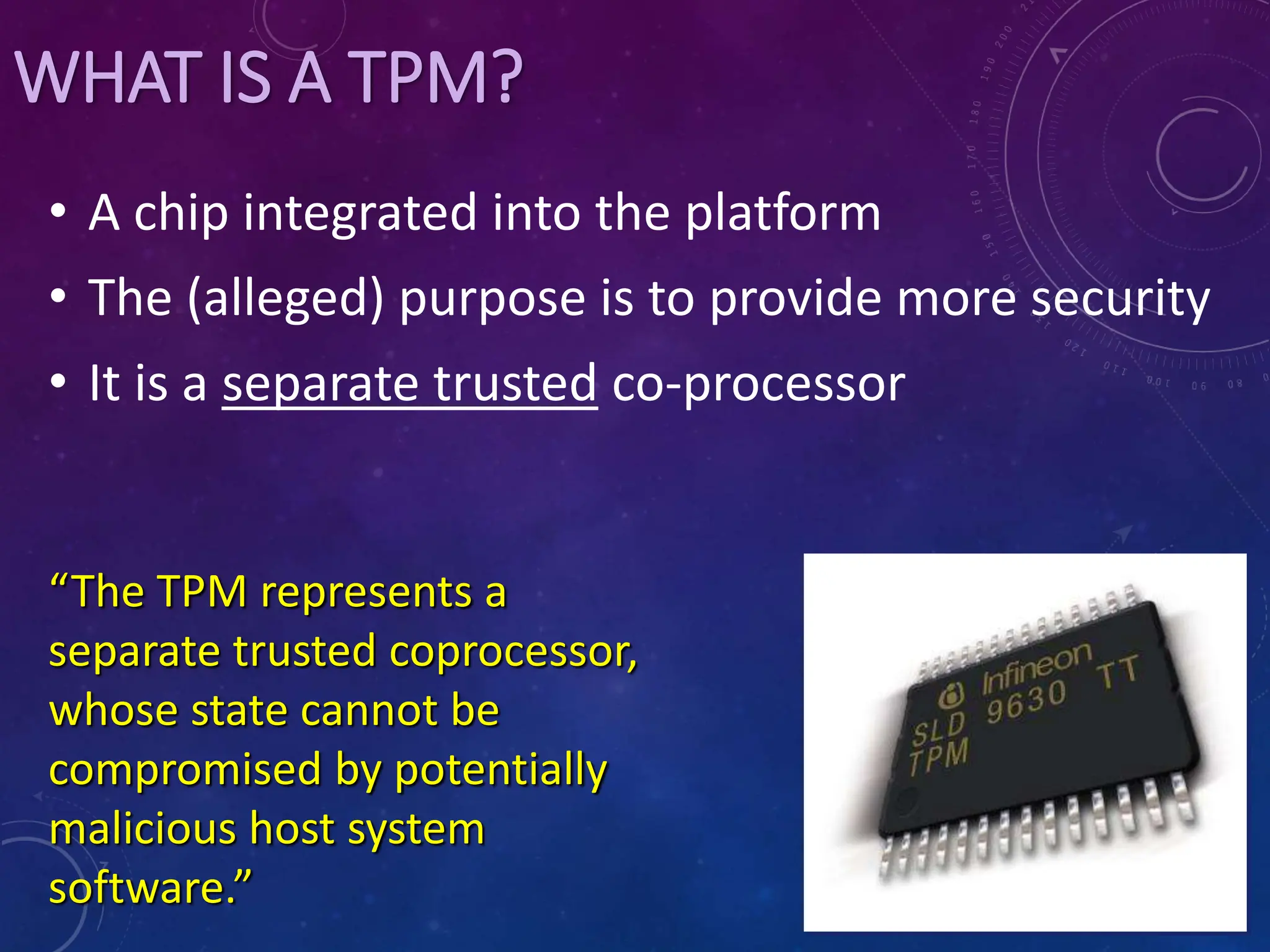
This document discusses trusted computing and the trusted platform module (TPM). It provides background on TPM, explaining that TPM is a hardware-based security chip that provides cryptographic and security functions. This allows increased trust that a computing system will behave as expected. The document covers how TPM works, providing sealed storage for keys and on-chip crypto. It also discusses the potential for abuse of features like attestation by software vendors. While TPM increases security, there are concerns about user privacy and control over their own devices.






![ATTESTATION
The TPM's most controversial feature is
attestation, the ability to measure the state of
a computer and send a signed message
certifying that particular hardware or
software is or isn't present. Most TC
opponents fear that this will be abused by
vendors [1].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trustedcomputing-240223101217-cb0b1a68/75/Trusted-_Computing-_security-mobile-ppt-8-2048.jpg)

![HOW?
• Protection from malware and detection of
compromised systems. [4] Shows that syslogd has
been compromised by a root kit.
• Tick counter, Timestamps are a security critical
parameter in KERBEROS.
• Provide stronger 2 factor authentication.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trustedcomputing-240223101217-cb0b1a68/75/Trusted-_Computing-_security-mobile-ppt-10-2048.jpg)



![PRO VS. CON
• “Trusted Computing requires you to surrender
control of your machine to the vendors of your
hardware and software, thereby making the
computer less trustworthy from the user’s
perspective” [11] Ross Anderson](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trustedcomputing-240223101217-cb0b1a68/75/Trusted-_Computing-_security-mobile-ppt-14-2048.jpg)

![“For years Bill Gates has dreamed of finding
a way to make the Chinese pay for
software, TC looks like being the answer to
his prayer.” [11] Ross Anderson.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trustedcomputing-240223101217-cb0b1a68/75/Trusted-_Computing-_security-mobile-ppt-16-2048.jpg)

![BIBLIOGRAPHY
• [1] Andy Doman, Trusted Computing: A matter of Trust,
http://www.networkmagazine.com/shared/article/showArticle.jhtml?articleId=221028
89
• [2] DigitalIDWorld, "Assuring Networked Data and Application Reliability", Digital ID
World Jan/Feb 2004 https://www.trustedcomputinggroup.org/press/1-
3412425E_SC.pdf
•
• [4] Reiner Sailer, et al, , "The Role of TPM in Enterprise Security",
https://www.trustedcomputinggroup.org/press/news_articles/rc23363.pdf
• [11] Ross Anderson, http://www.againsttcpa.com/index.shtml](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trustedcomputing-240223101217-cb0b1a68/75/Trusted-_Computing-_security-mobile-ppt-18-2048.jpg)
