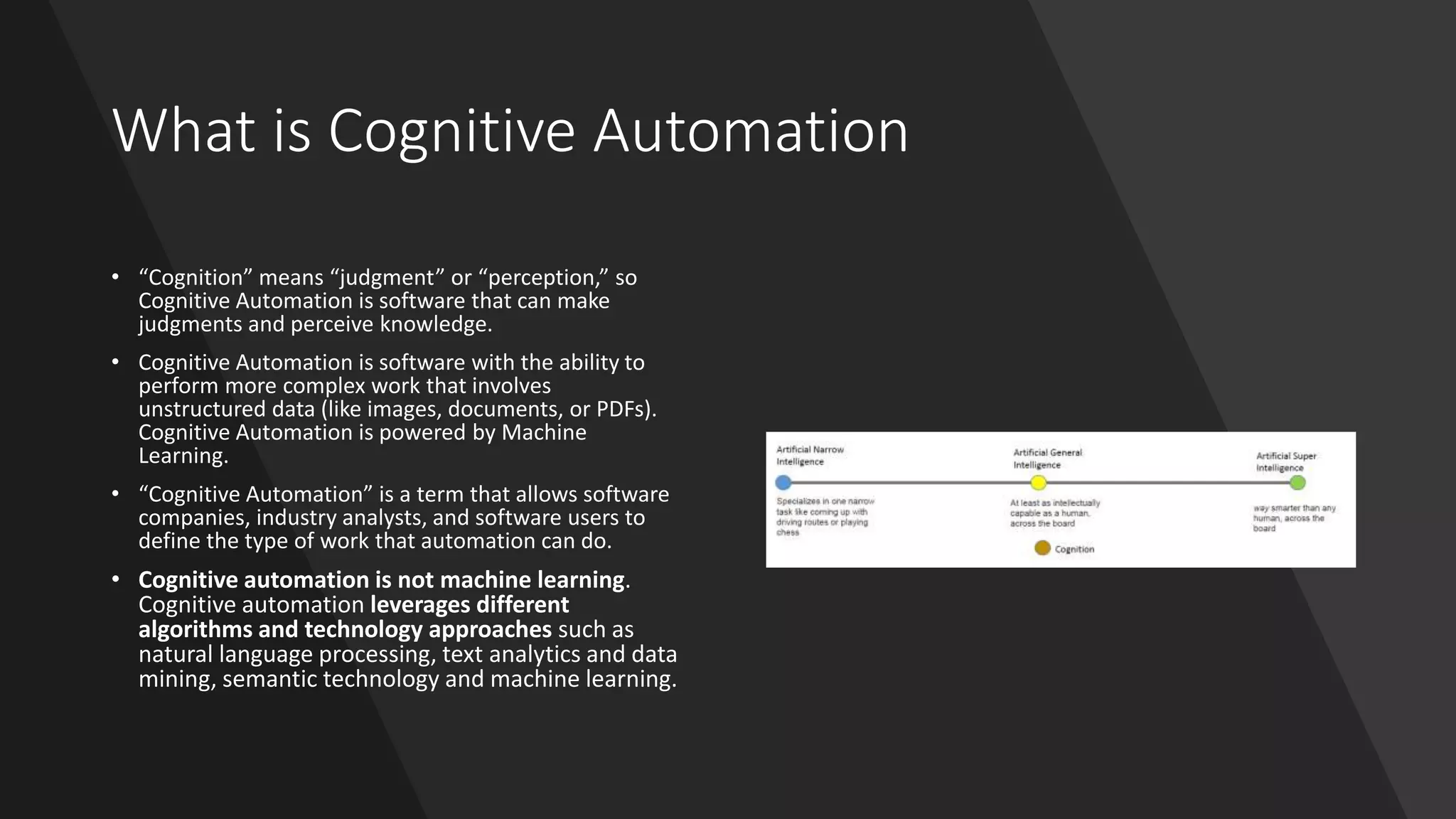
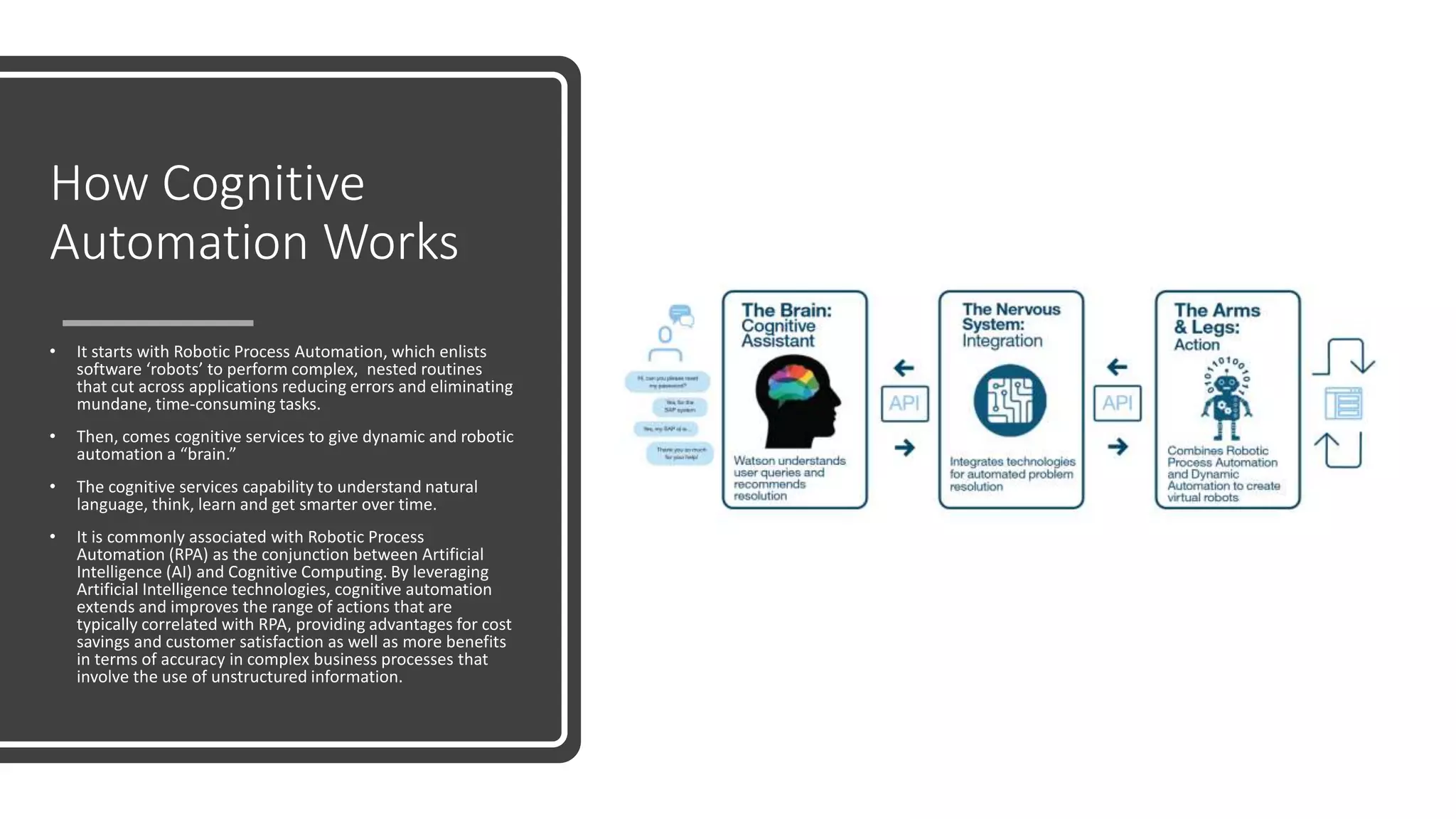
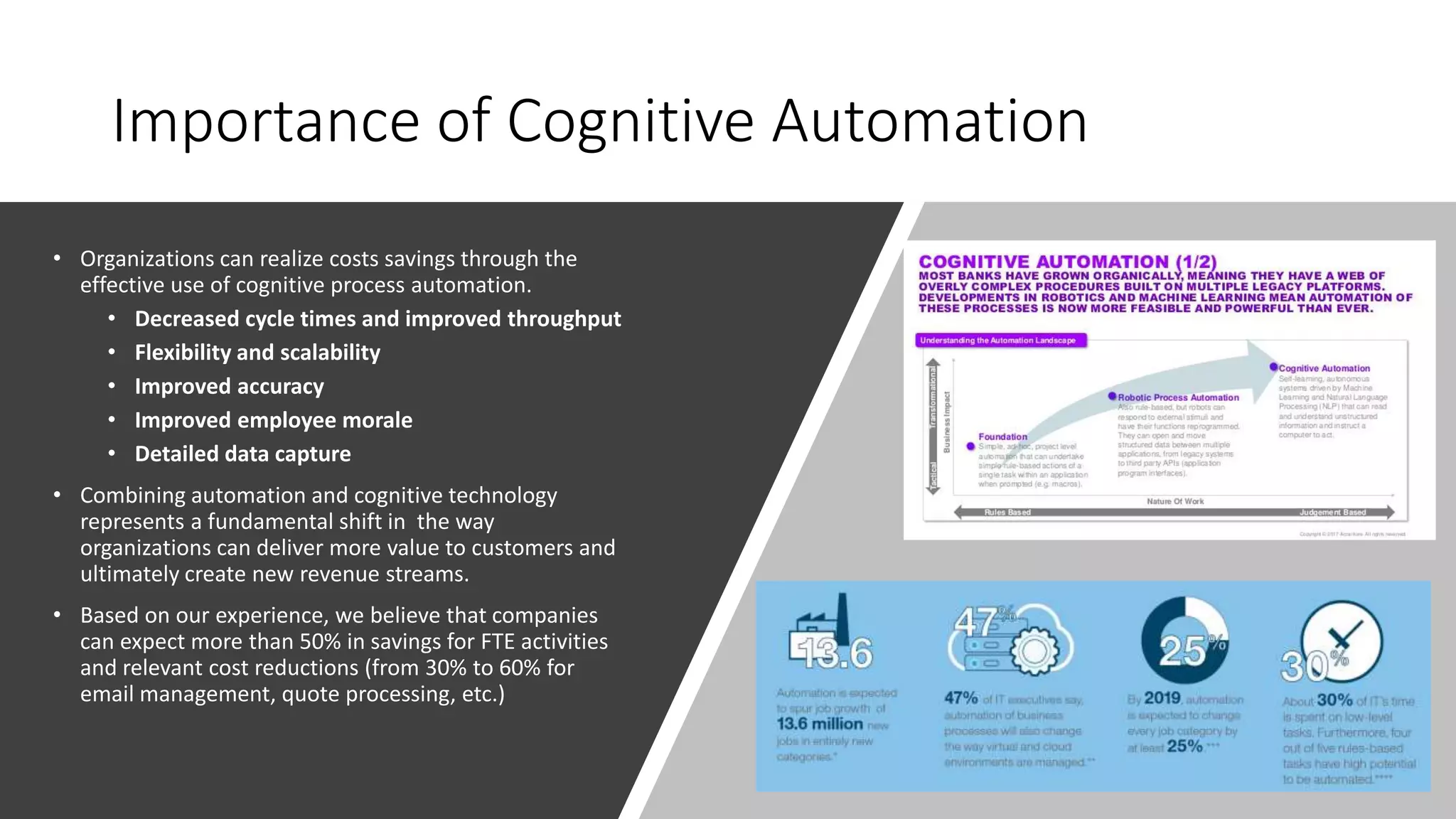
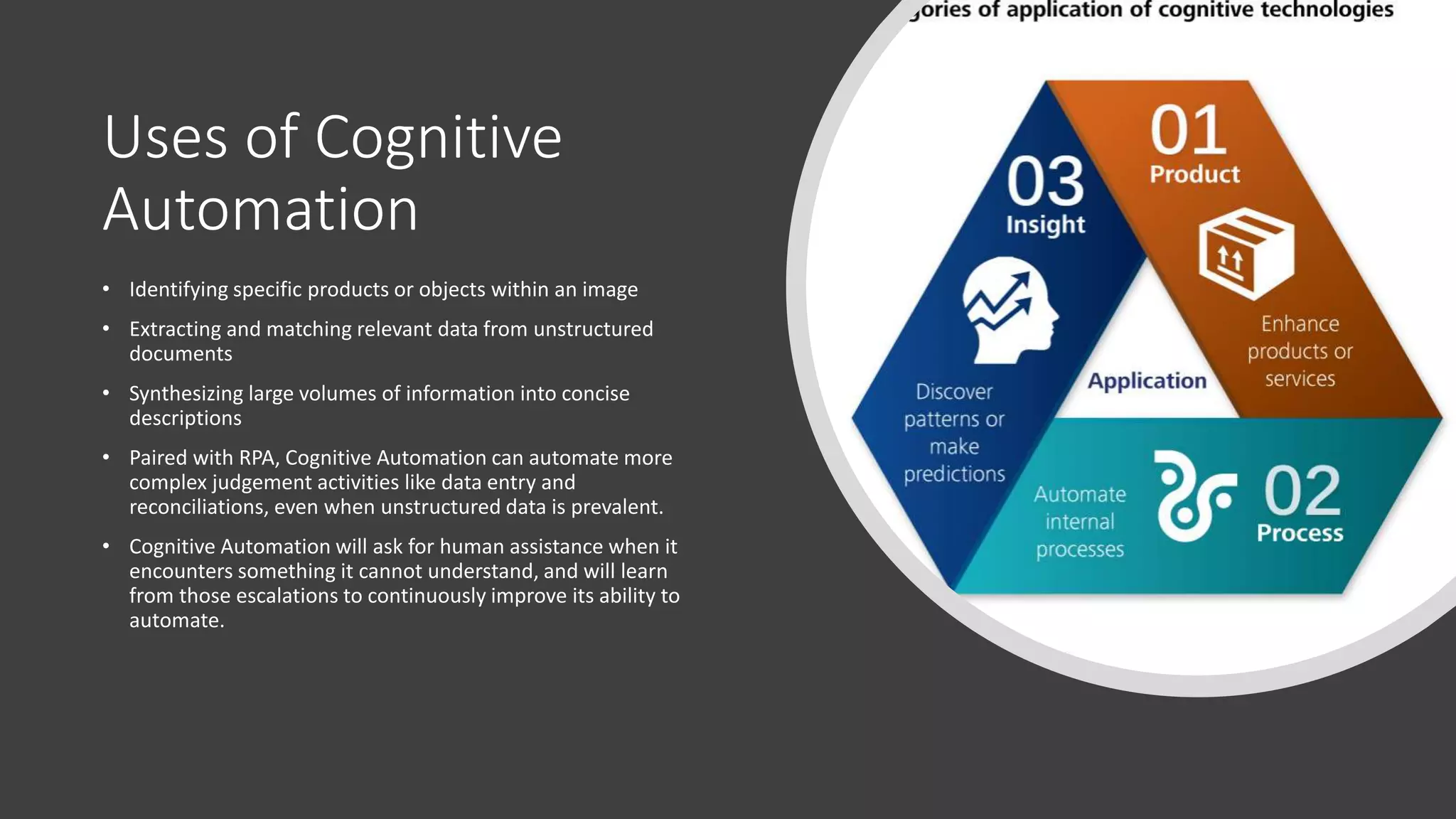
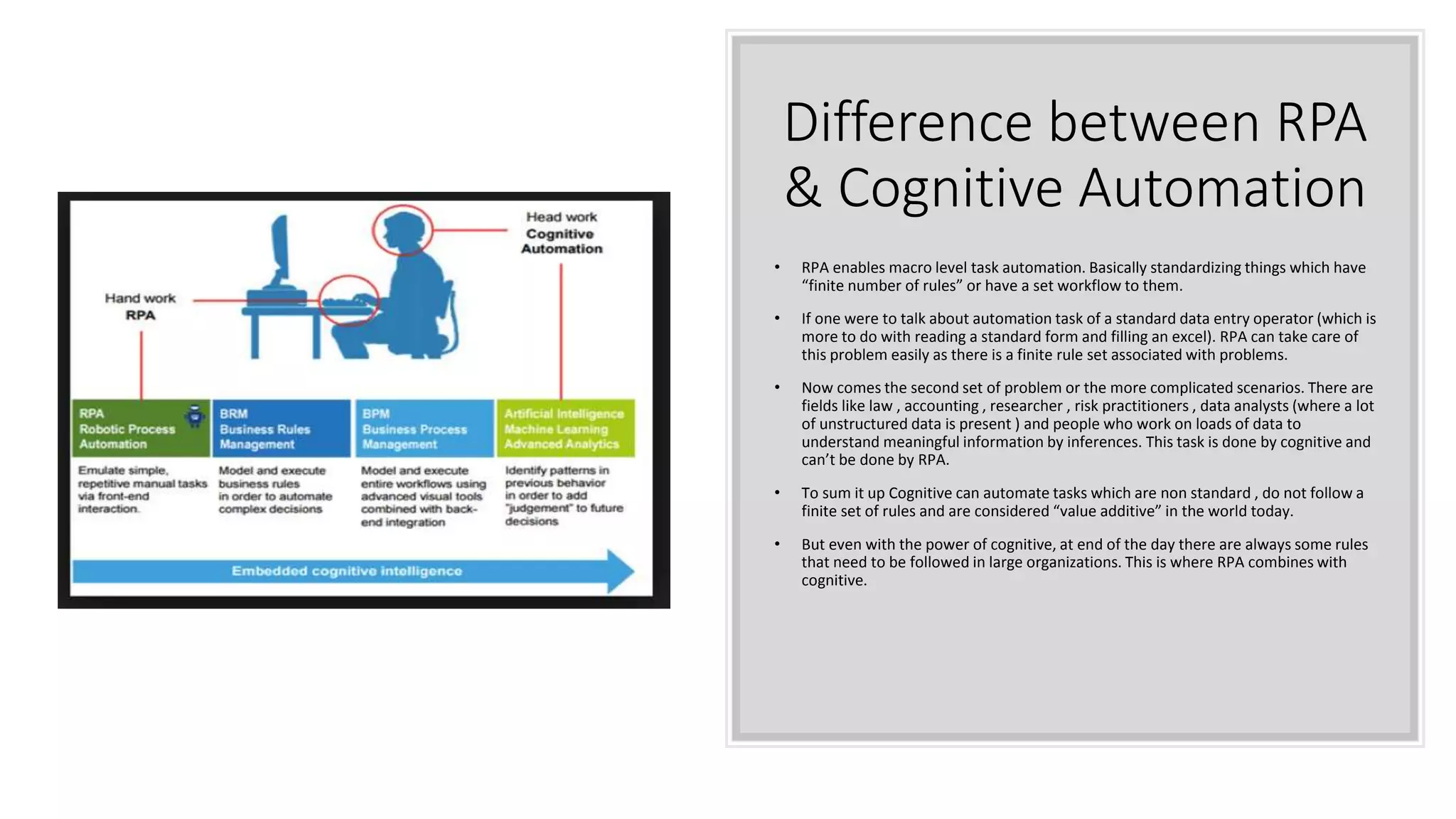
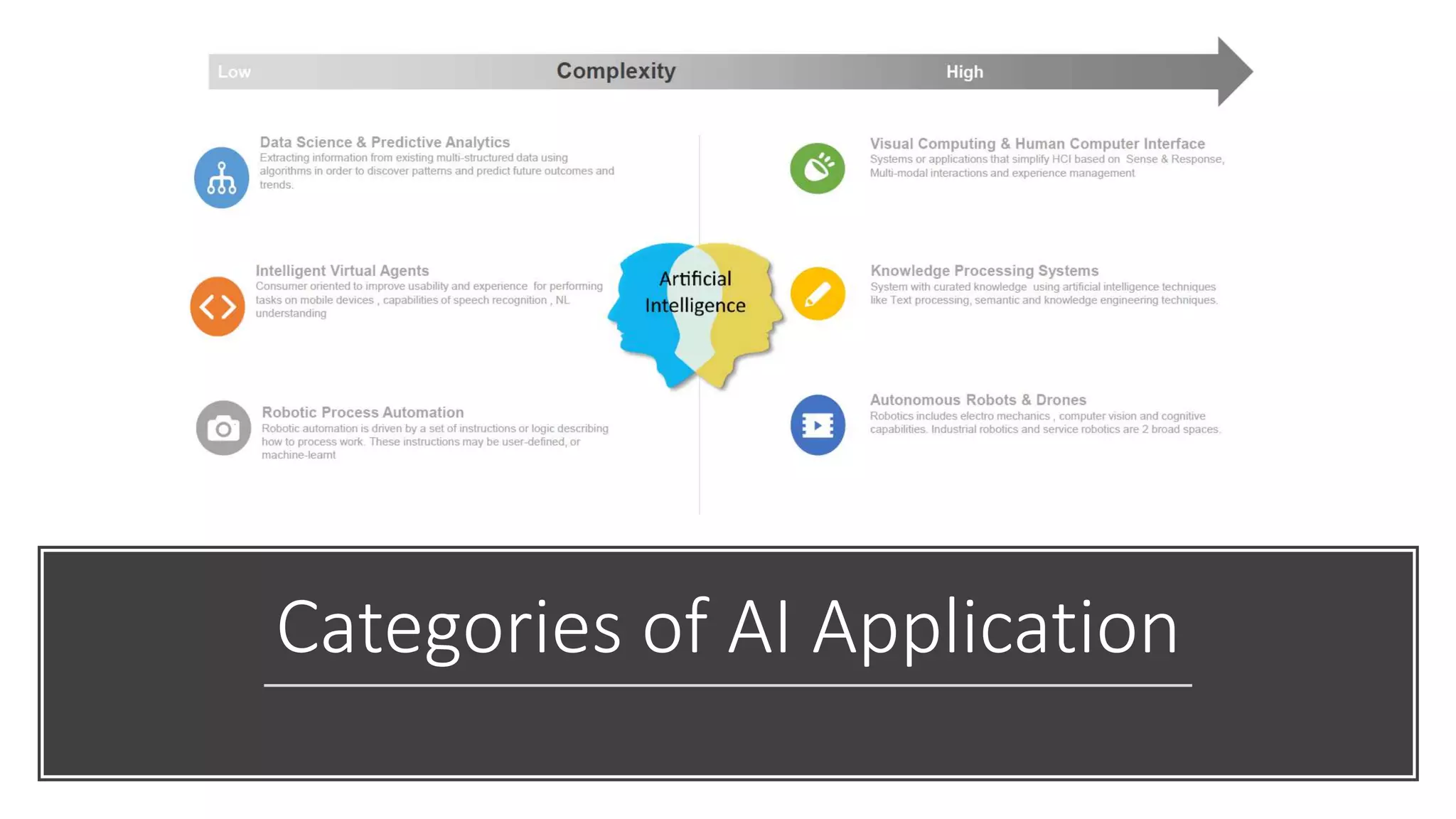
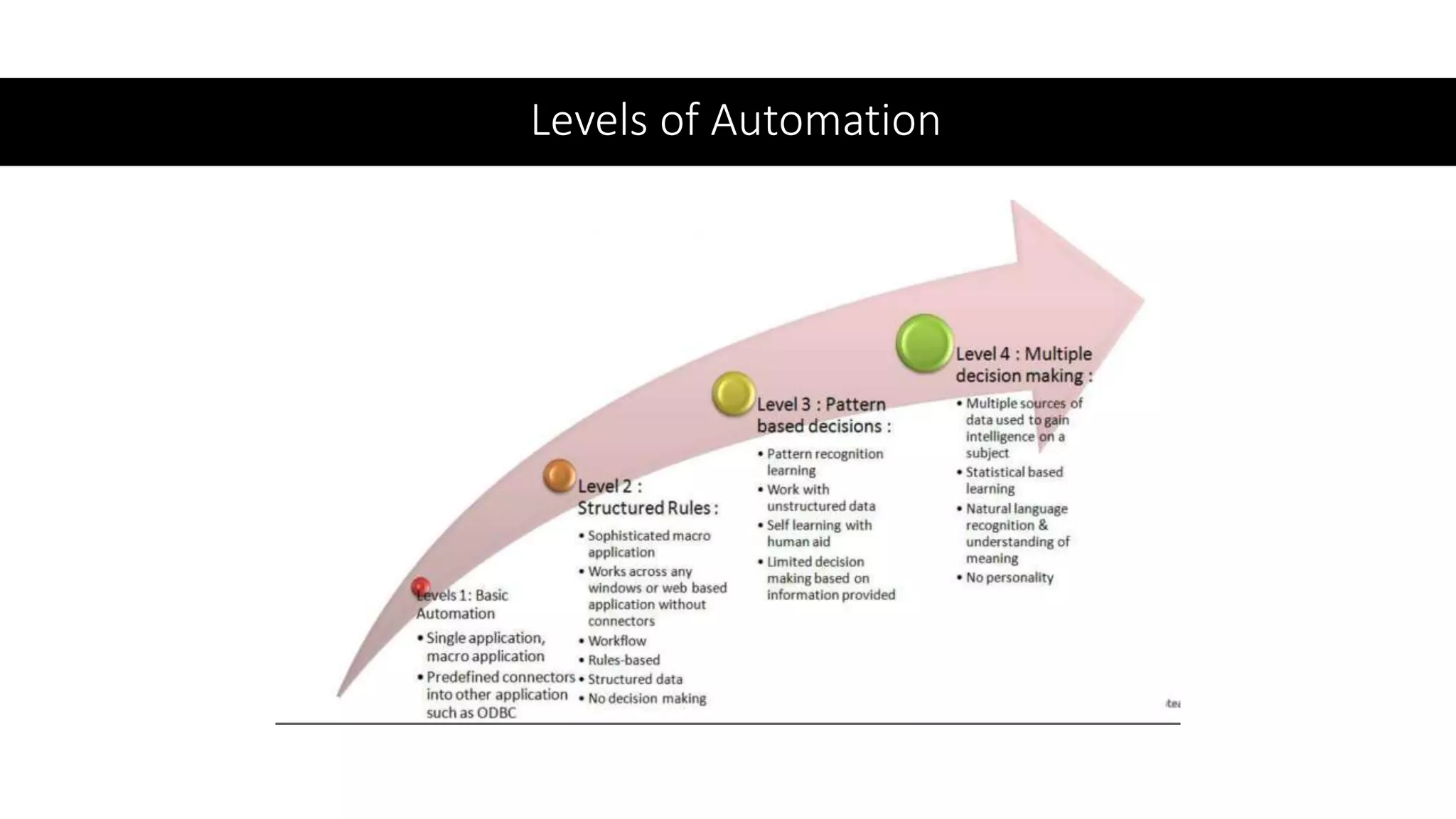
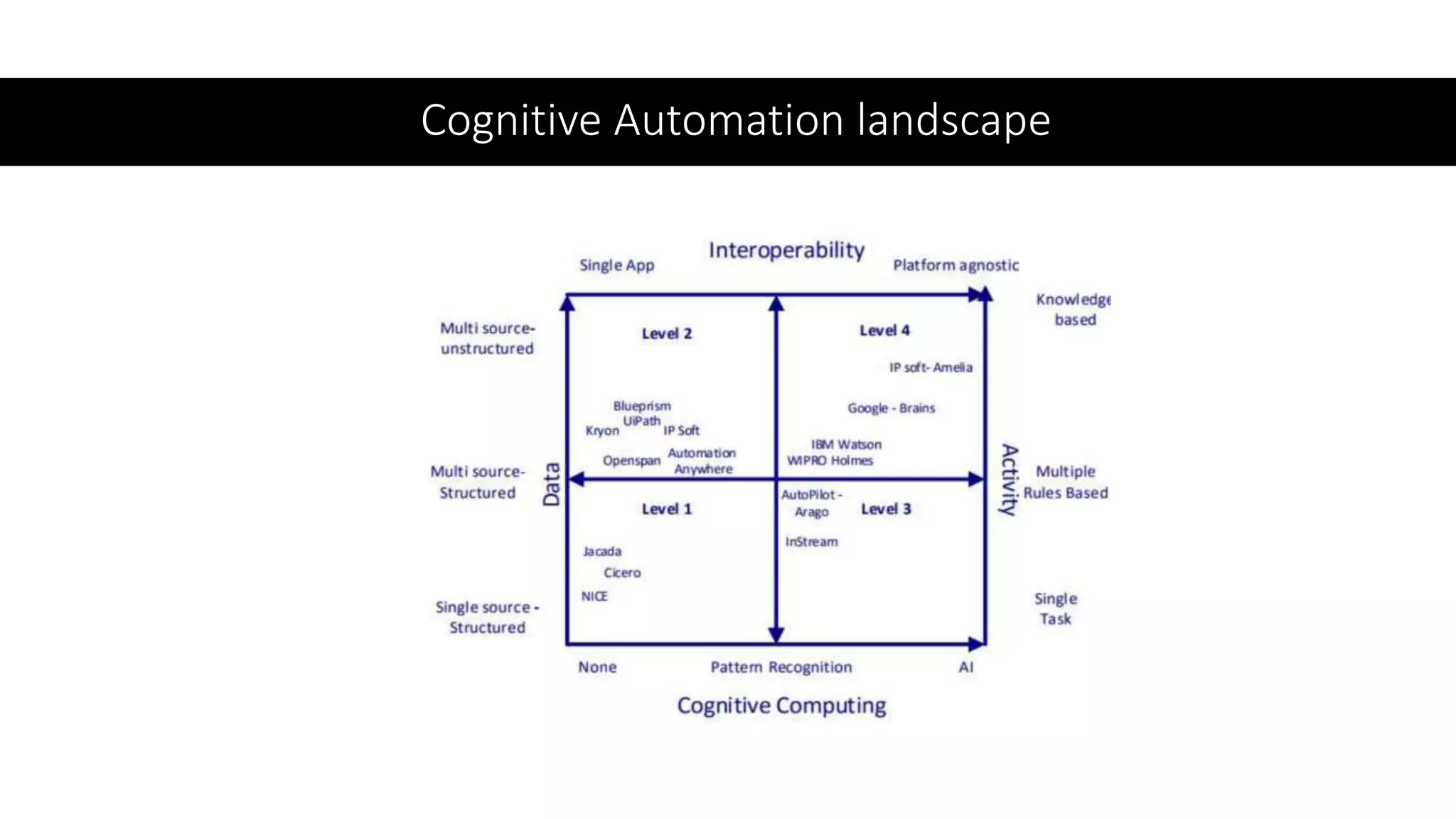
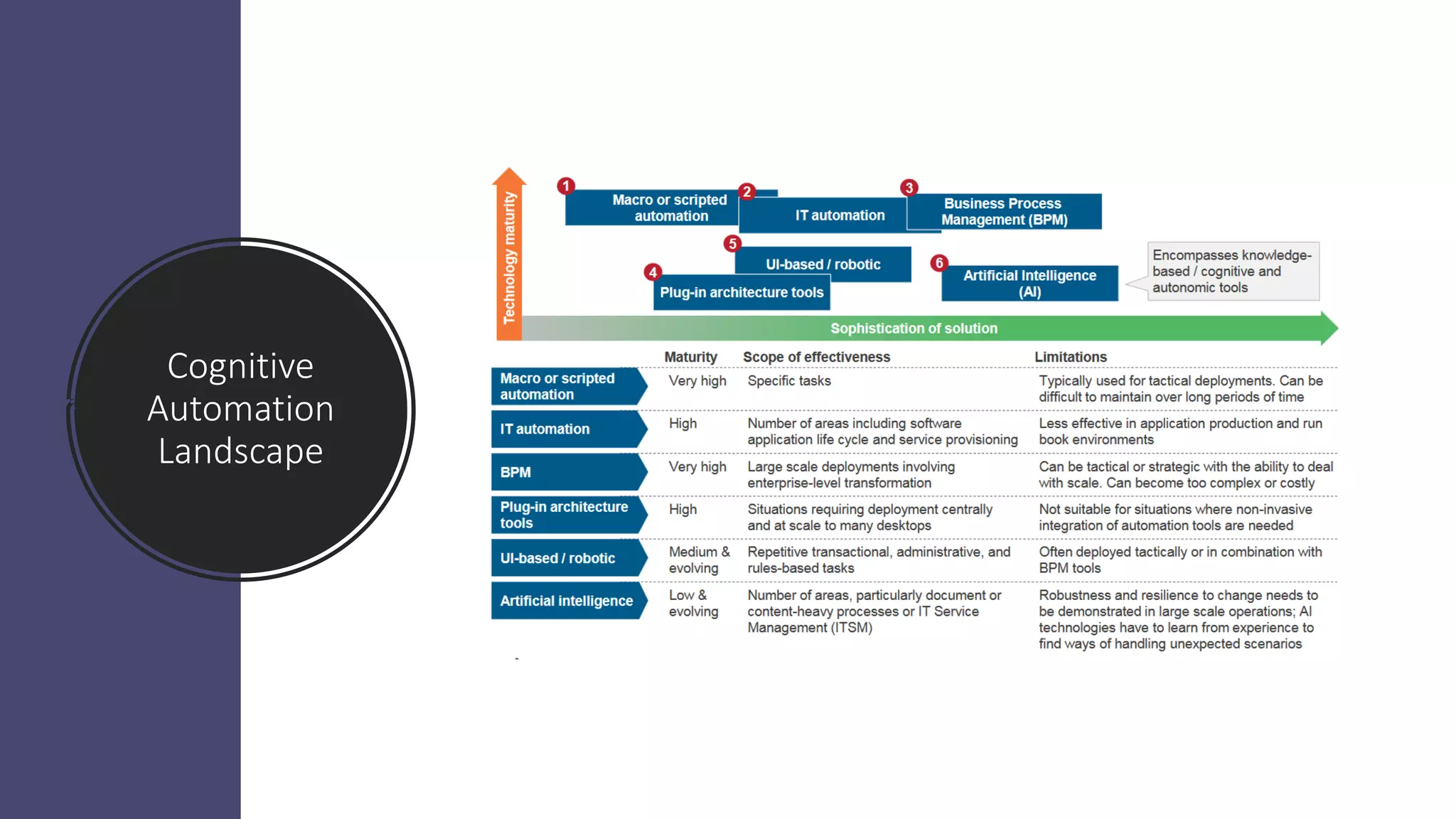
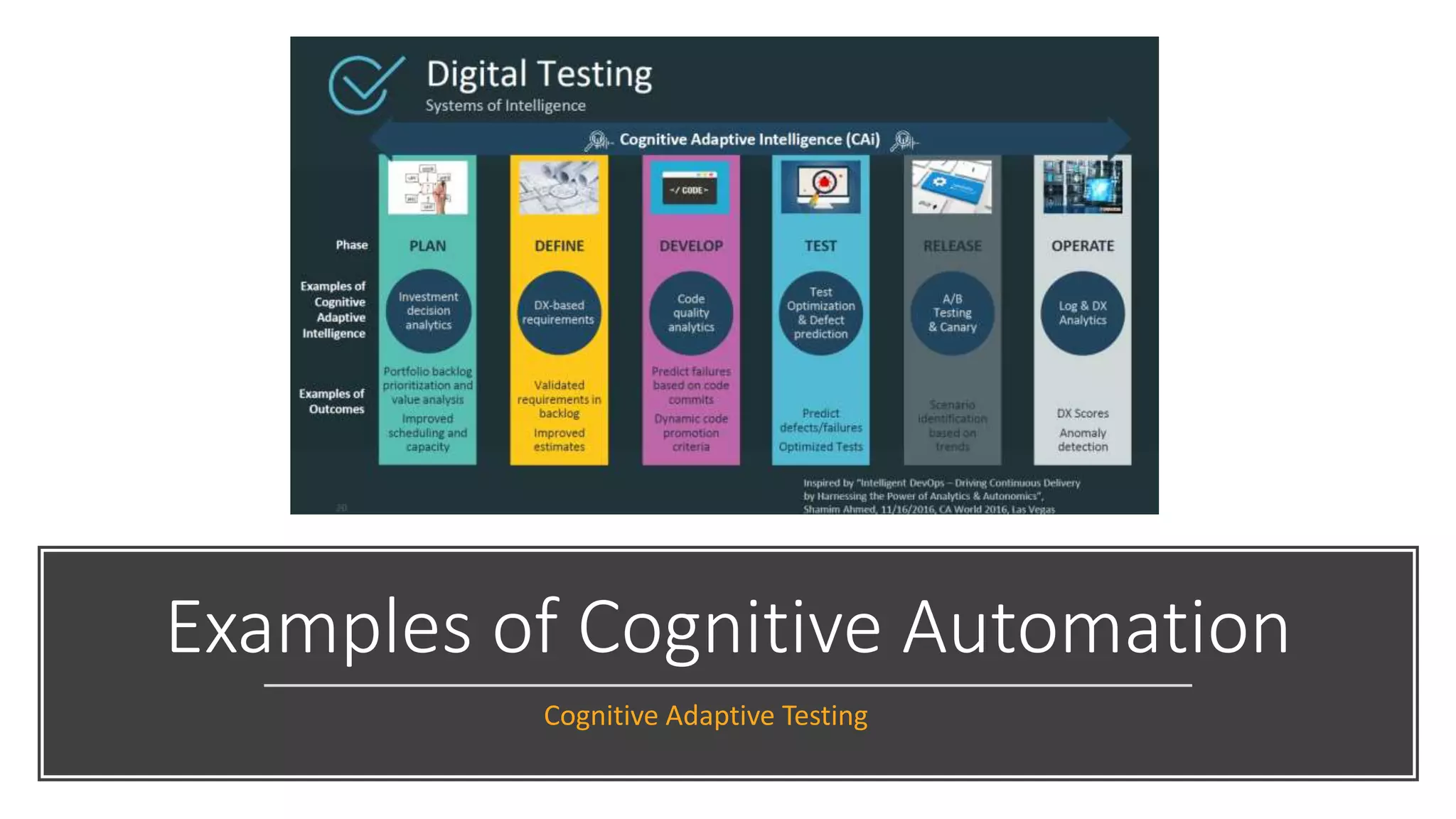
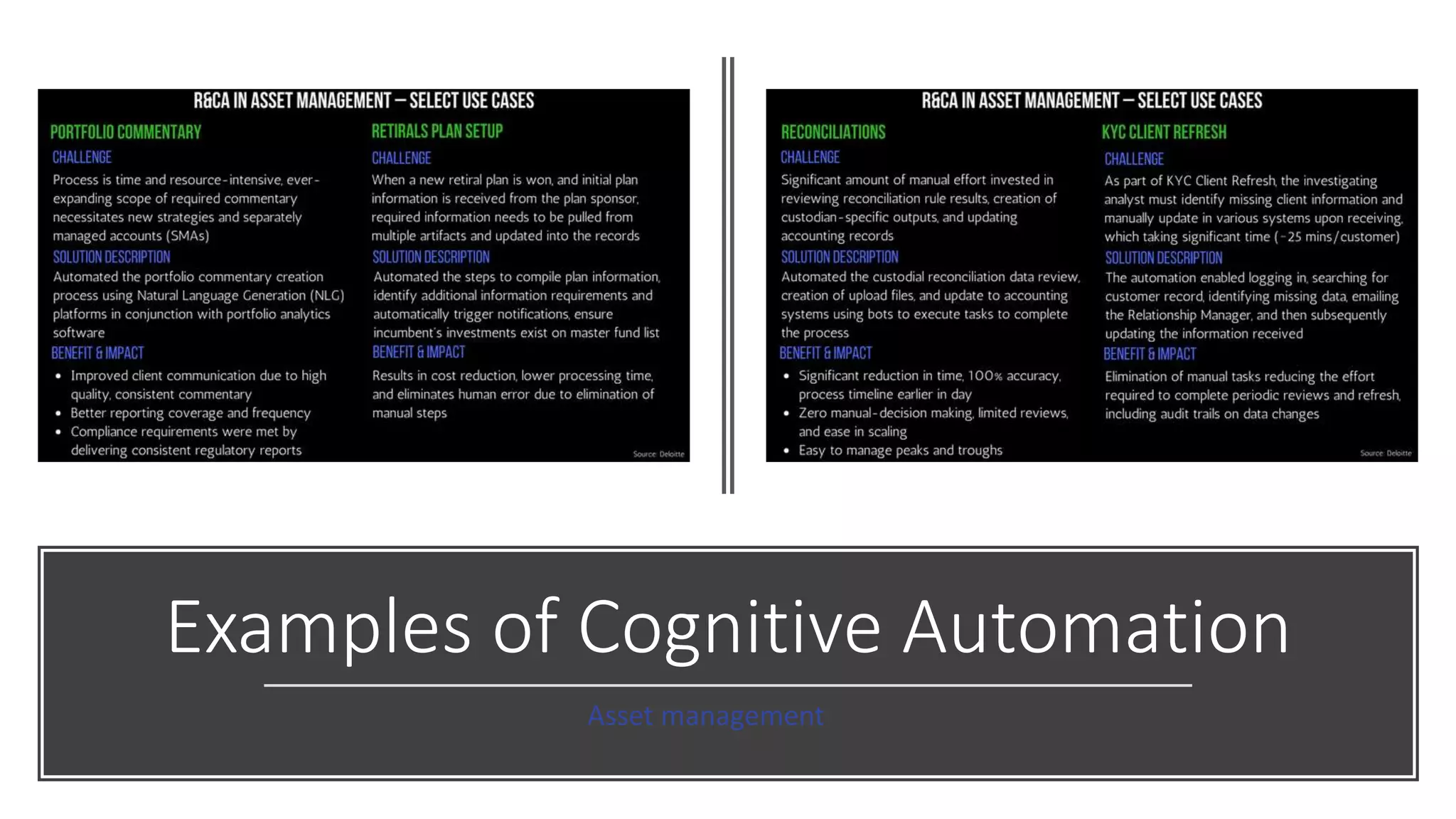
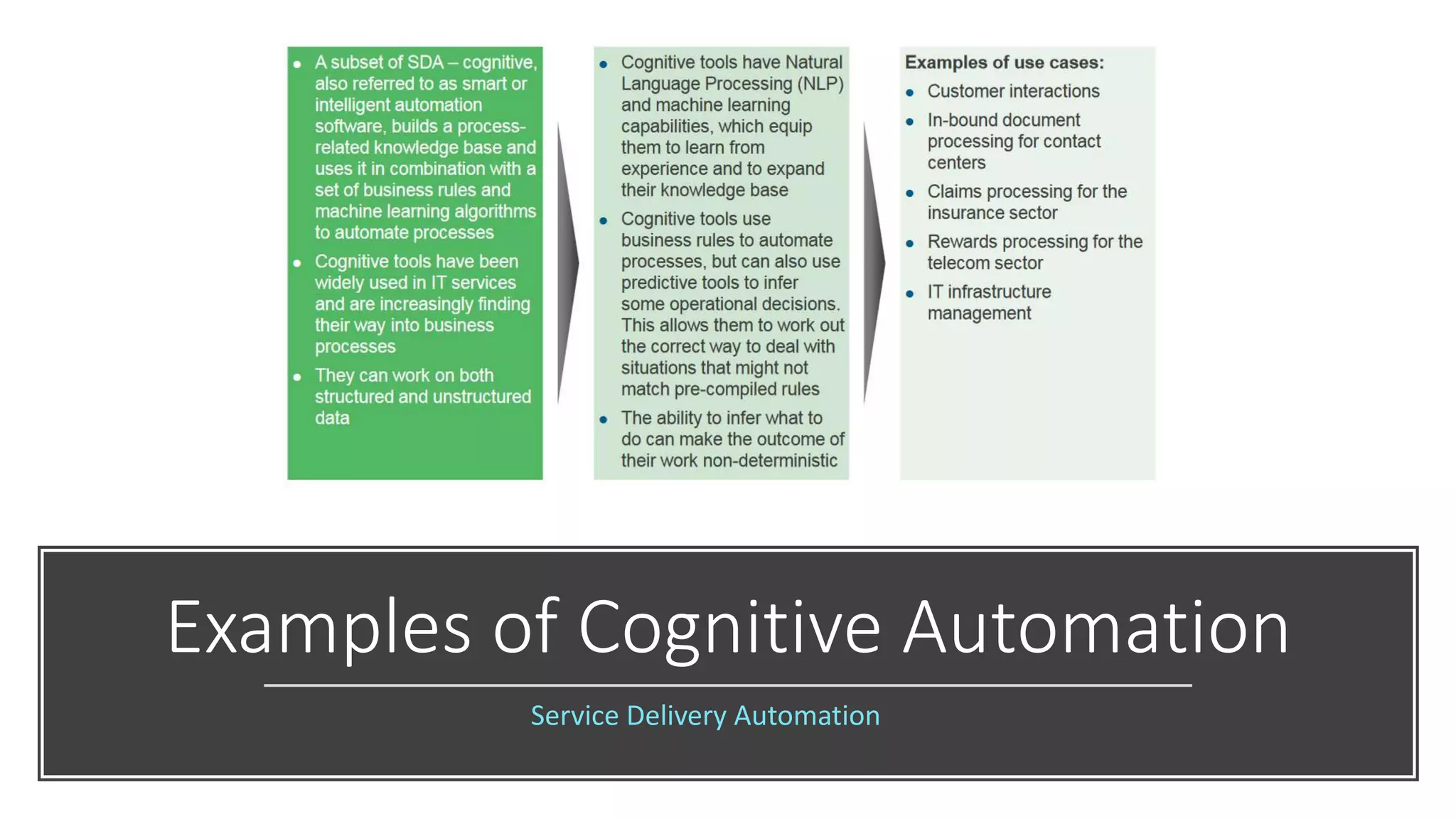
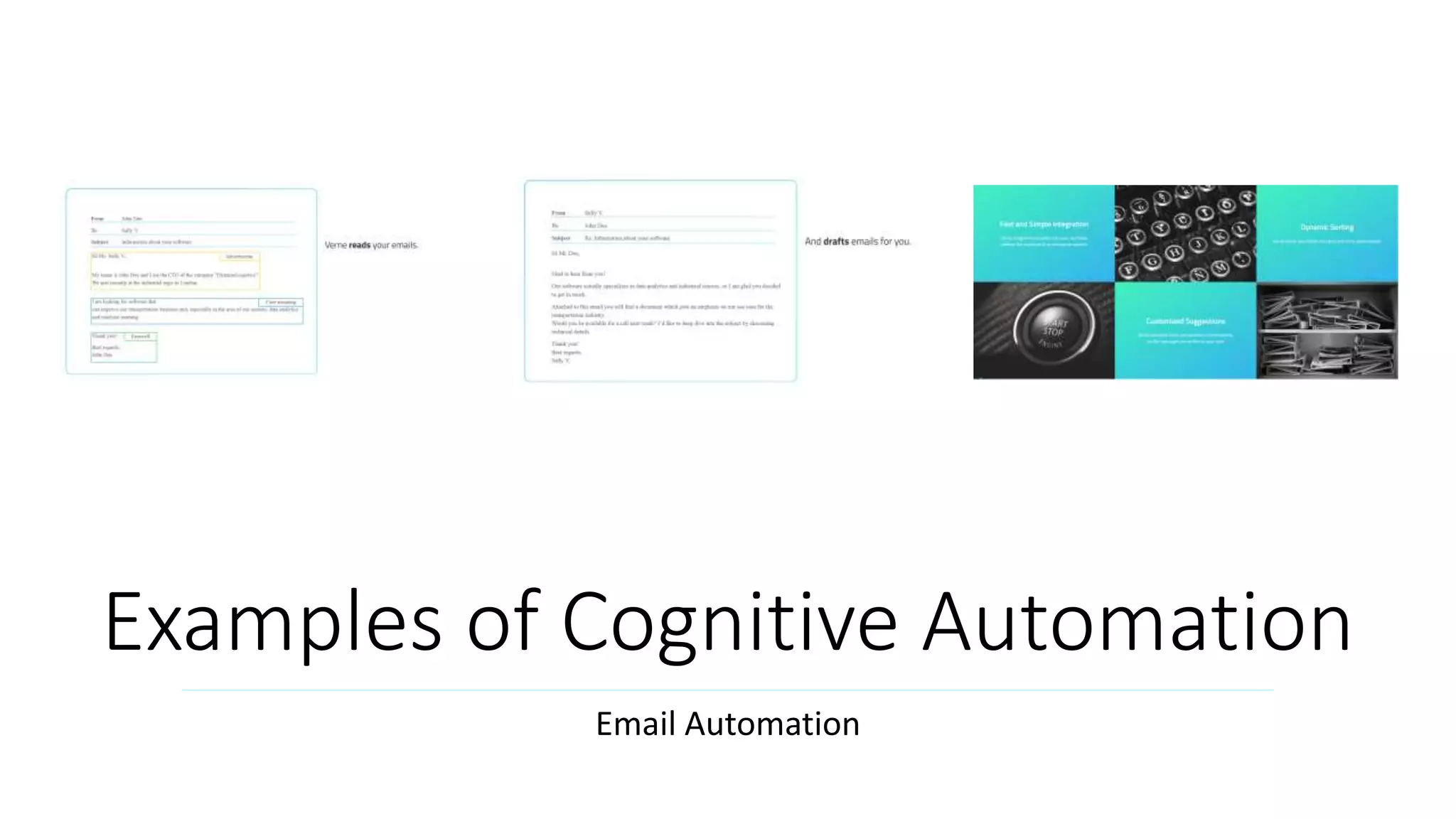
The document provides an introduction to cognitive automation, defining it as software capable of making judgments and handling unstructured data through machine learning, differentiating it from robotic process automation (RPA). It highlights the importance and benefits of cognitive automation in organizations, including cost savings and improved accuracy, along with its various applications, challenges, and integration with RPA. The content emphasizes continuous learning and robust decision-making as key factors for future-proofing automation technologies.