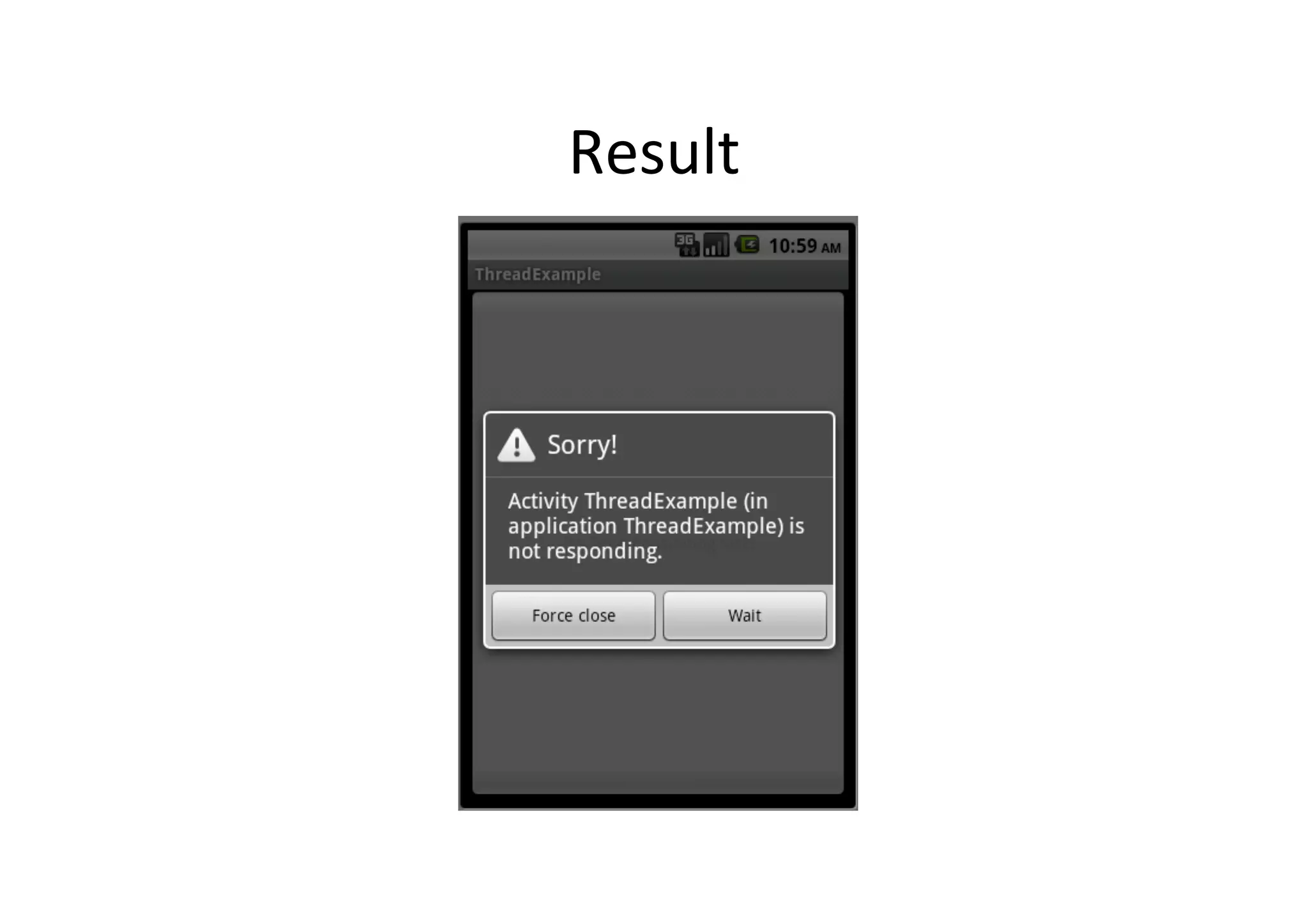
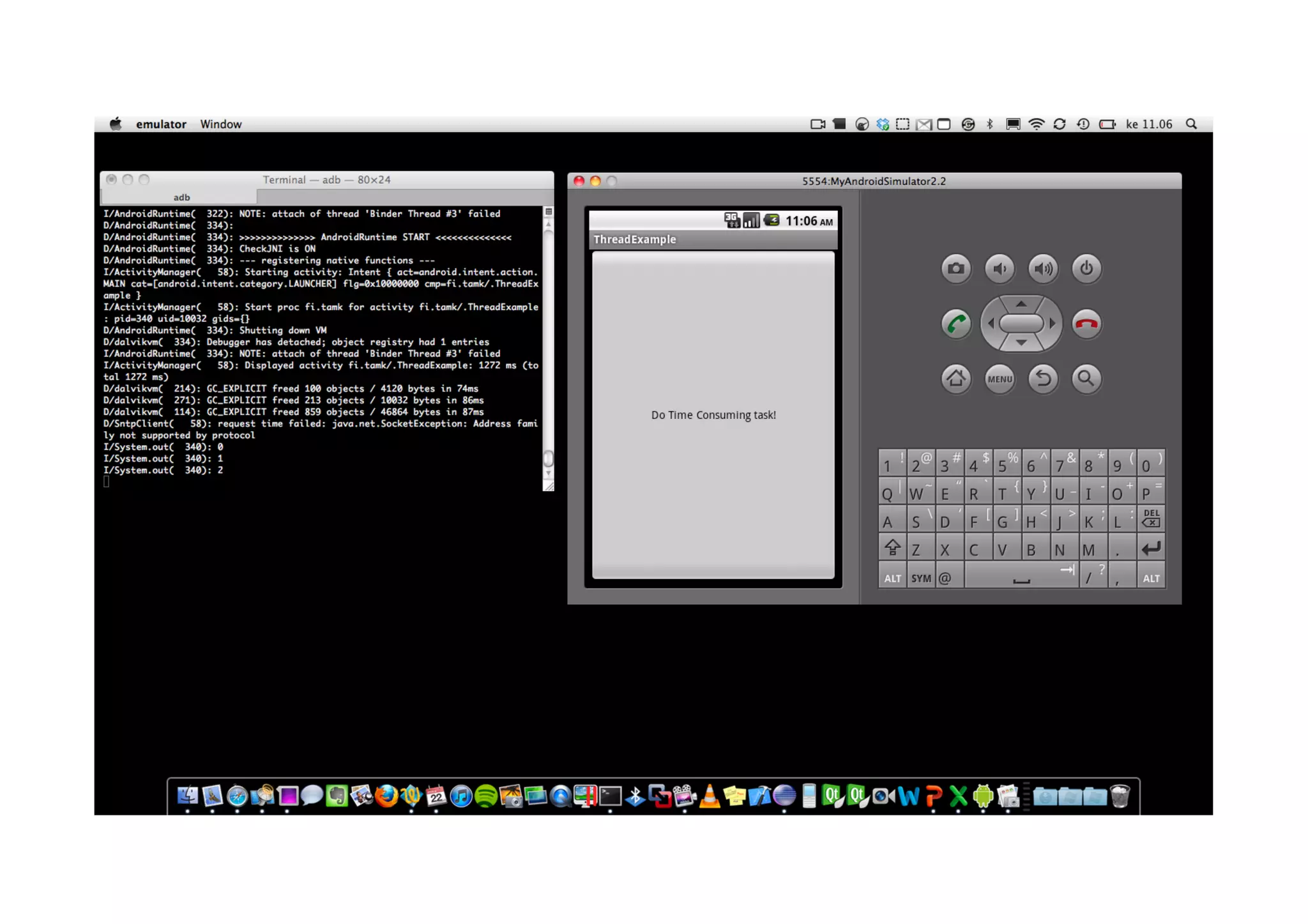
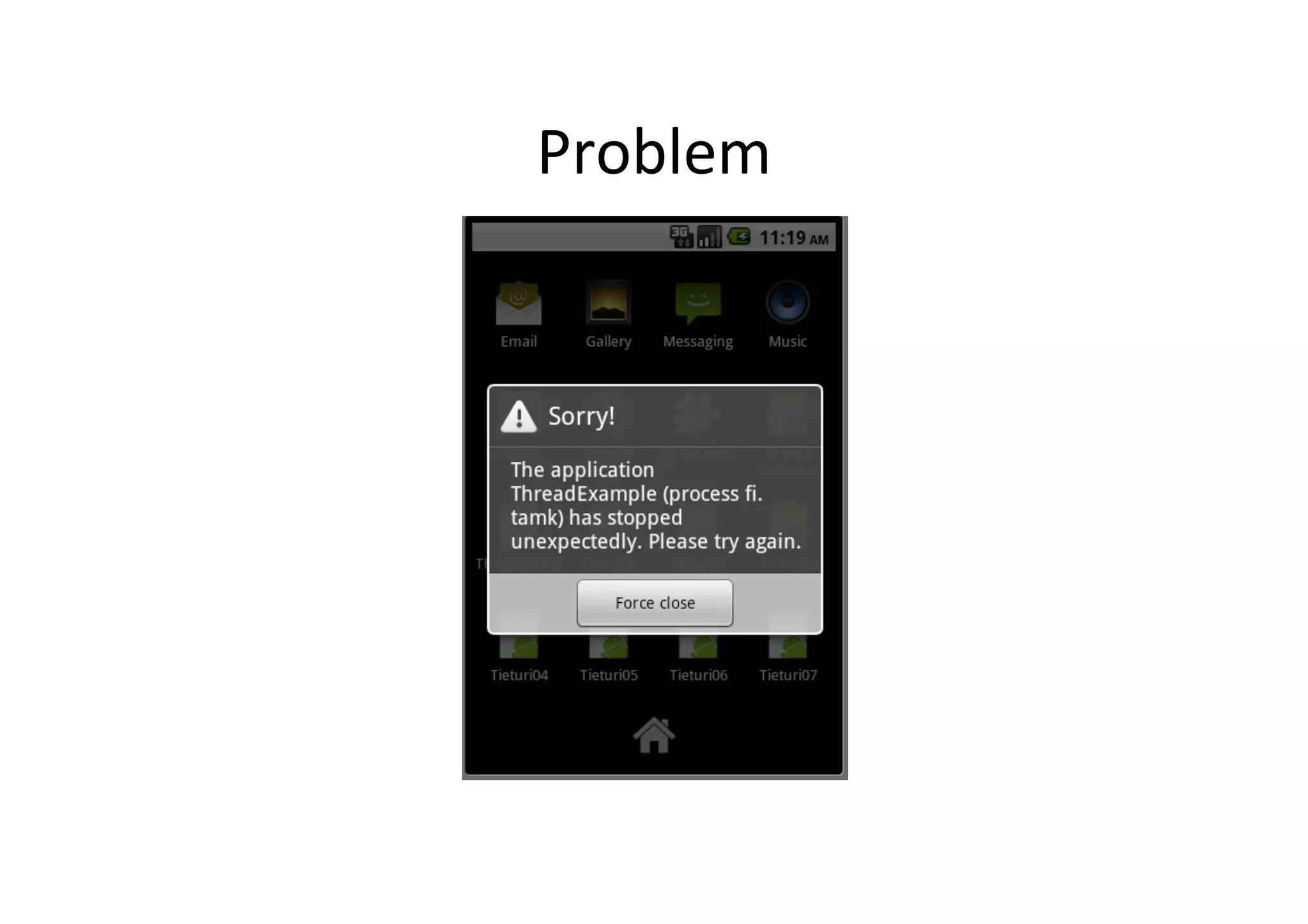
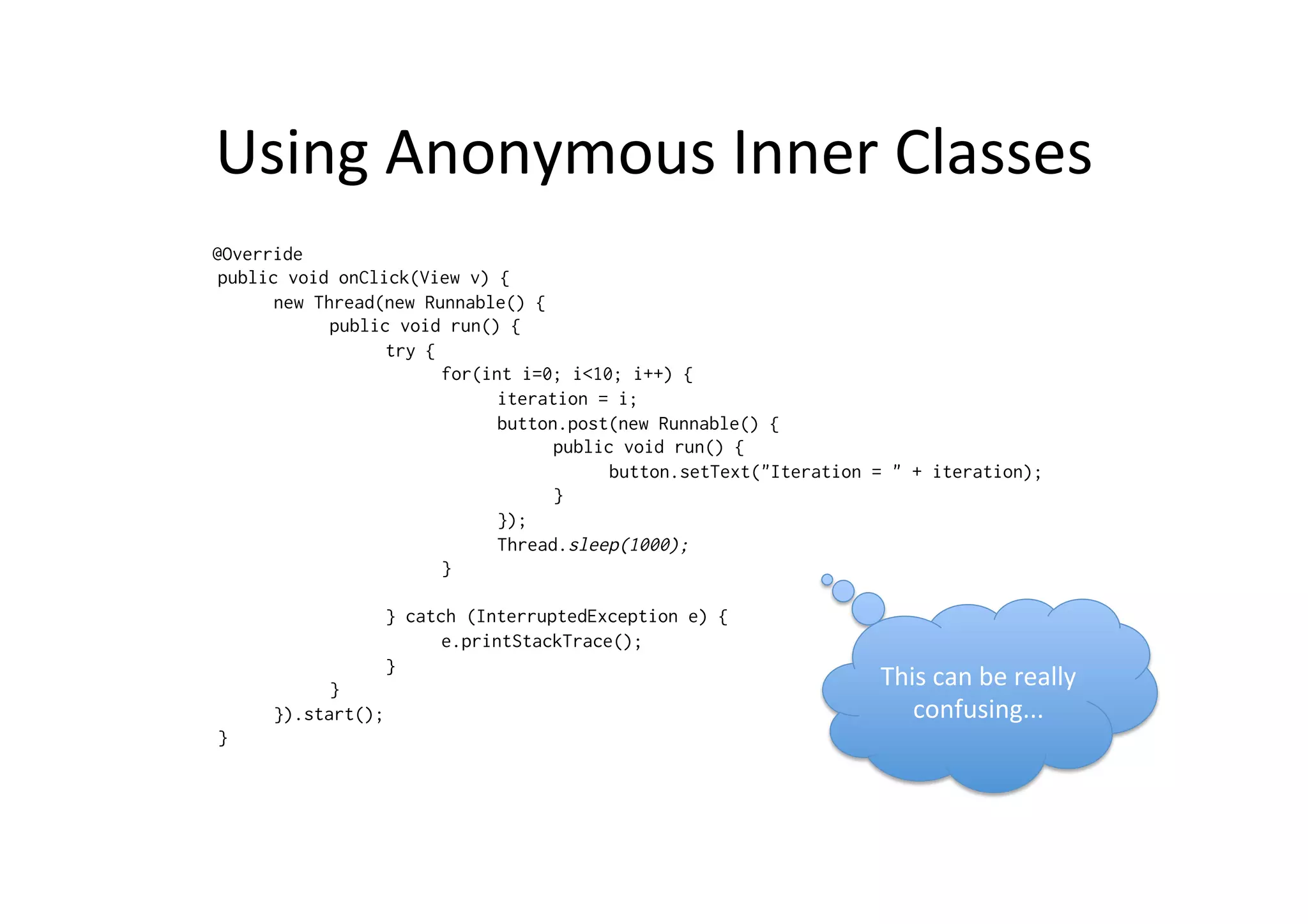
The document discusses Android threading and how to handle long running tasks to avoid blocking the UI thread. It covers the main UI thread, how to run tasks on a background thread using Thread and Runnable, and how to update the UI from the background thread using runOnUiThread(), post(), postDelayed() and AsyncTask. AsyncTask is recommended as it handles threading for you by running background tasks on a worker thread and calling publishProgress() to update the UI on the main thread.











![Example
(Google
SDK)
private class DownloadFilesTask extends AsyncTask<URL, Integer, Long> {
protected Long doInBackground(URL... urls) {
int count = urls.length;
long totalSize = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
totalSize += Downloader.downloadFile(urls[i]);
publishProgress((int) ((i / (float) count) * 100));
}
return totalSize;
}
protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... progress) {
setProgressPercent(progress[0]);
}
protected void onPostExecute(Long result) {
showDialog("Downloaded " + result + " bytes");
}
}
new DownloadFilesTask().execute(url1, url2, url3);
Params,
Progress,
Result](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/android-threading-140401044337-phpapp01/75/Android-Threading-16-2048.jpg)
![public class ThreadExample extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private Button button;
...
class MyBackgroundTask extends AsyncTask<Integer, Integer, Integer> {
protected Integer doInBackground(Integer... ints) {
int i = ints[0];
try {
for(i=0; i<10; i++) {
System.out.println("doInBackground!");
publishProgress(new Integer(i));
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return i;
}
protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer iteration) {
button.setText("Iteration = " + iteration);
}
protected void onPostExecute(Integer result) {
button.setText("Finished with result of: " + result);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/android-threading-140401044337-phpapp01/75/Android-Threading-17-2048.jpg)