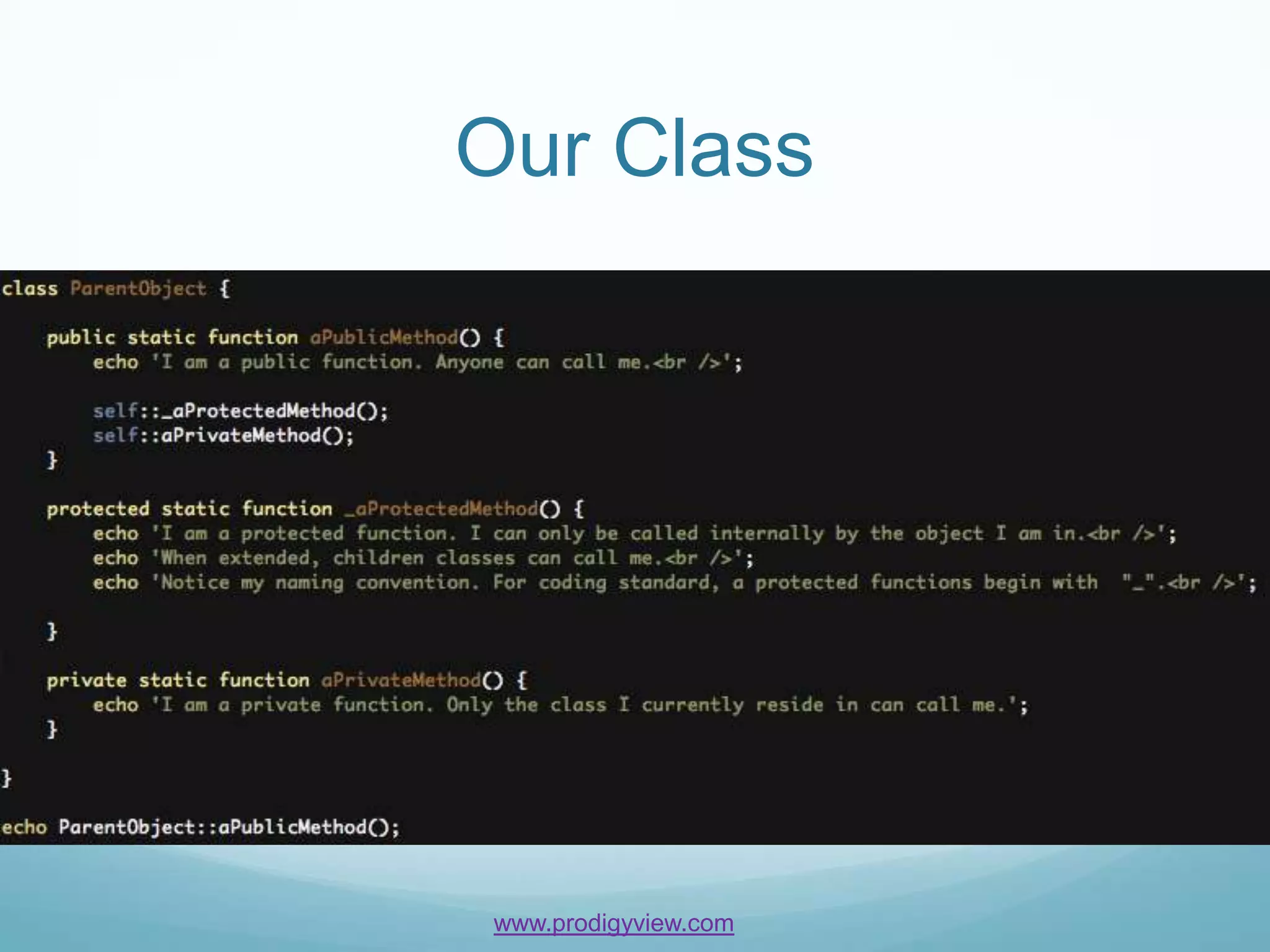
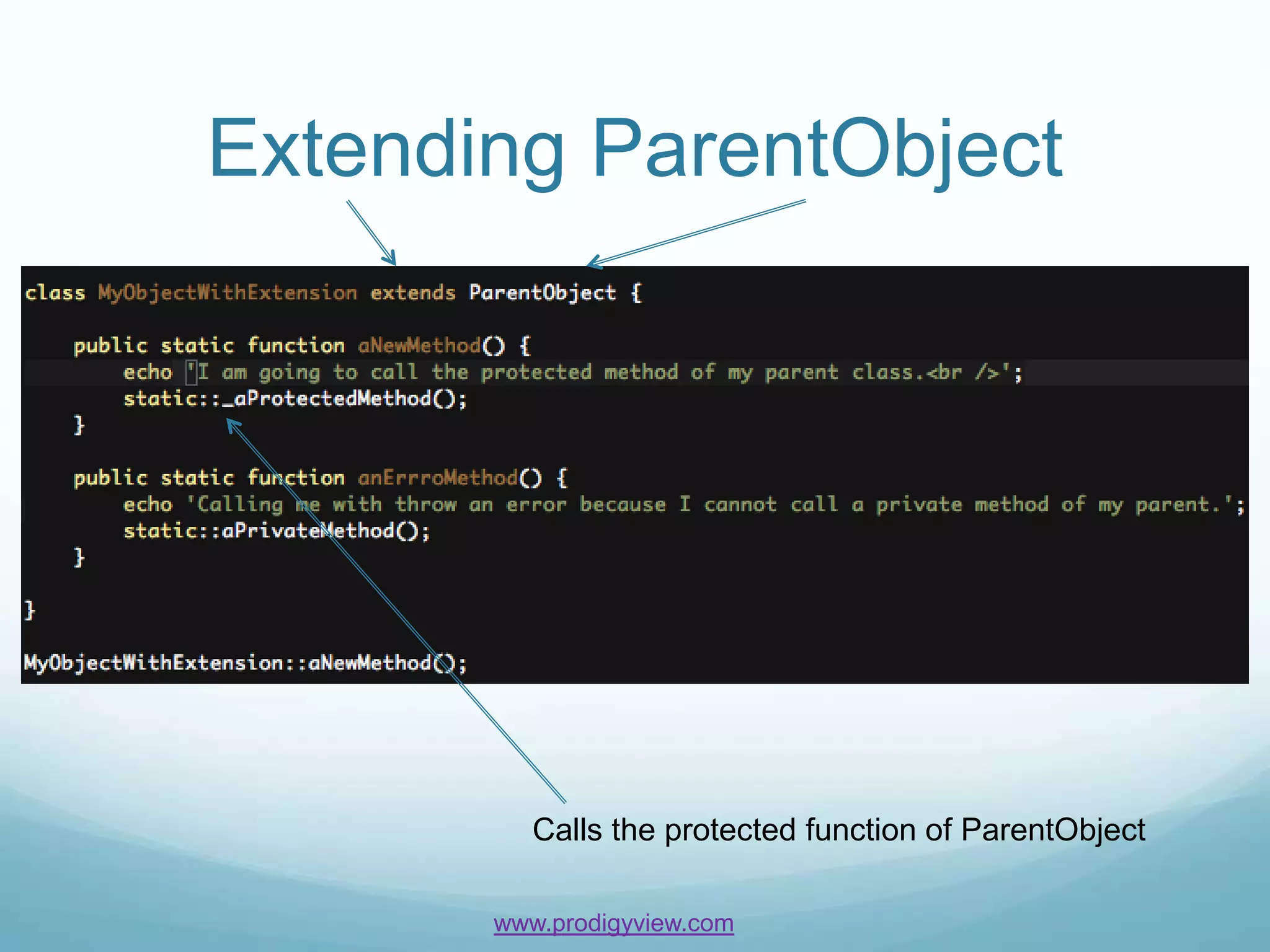
The document provides an overview of PHP objects and functions for beginners. It discusses static methods, public methods, protected methods, private methods, and anonymous functions. Examples are given for each concept to demonstrate how to define them and call them. The document concludes by challenging readers to create a class with a static protected method containing an anonymous function.