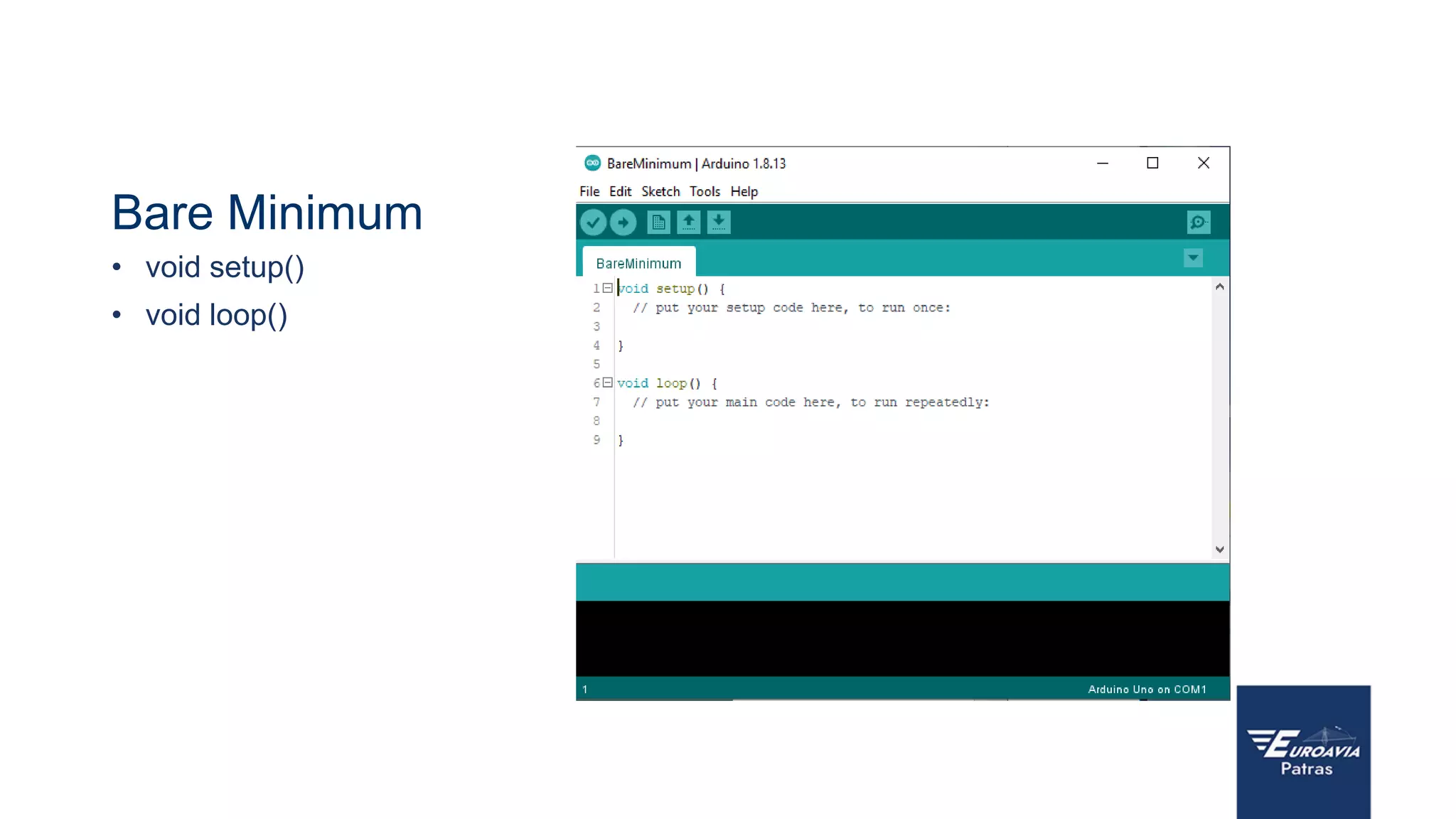
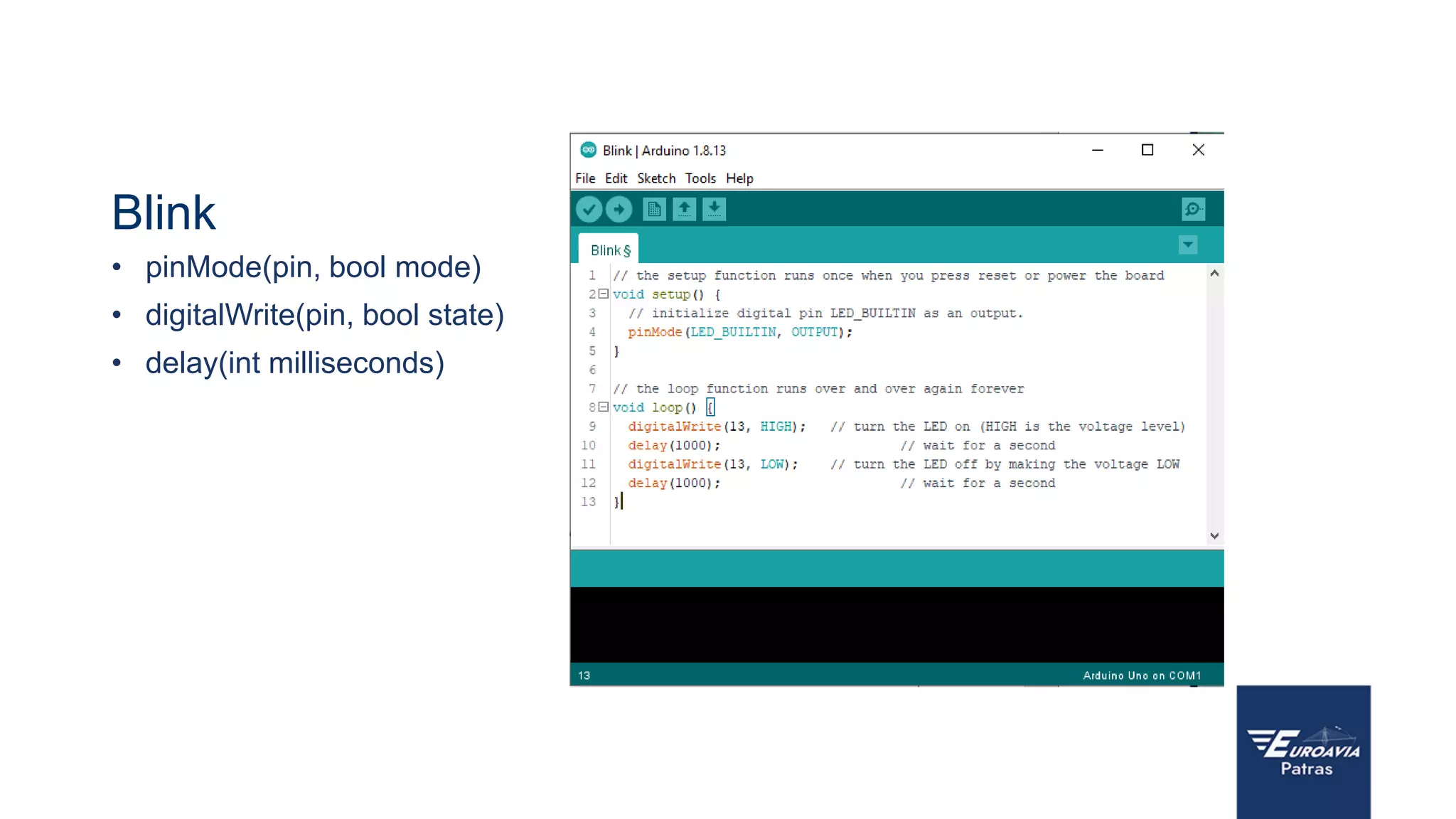
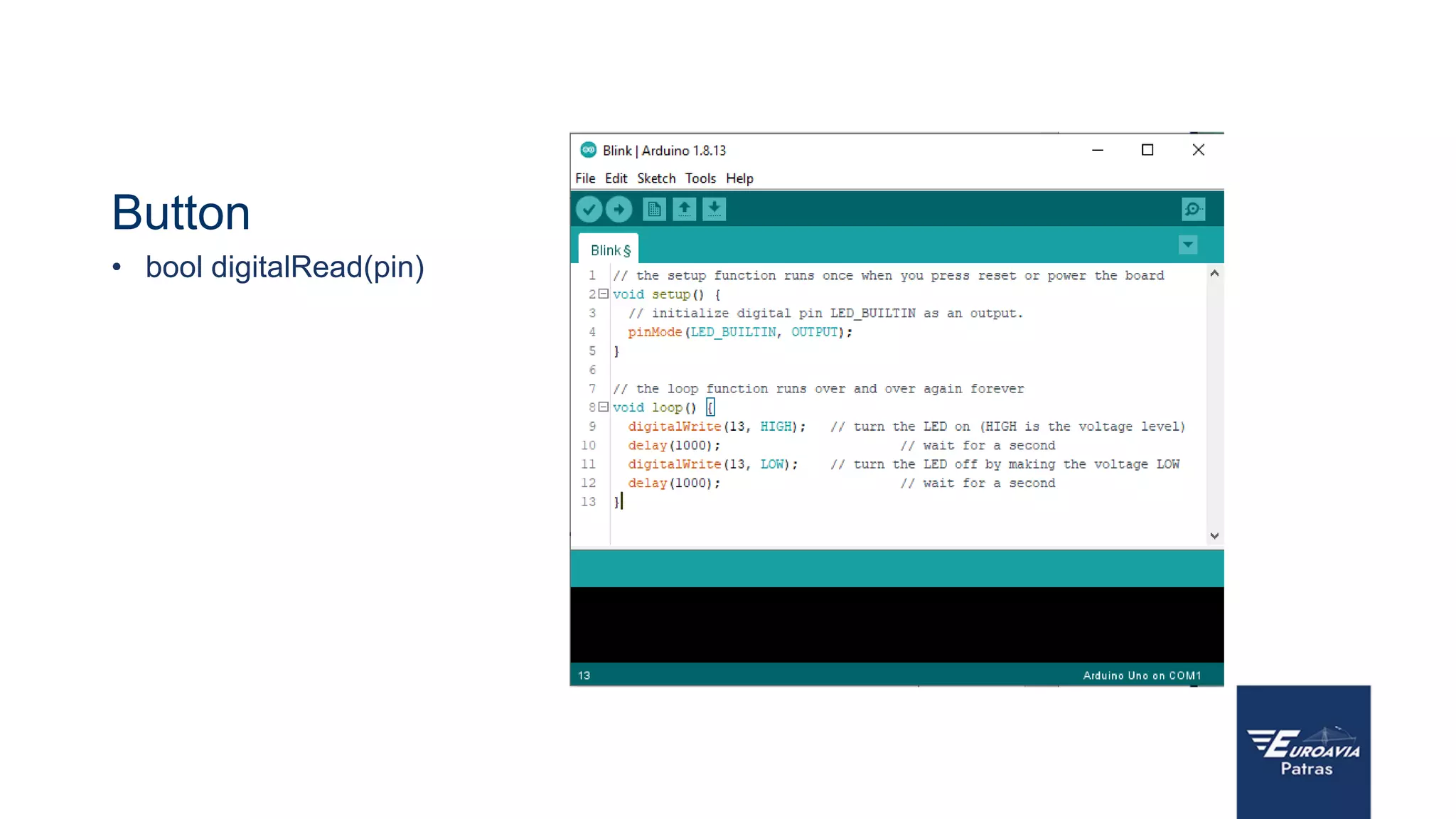
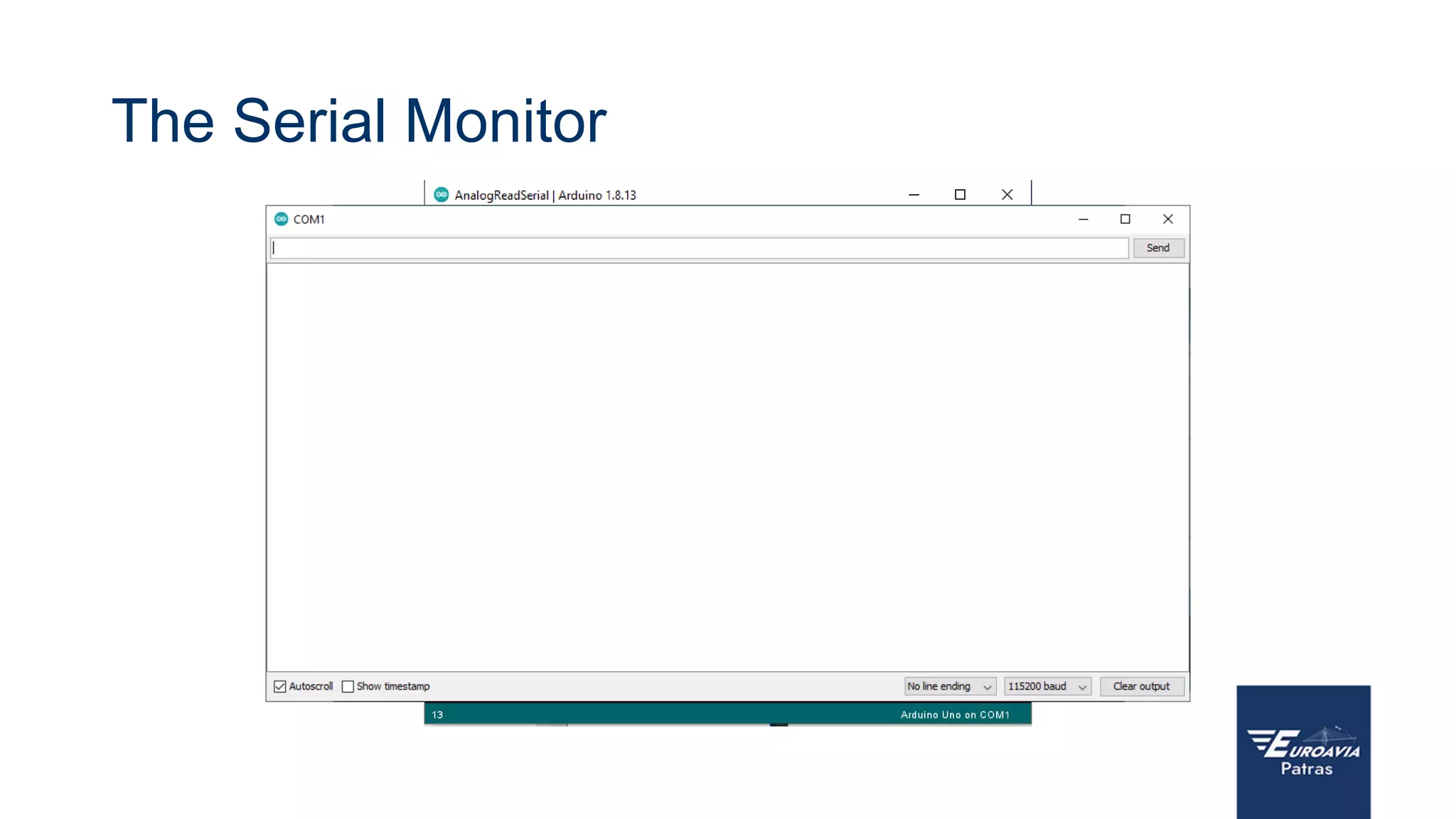
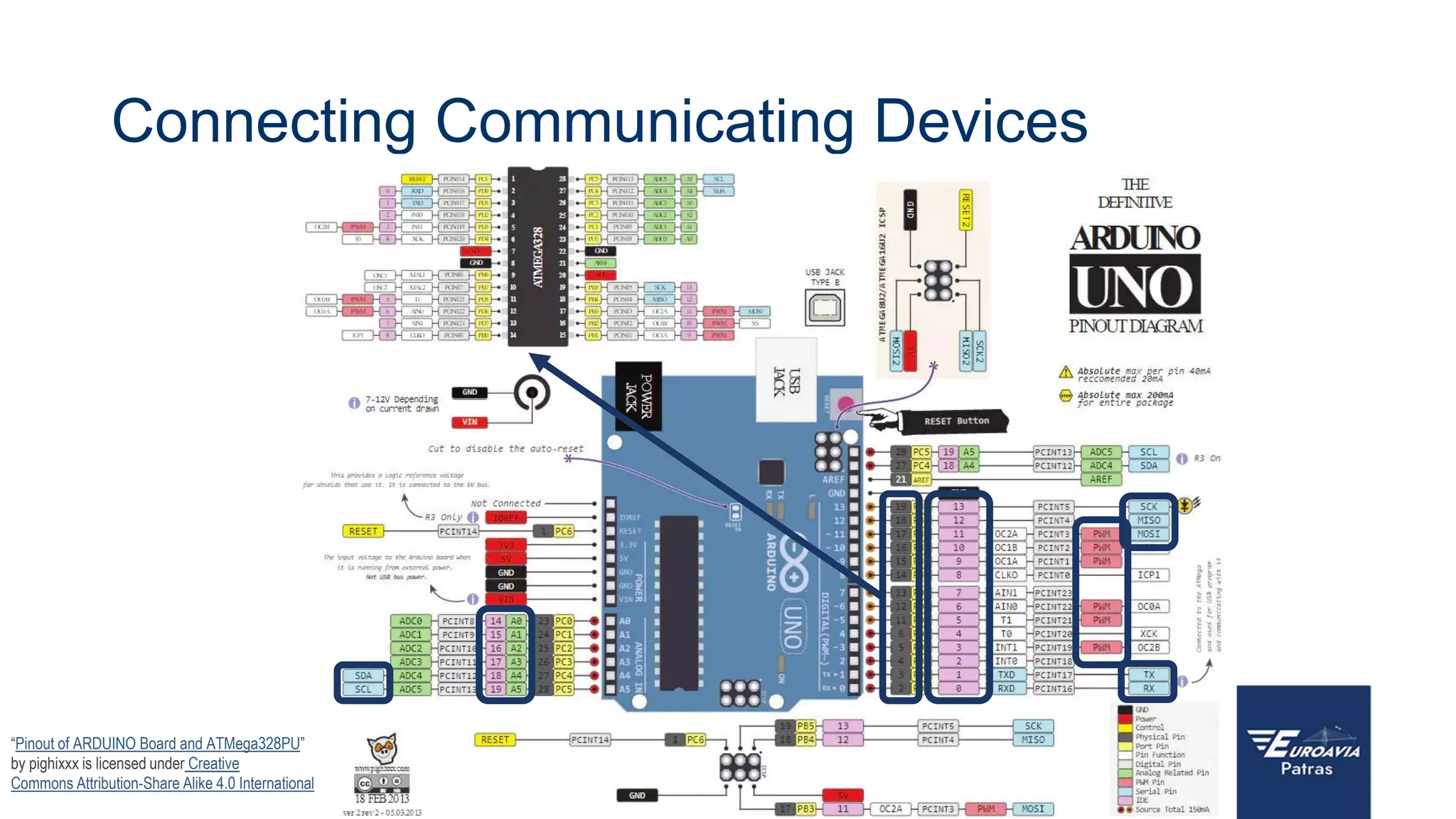
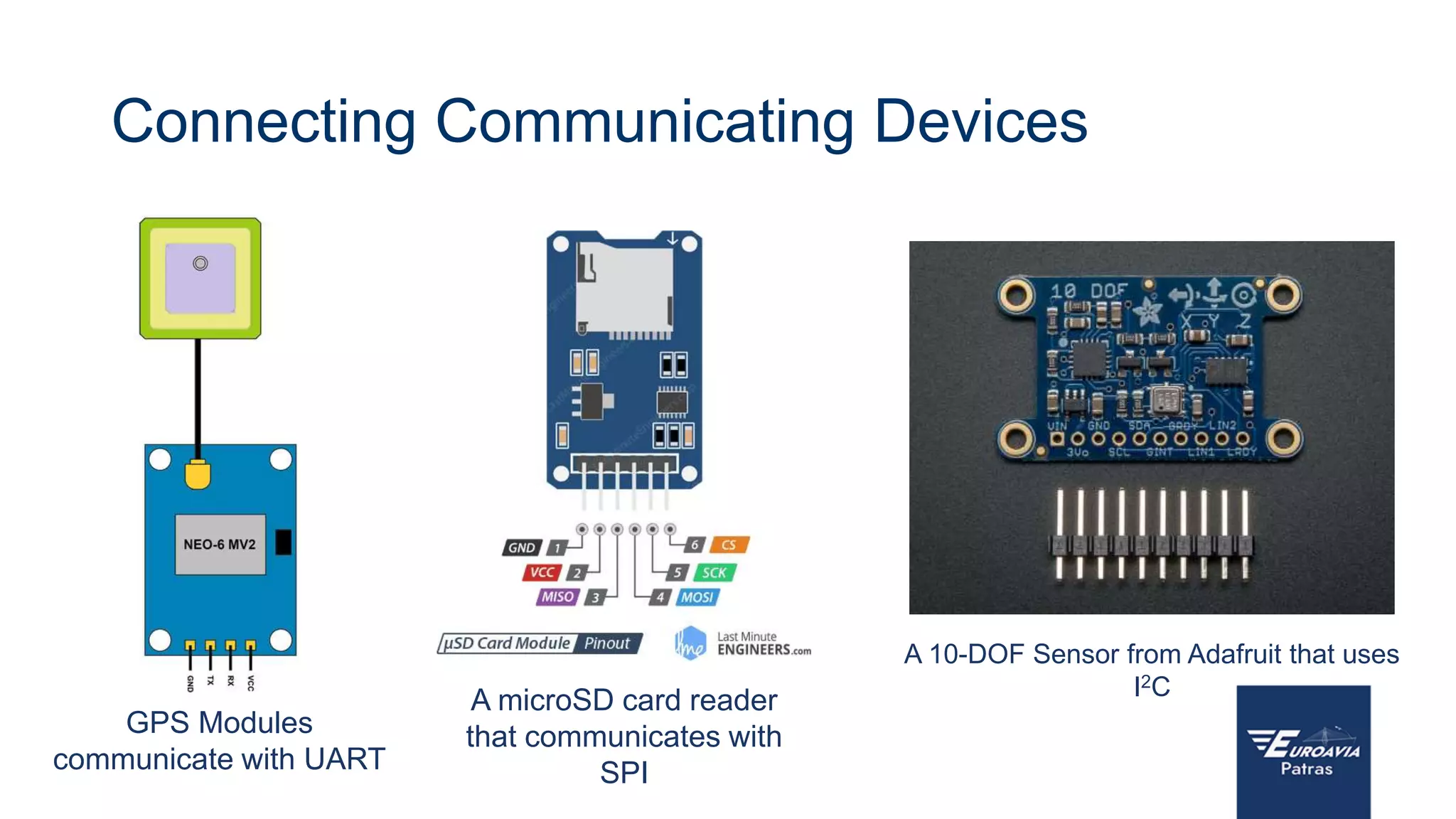
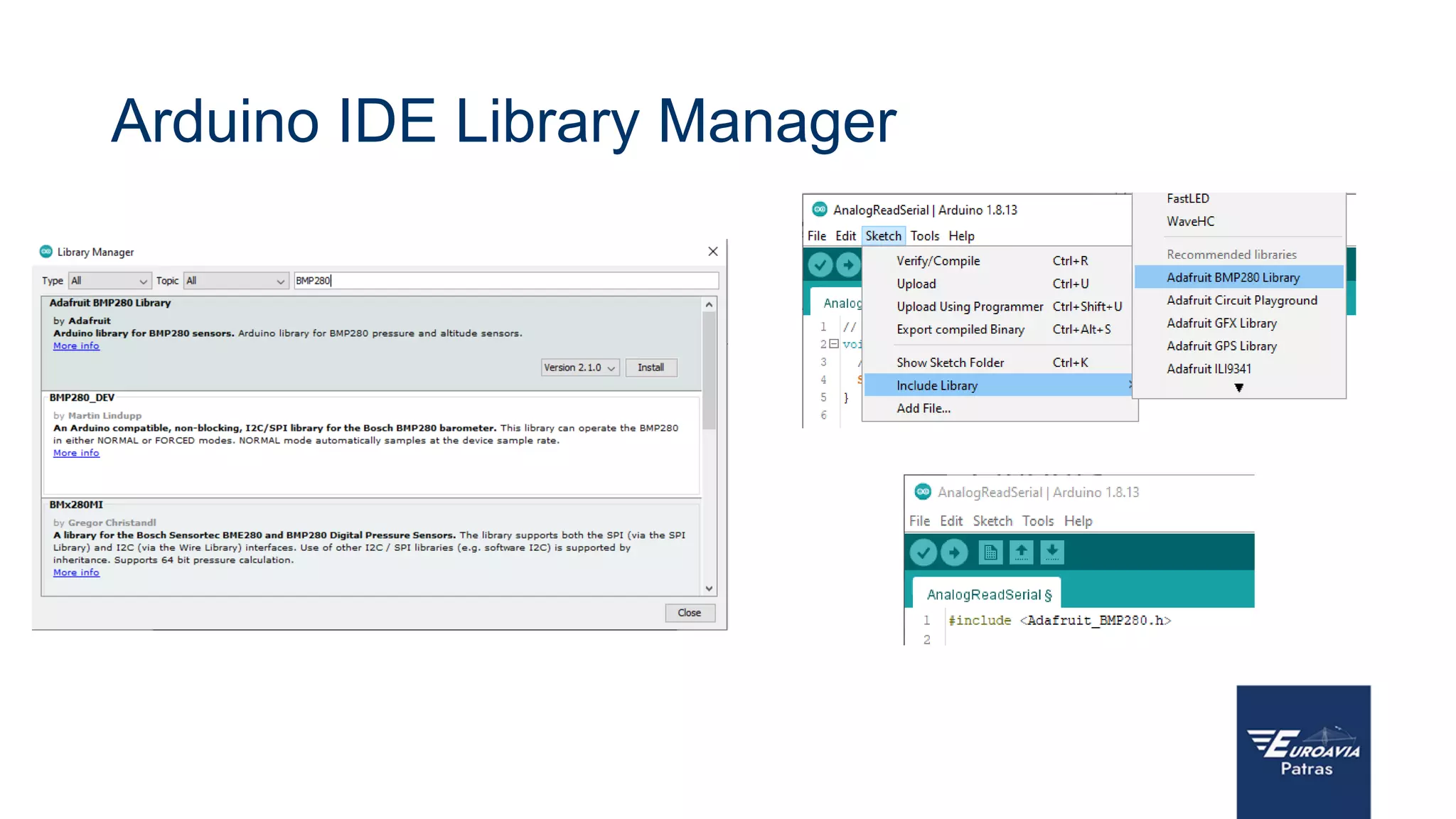
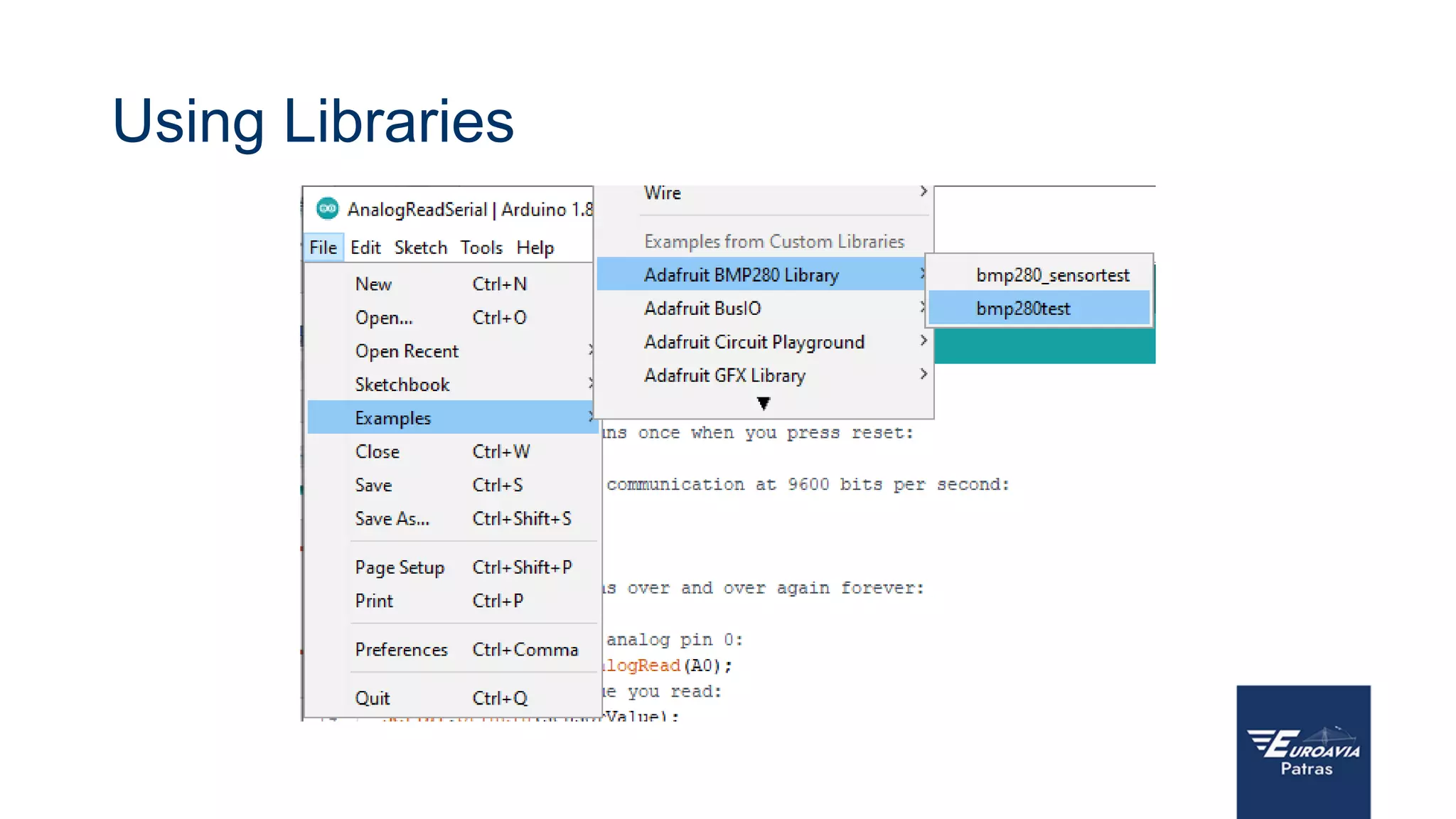
The document serves as an introduction to Arduino, outlining its hardware capabilities and software functionalities, as well as the benefits of learning to use it. It covers essential concepts such as digital and analog I/O, Arduino board types, and basic programming in C++. Additionally, it provides resources for learning and examples of practical applications related to Arduino projects.