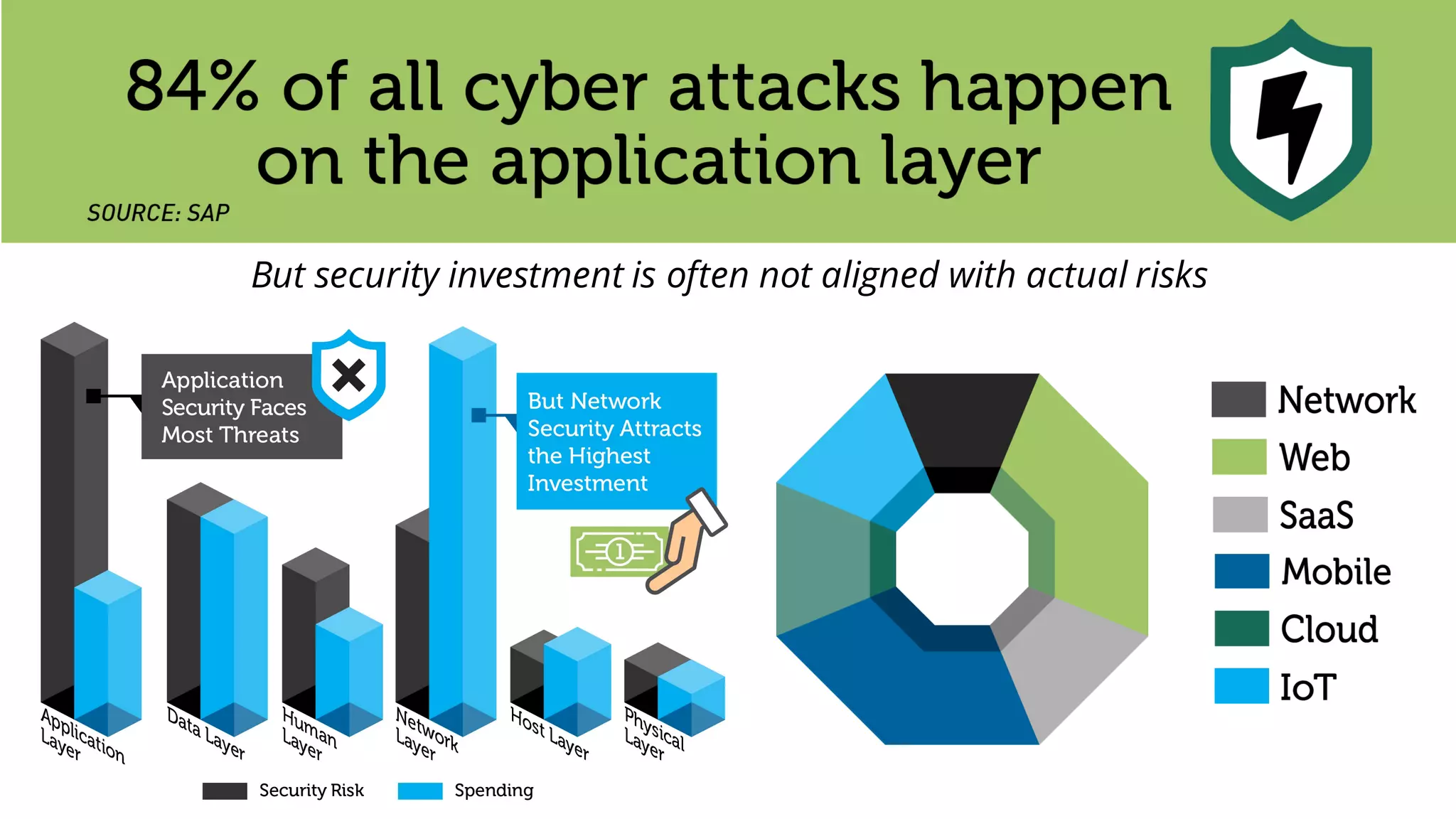
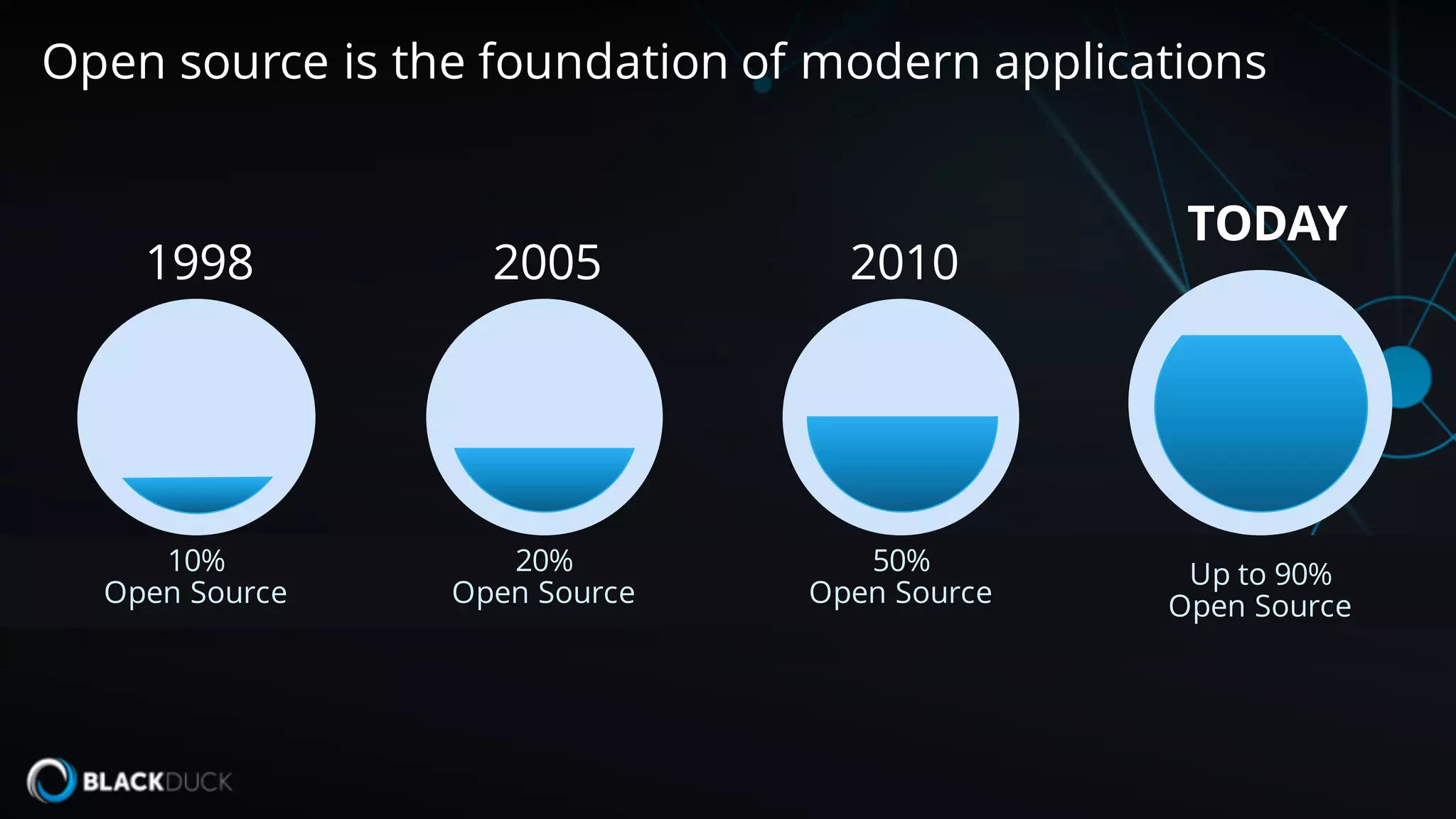
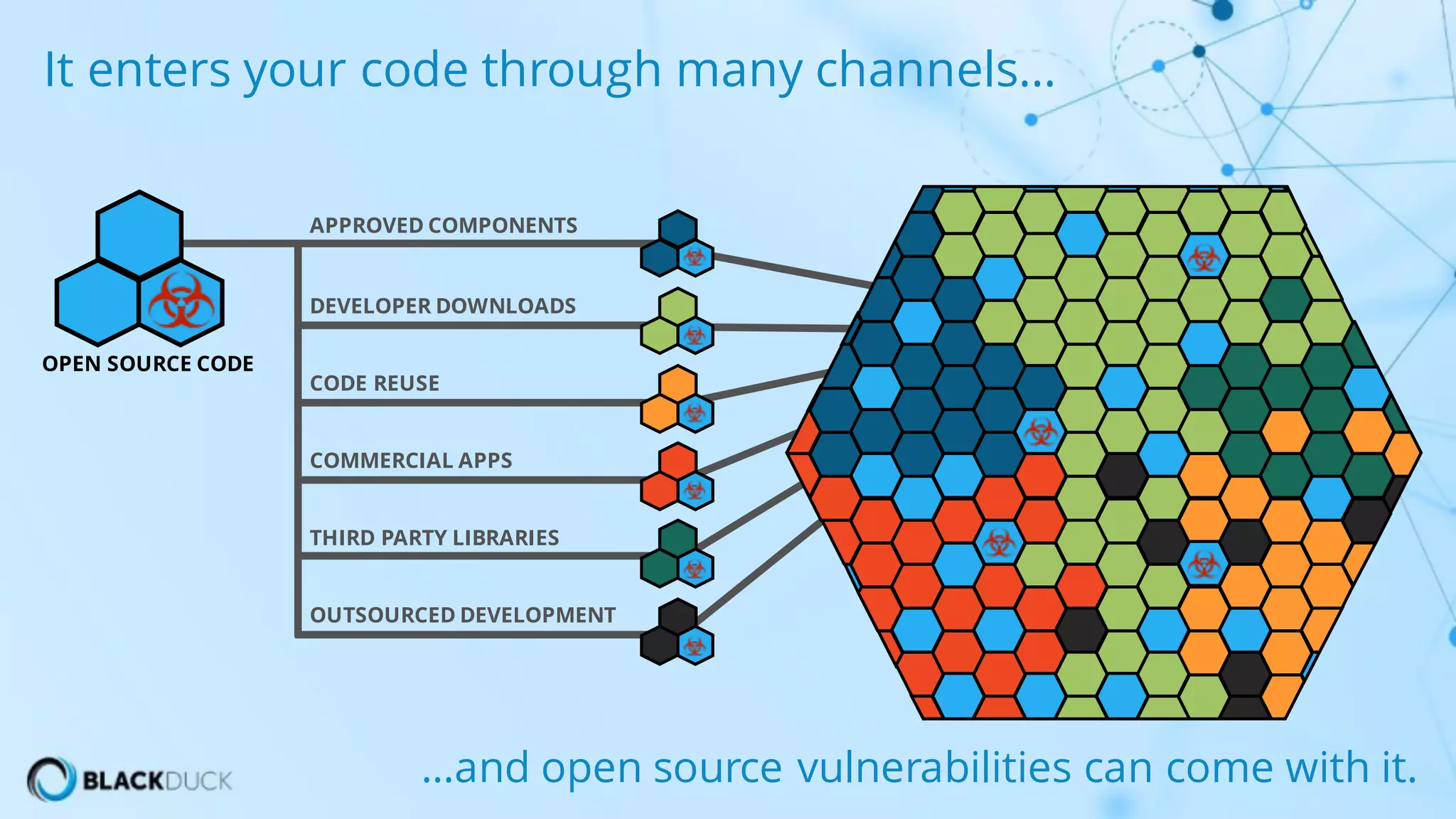
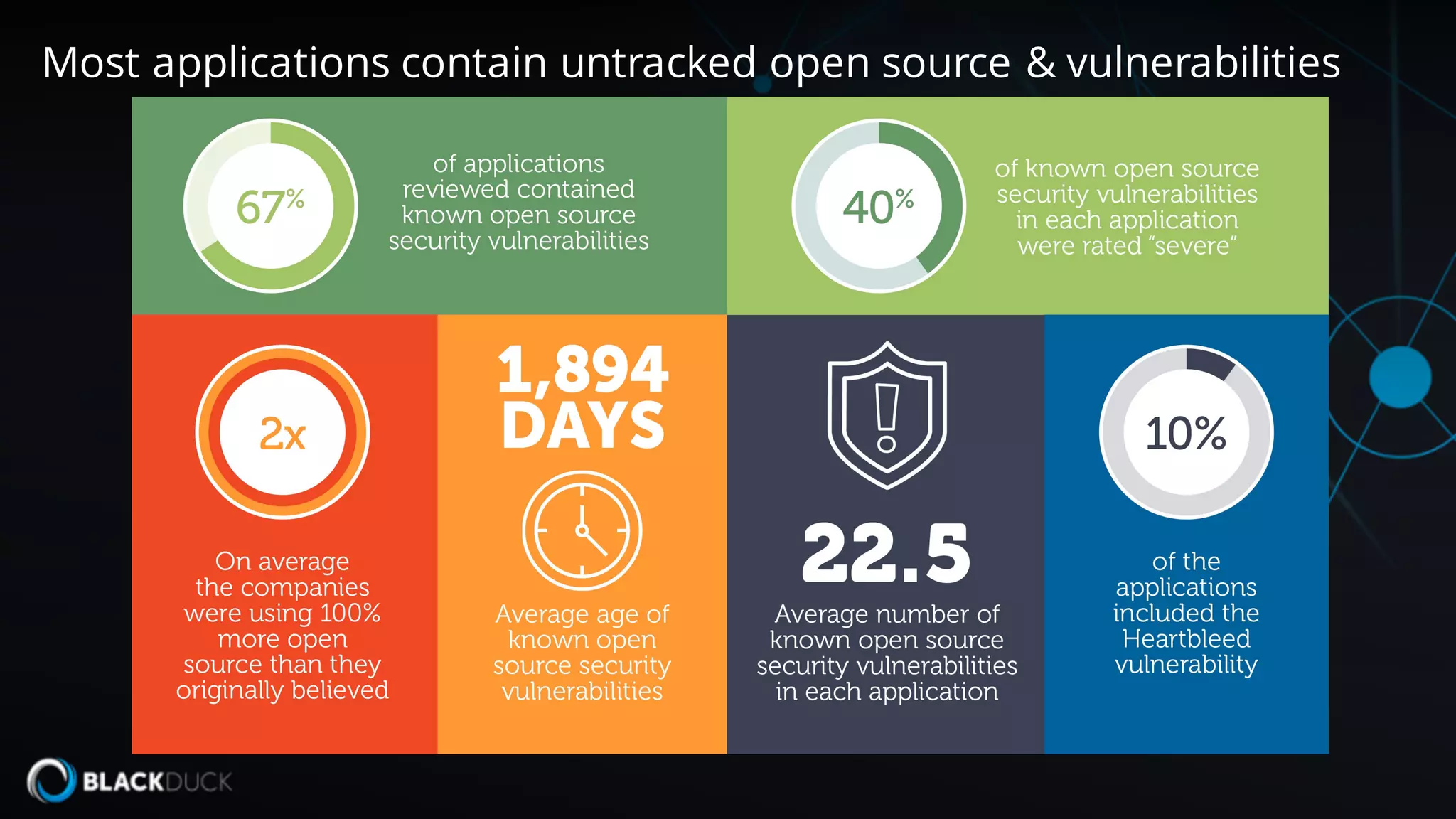
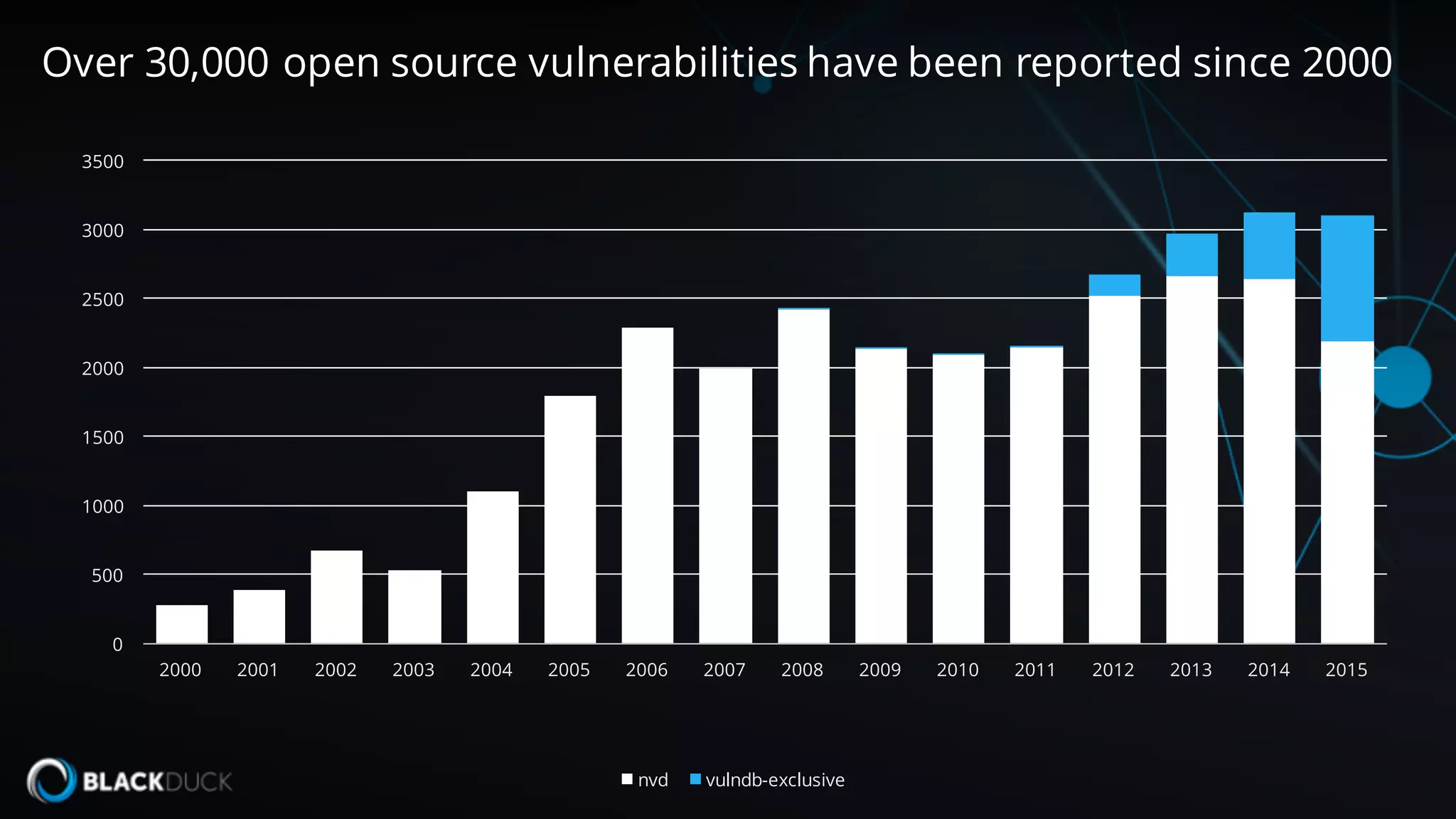
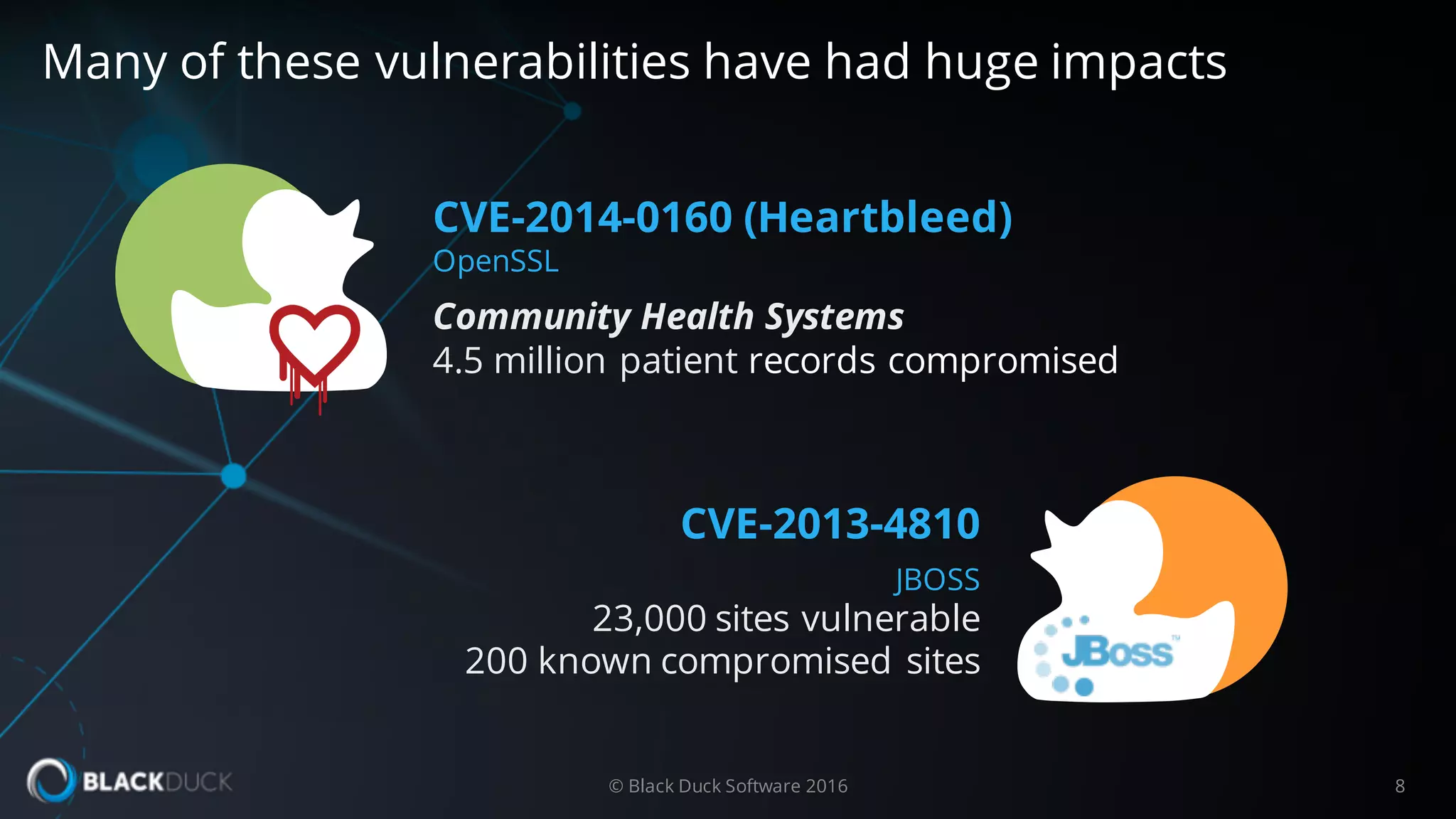
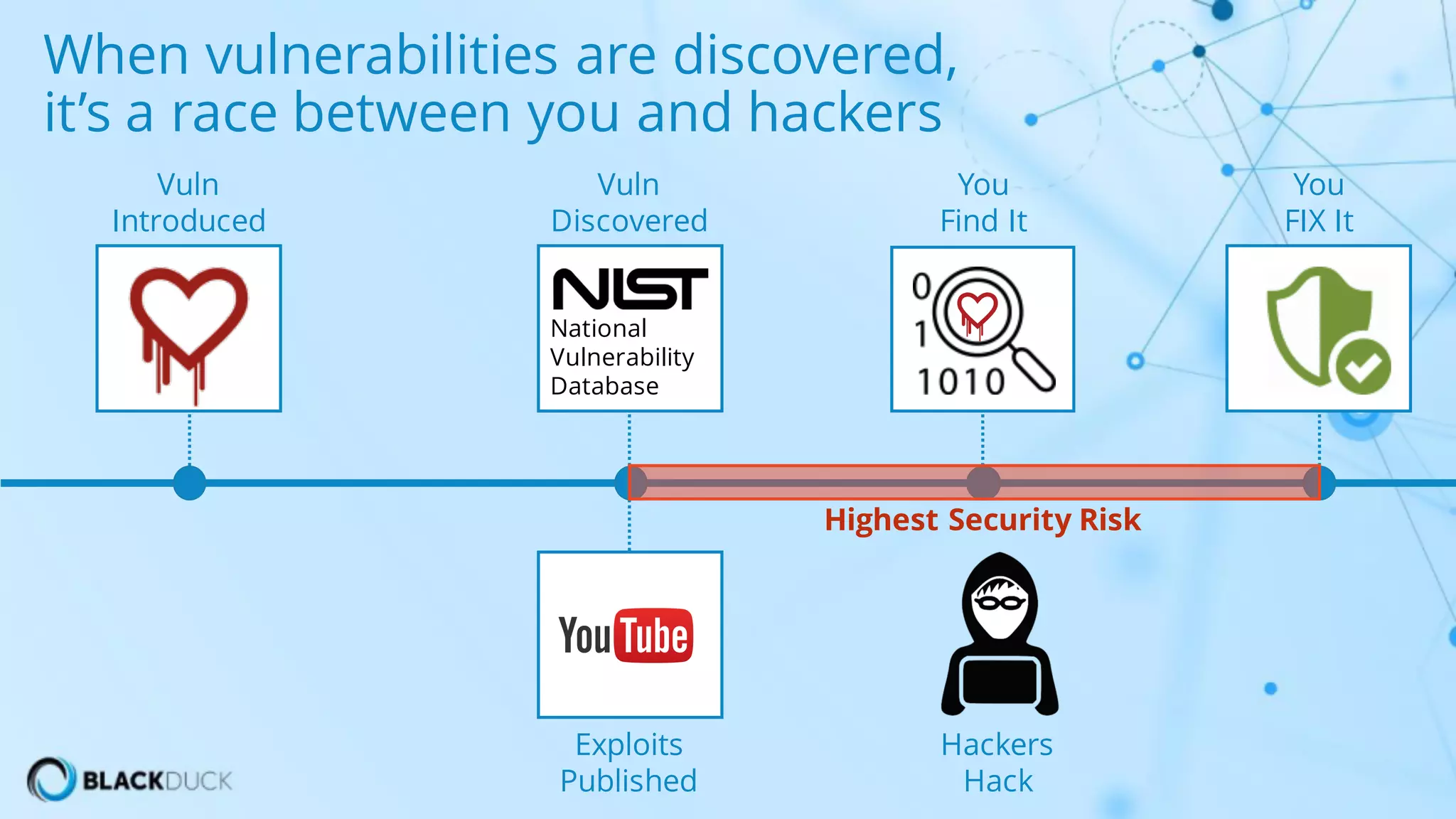
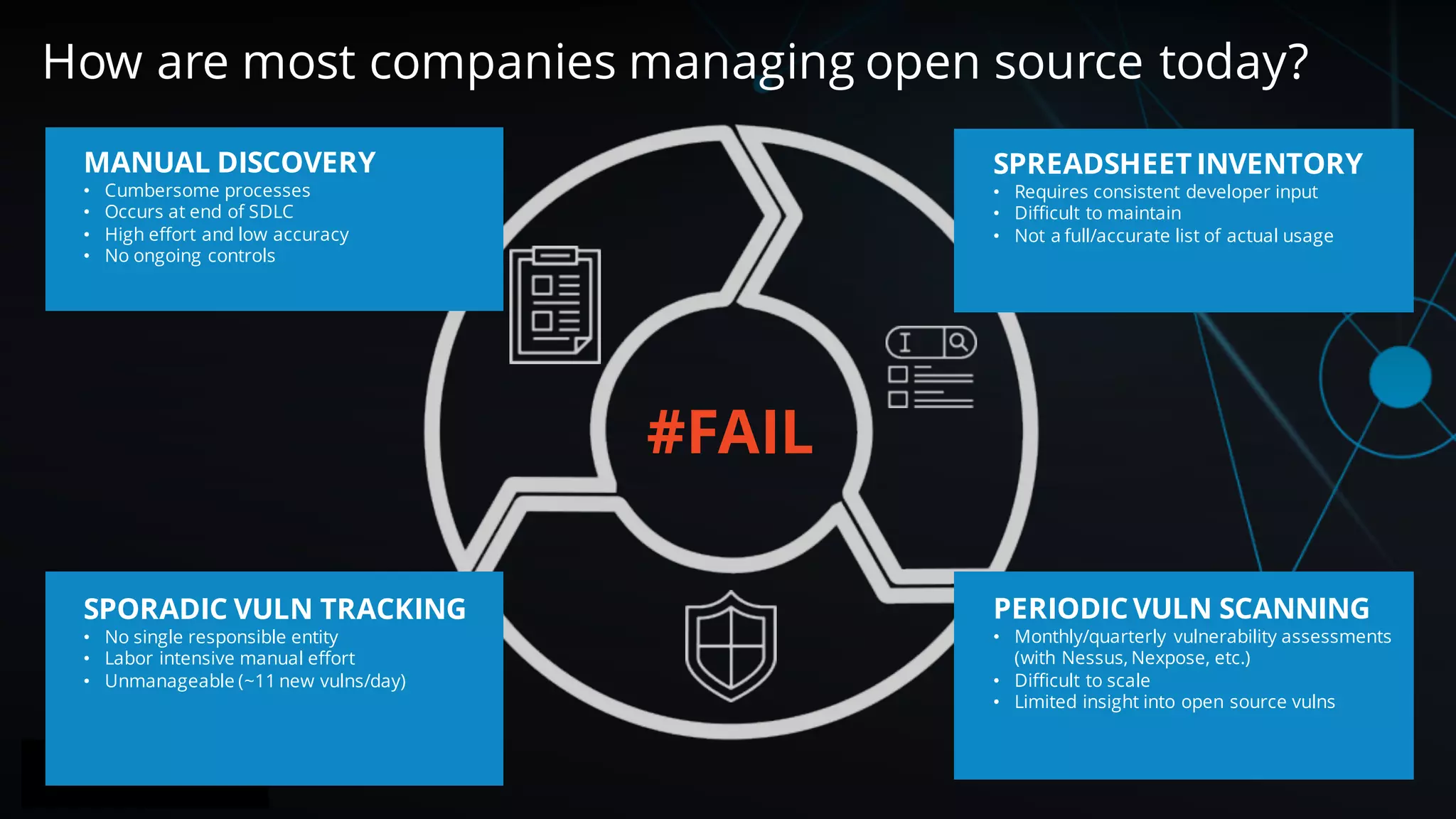
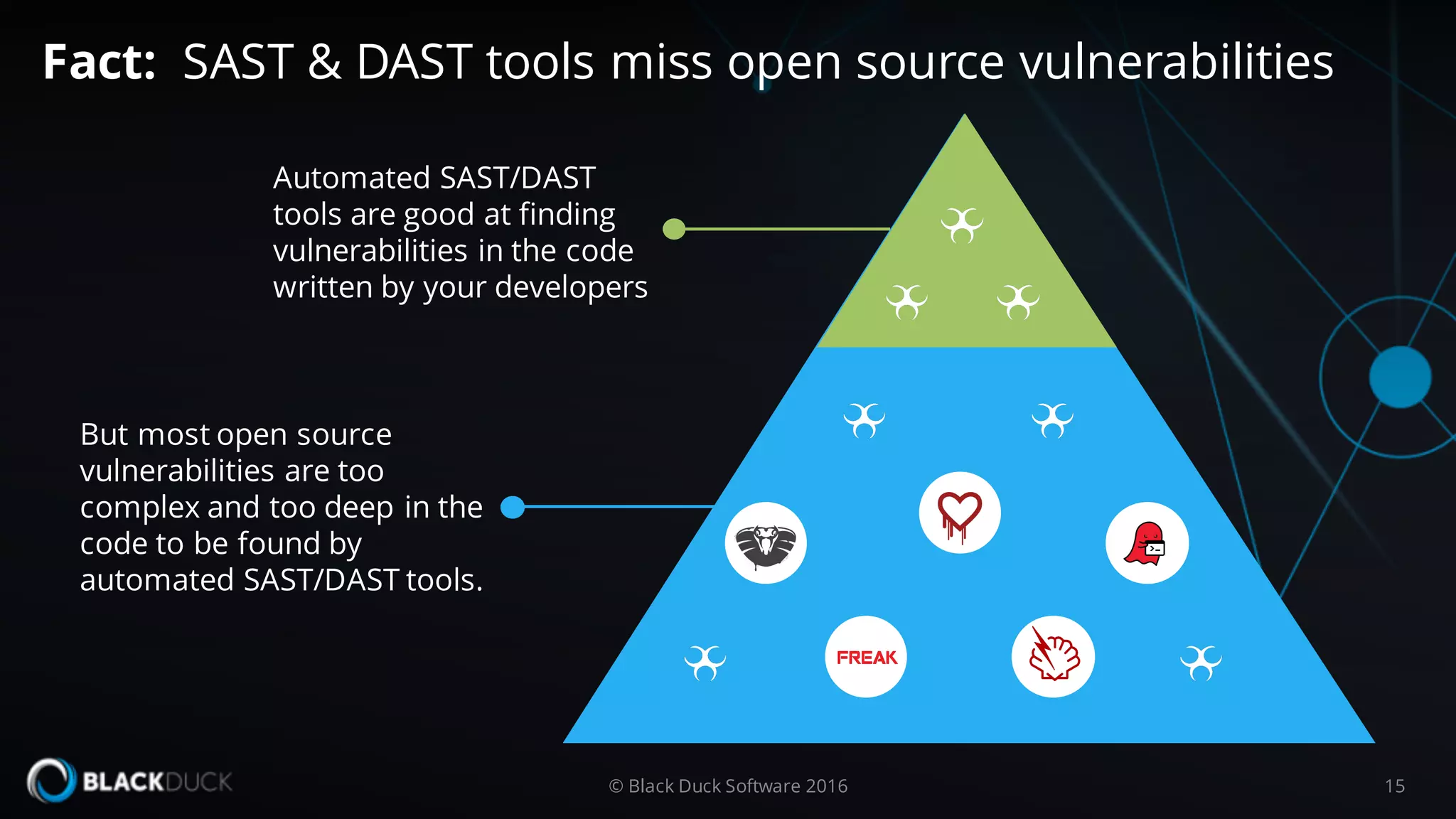
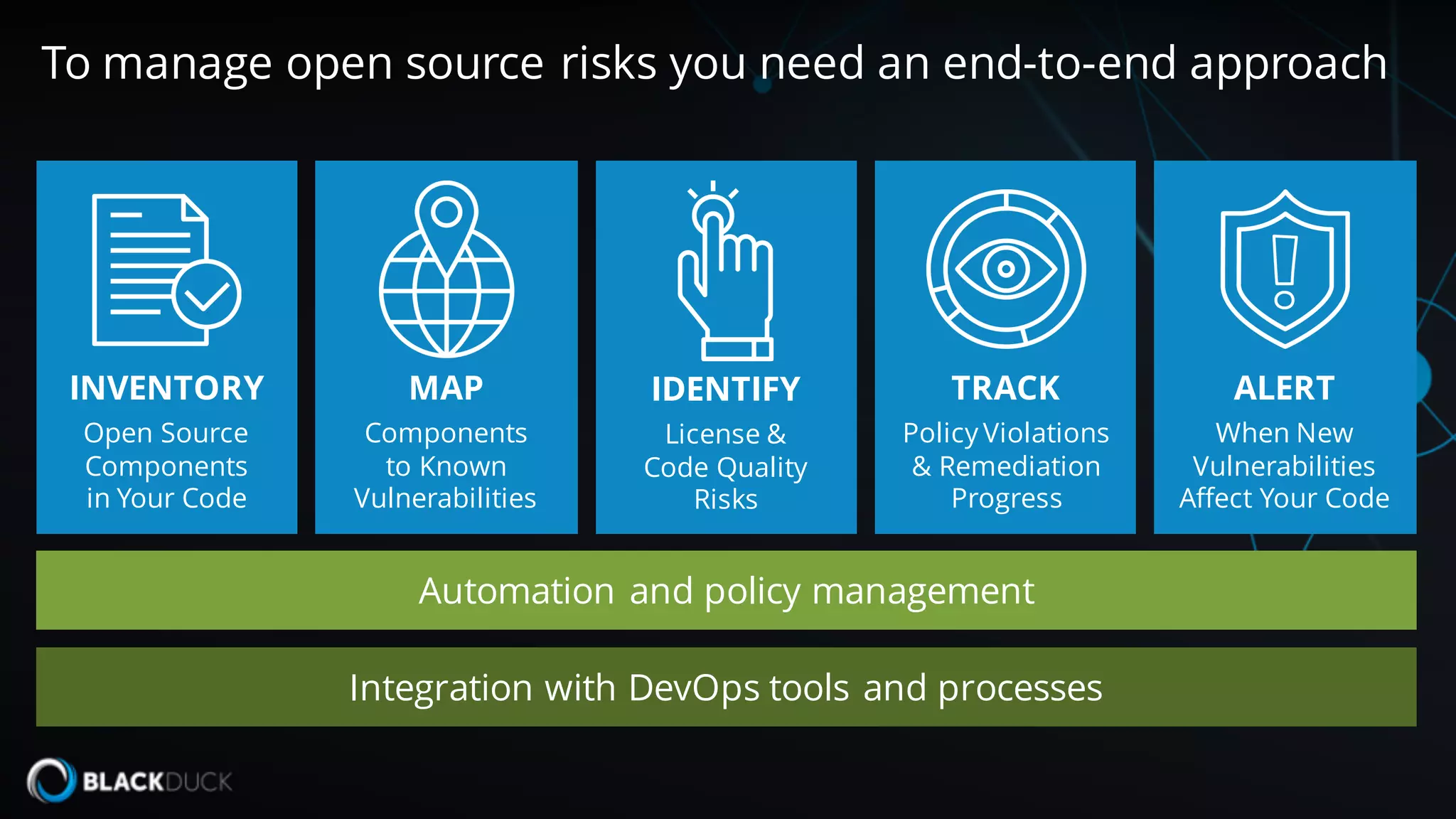
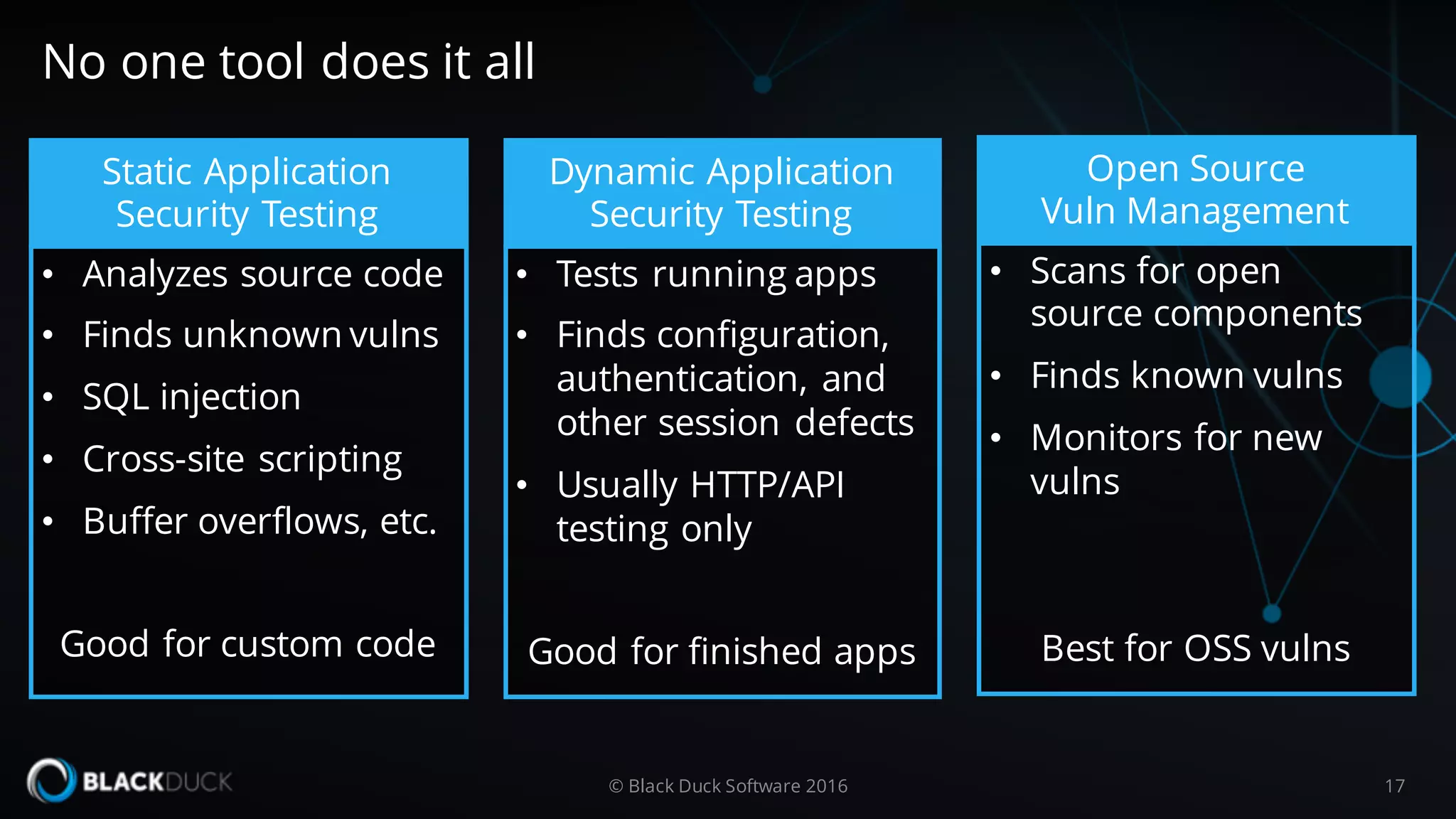
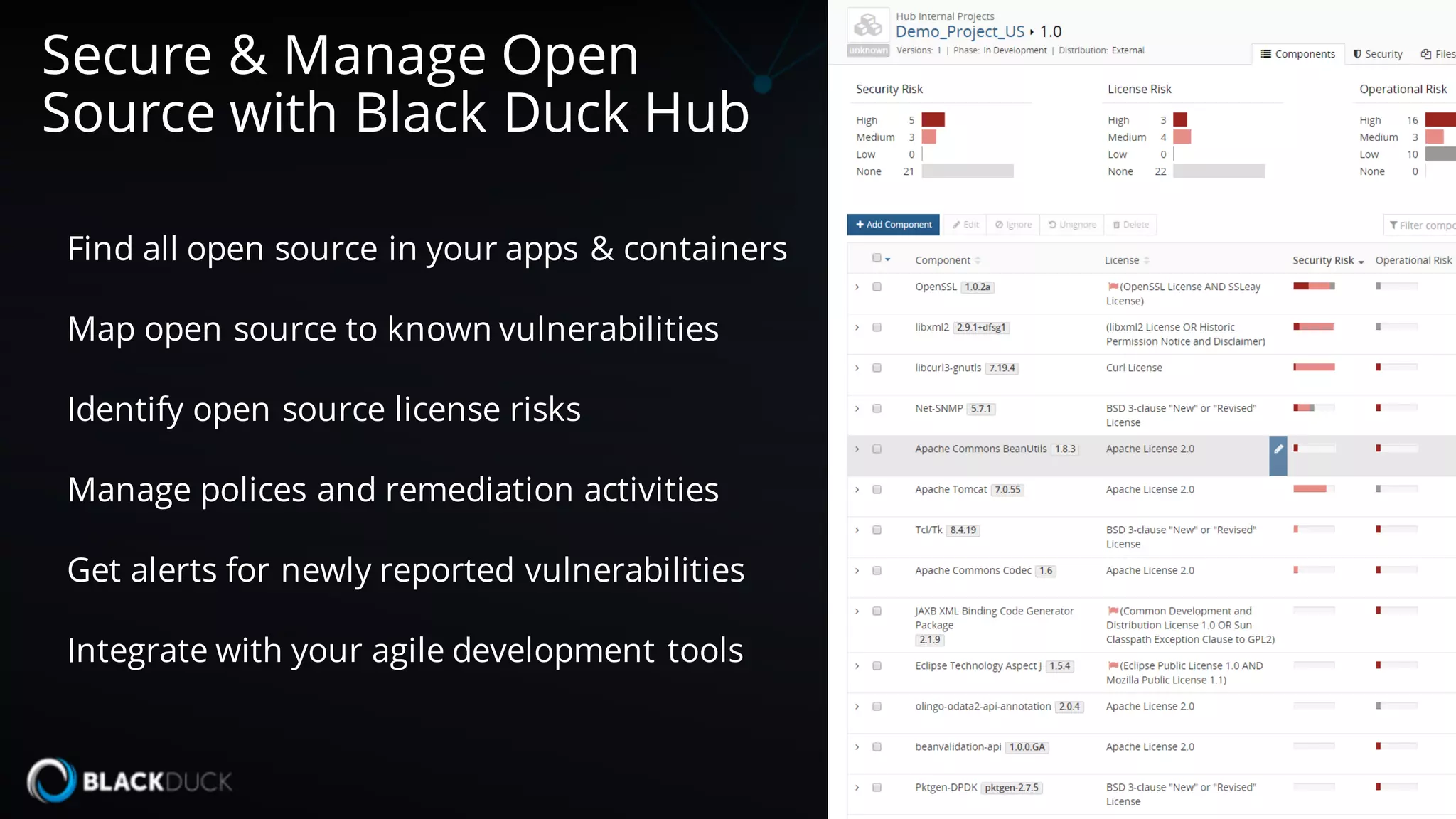
The document discusses the importance of managing open source software security, highlighting that the majority of applications contain untracked open source components and associated vulnerabilities. It underscores the inadequacies of current management practices, such as sporadic tracking and reliance on outdated tools, and emphasizes the need for a comprehensive approach to identify and remediate vulnerabilities. Additionally, it proposes using an integrated tool like Black Duck Hub to enhance open source security and integrate seamlessly with development processes.