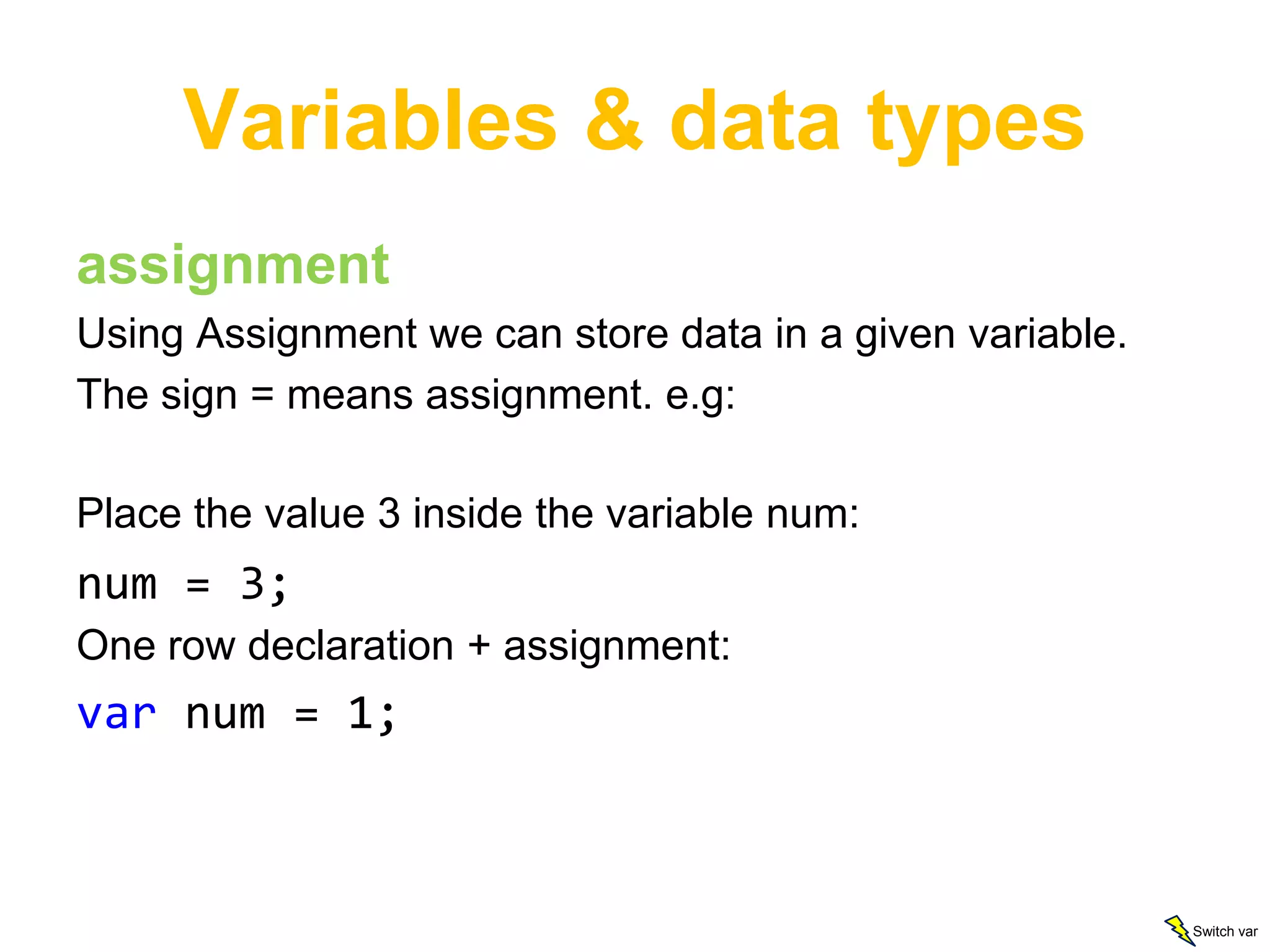
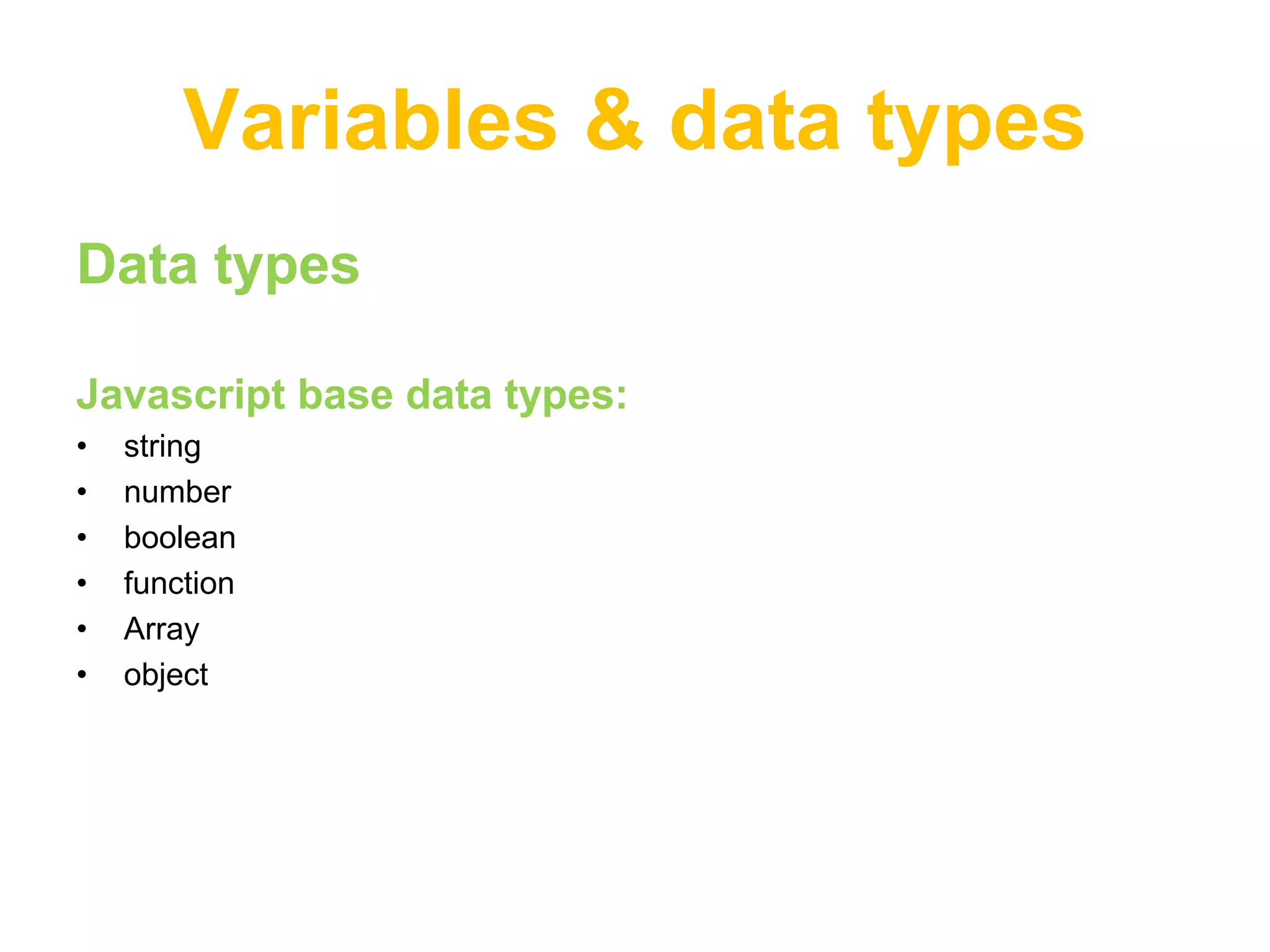
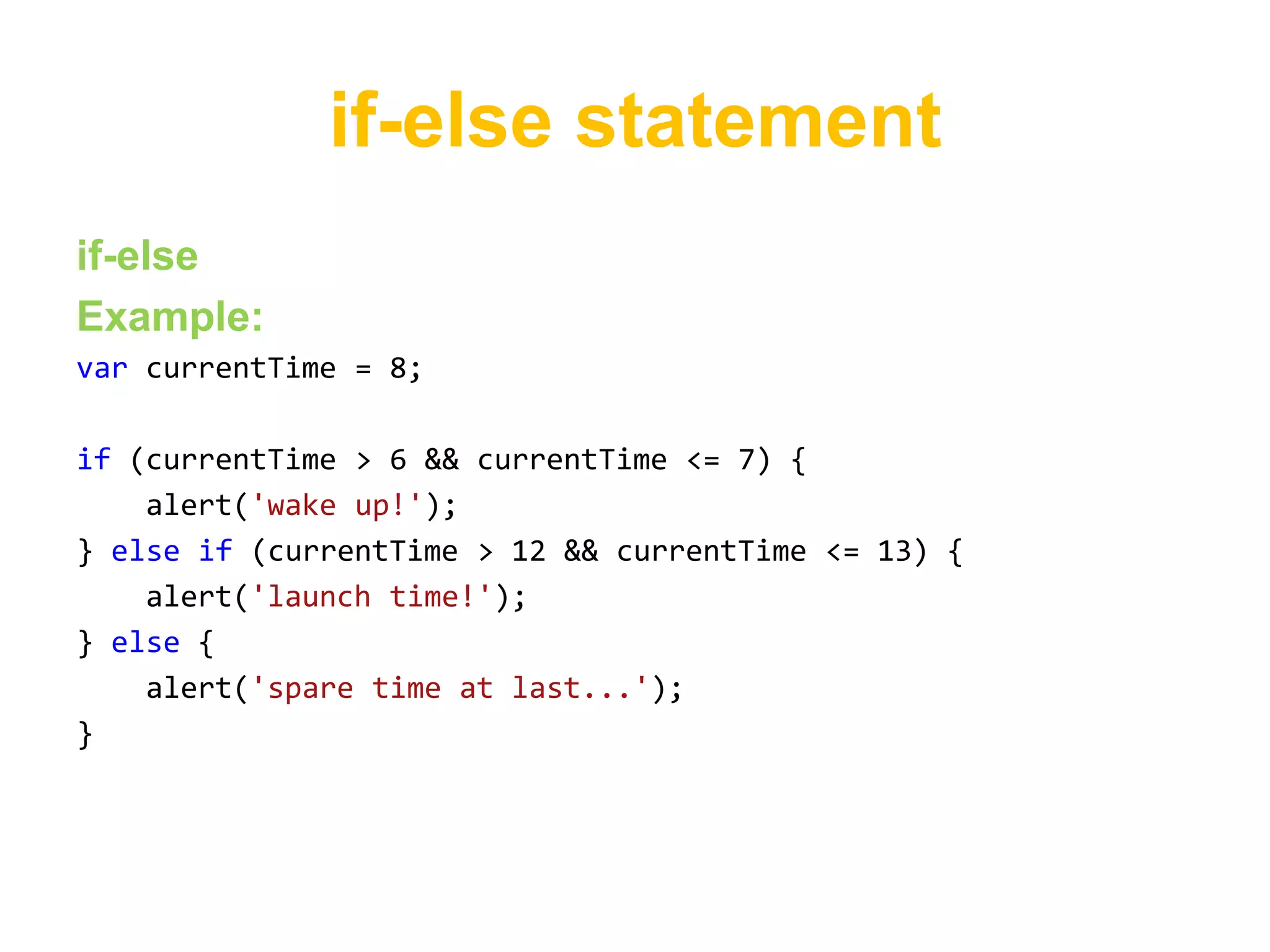
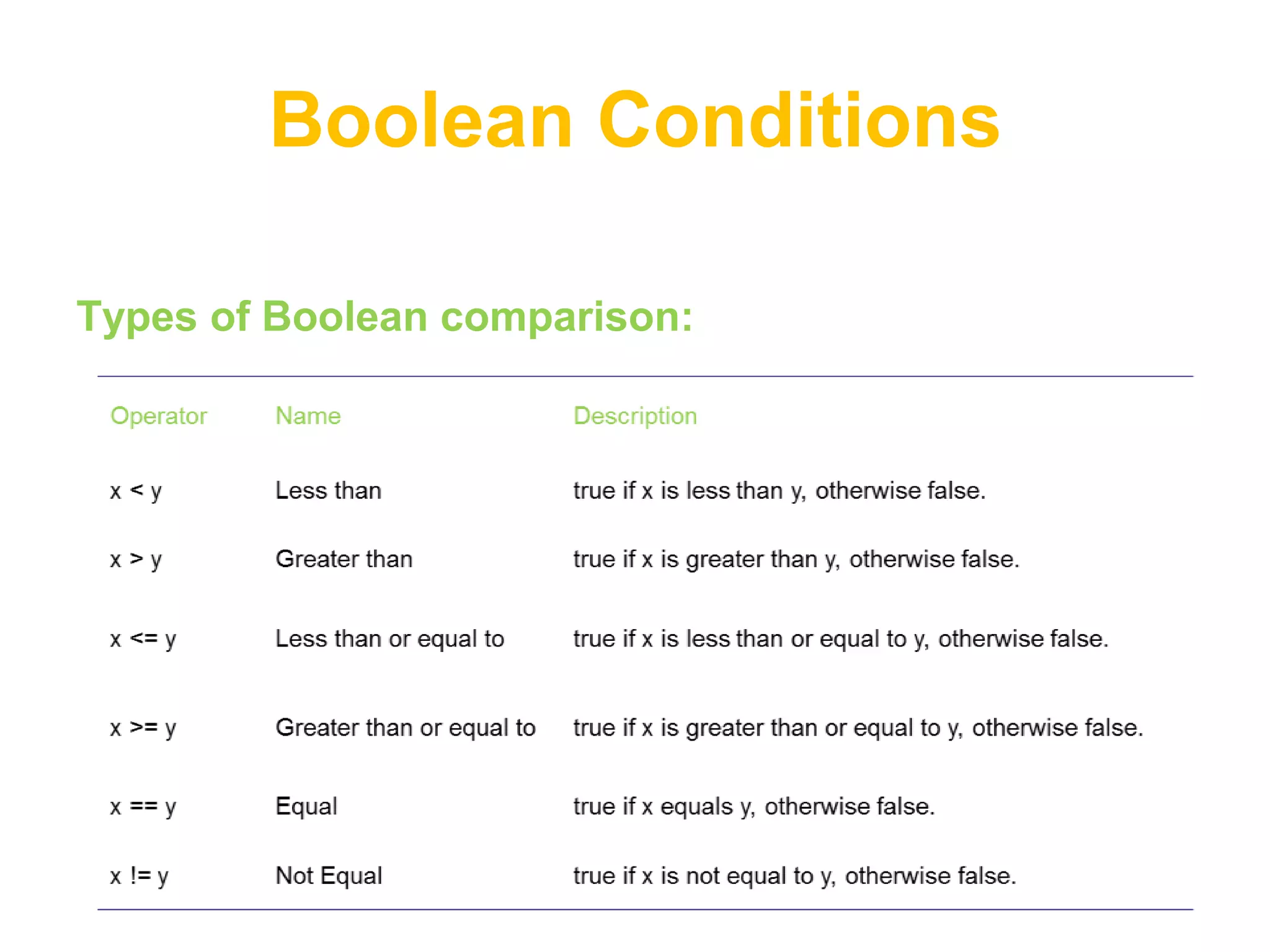
This document provides an introduction to JavaScript, covering basic concepts like data types, variables, operators, conditionals, loops, functions, arrays, and objects. It explains that JavaScript is an interpreted language that allows dynamic and interactive functionality on websites. Key points are demonstrated through examples, like using alert to output "Hello World" and basic math operations with variables.






![Variables & data types
// string
var companyName = ‘Google';
// number
var pi = 3.14;
var year = 2013;
// boolean
var flag = true;
var FALSE = false;
// function
var sayHello = function () {
alert('hello world!');
}
// array
var numberArray = [1, 2, 3];
var animals = new Array("cat", "dog", "mouse", "lion");
// object / json
var person = {
name: 'Barack Hussein Obama II',
age: '51',
title: '44th President of the United States'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript101-130202034326-phpapp01/75/Javascript-101-9-2048.jpg)


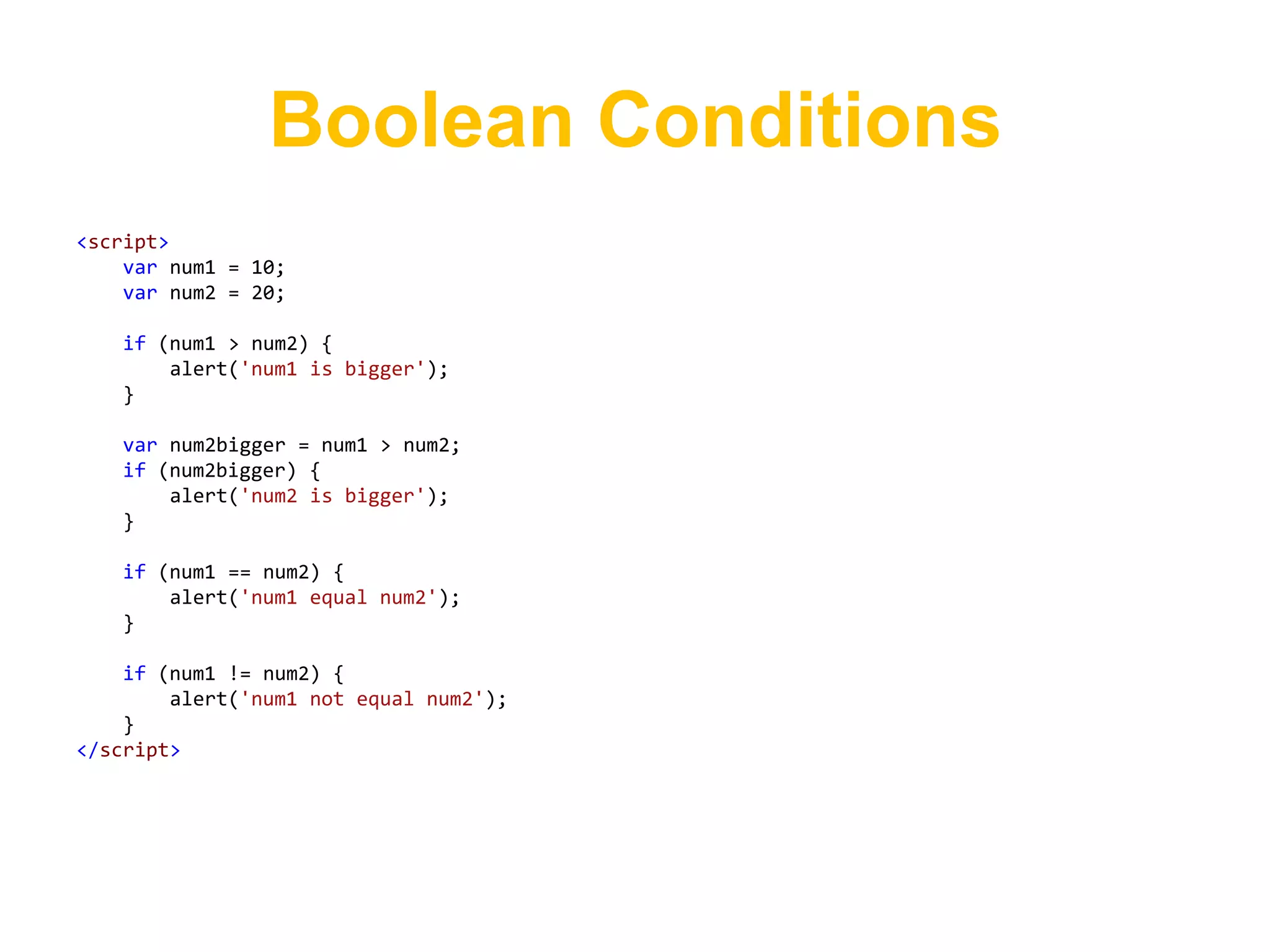
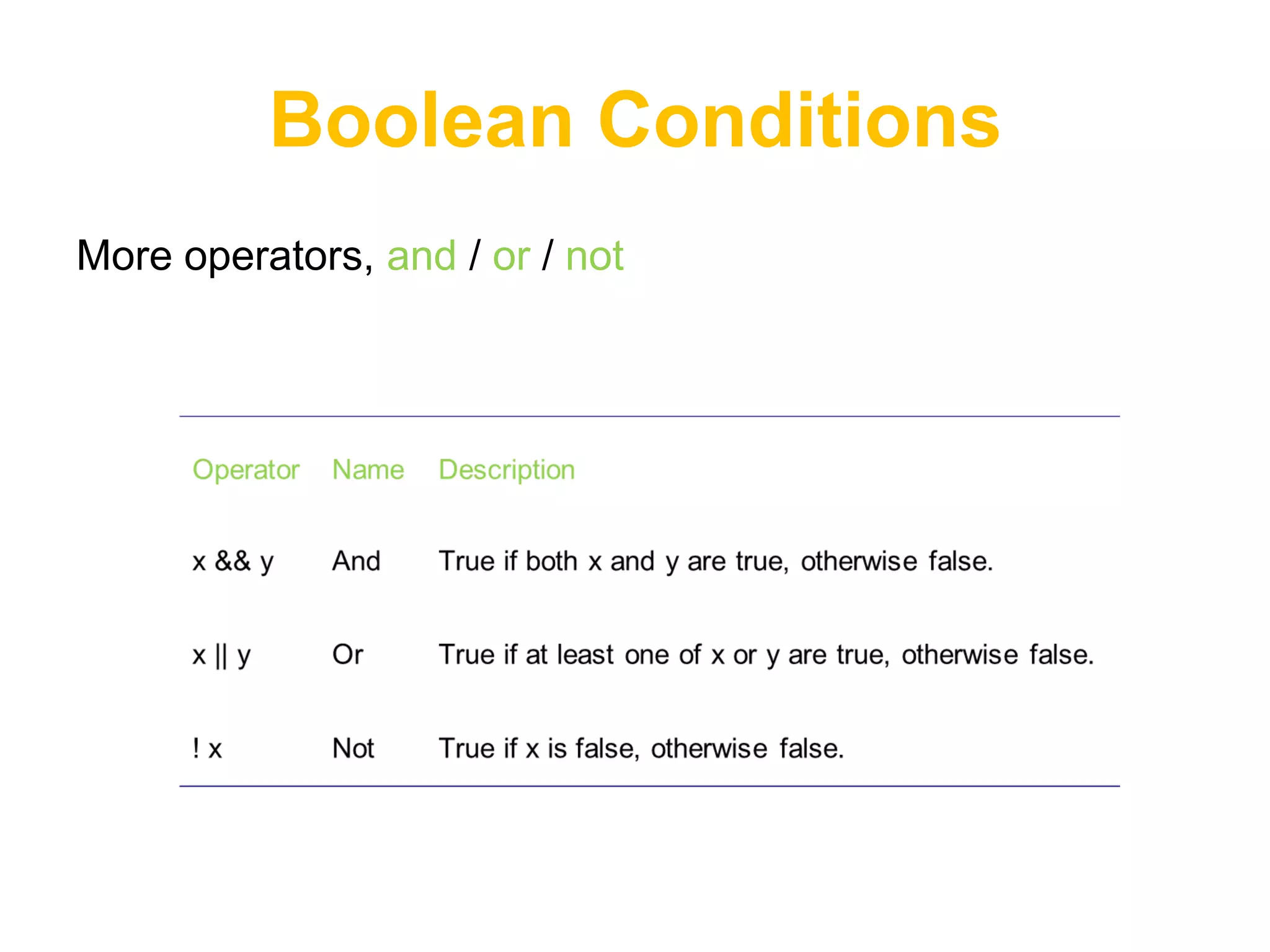
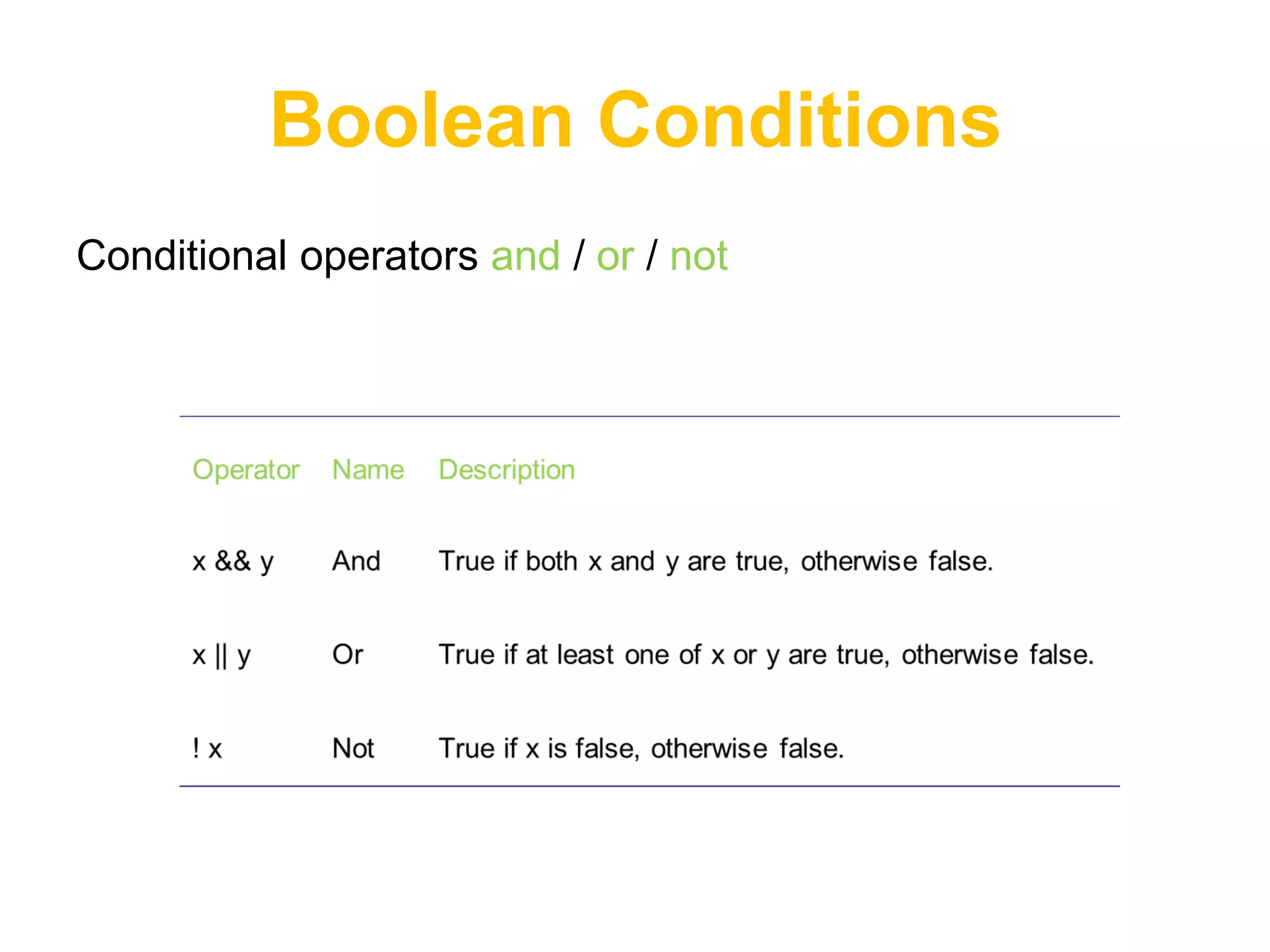
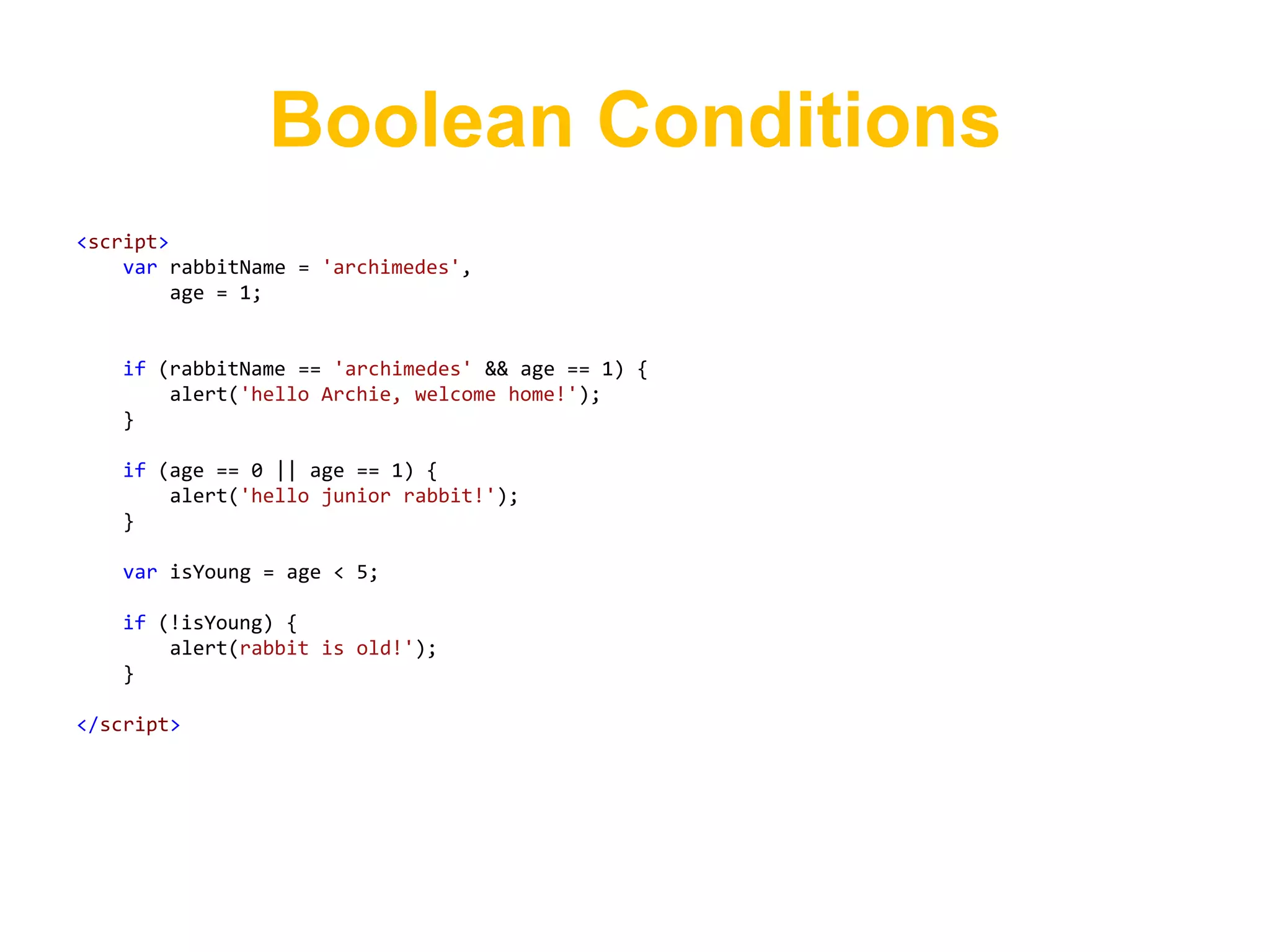

![Arrays
Declaring Arrays & Initialization
var myArray1 = new Array(10, 22);
var myArray2 = new Array();
var myArray3 = [];
var myArray4 = [1, 2, 3];
var myArray5 = new Array("cat", "dog", "mouse", "lion");
var myArray6 = new Array(10); // predefined size array
var myArray7 = [1, "hello world!", 1.24, function () { }, [1, 2, 3],
null, undefined, { a: 1, b: 2 }, document.body];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript101-130202034326-phpapp01/75/Javascript-101-26-2048.jpg)
![Arrays
Arrays can be accessed via index:
var animals = new Array("Cat", "Dog", "Mouse", "Lion");
Get the first value of the array:
var cat = animals[0];
Assign value to the third index of the array:
animals[2] = 'Giraffe';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript101-130202034326-phpapp01/75/Javascript-101-27-2048.jpg)
![Arrays
Get the current items in the array with the length property:
var animals = new Array("Cat", "Dog", "Mouse", "Lion");
var animalsCount = animals.length;
// animalsCount = 4
Push a new item to the array:
Animals.push('Kangaroo‘);
Checking the length again:
animalsCount = animals.length;
// animalsCount = 5
Iterate over the values of the array and use alert to show them;
for (var i = 0; i < animals.length; i++) {
alert(animals[i]);
}
Sum-array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript101-130202034326-phpapp01/75/Javascript-101-28-2048.jpg)

![Objects
Access to Object properties:
var person = {
name: 'Barack Hussein Obama II',
age: '51',
title: '44th President of the United States'
}
alert(person.name); // Barack Hussein Obama II
alert(person['name']); // Barack Hussein Obama II
person.age = 51;
person['age'] = 51;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript101-130202034326-phpapp01/75/Javascript-101-30-2048.jpg)

