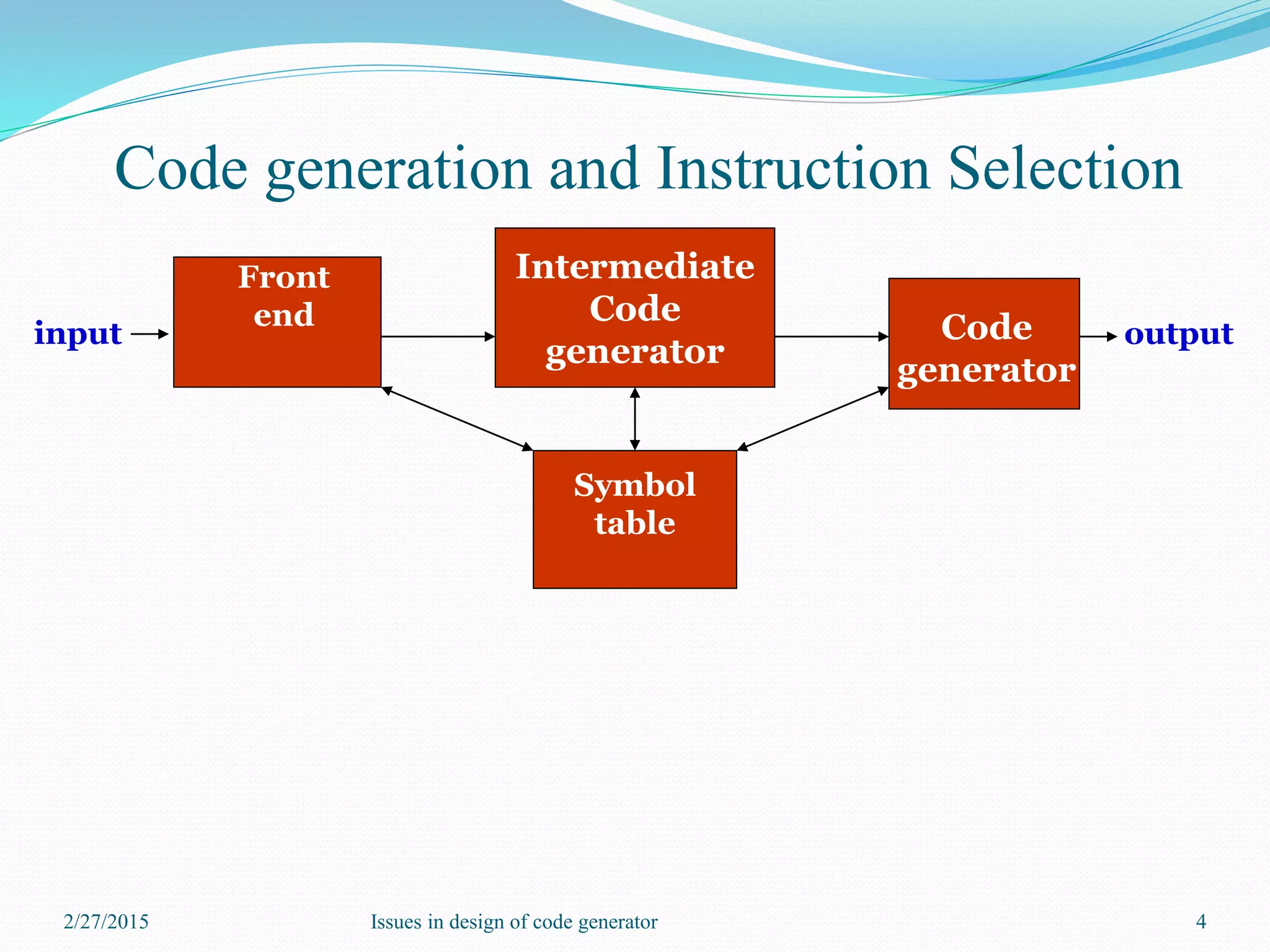
The document discusses the key issues in designing a code generator, which is the final phase of a compiler that generates target code from an optimized intermediate representation. It outlines several important considerations for the code generator, including the input representation, memory management, instruction selection, register allocation, evaluation order, and different approaches to code generation. The overall goal is to generate correct and high-quality target code that runs efficiently.