This document provides an overview of Java applets, including:
- Applets are small Java programs that can be transported over the network and embedded in HTML pages.
- The main types of Java programs are standalone programs and web-based programs like applets.
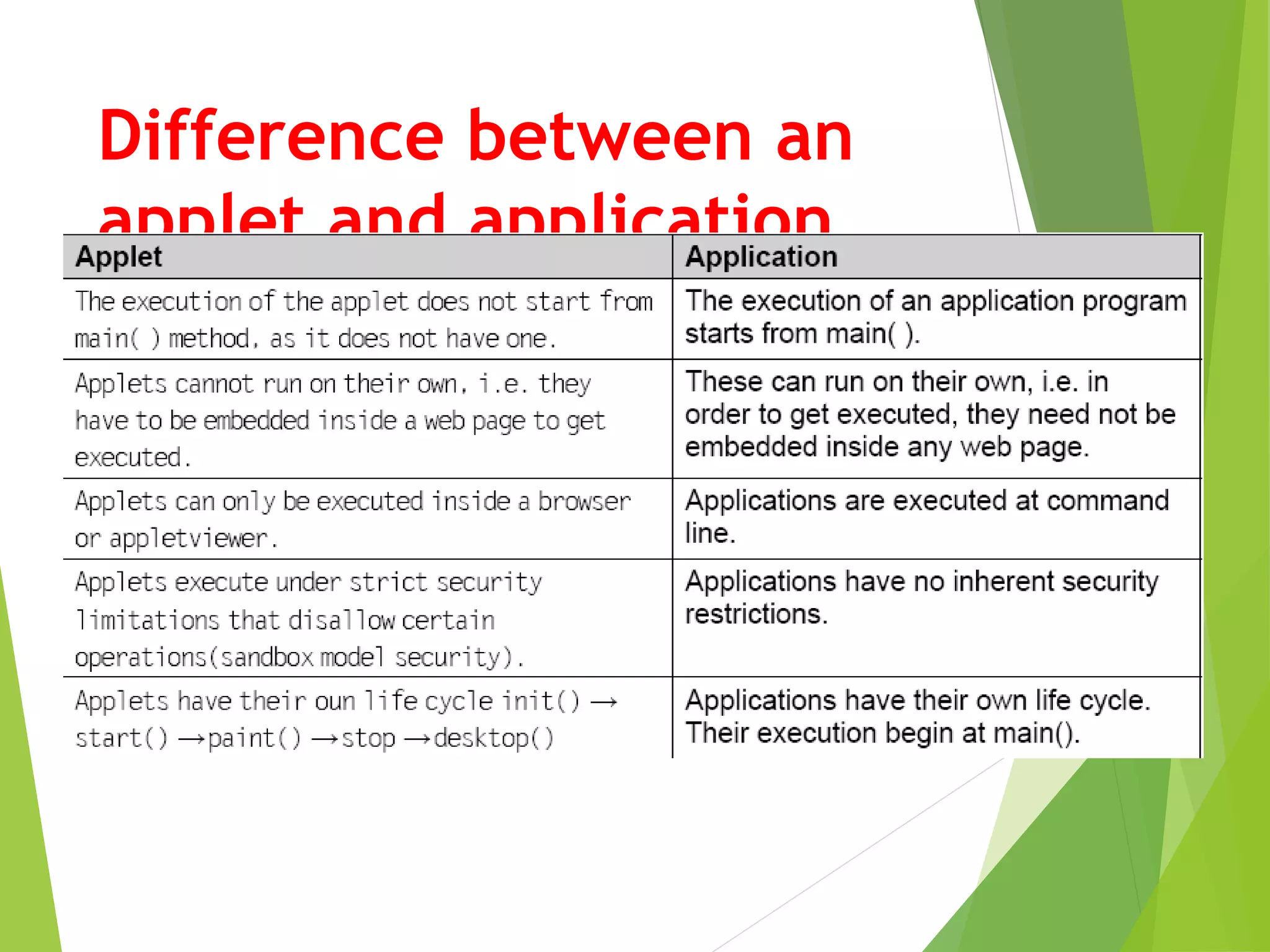
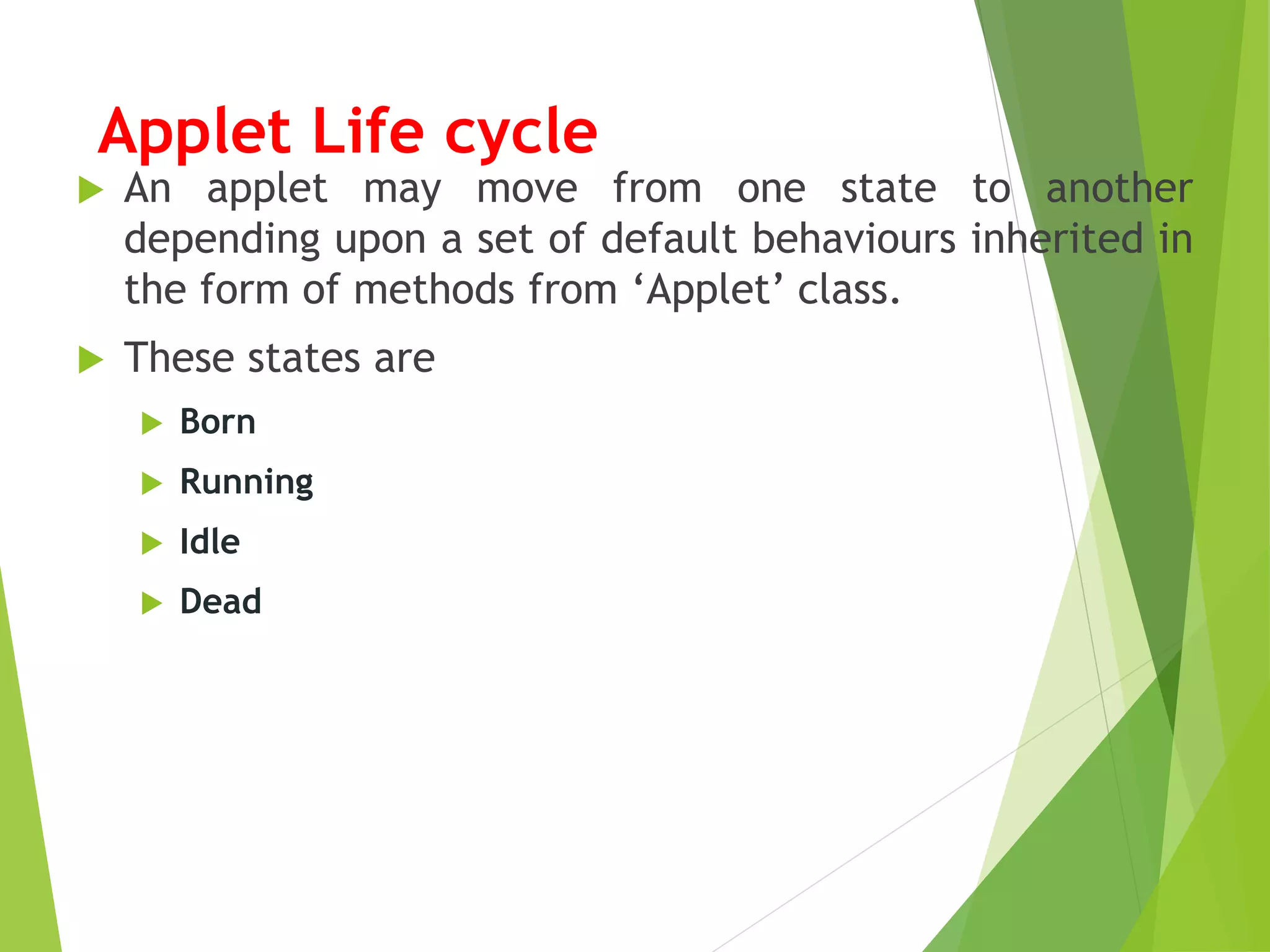
- Applets differ from applications in that they have a predefined lifecycle and are embedded in web pages rather than running independently.
- The Applet class is the superclass for all applets and defines methods corresponding to the applet lifecycle stages like init(), start(), paint(), stop(), and destroy().
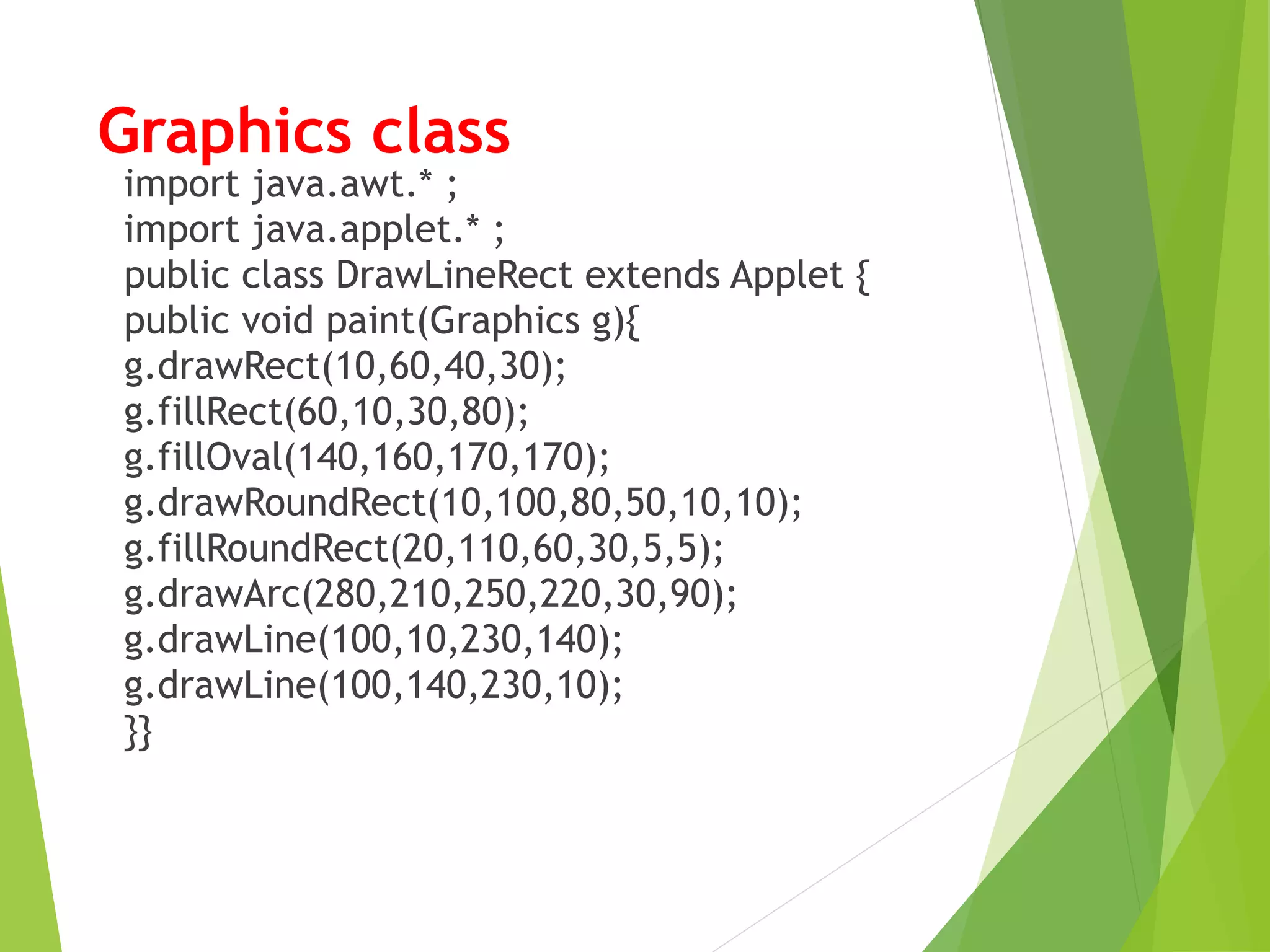
- Common methods for applets include drawString() for output, setBackground()/getBackground() for colors, and showStatus() to display in