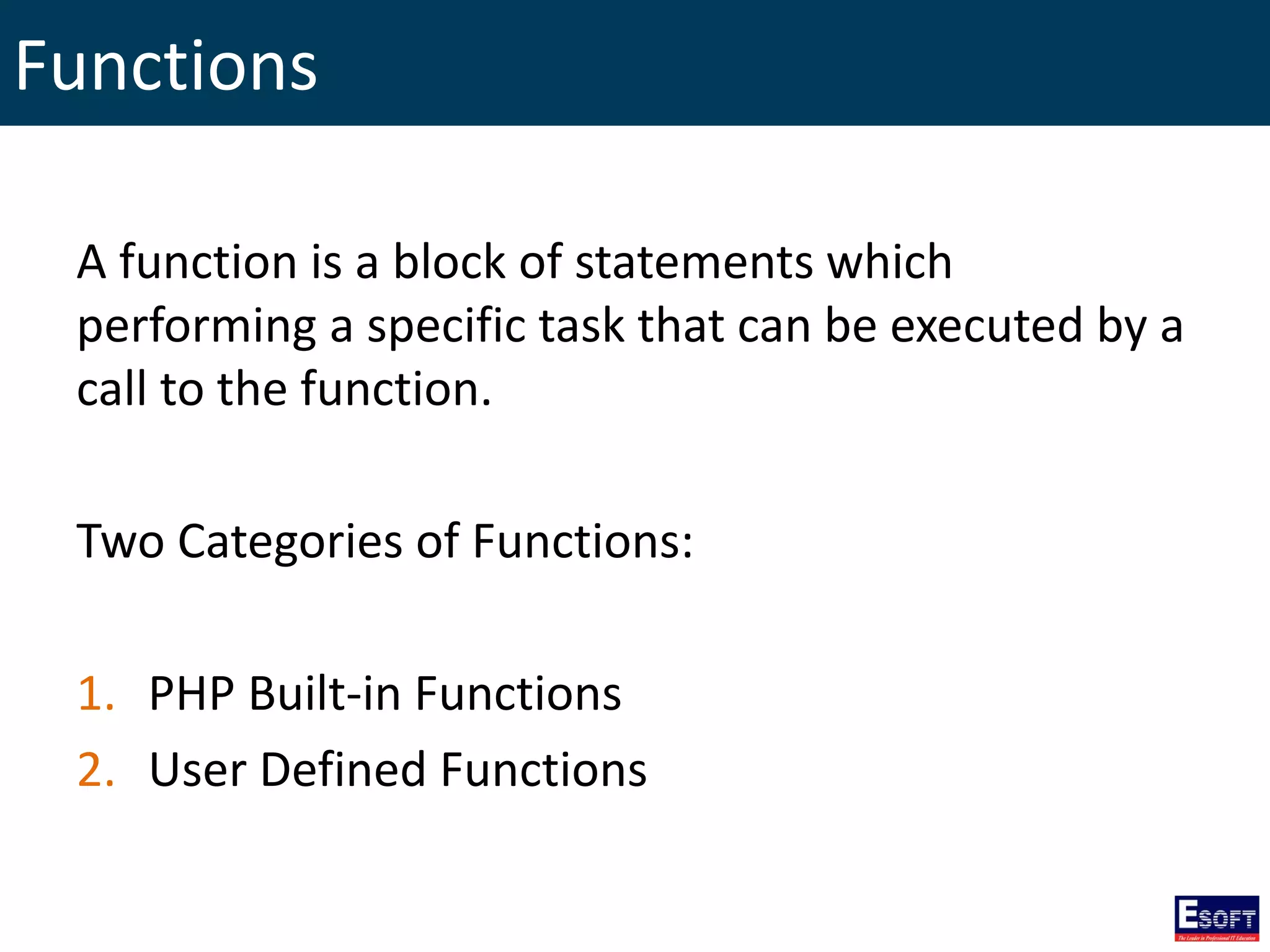
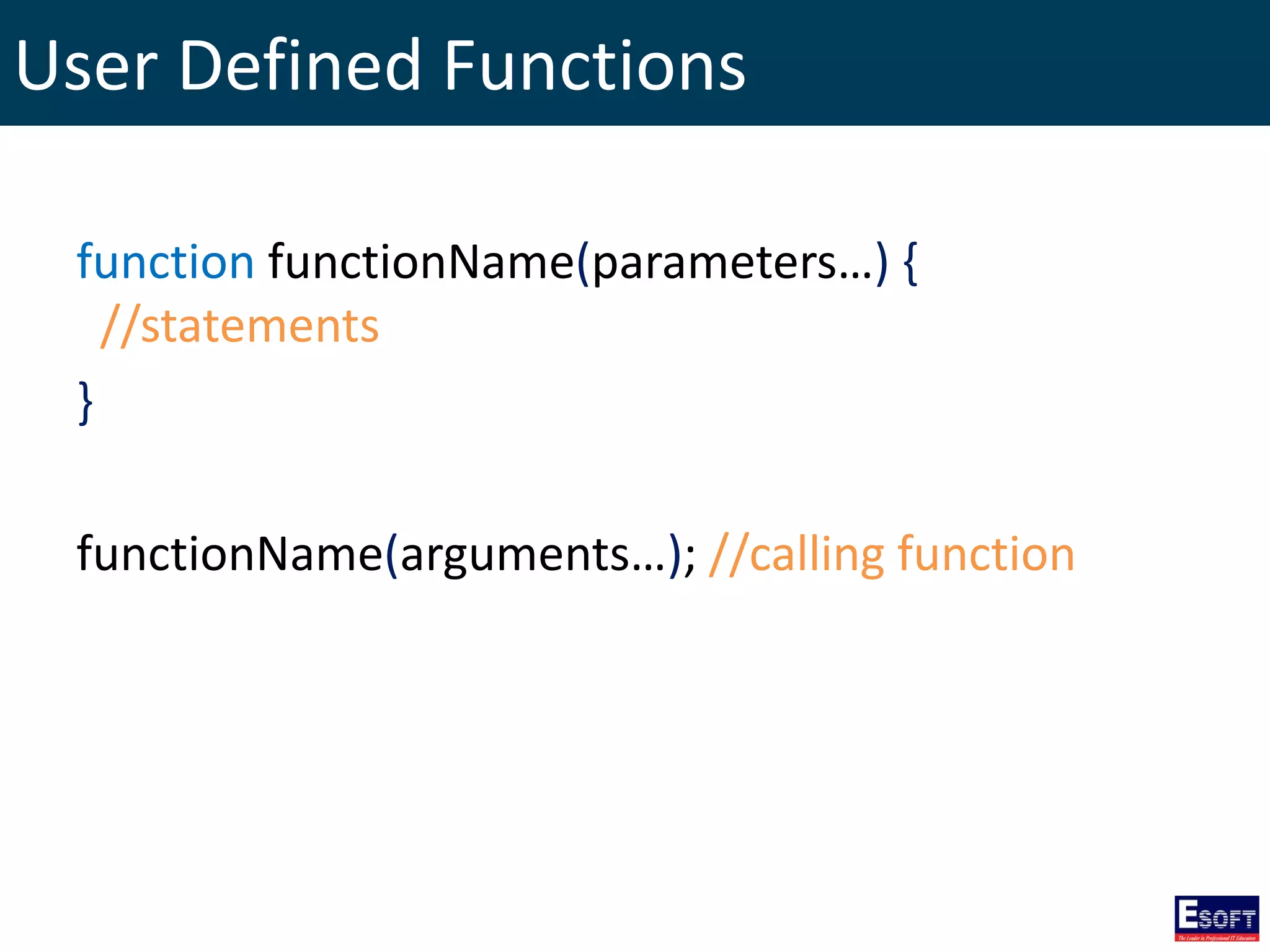
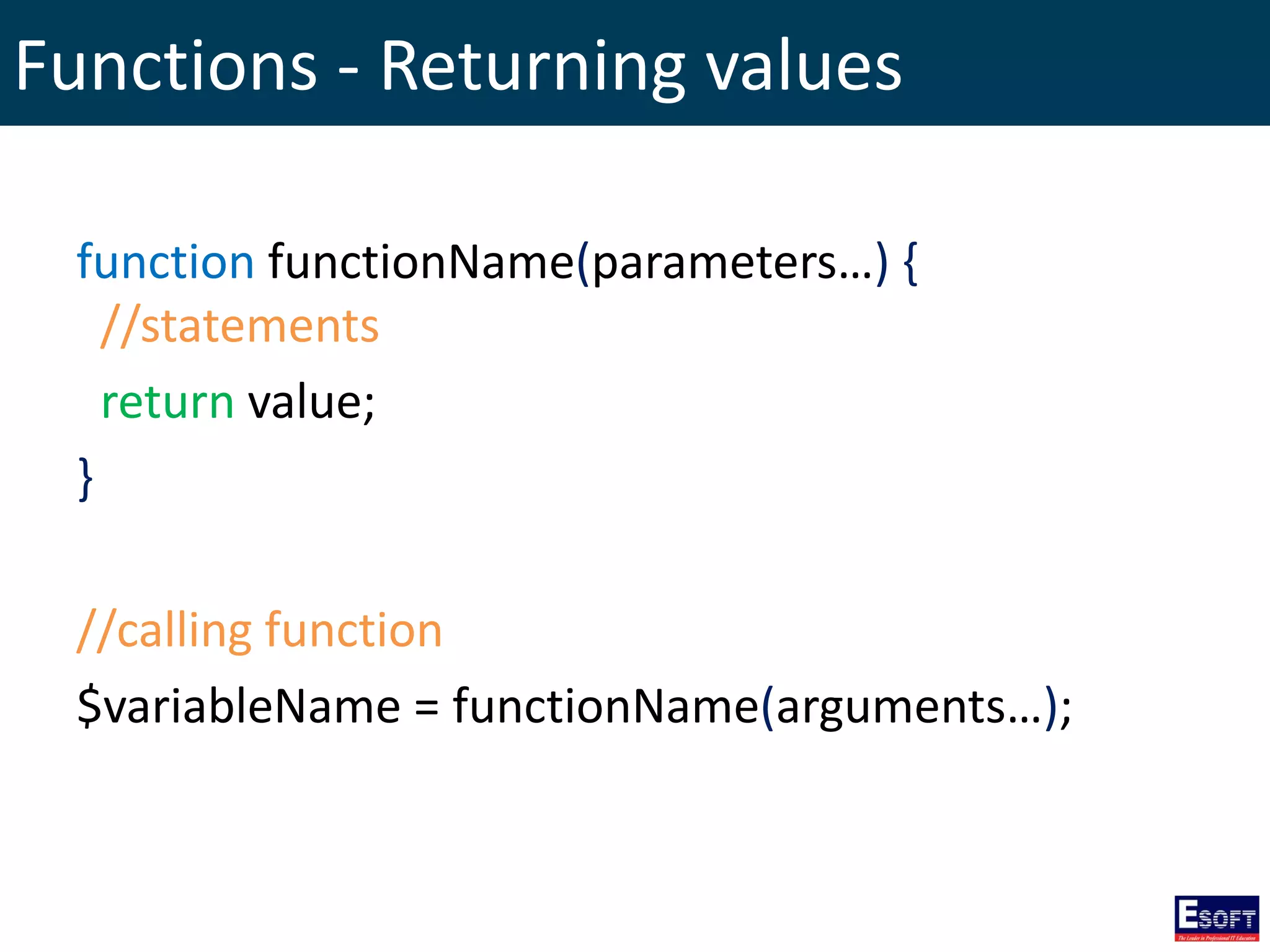
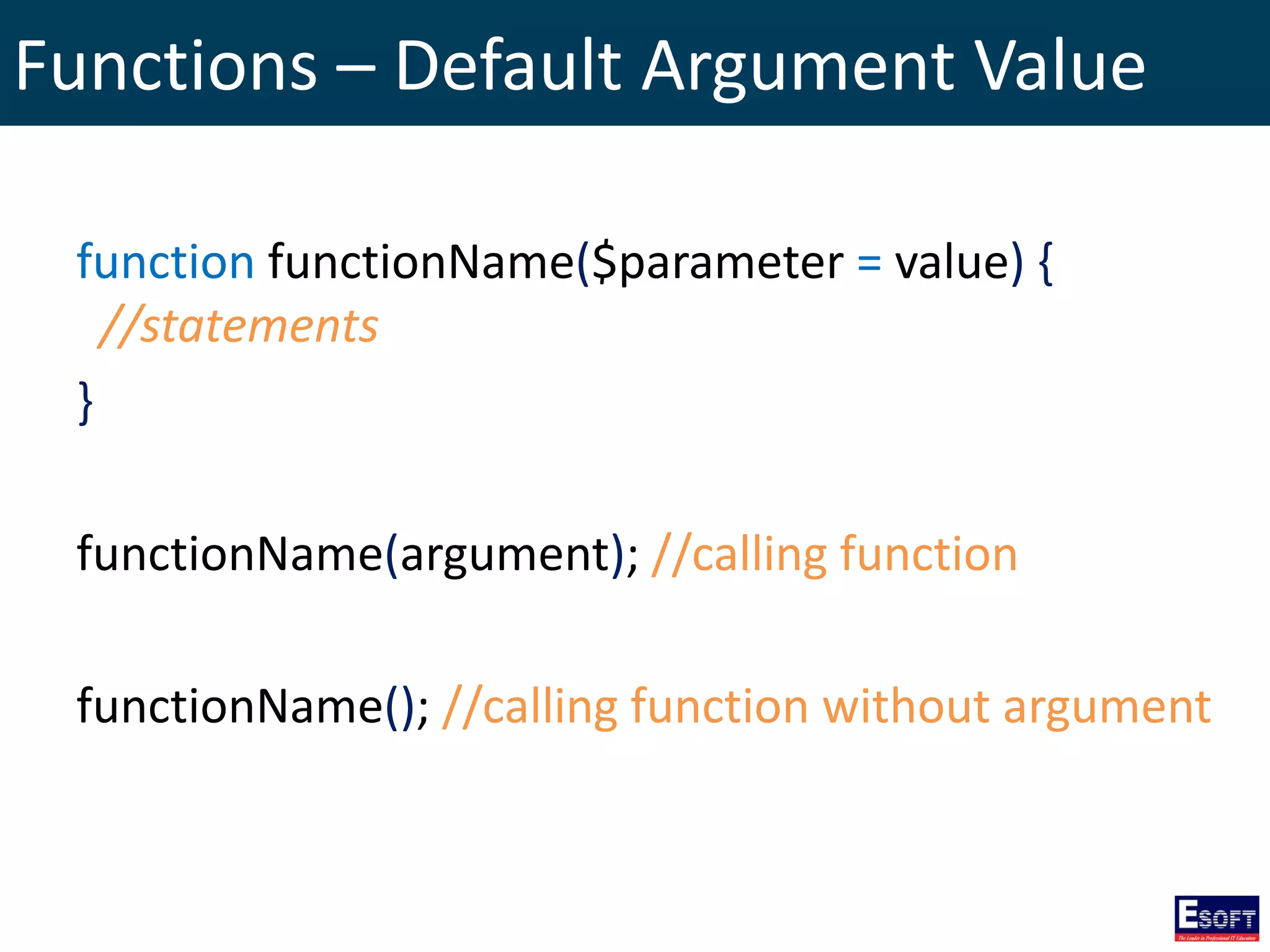
This document provides an extensive overview of PHP, a server-side scripting language for web development, including its syntax, data types, variables, operators, control structures, and function definitions. It also covers how to set up a PHP environment and details the distinctions between built-in and user-defined functions. Key topics include file handling, cookie management, and the use of superglobal variables.










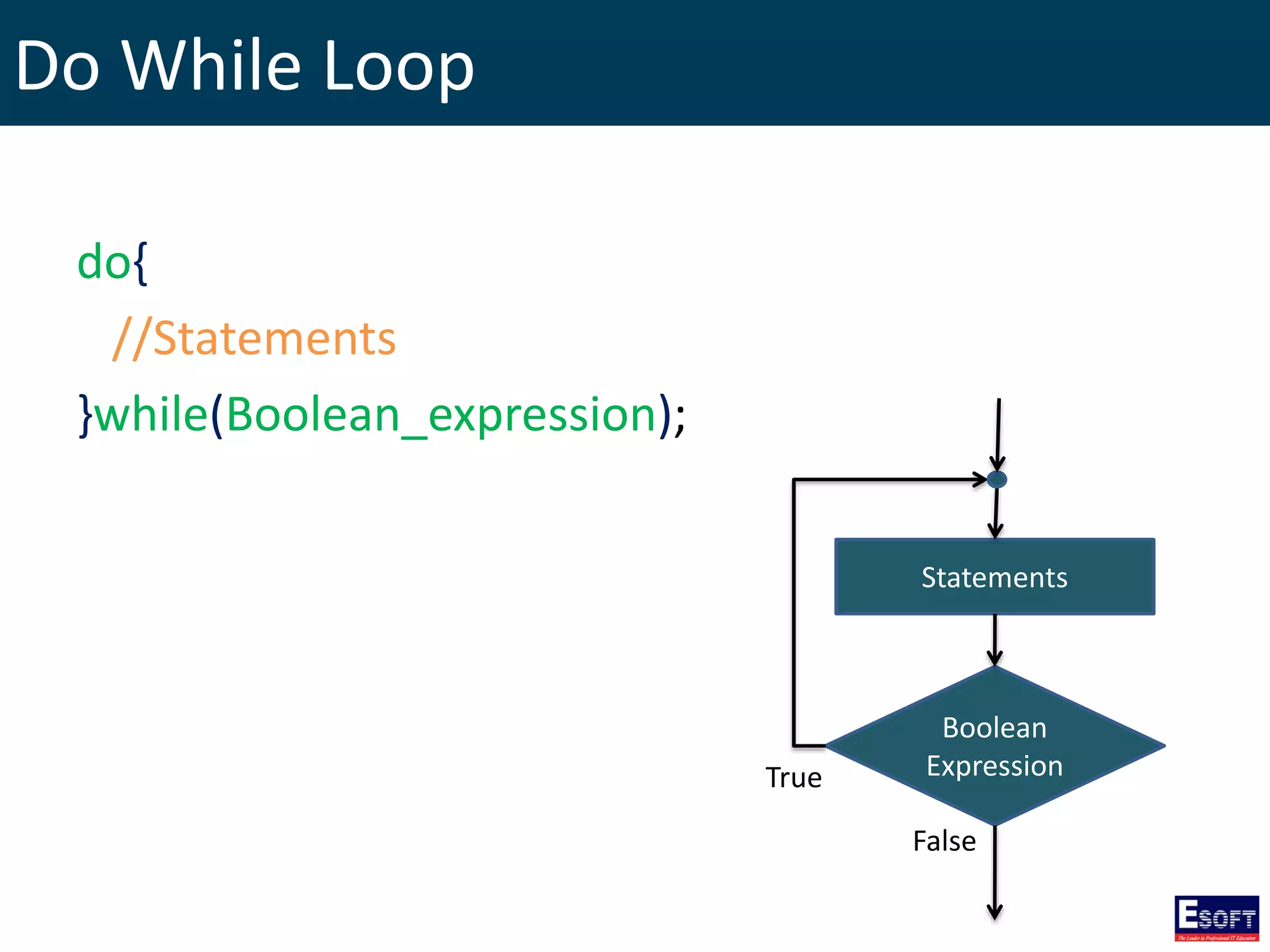
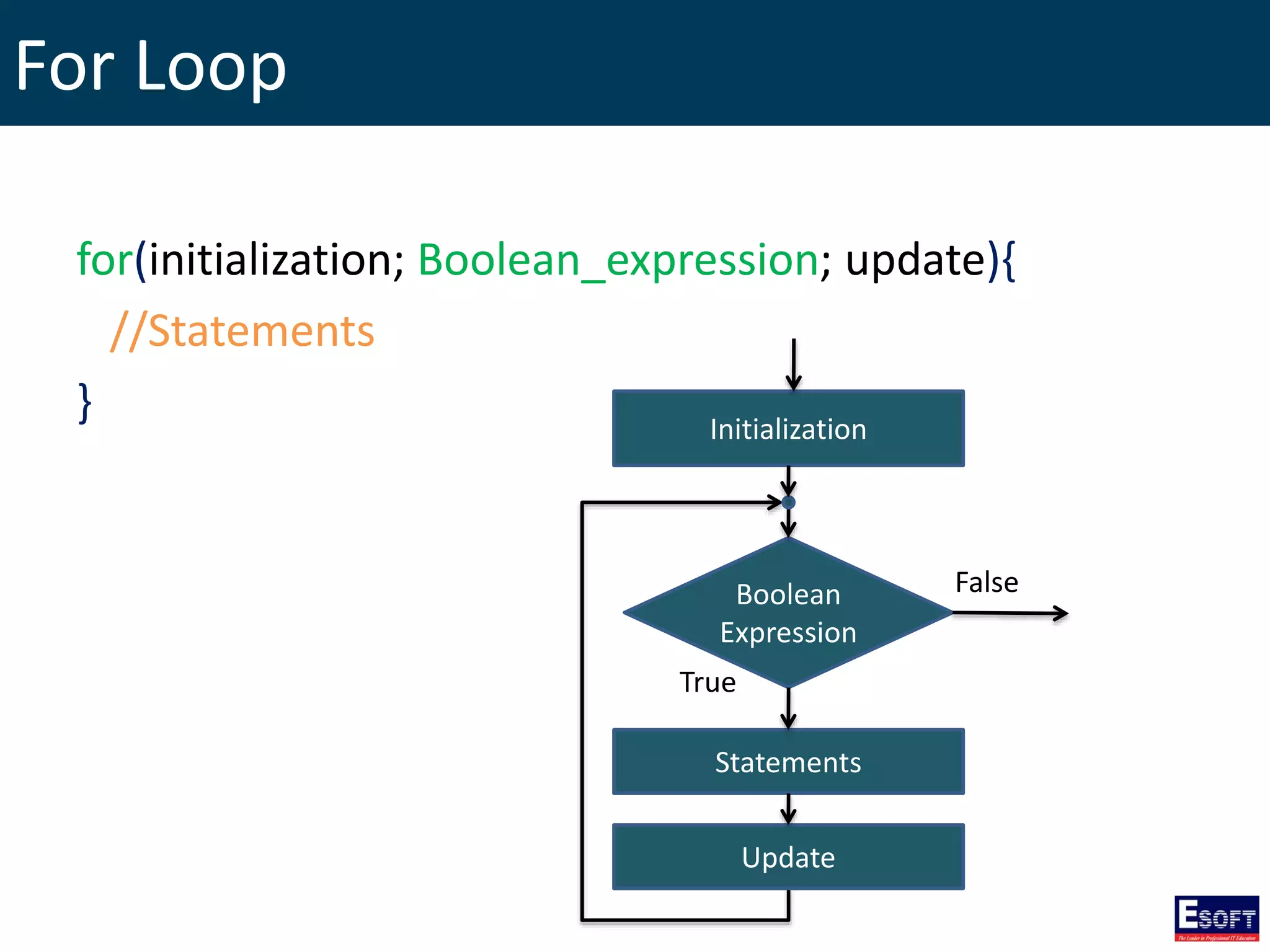
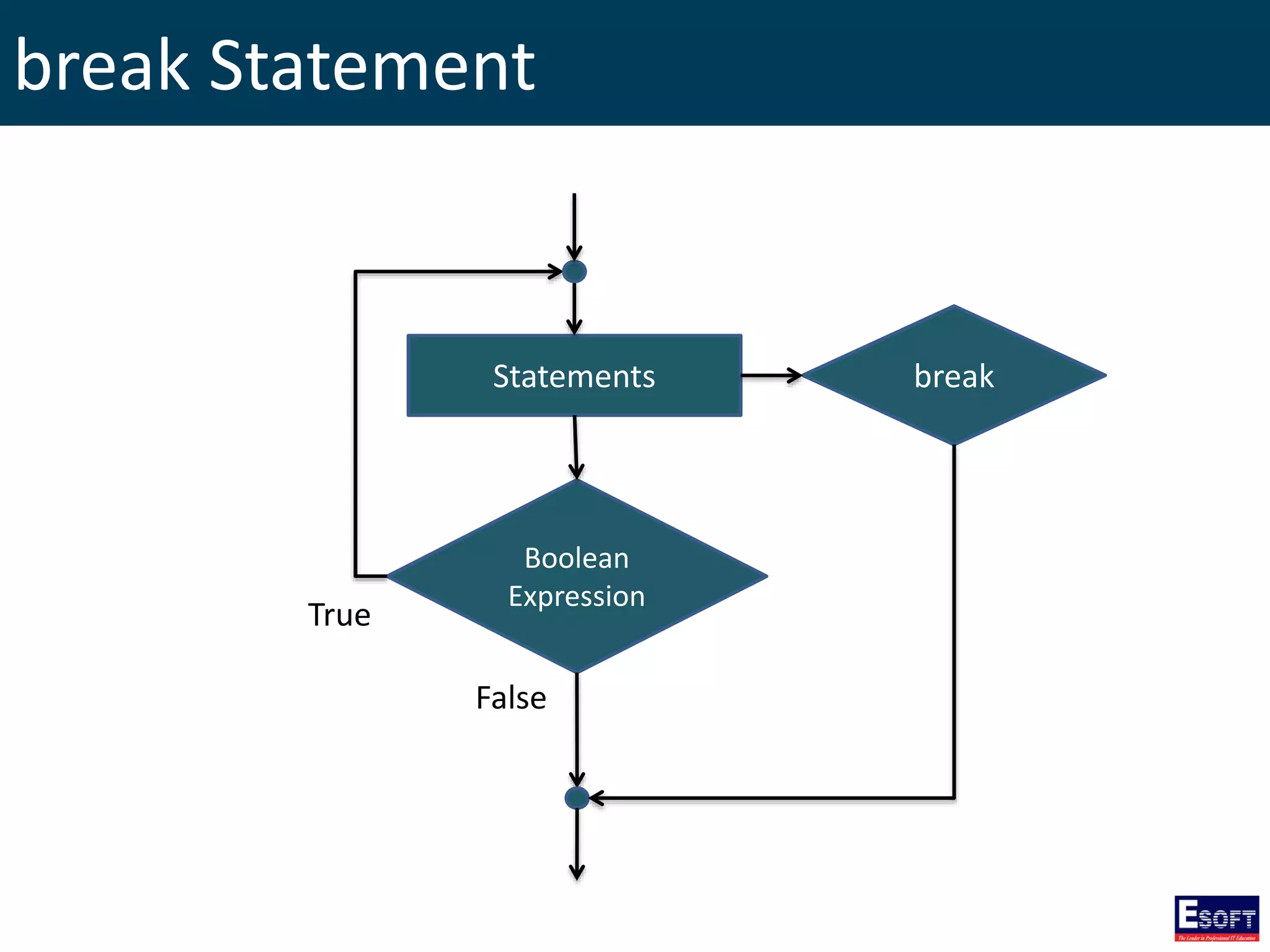
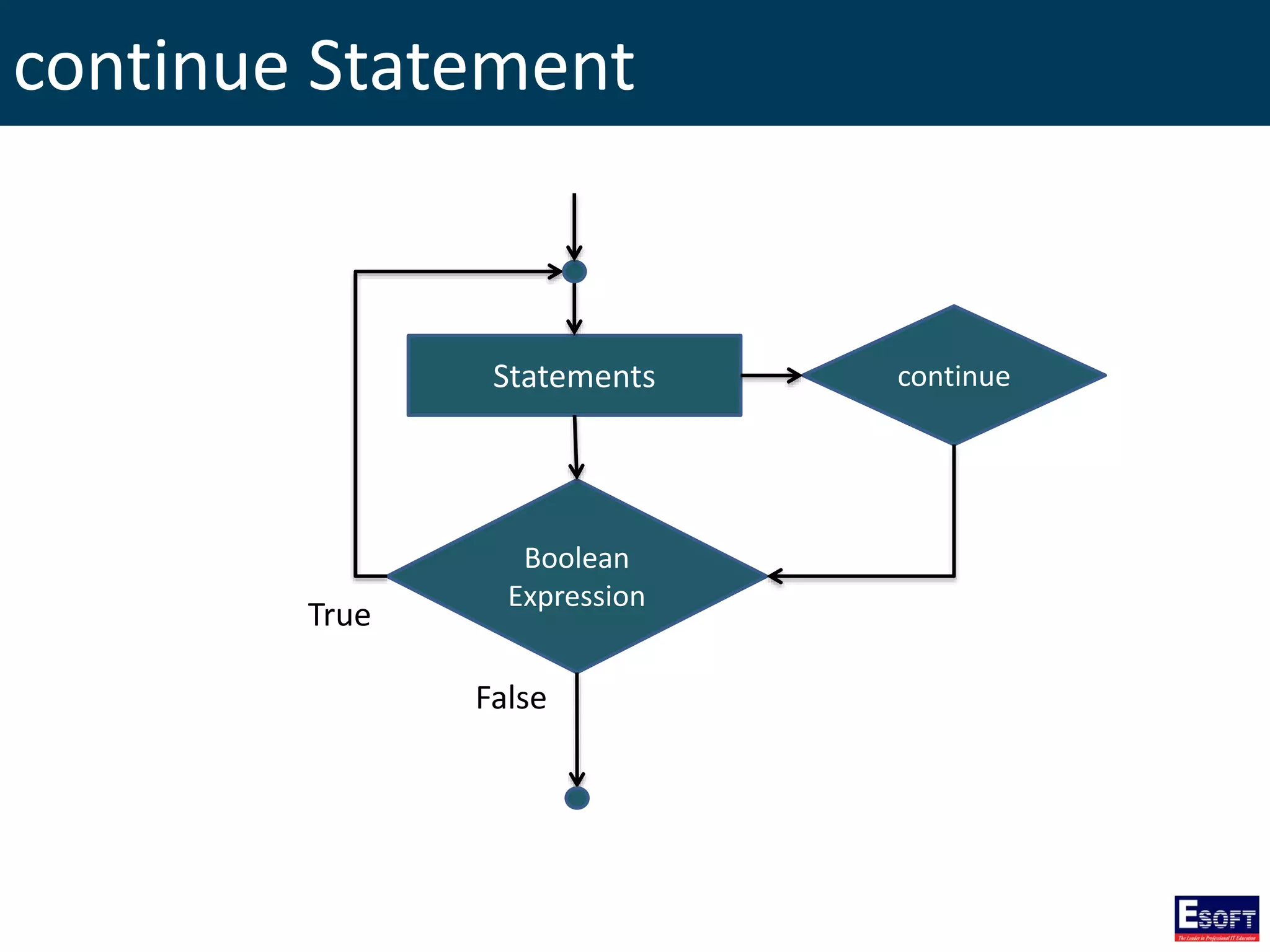


![GLOBALS Array
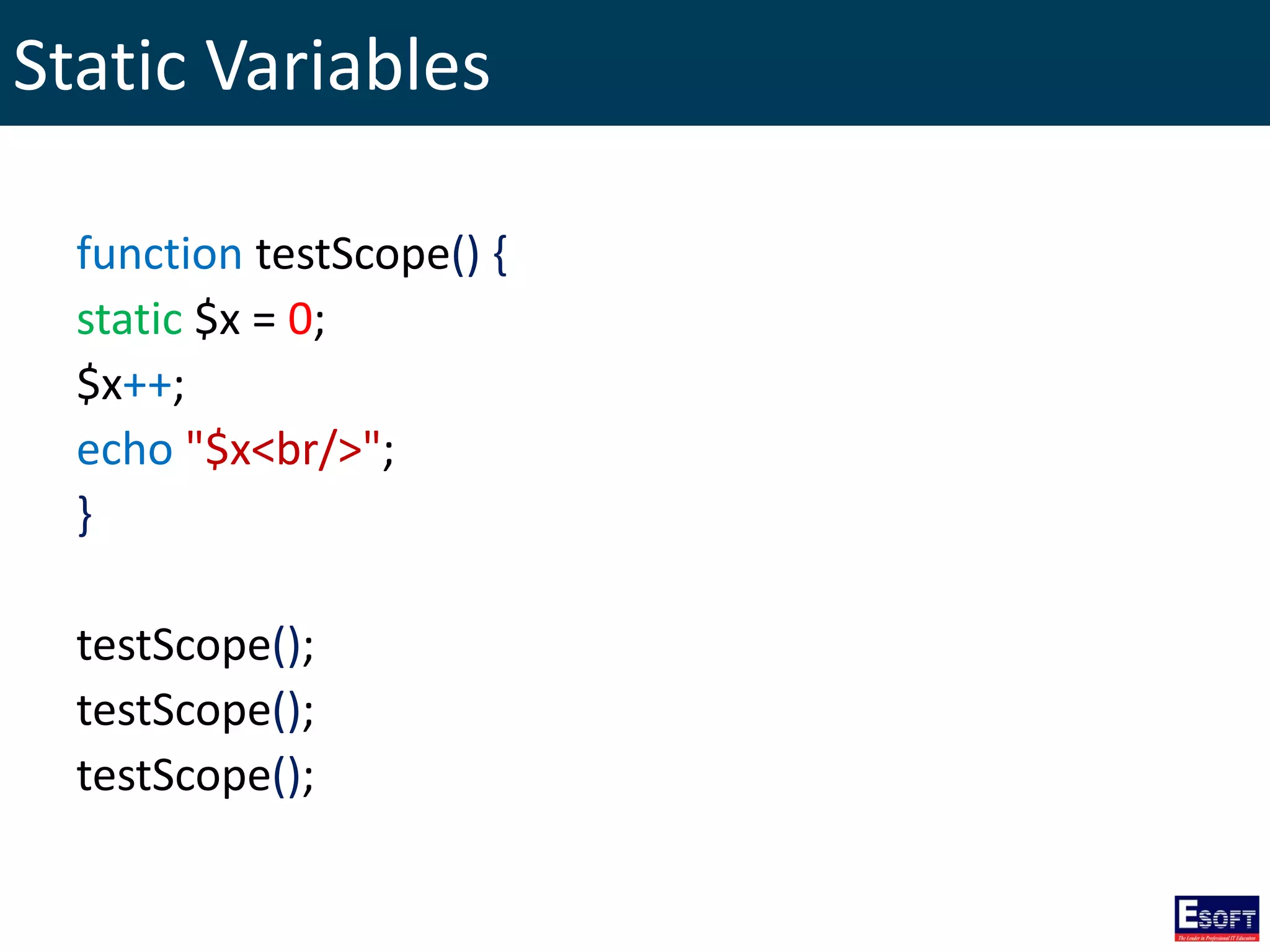
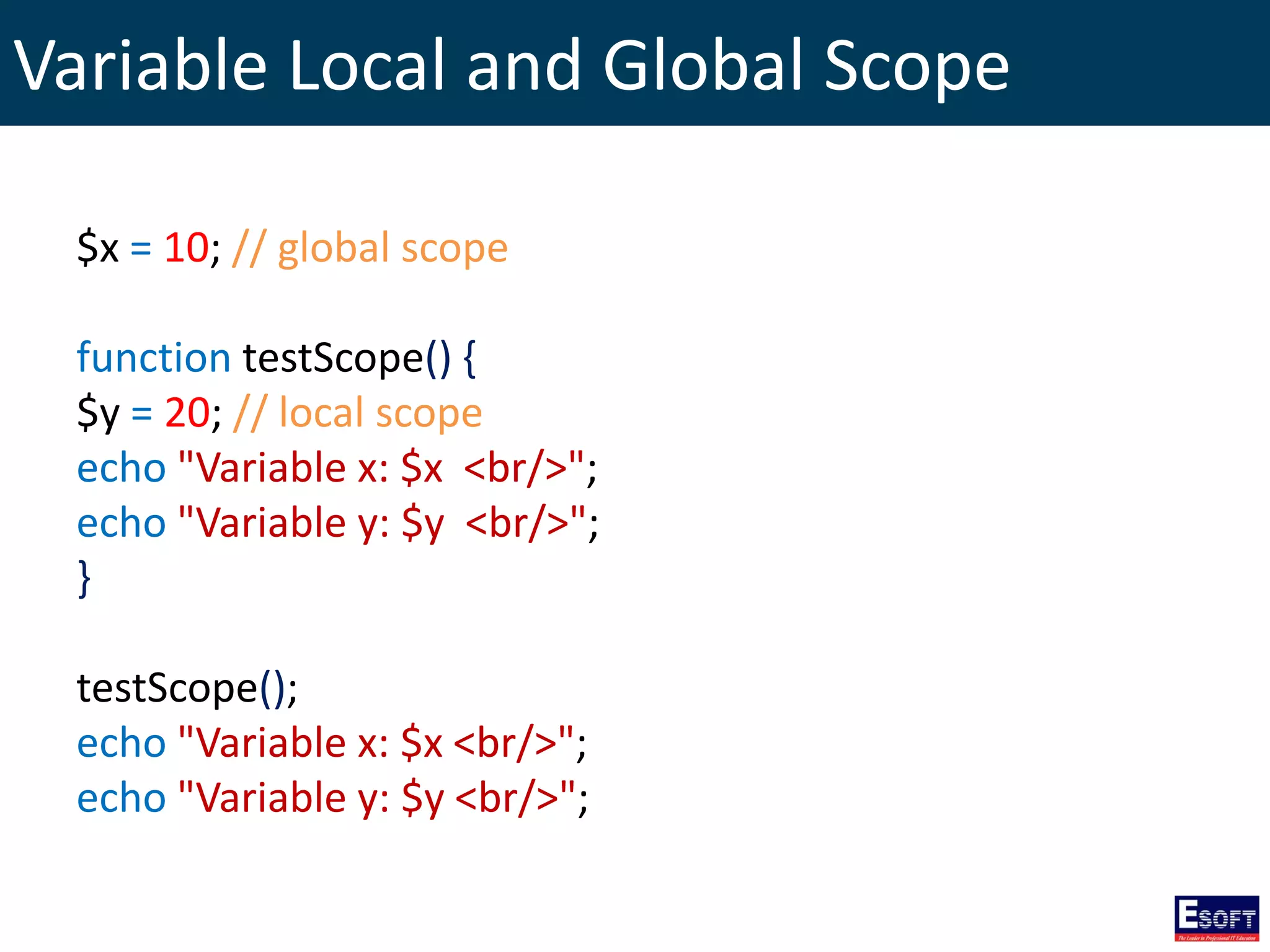
$x = 10; // global scope
function testScope() {
$GLOBALS['x'] = 20;
}
testScope();
echo "Variable x: $x <br/>";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulevi-170204094258/75/DIWE-Fundamentals-of-PHP-42-2048.jpg)