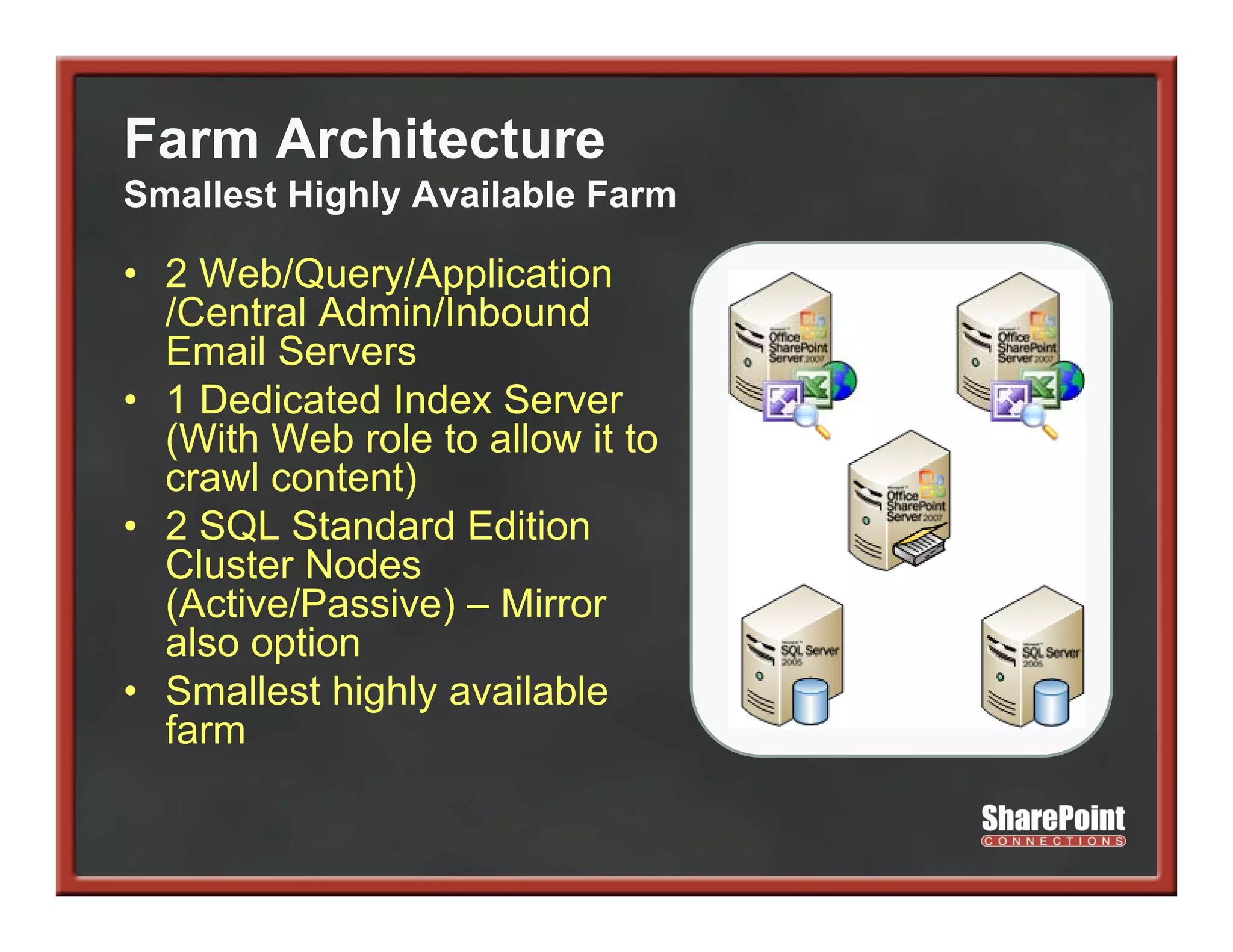
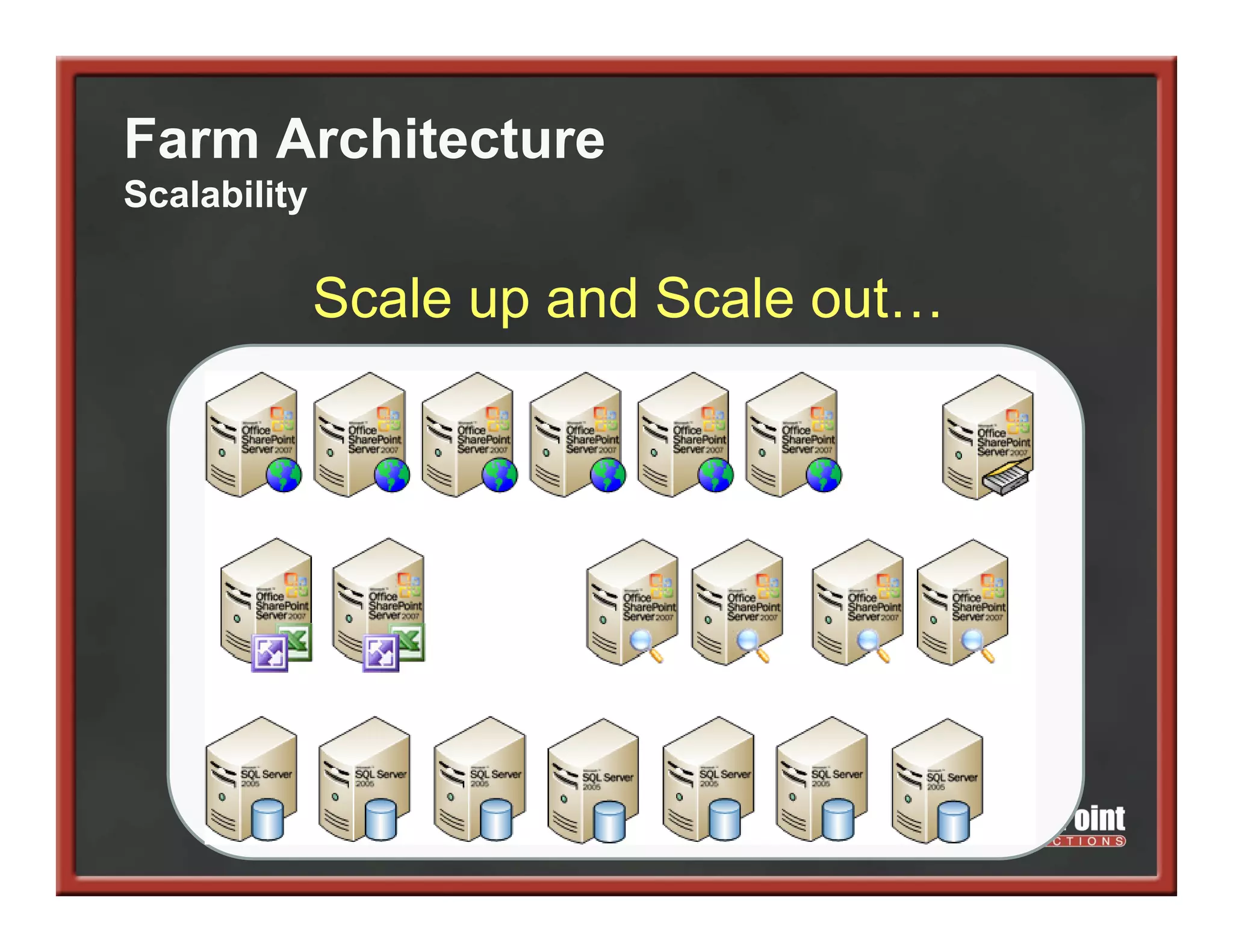
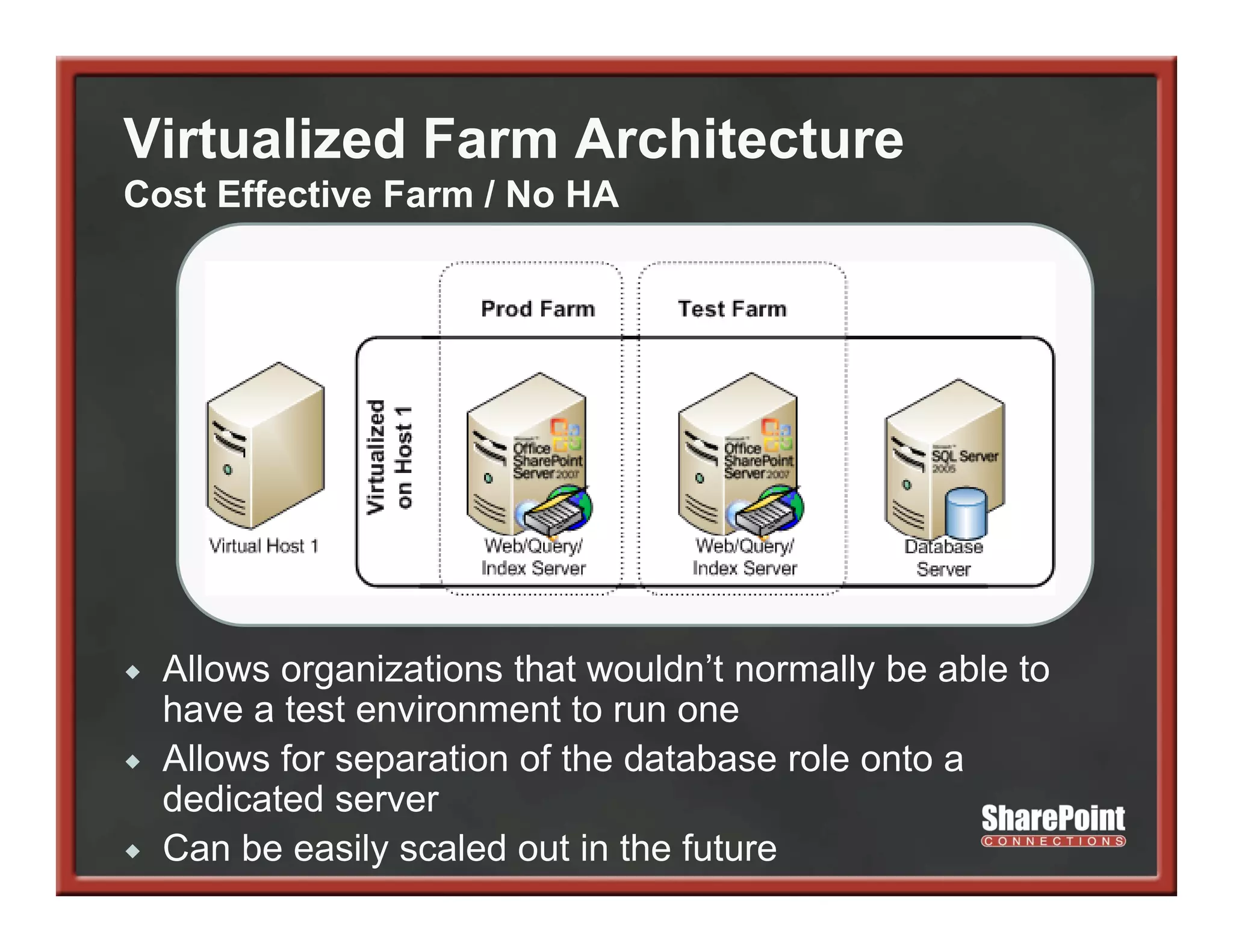
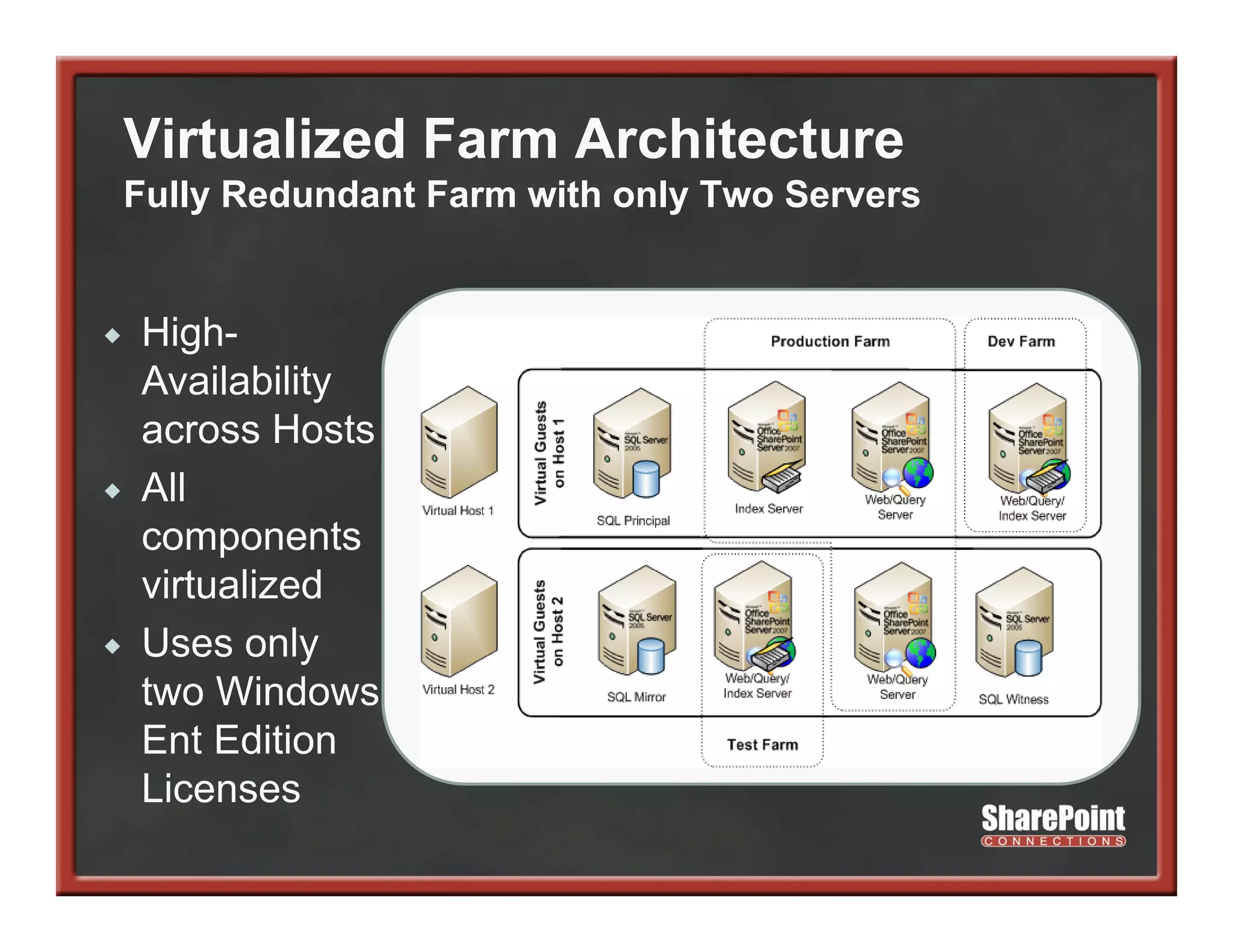
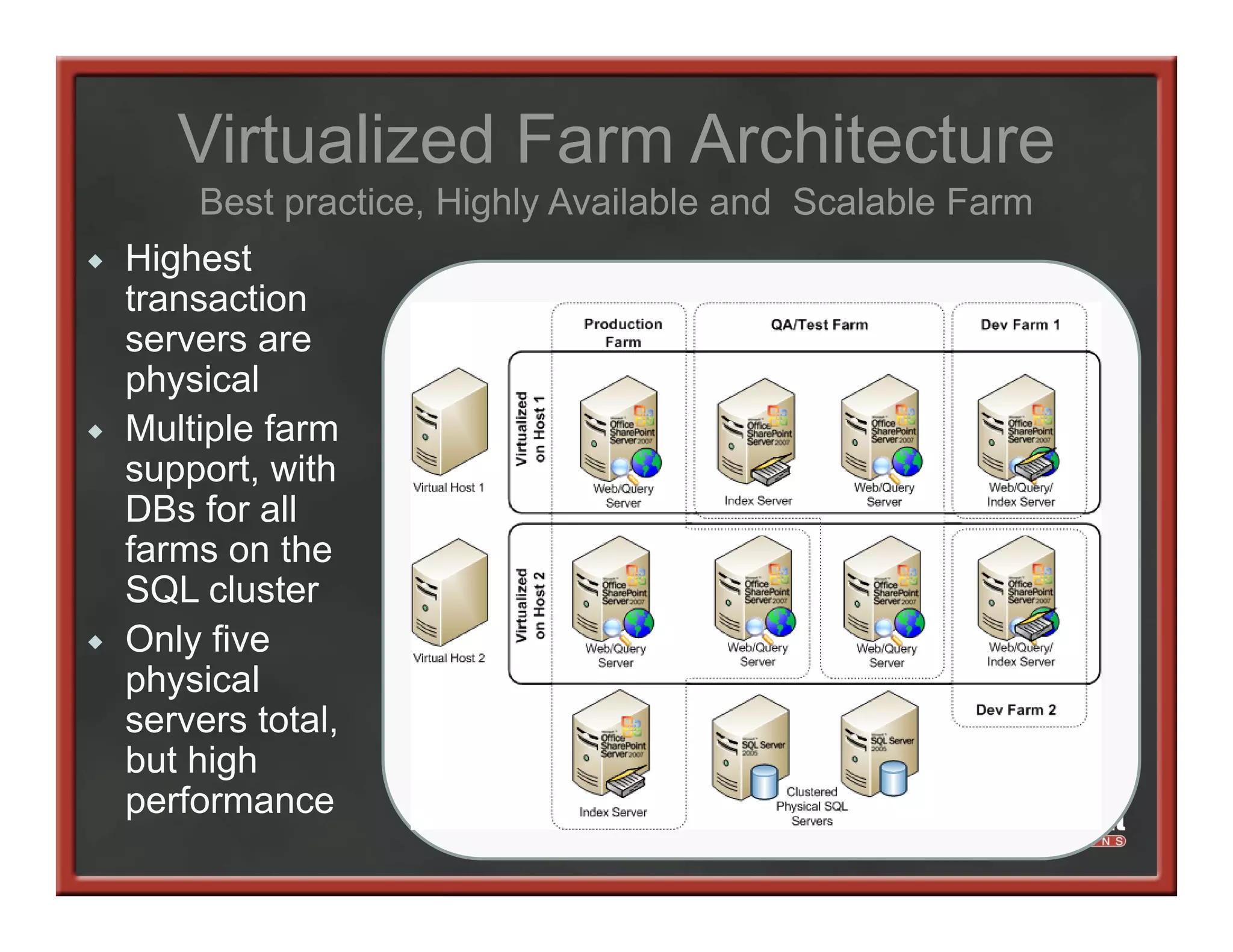
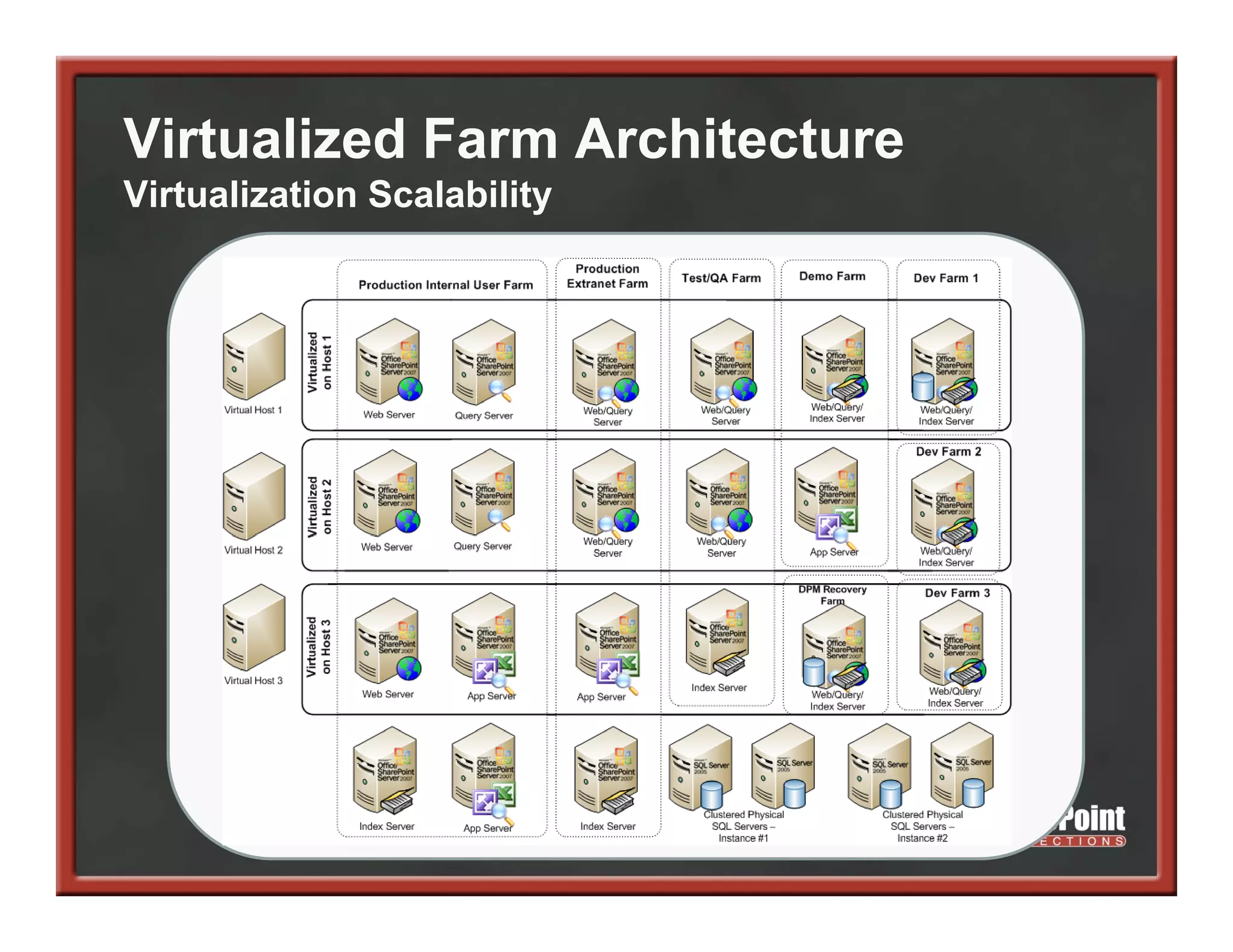
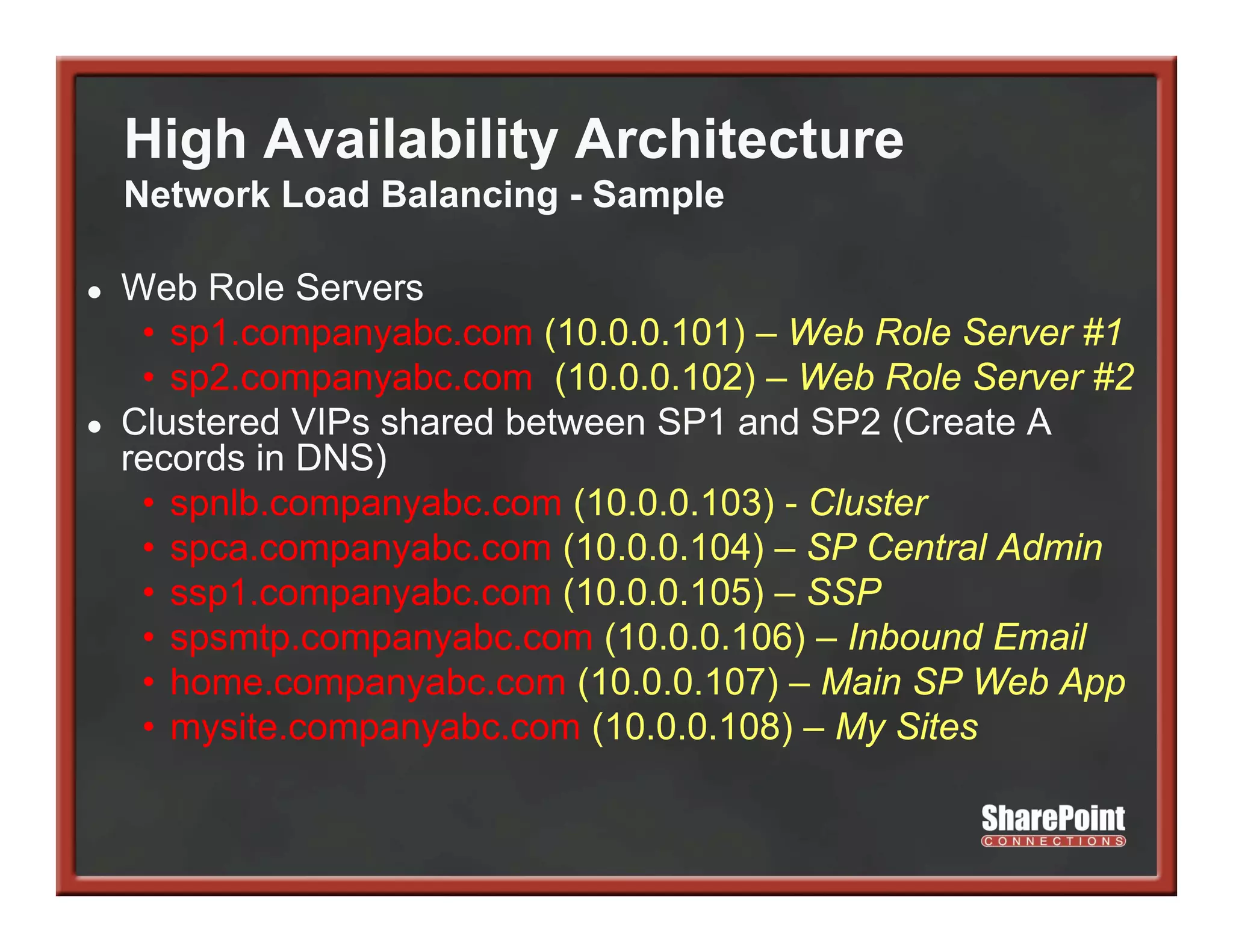
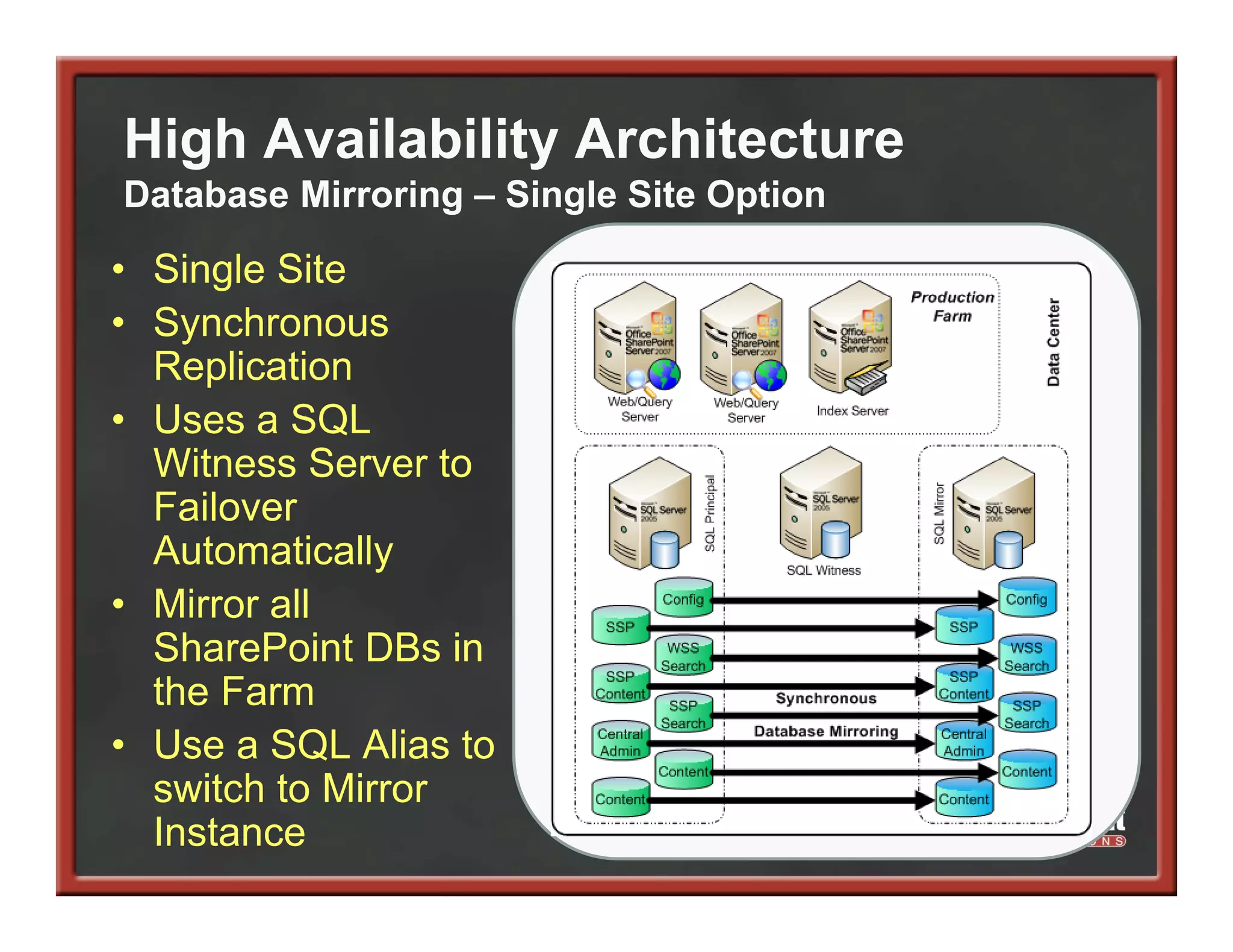
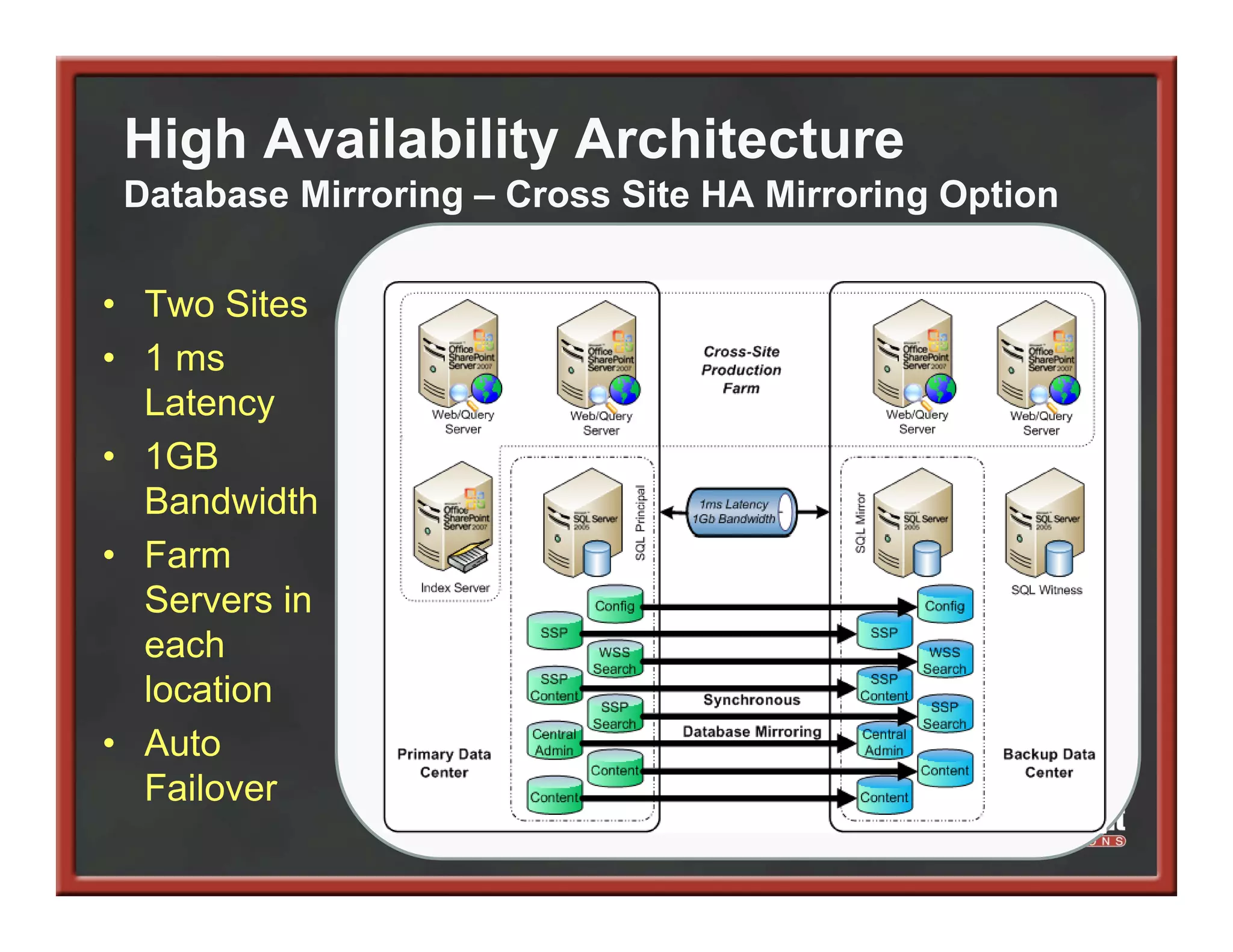
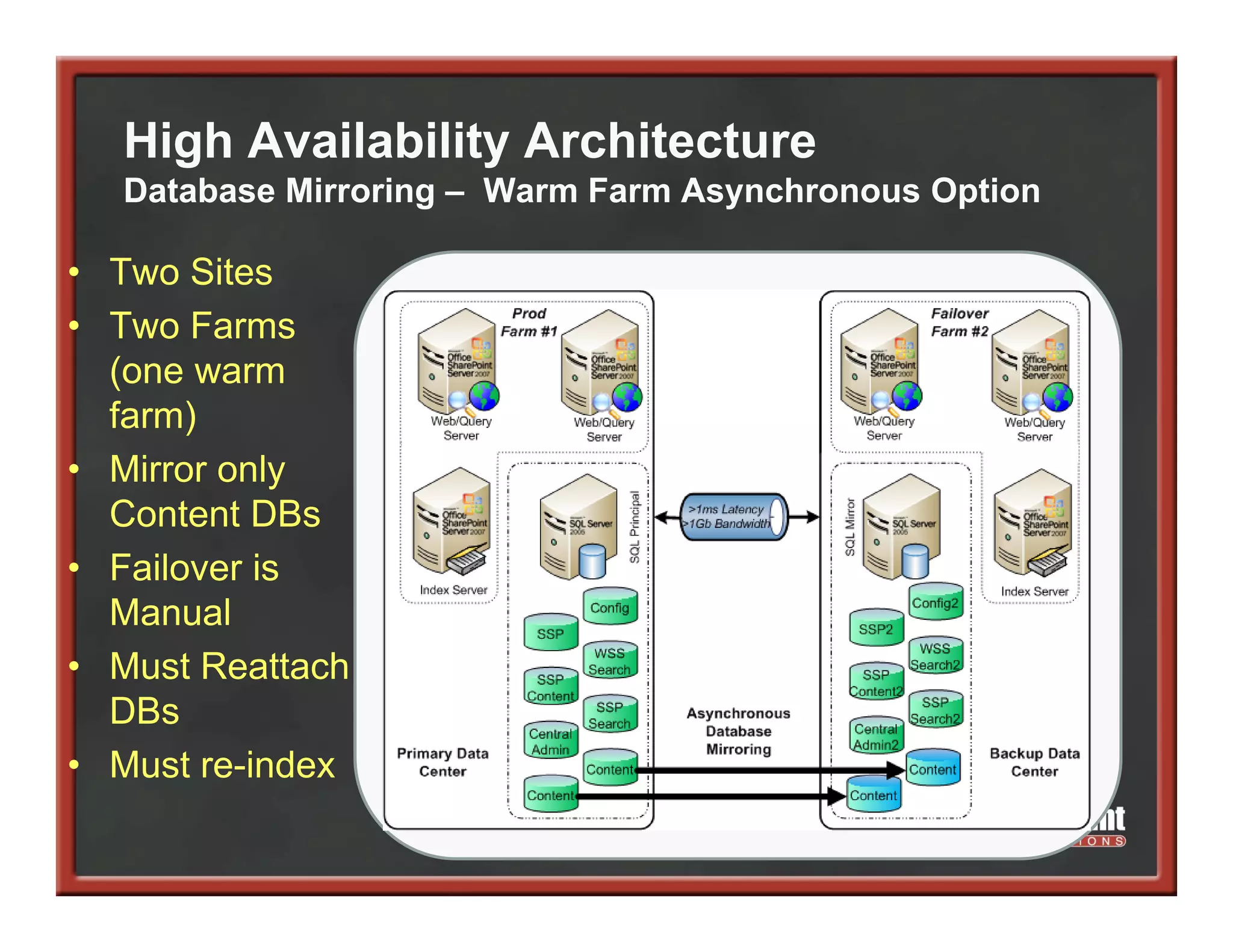
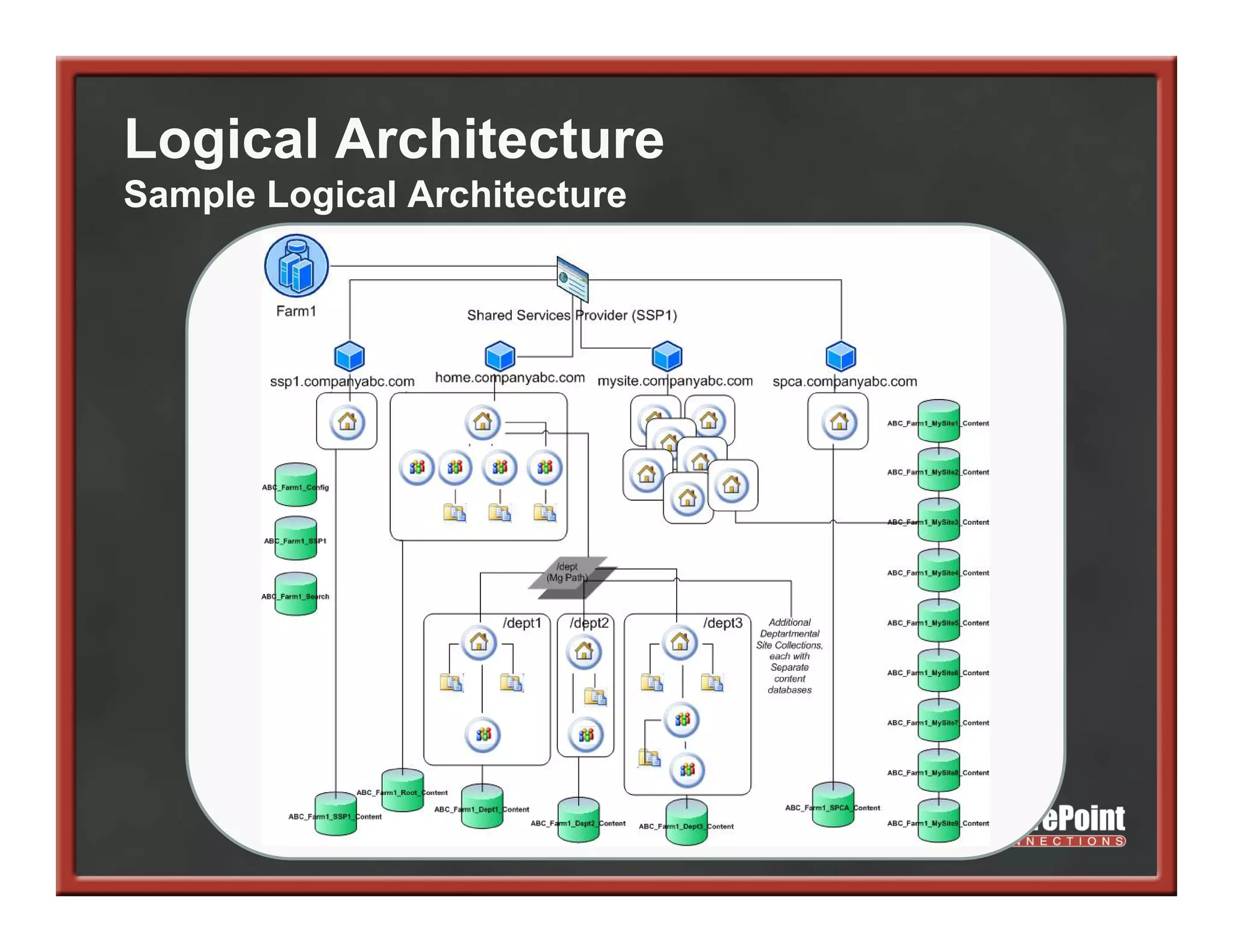
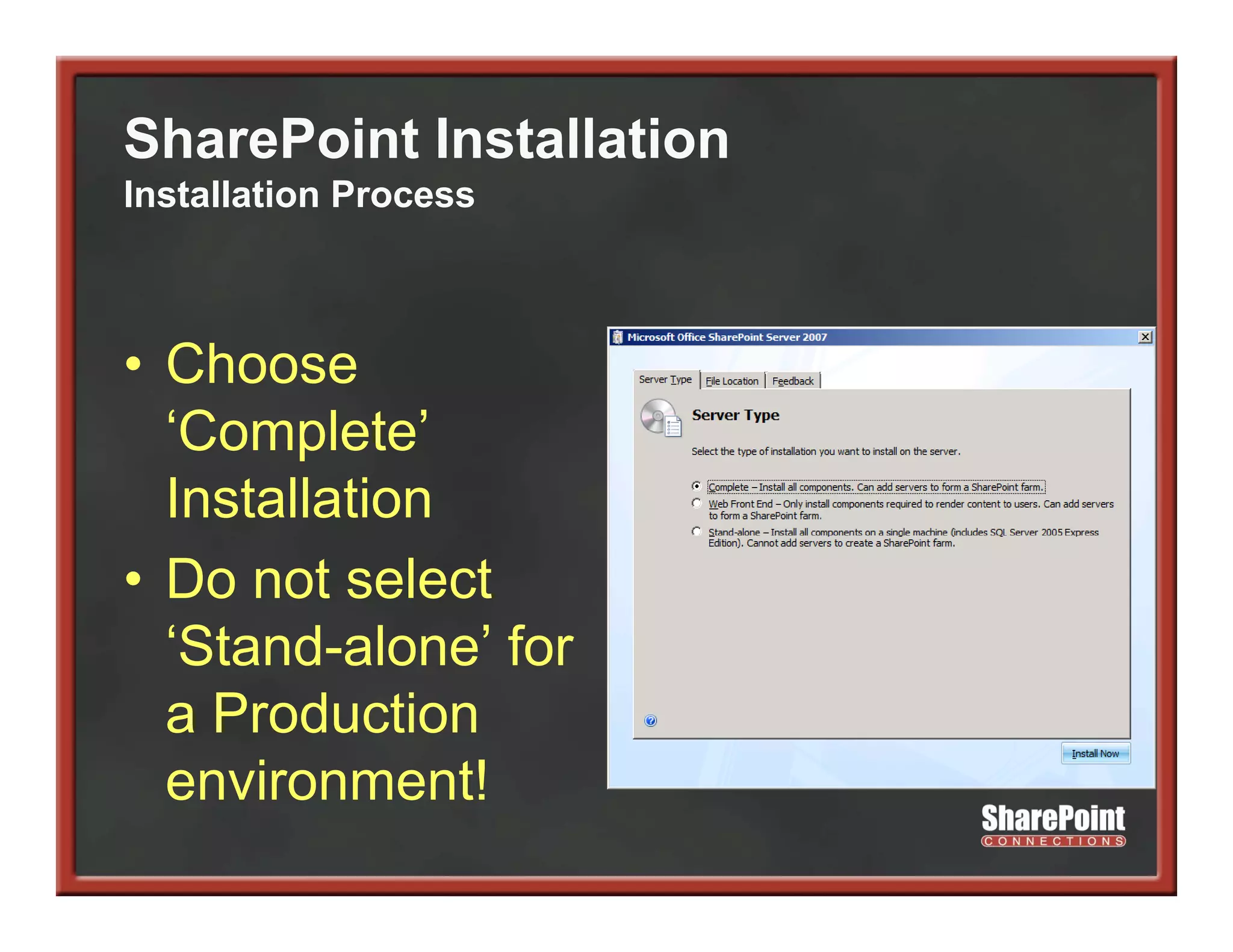
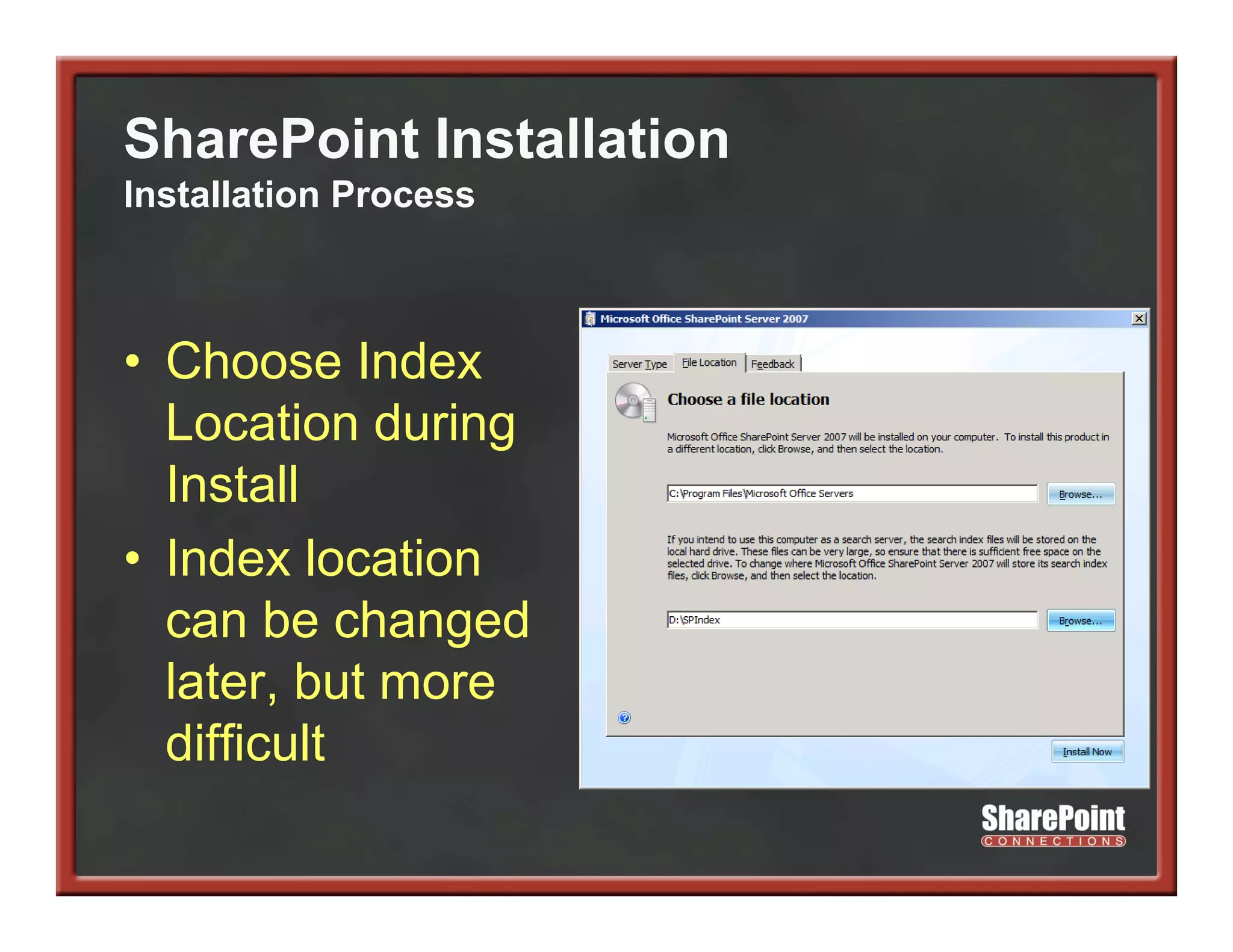
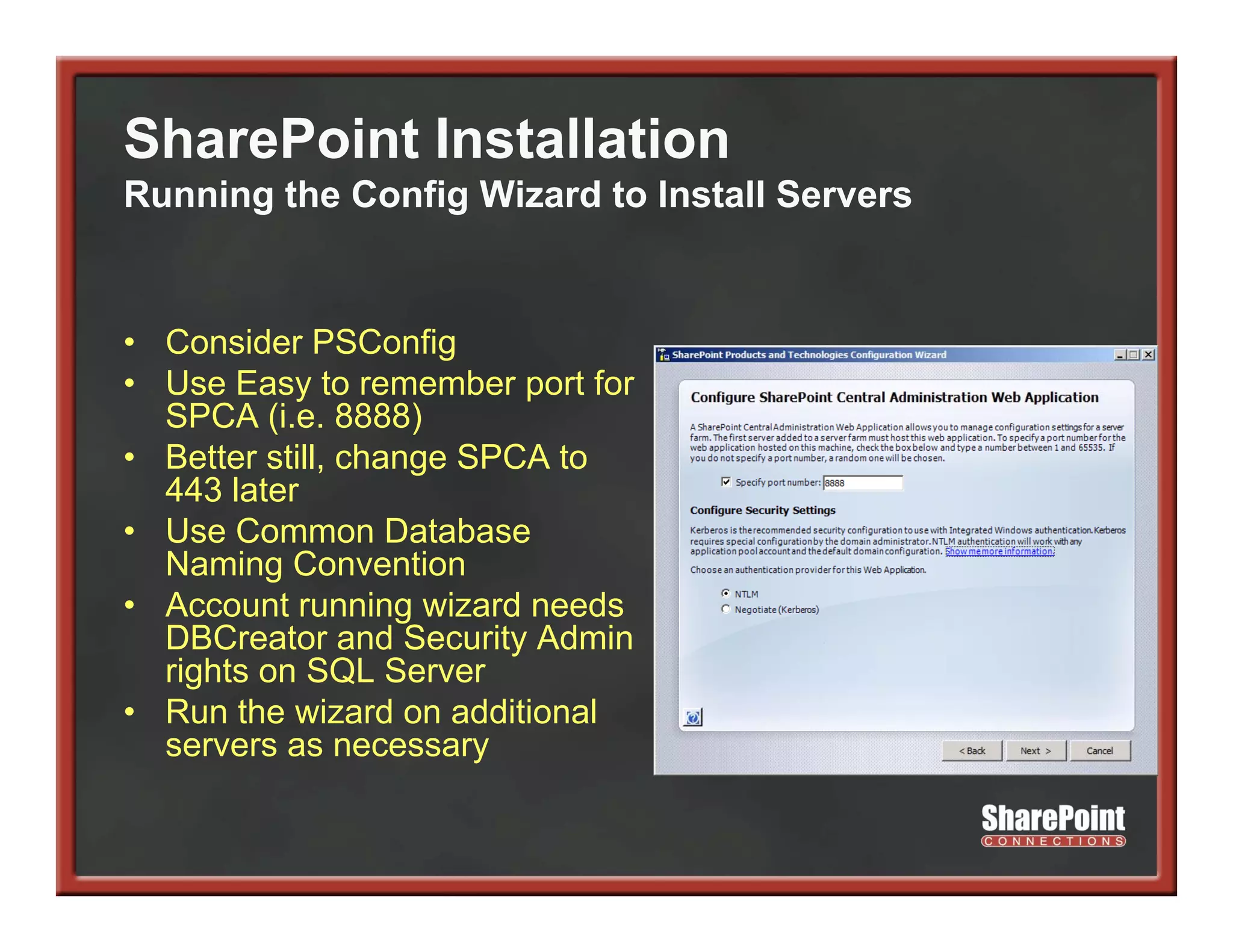
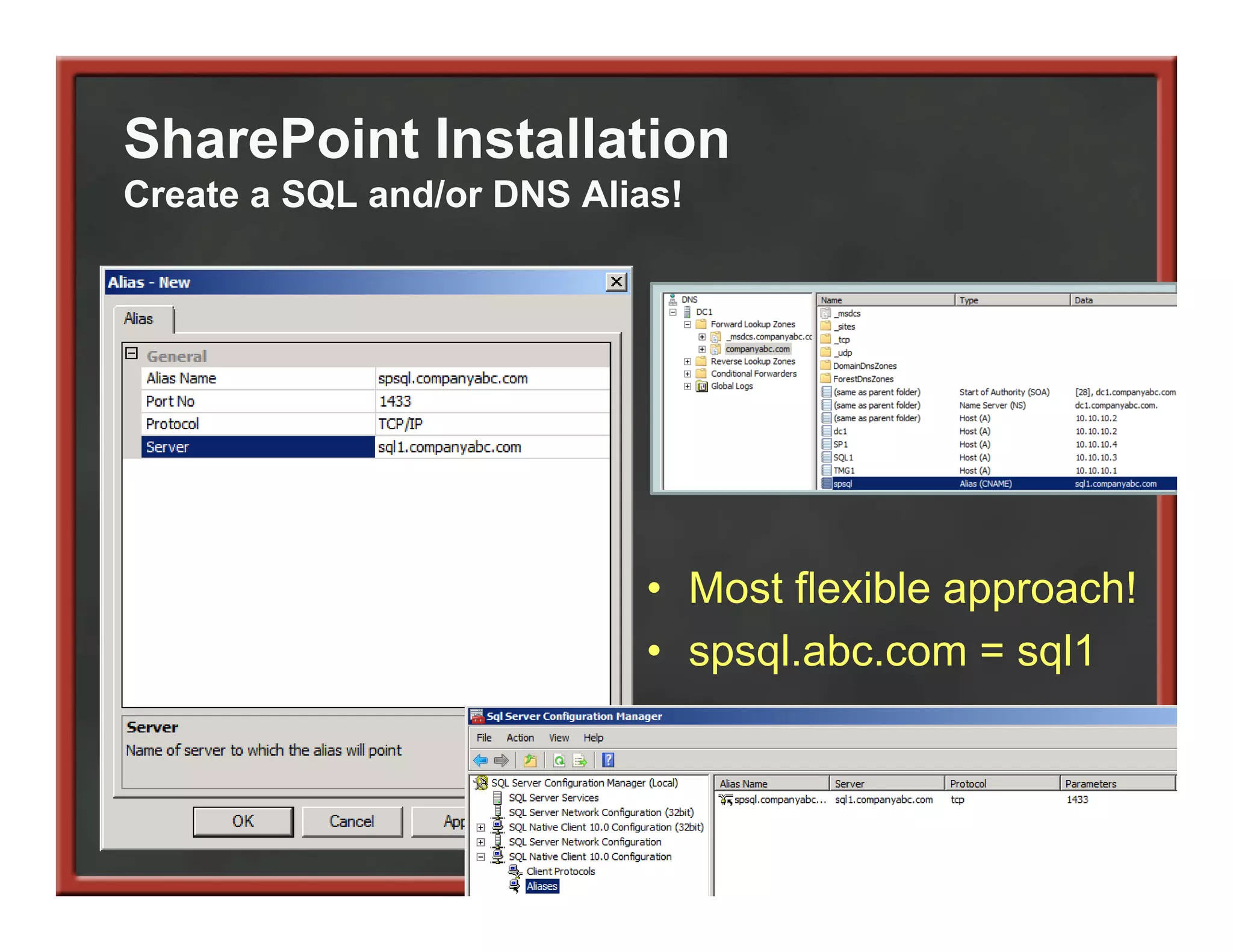
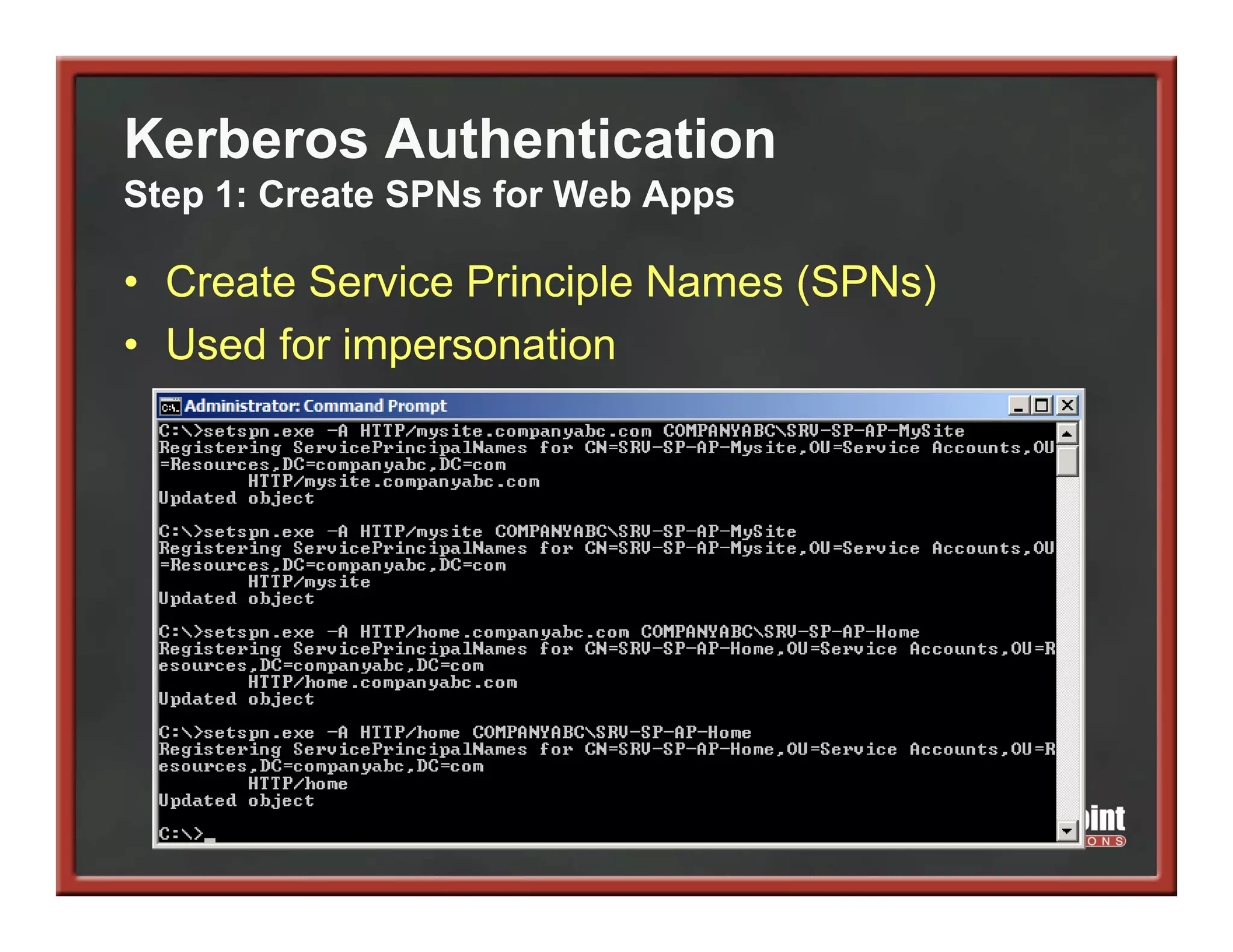
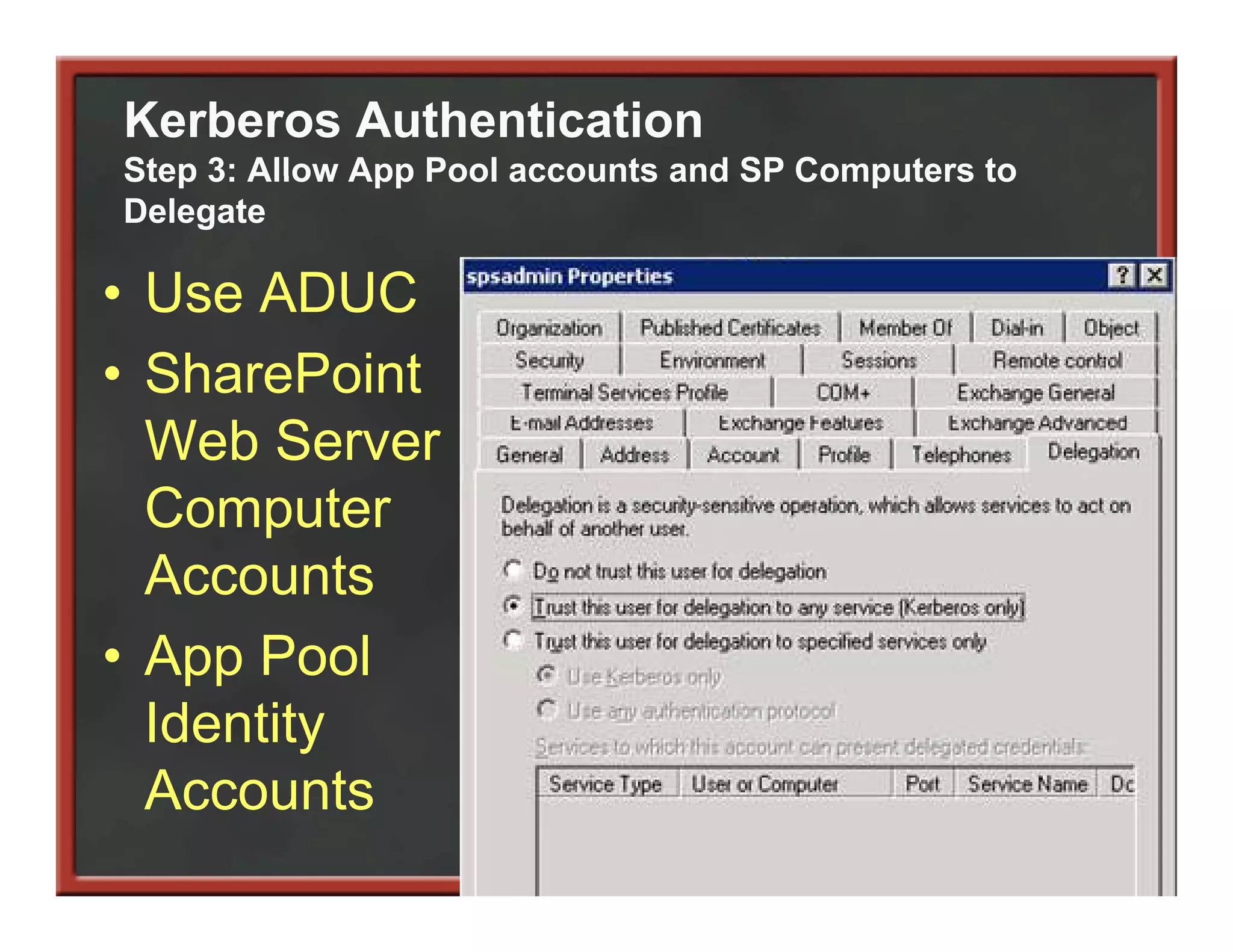
This document summarizes best practices for SharePoint farm architecture based on lessons learned from years of SharePoint deployments. It discusses farm architecture options including all-in-one, dedicated SQL, and virtualized farms. It also covers high availability design using network load balancing and SQL database mirroring. Additional topics include logical architecture, hardware and software considerations, the SharePoint installation process, and enabling Kerberos authentication for security.