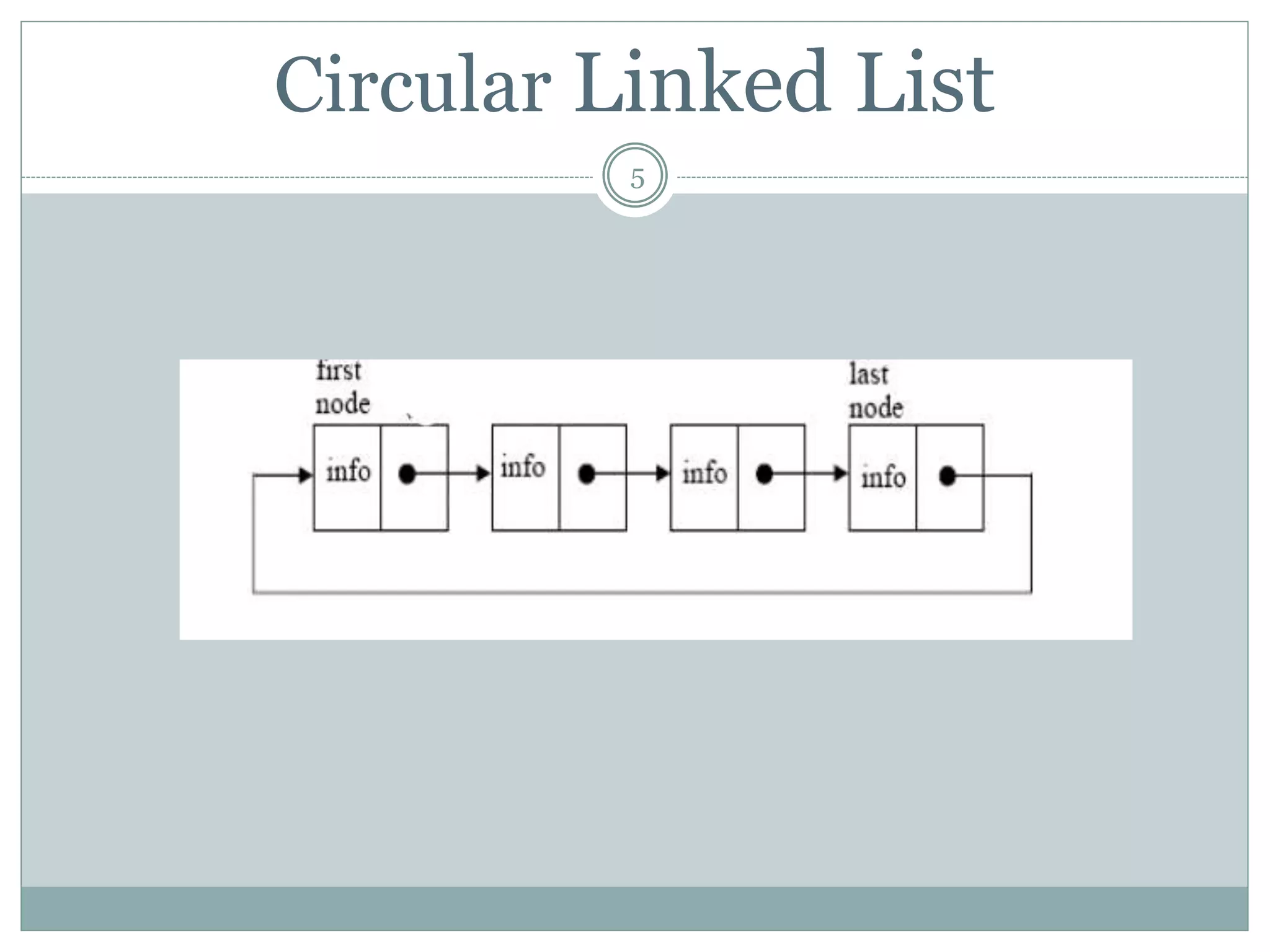
This document discusses different types of linked lists, including singly linked lists, circular linked lists, and doubly linked lists. It provides examples of circular linked lists and explains that in a circular linked list, the last node contains the address of the first node so that the list can be traversed repeatedly. The document also discusses common linked list operations like insertion and deletion of nodes. Finally, it covers stacks and queues, defining them as LIFO and FIFO data structures, respectively, and providing examples of their implementation and different types.