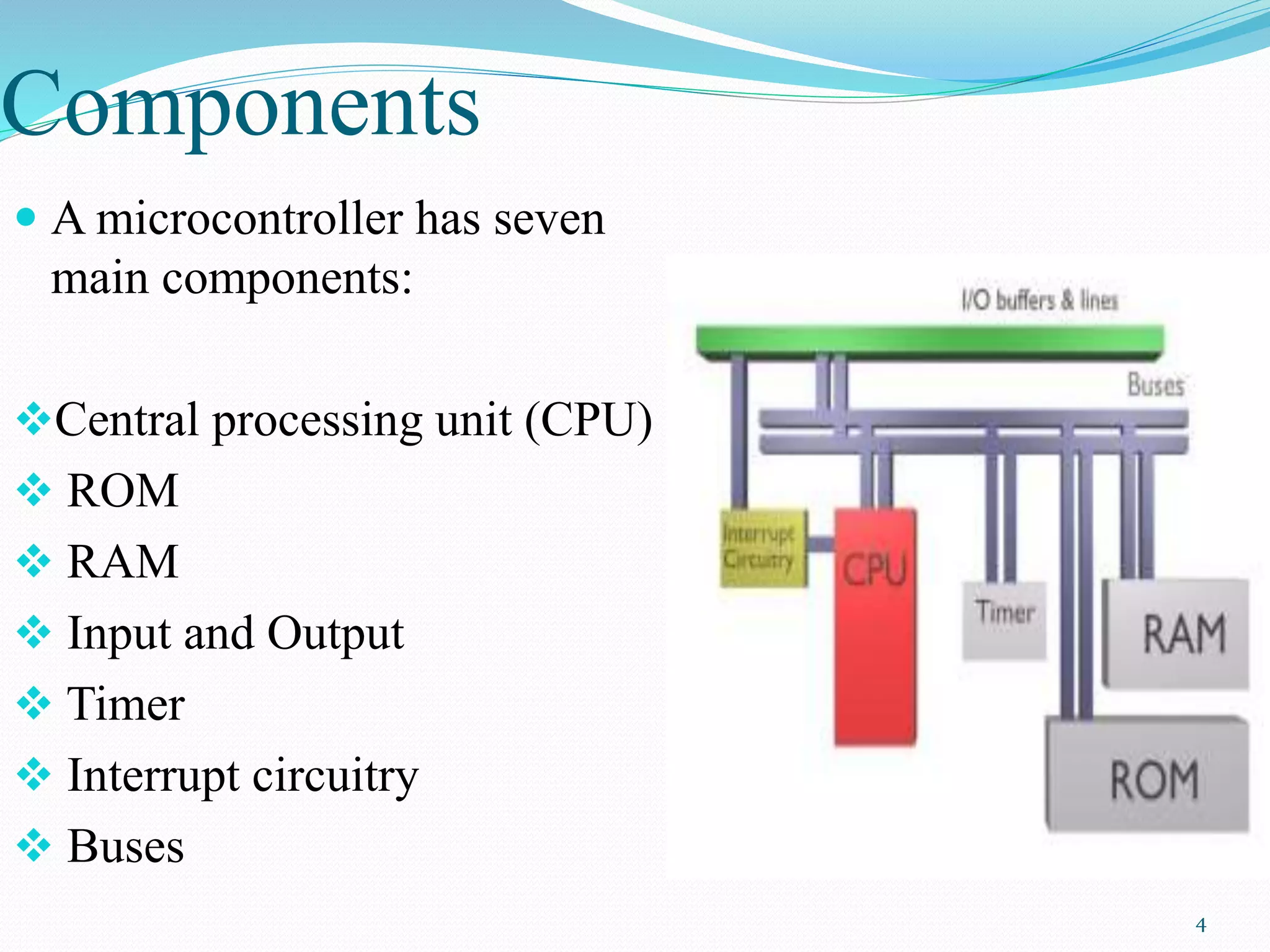
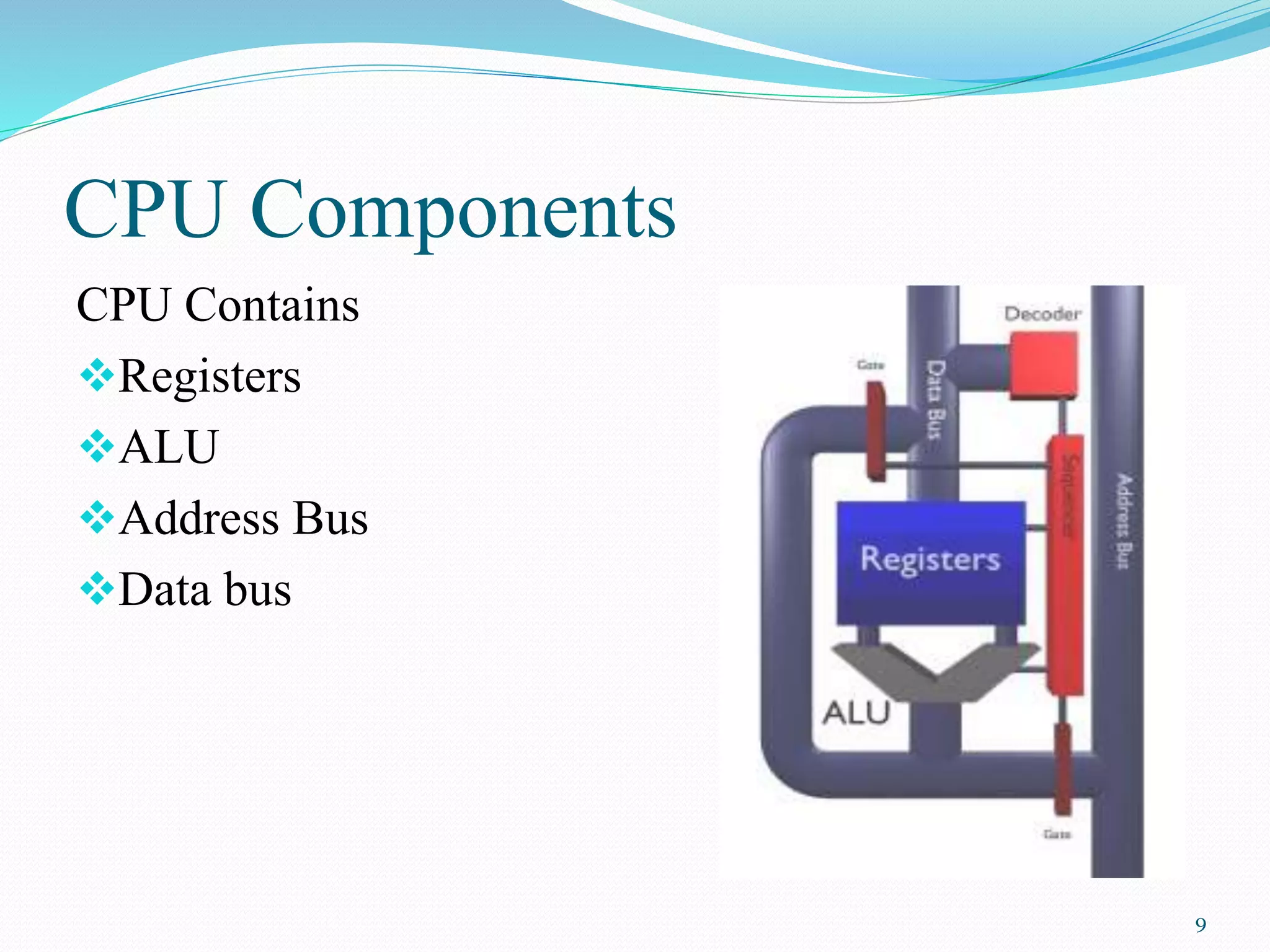
A microcontroller is a single-chip computer contained on an integrated circuit. It contains a CPU, memory (ROM and RAM), input/output ports, and other components to control electronic devices and systems. The CPU fetches and executes instructions stored in ROM or RAM and directs data flow. Microcontrollers use either a Harvard or Von Neumann architecture, with Harvard being more common. Microcontrollers differ from microprocessors in that they do not require additional chips to function as a complete computing system.