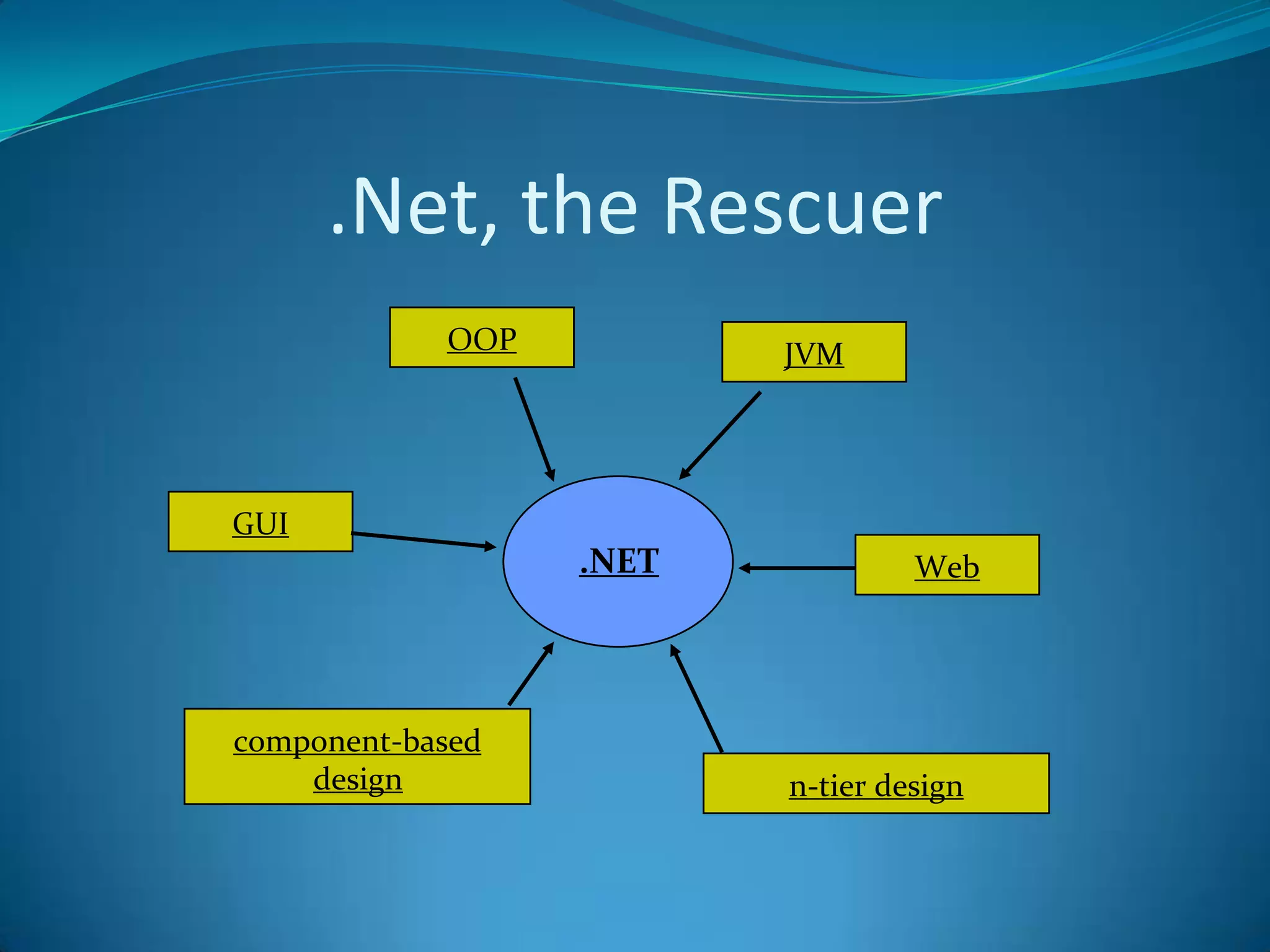
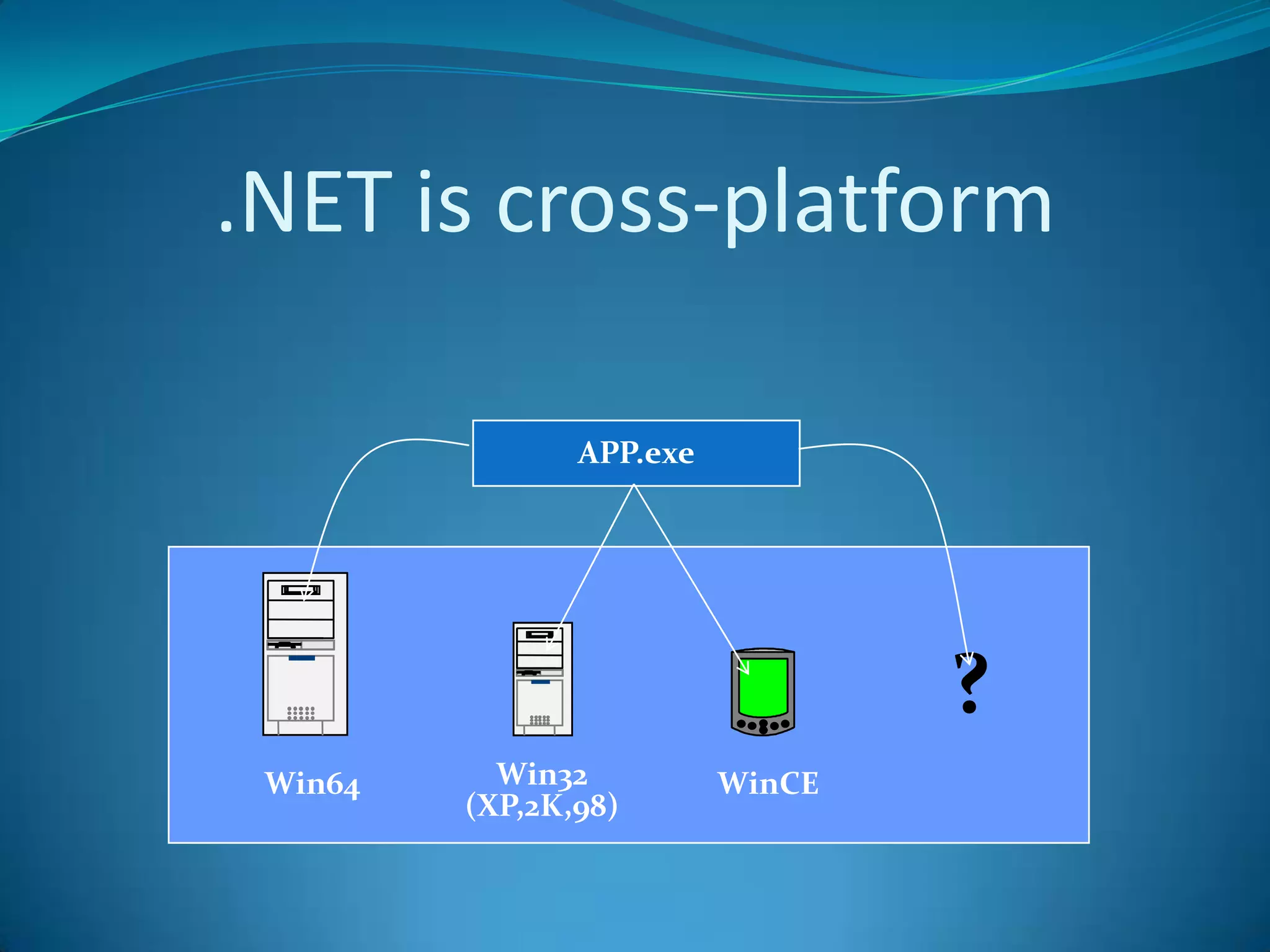
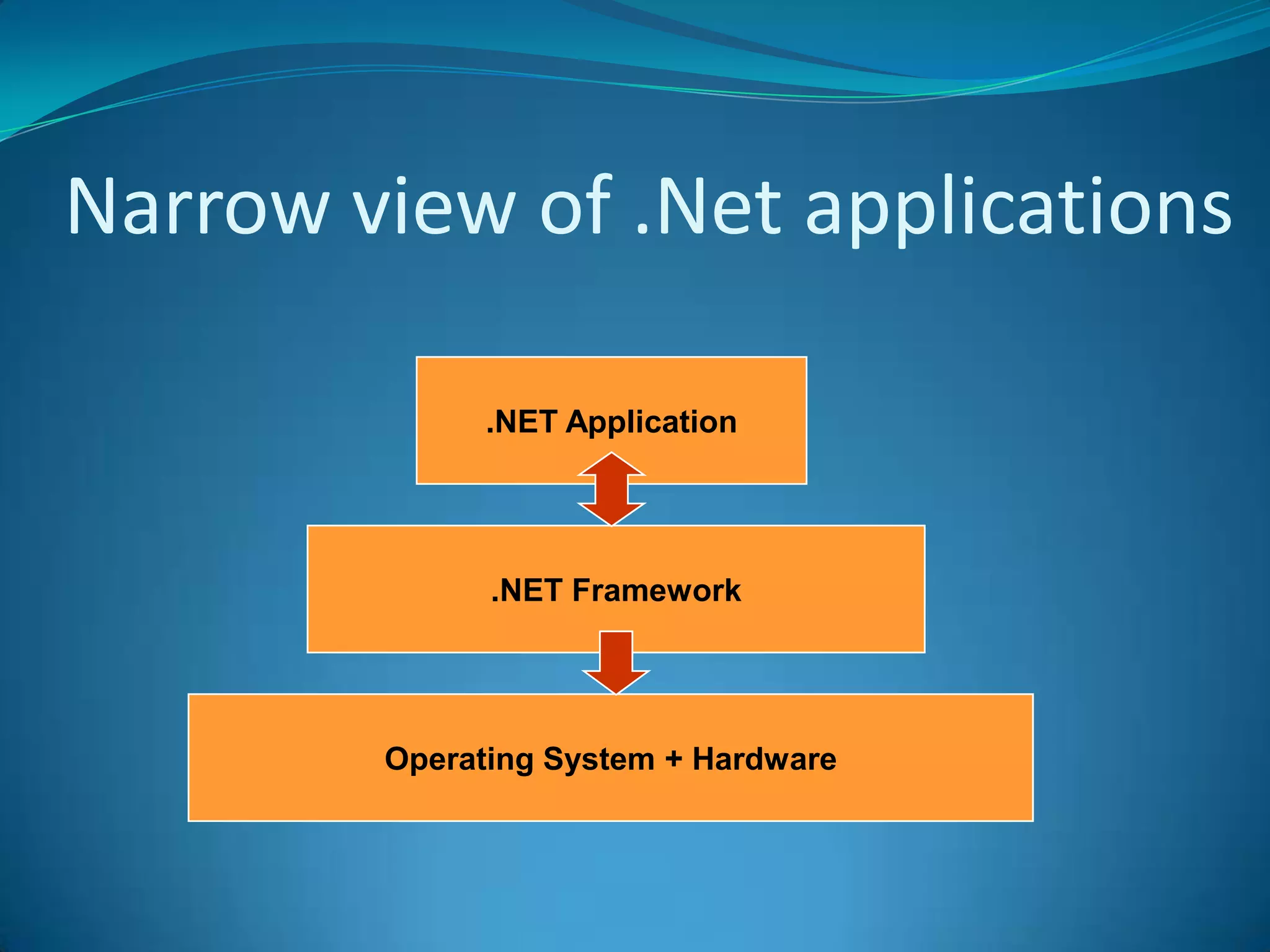
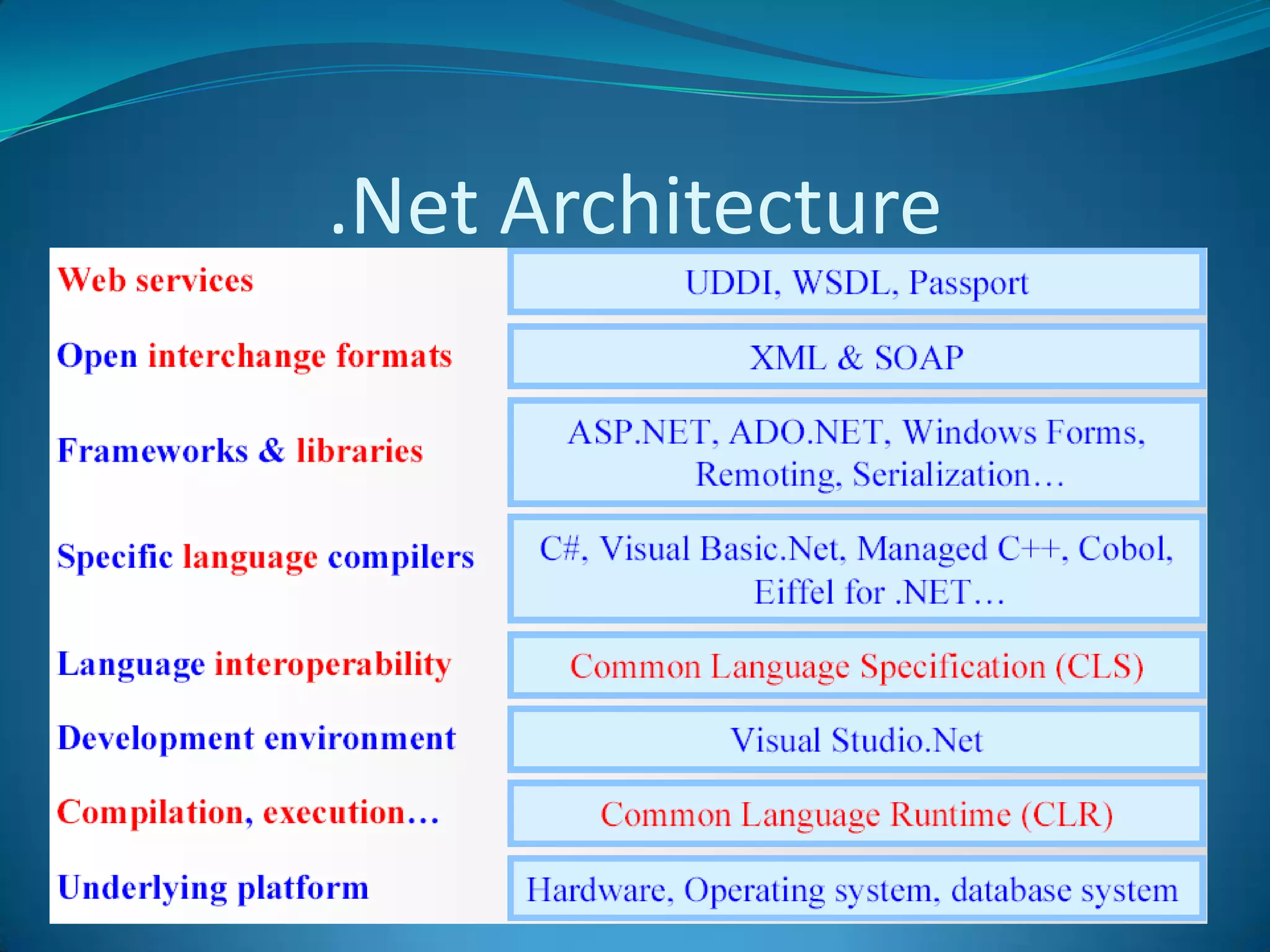
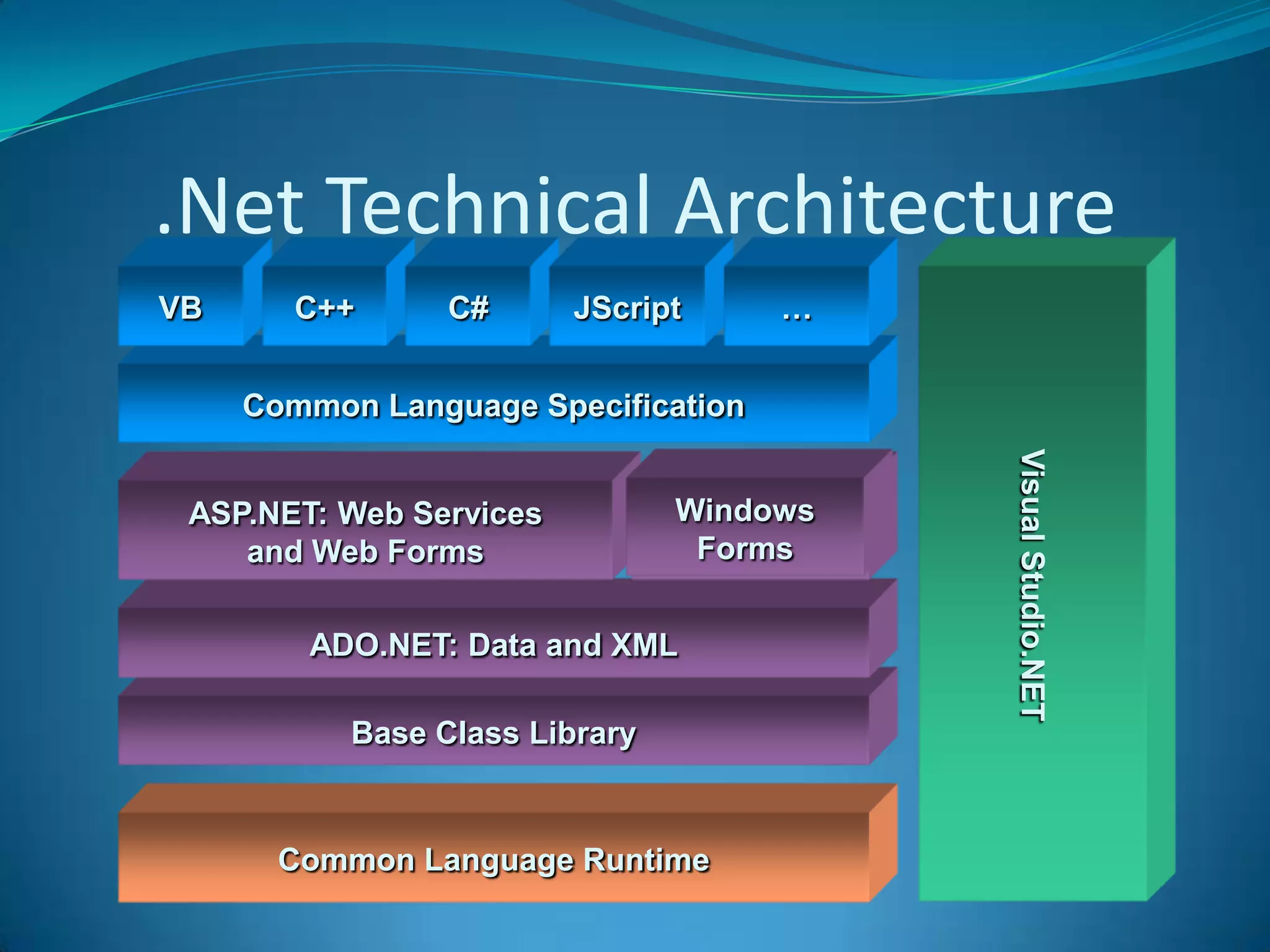
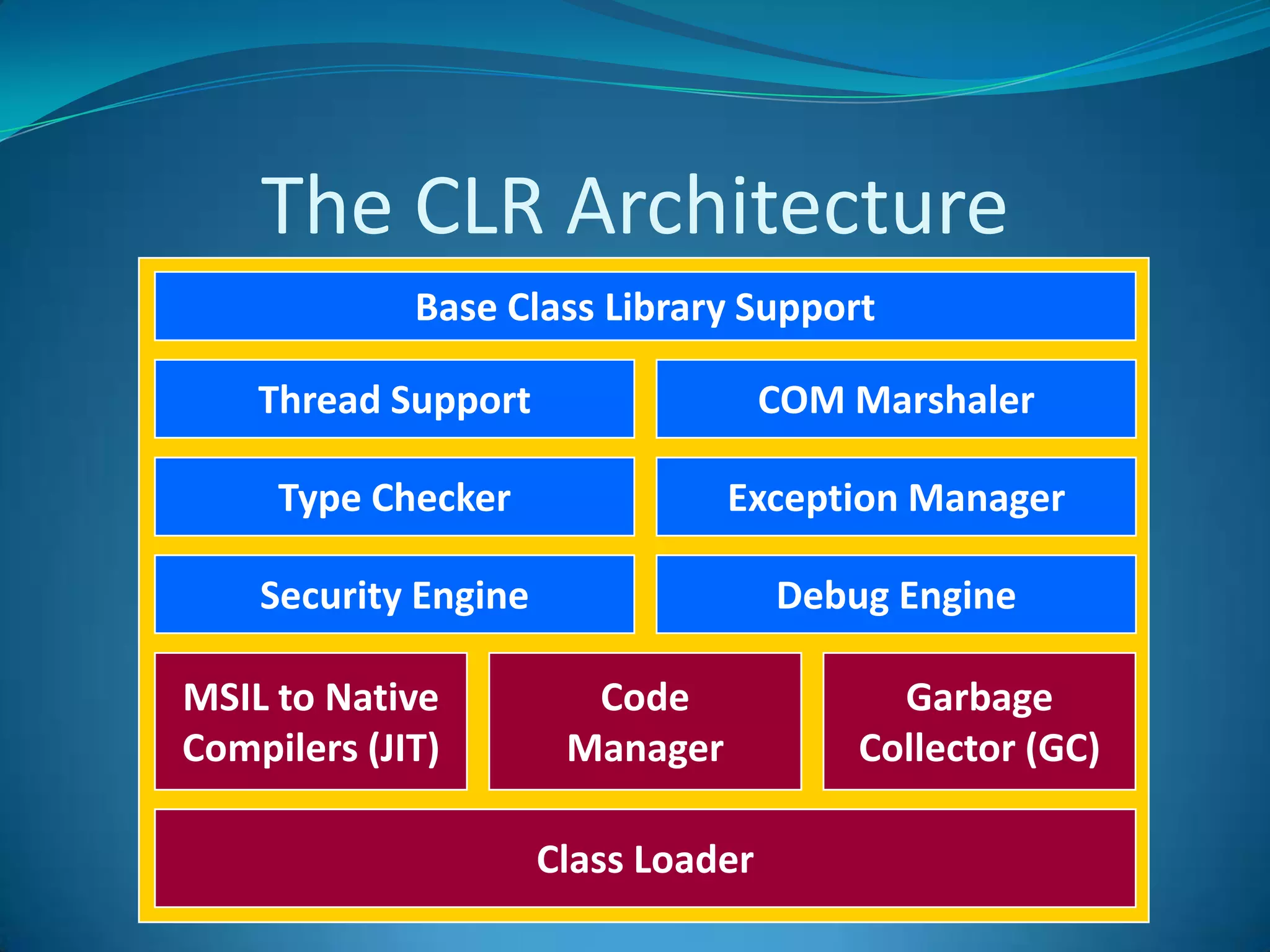
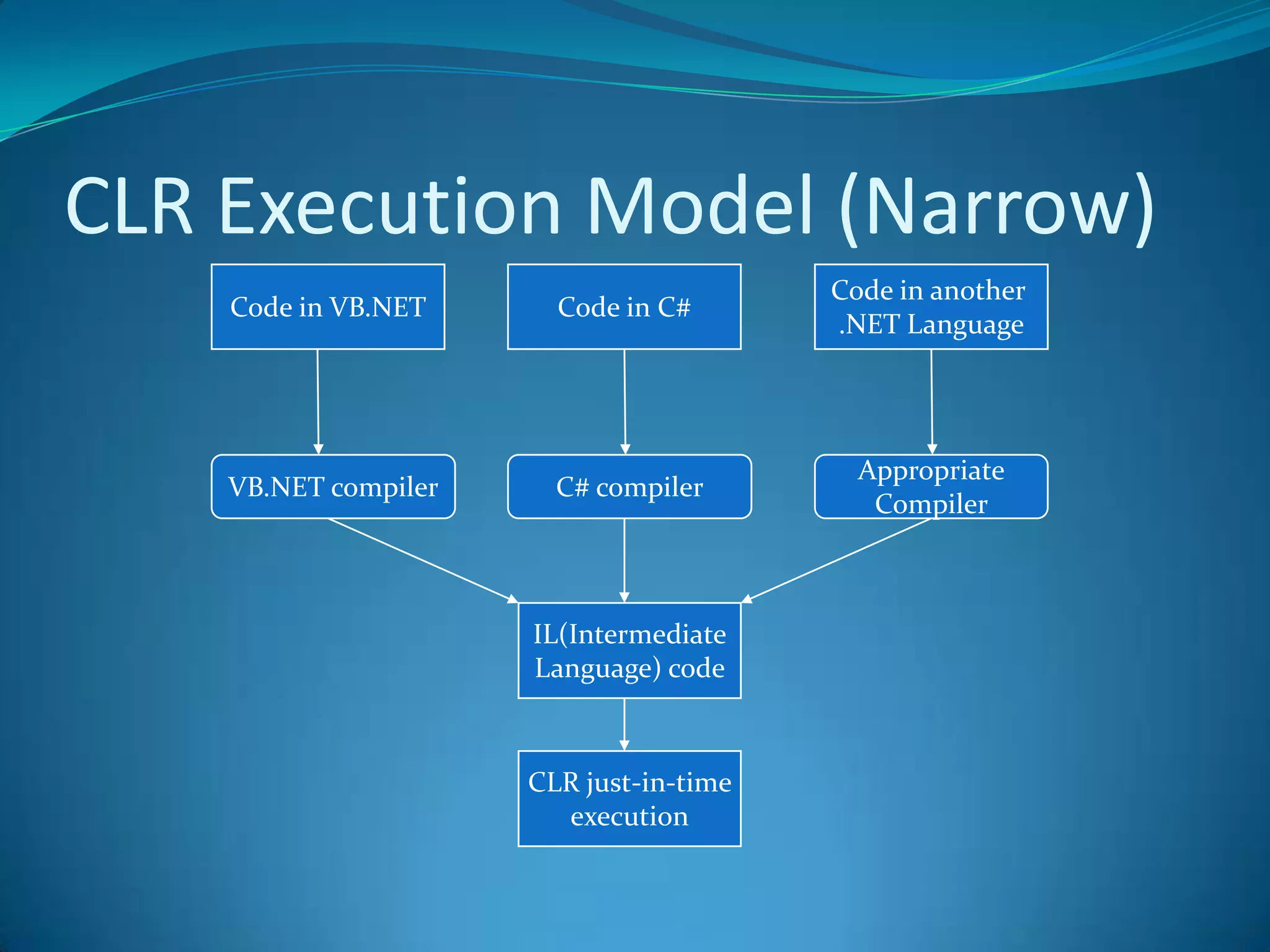
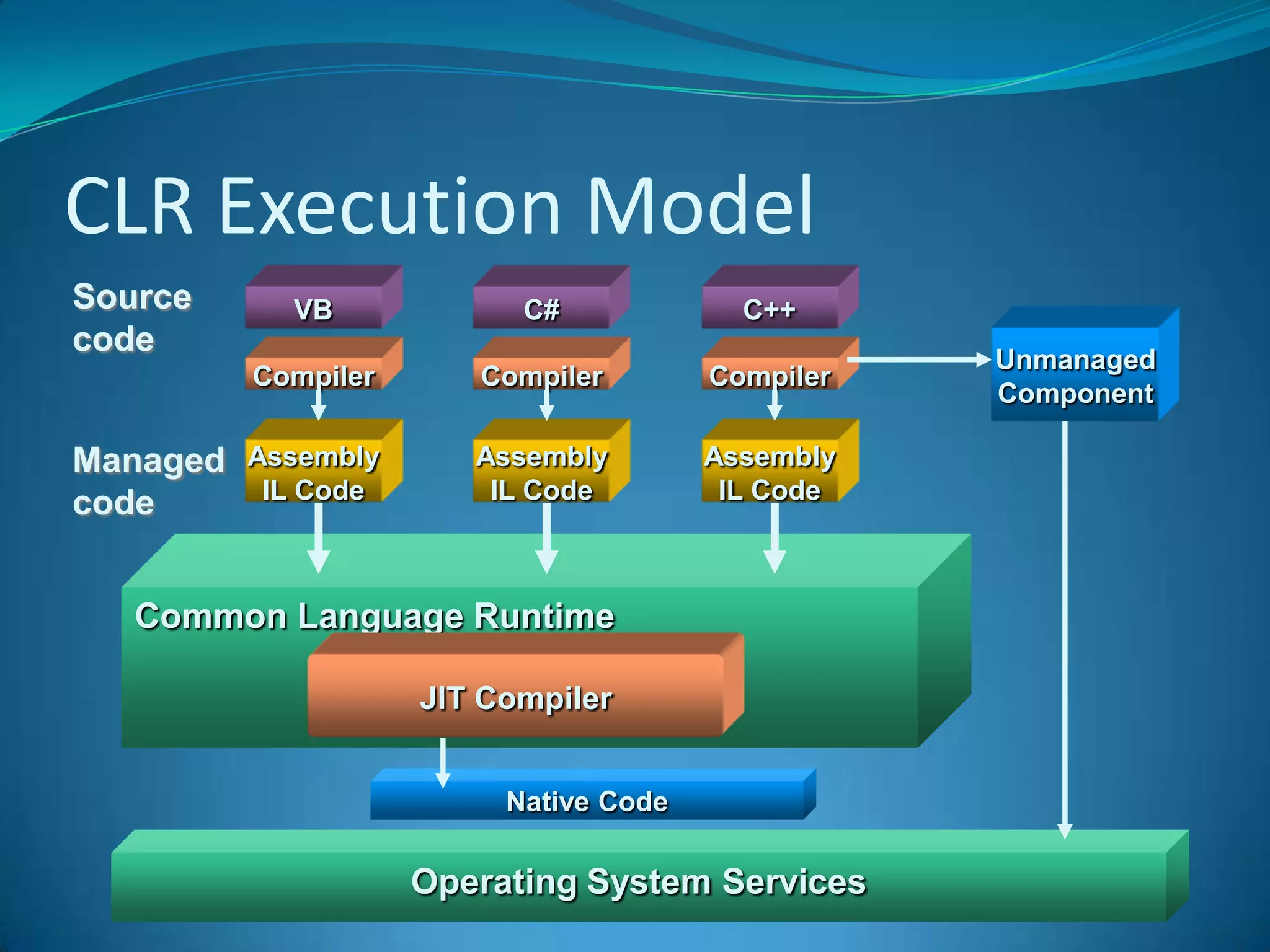
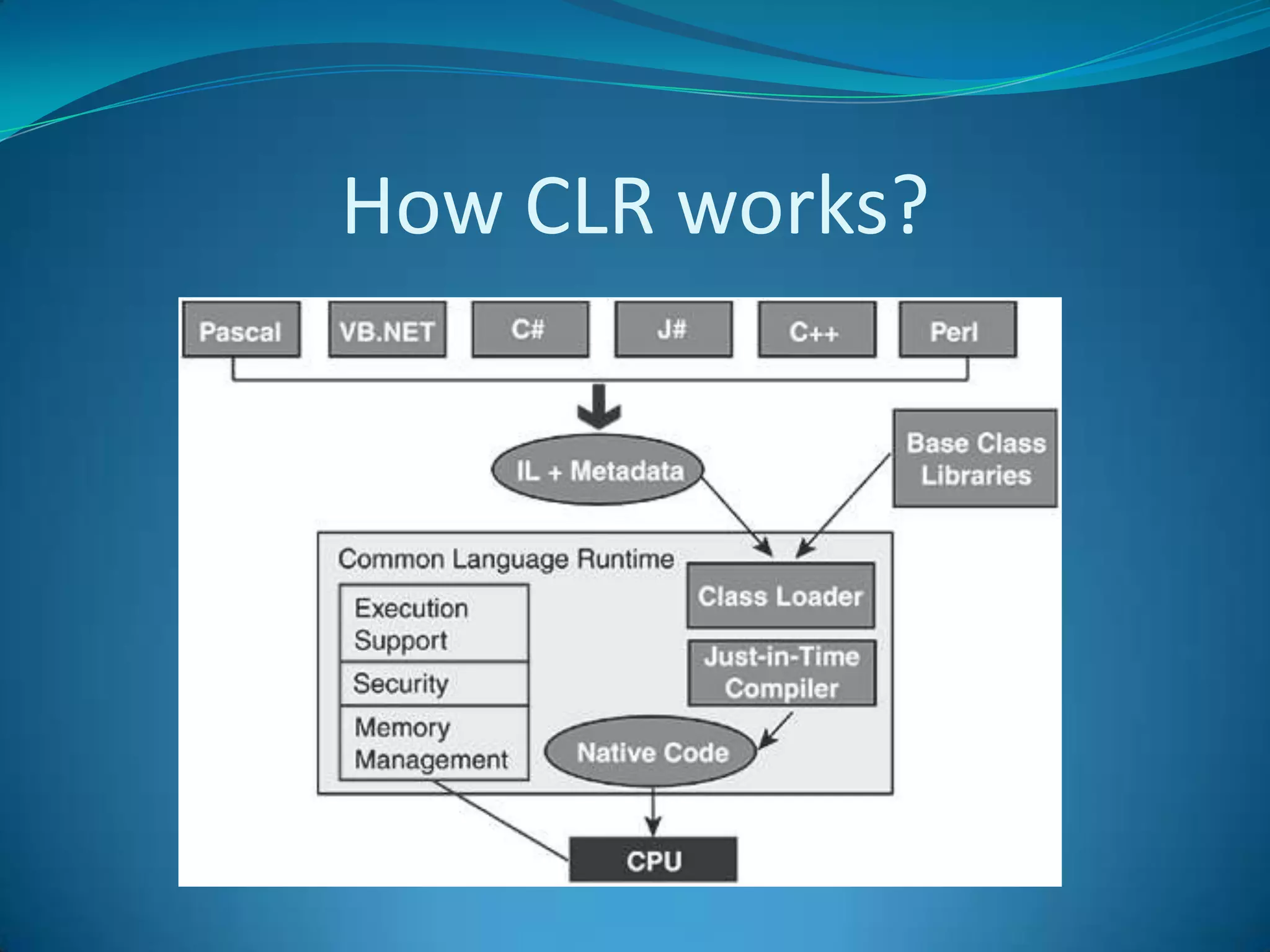
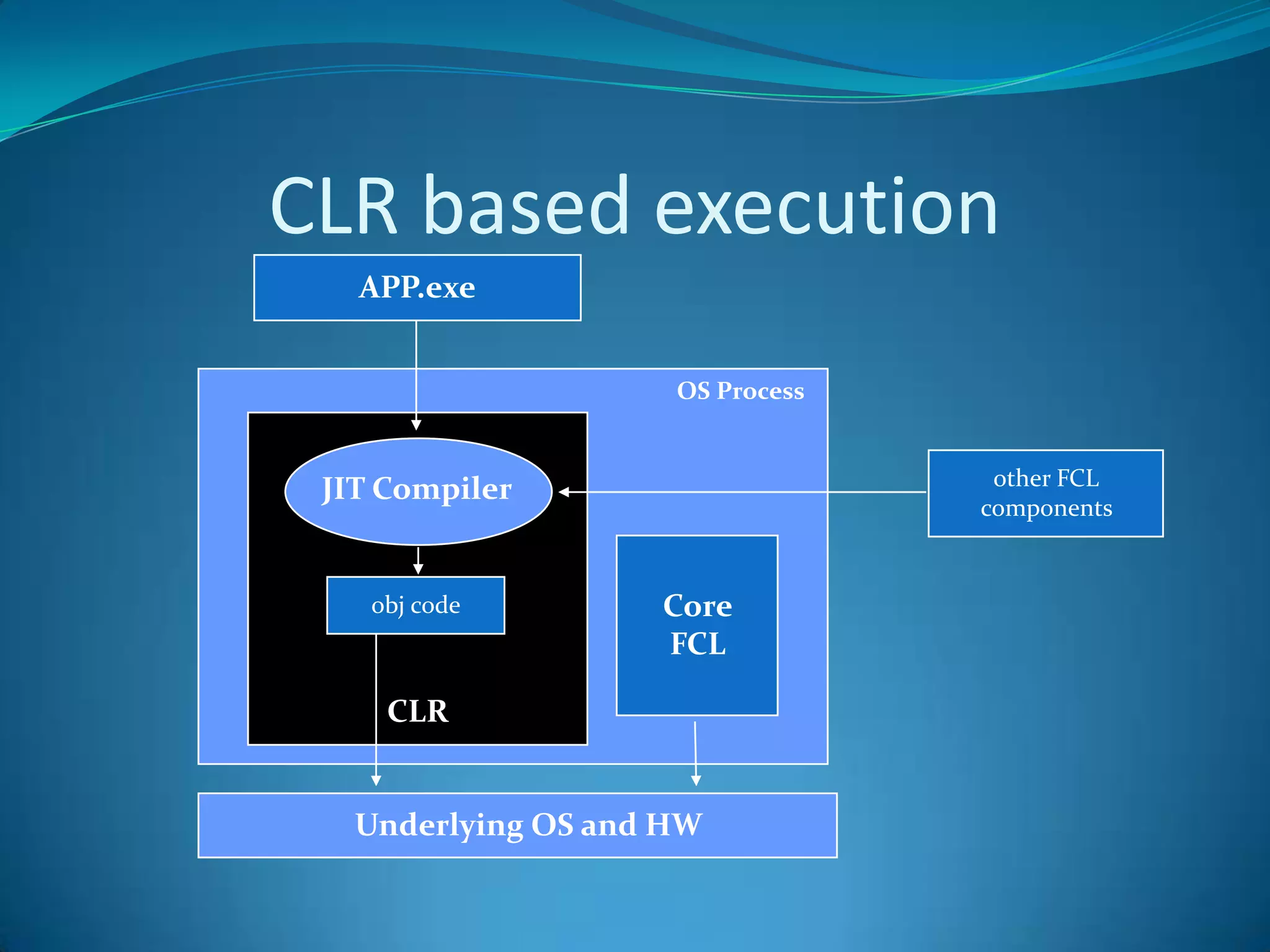
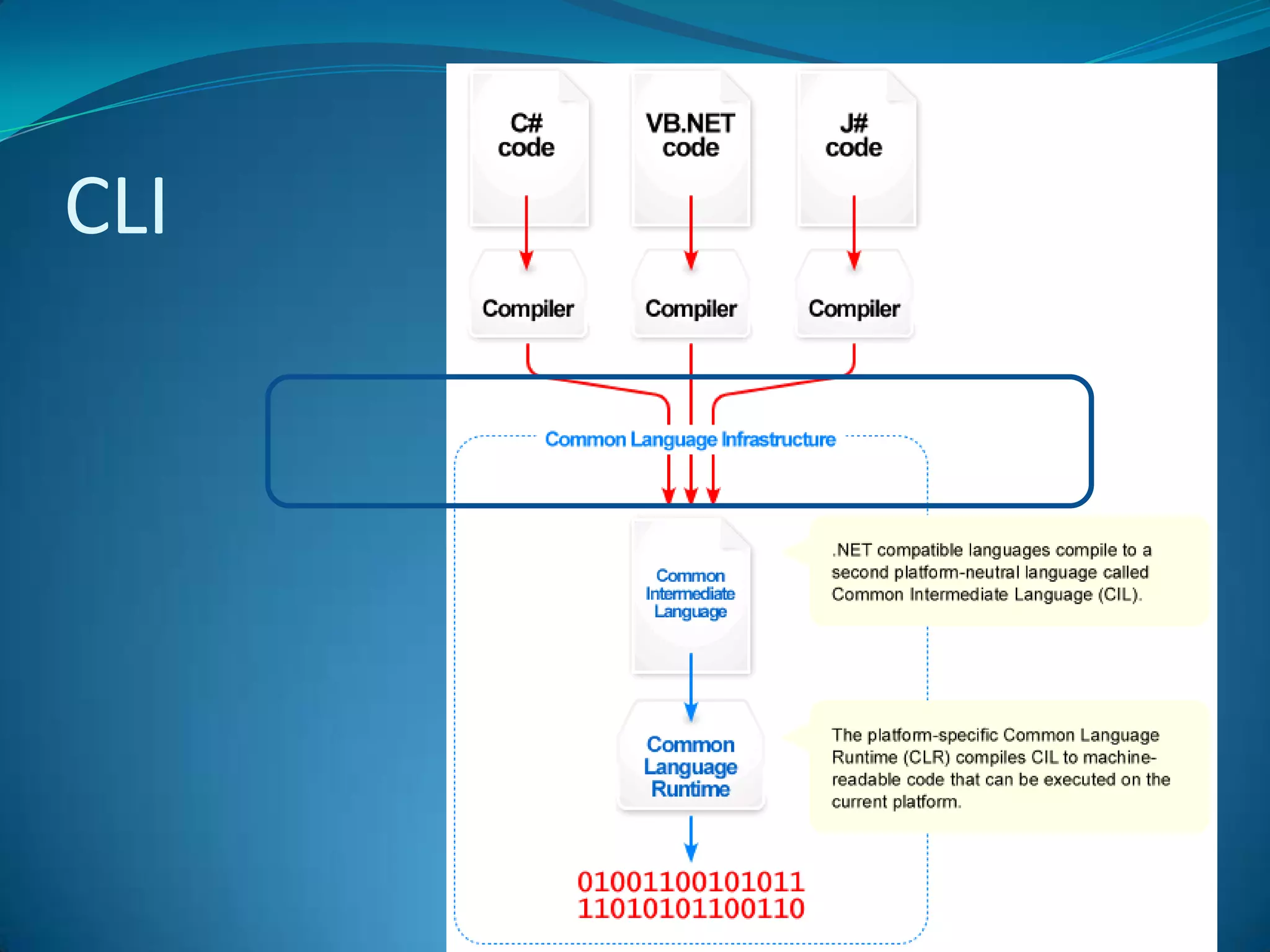
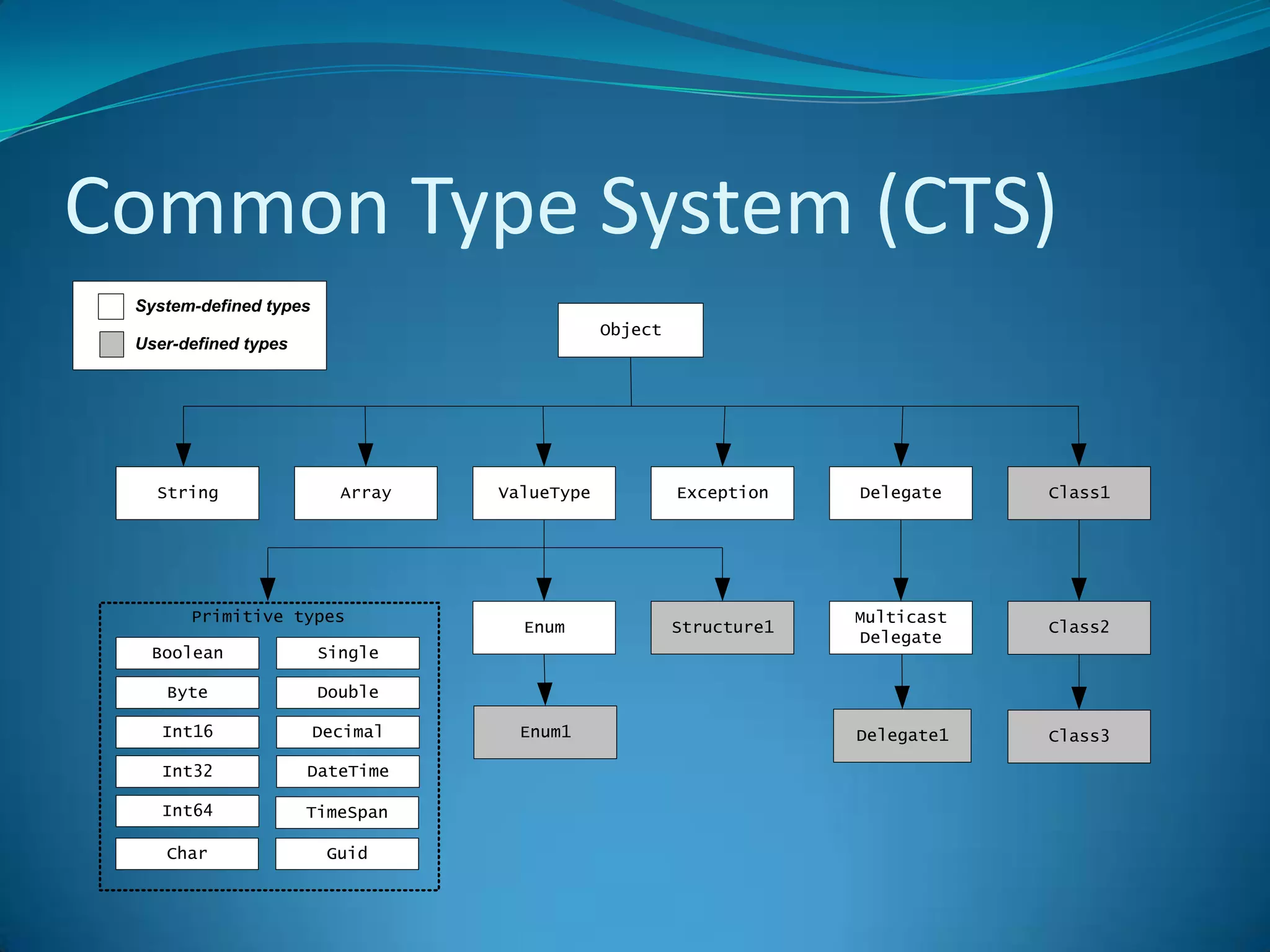
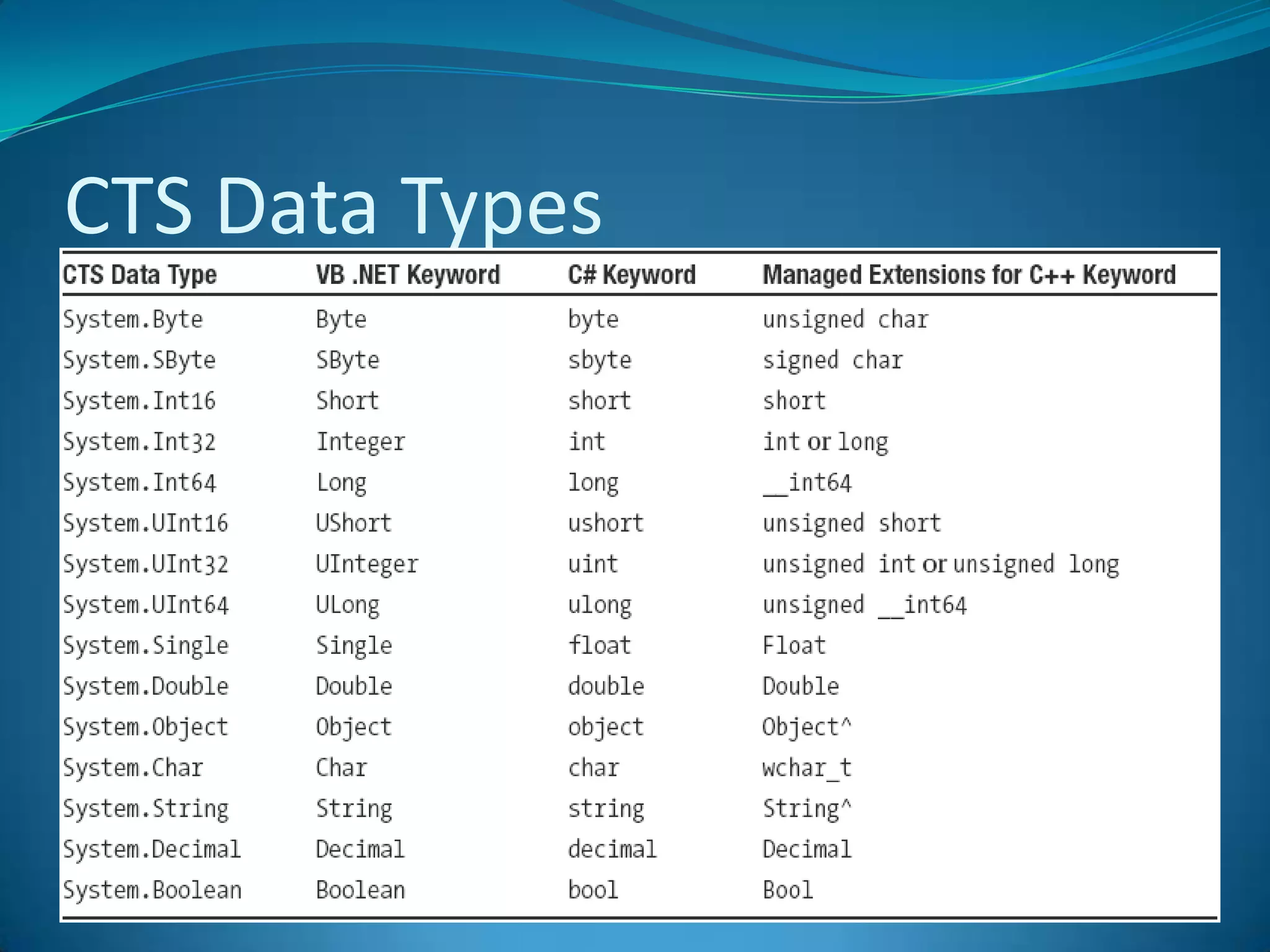
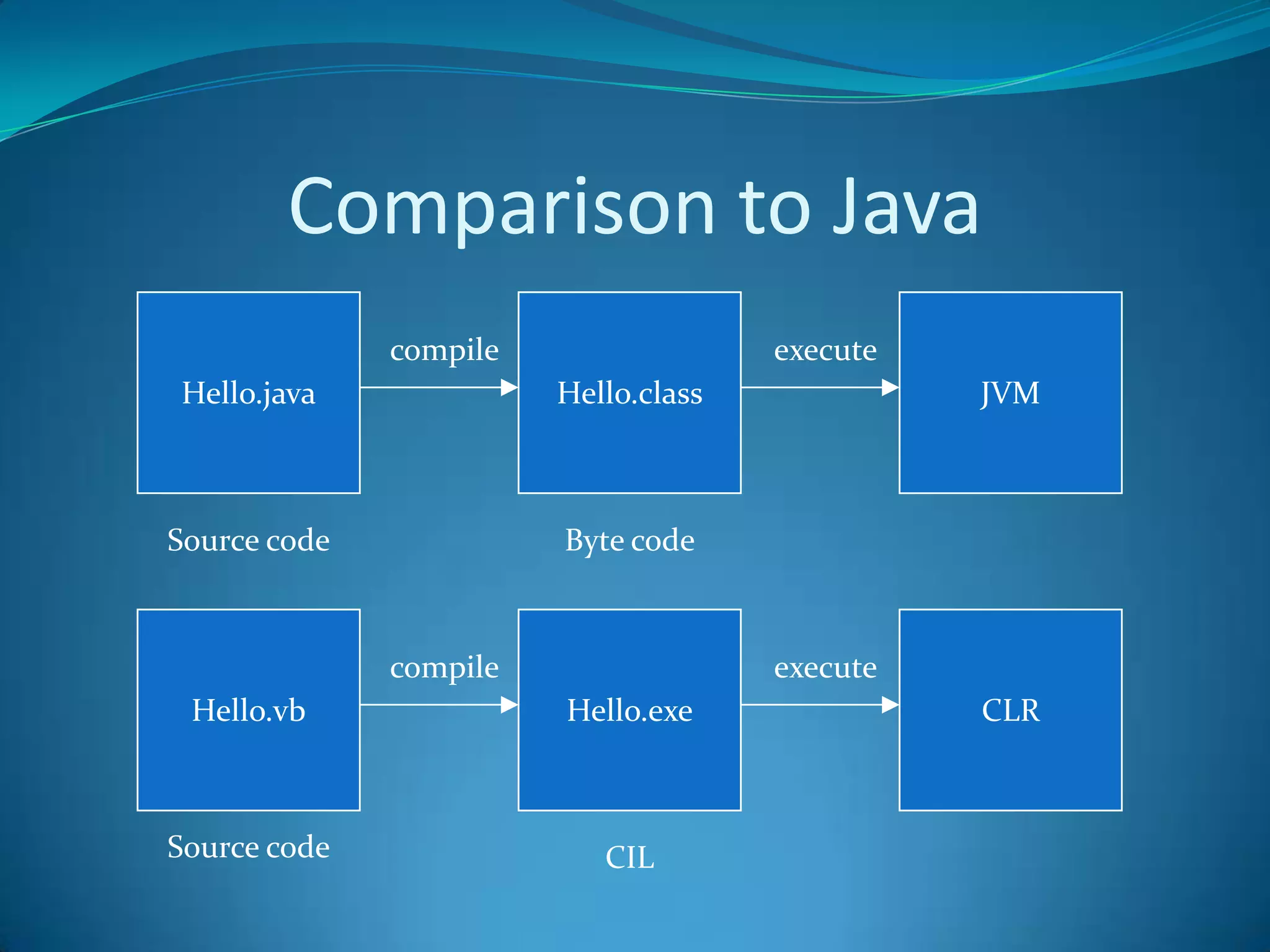
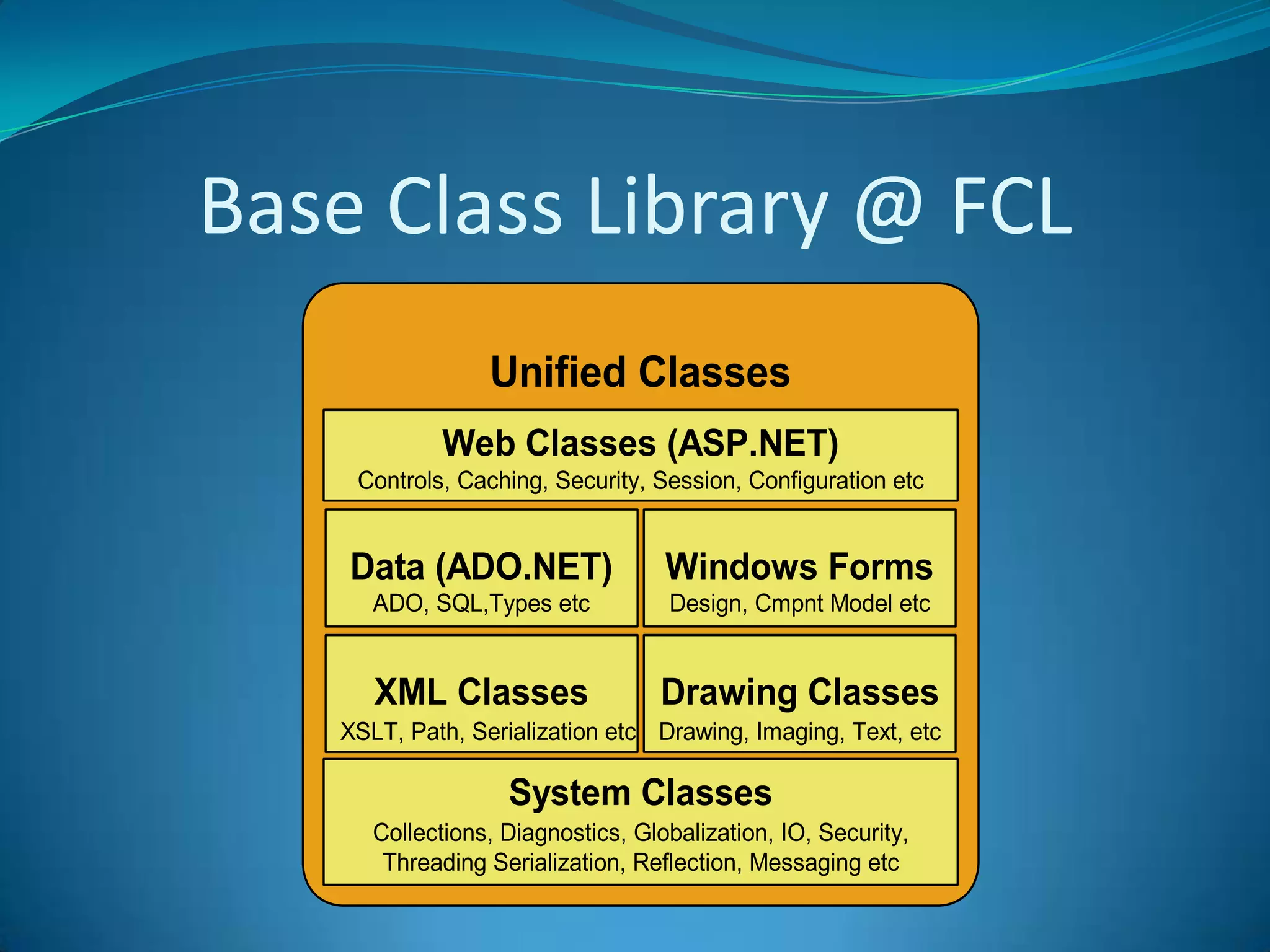
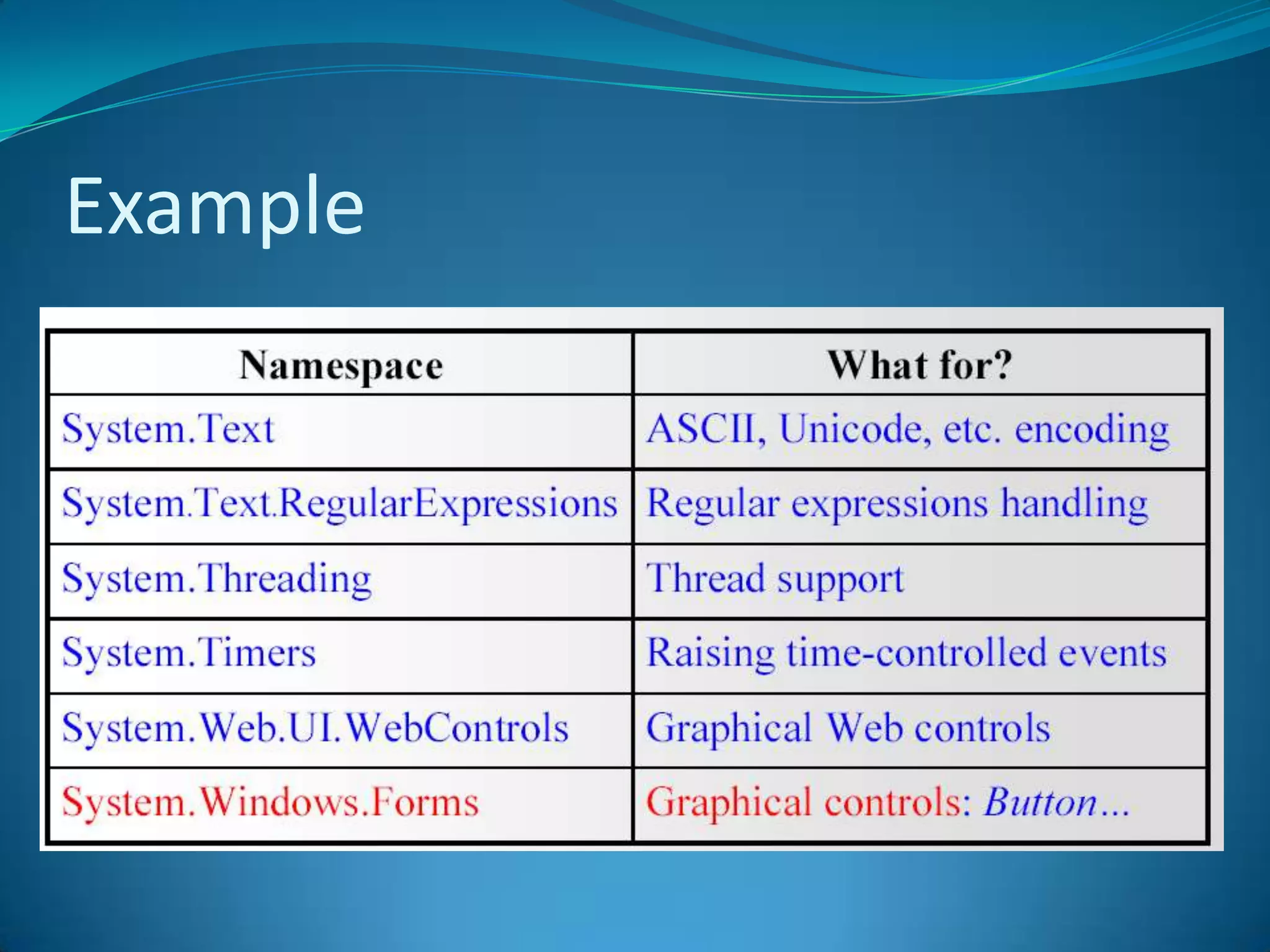
.NET is a versatile and managed programming framework that allows for cross-platform development and integrates various programming languages. It offers a common runtime environment that handles language interoperability, memory management, and security features while simplifying complex coding practices inherent in previous programming methods. This document compares traditional programming challenges with those solved by .NET, highlighting its architectural advantages such as the Common Language Runtime (CLR) and the Framework Class Library (FCL).