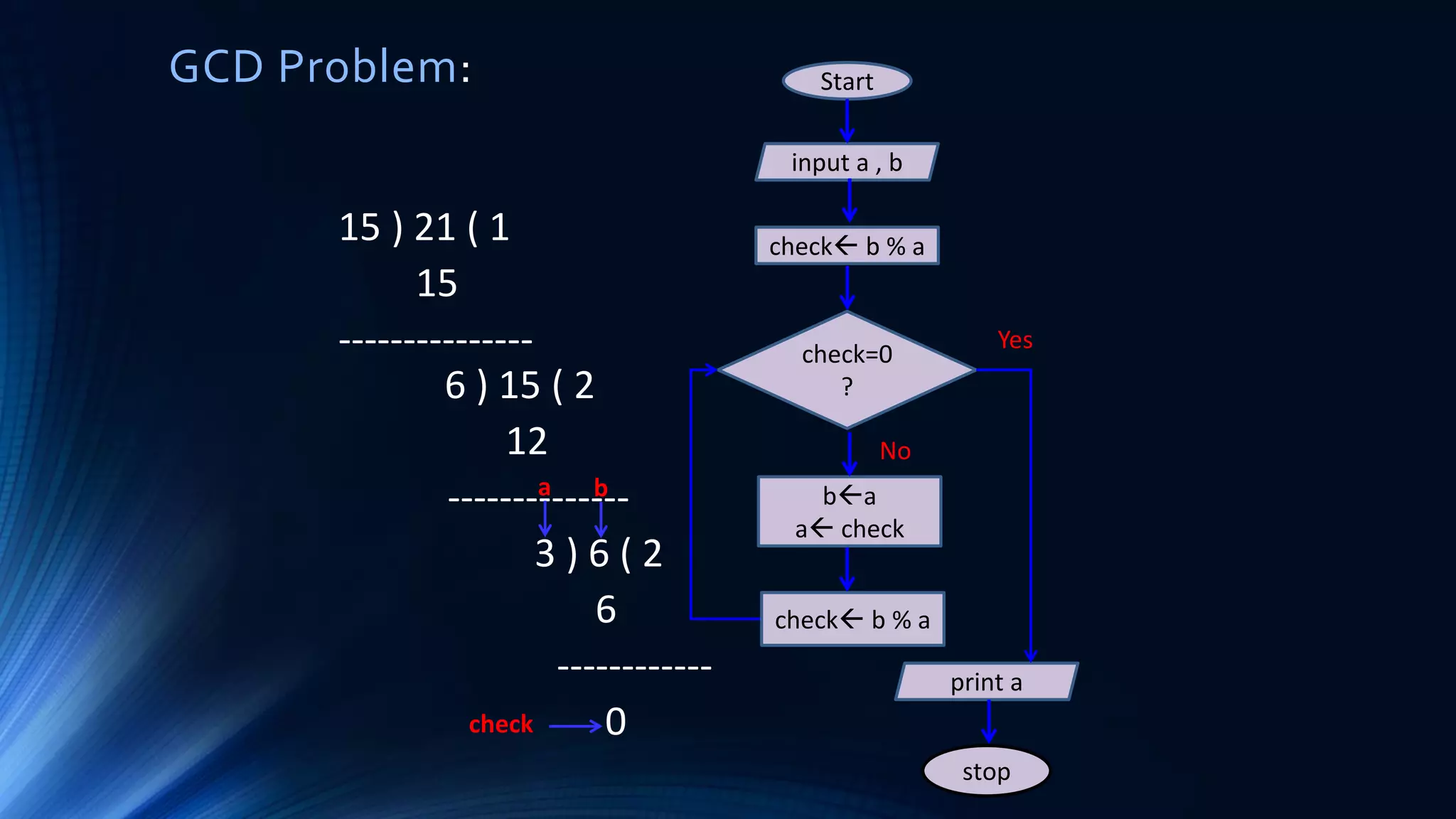
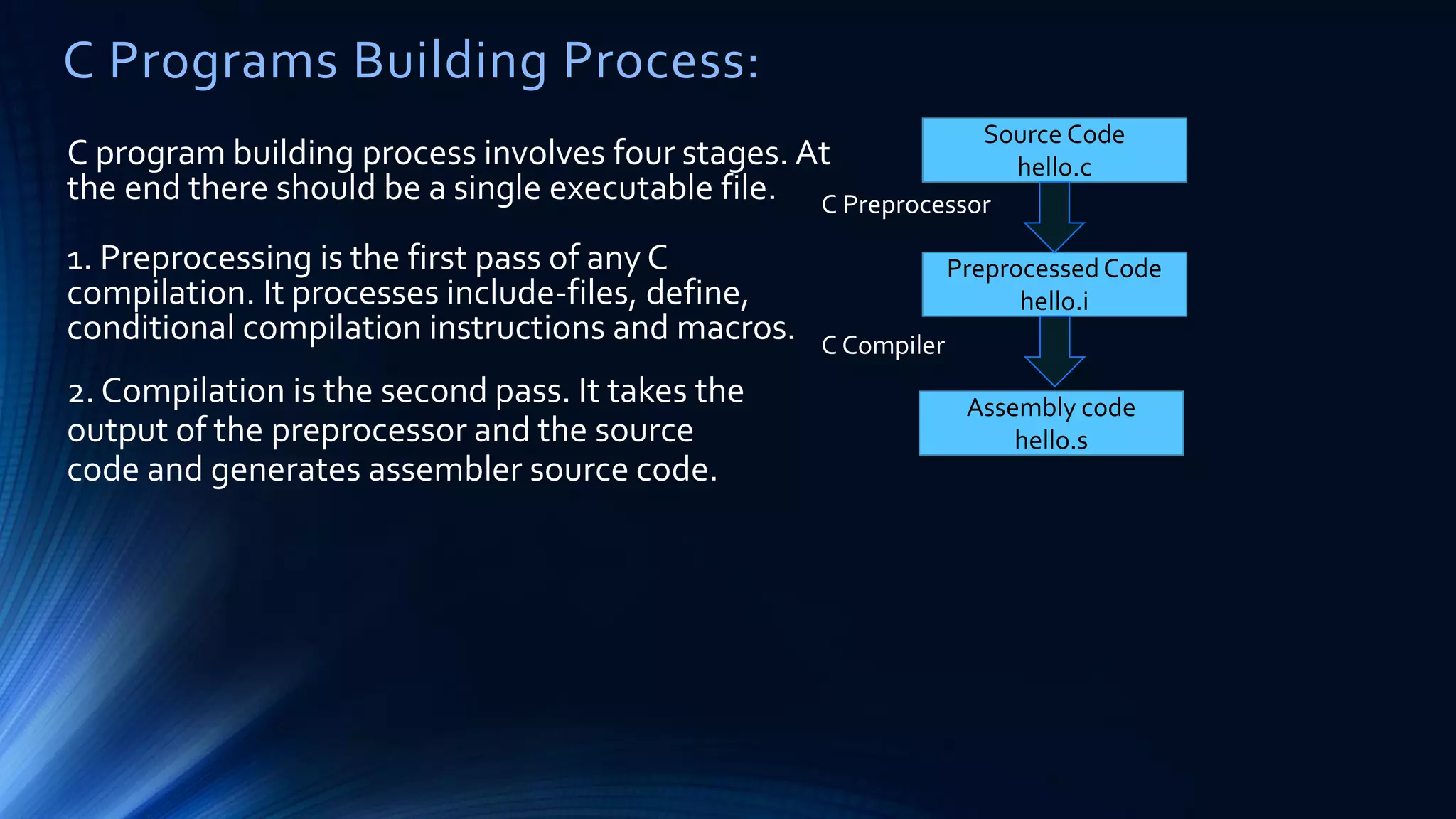
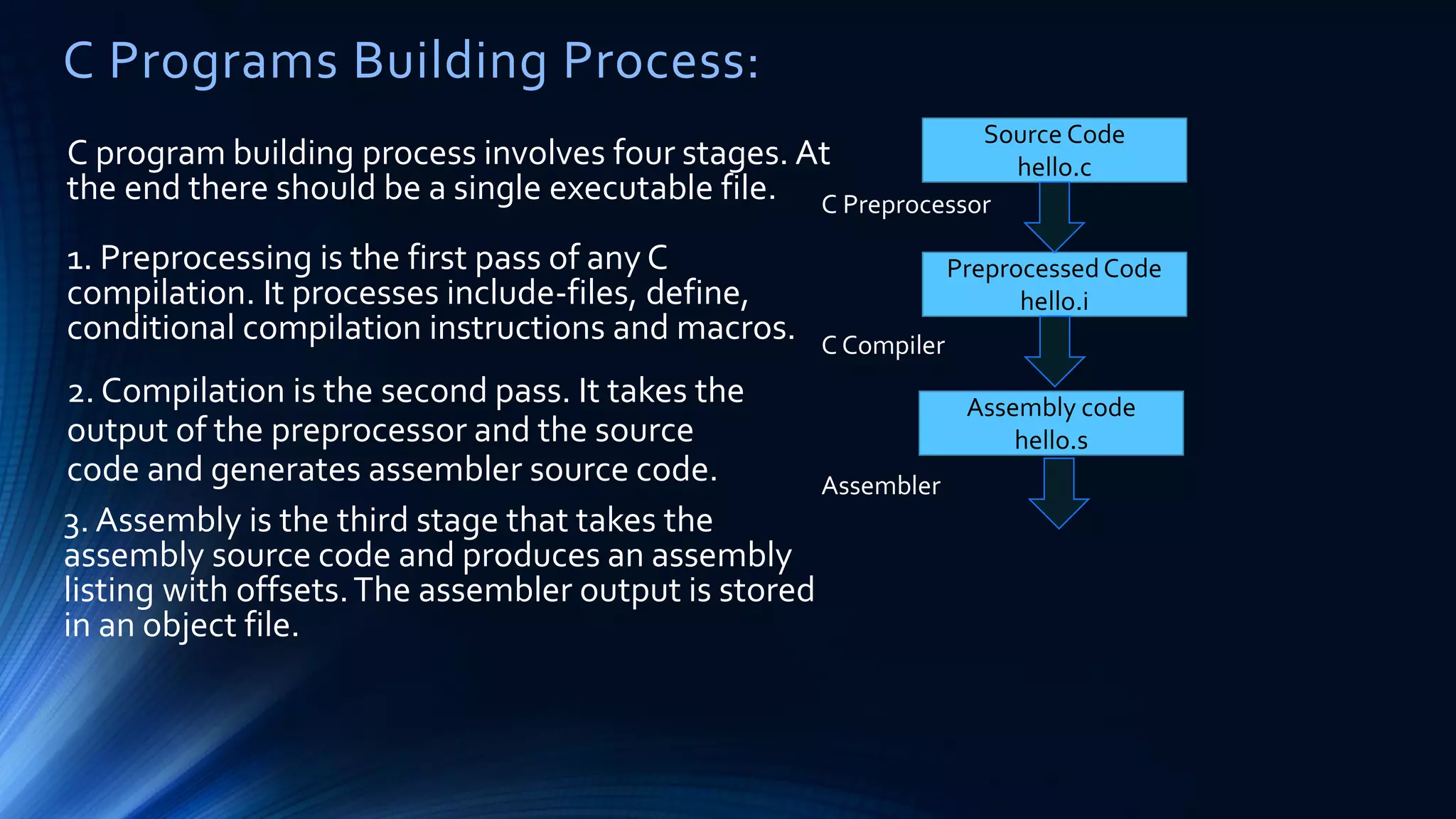
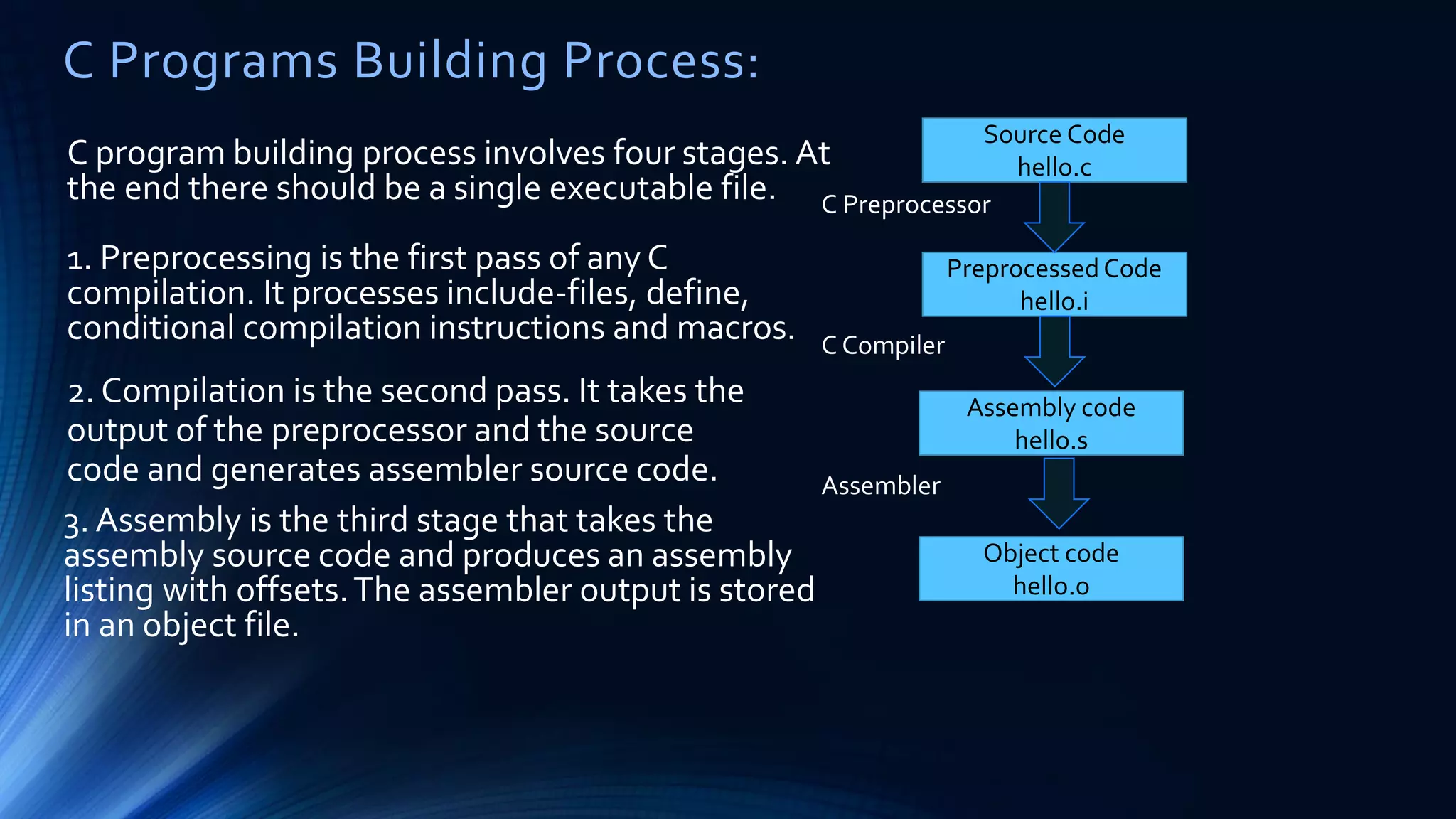
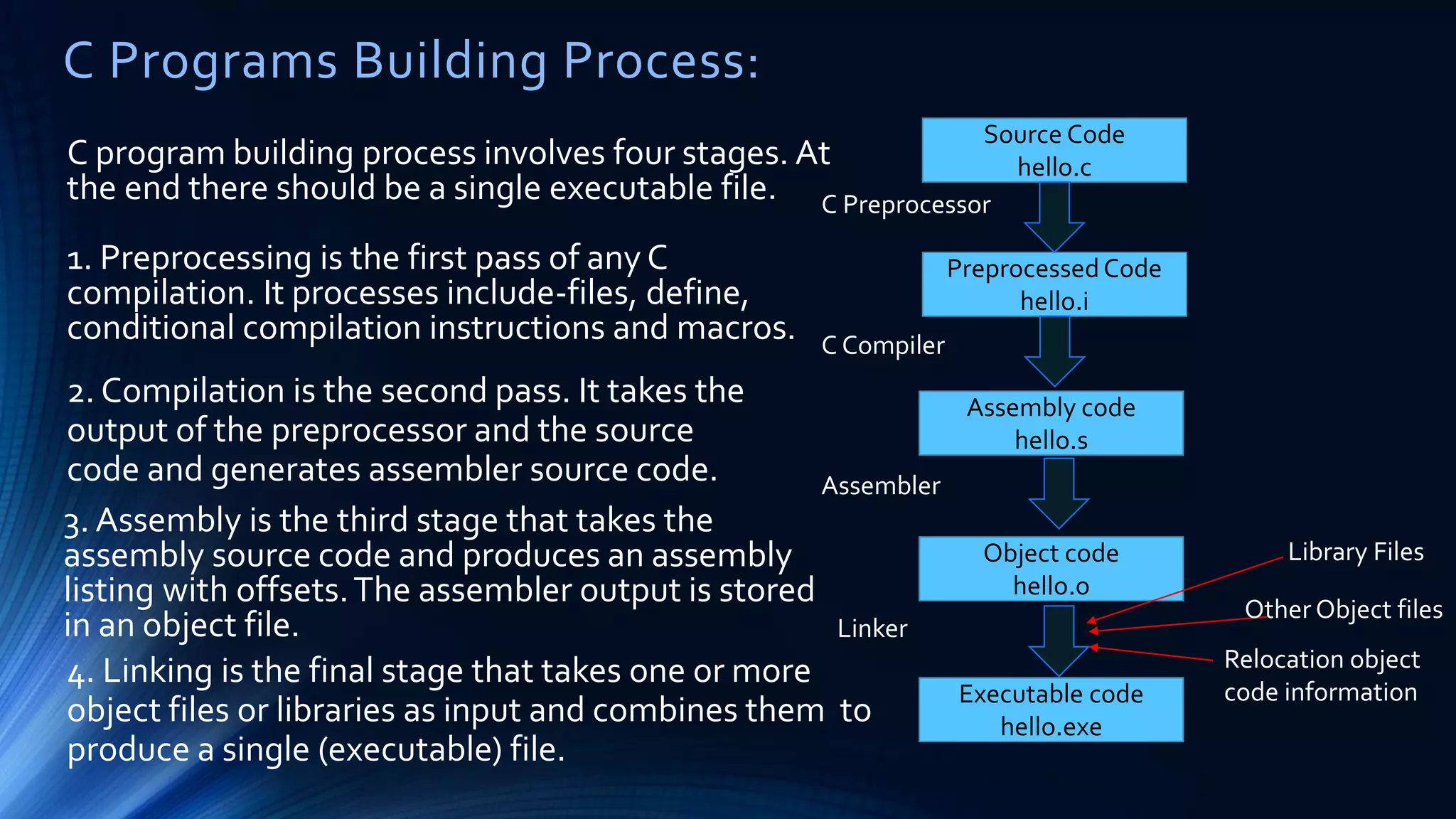
The document discusses structured programming languages and the compilation process. It provides algorithms, pseudocode, and flowcharts for finding the average of n numbers as an example. It then explains the four stages of compiling a C program: preprocessing, compilation, assembly, and linking. Preprocessing handles includes, defines, and macros. Compilation generates assembly code. Assembly produces object code. Linking combines object files and libraries into a single executable file.